Python中第三方模块requests解析
一、简述
Requests HTTP Library
二、模块框架
'''
__version__
_internal_utils
adapters
api
auth
certs
compat
cookies
exceptions
help
hooks
models
packages
sessions
status_codes
structures
utils
'''
Packages
'''
GET 请求获取URL位置的资源
HEAD 请求获取URL位置资源的响应消息报告,即获得该资源的头部信息
POST 请求向URL位置的资源后附加新的数据
PUT 请求向URL位置存储一个资源,覆盖原URL位置的资源
PATCH 请求局部更新URL位置的资源,即改变该处资源的部分内容
DELETE 请求删除URL位置存储的资源
HTTP协议方法于requests库方法是一一对应的。
requests库的7个主要方法:
requests.request() 构造一个请求,支撑以下各方法的基础方法
requests.get() 获取HTML网页的主要方法,对应于HTTP的GET
requests.head() 获取HTML网页头信息的方法,对应于HTTP的HEAD
requests.post() 向HTML网页提交POST请求的方法,对应于HTTP的POST
requests.put() 向HTML网页提交PUT请求的方法,对应于HTTP的PUT
requests.patch() 向HTML网页提交局部修改请求,对应于HTTP的PATCH
requests.delete() 向HTML页面提交删除请求,对应于HTTP的DELETE
'''
Function
三、运用
#coding=utf-8
# 1、导入模块
import requests
# 2、使用get方法获取html网页对象obj
obj = requests.get("https://www.baidu.com/")
# 3、 查看状态码,状态码为200表示访问成功
print obj.status_code
# 4、更改网页编码格式为utf-8
obj.encoding = 'utf-8'
# 5、打印网页内容
print obj.text
A Simple Example:
'''
obj是一个<class 'requests.models.Response'>对象 Help on Response in module requests.models object:
class Response(__builtin__.object)
| The :class:`Response <Response>` object, which contains a
| server's response to an HTTP request.
|
| Methods defined here:
|
| __bool__(self)
| Returns True if :attr:`status_code` is less than 400.
|
| This attribute checks if the status code of the response is between
| 400 and 600 to see if there was a client error or a server error. If
| the status code, is between 200 and 400, this will return True. This
| is **not** a check to see if the response code is ``200 OK``.
|
| __enter__(self)
|
| __exit__(self, *args)
|
| __getstate__(self)
|
| __init__(self)
|
| __iter__(self)
| Allows you to use a response as an iterator.
|
| __nonzero__(self)
| Returns True if :attr:`status_code` is less than 400.
|
| This attribute checks if the status code of the response is between
| 400 and 600 to see if there was a client error or a server error. If
| the status code, is between 200 and 400, this will return True. This
| is **not** a check to see if the response code is ``200 OK``.
|
| __repr__(self)
|
| __setstate__(self, state)
|
| close(self)
| Releases the connection back to the pool. Once this method has been
| called the underlying ``raw`` object must not be accessed again.
|
| *Note: Should not normally need to be called explicitly.*
|
| iter_content(self, chunk_size=1, decode_unicode=False)
| Iterates over the response data. When stream=True is set on the
| request, this avoids reading the content at once into memory for
| large responses. The chunk size is the number of bytes it should
| read into memory. This is not necessarily the length of each item
| returned as decoding can take place.
|
| chunk_size must be of type int or None. A value of None will
| function differently depending on the value of `stream`.
| stream=True will read data as it arrives in whatever size the
| chunks are received. If stream=False, data is returned as
| a single chunk.
|
| If decode_unicode is True, content will be decoded using the best
| available encoding based on the response.
|
| iter_lines(self, chunk_size=512, decode_unicode=False, delimiter=None)
| Iterates over the response data, one line at a time. When
| stream=True is set on the request, this avoids reading the
| content at once into memory for large responses.
|
| .. note:: This method is not reentrant safe.
|
| json(self, **kwargs)
| Returns the json-encoded content of a response, if any.
|
| :param \*\*kwargs: Optional arguments that ``json.loads`` takes.
| :raises ValueError: If the response body does not contain valid json.
|
| raise_for_status(self)
| Raises stored :class:`HTTPError`, if one occurred.
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Data descriptors defined here:
|
| __dict__
| dictionary for instance variables (if defined)
|
| __weakref__
| list of weak references to the object (if defined)
|
| apparent_encoding
| The apparent encoding, provided by the chardet library.
|
| content
| Content of the response, in bytes.
|
| is_permanent_redirect
| True if this Response one of the permanent versions of redirect.
|
| is_redirect
| True if this Response is a well-formed HTTP redirect that could have
| been processed automatically (by :meth:`Session.resolve_redirects`).
|
| links
| Returns the parsed header links of the response, if any.
|
| next
| Returns a PreparedRequest for the next request in a redirect chain, if there is one.
|
| ok
| Returns True if :attr:`status_code` is less than 400, False if not.
|
| This attribute checks if the status code of the response is between
| 400 and 600 to see if there was a client error or a server error. If
| the status code is between 200 and 400, this will return True. This
| is **not** a check to see if the response code is ``200 OK``.
|
| text
| Content of the response, in unicode.
|
| If Response.encoding is None, encoding will be guessed using
| ``chardet``.
|
| The encoding of the response content is determined based solely on HTTP
| headers, following RFC 2616 to the letter. If you can take advantage of
| non-HTTP knowledge to make a better guess at the encoding, you should
| set ``r.encoding`` appropriately before accessing this property.
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Data and other attributes defined here:
|
| __attrs__ = ['_content', 'status_code', 'headers', 'url', 'history', '... None '''
Analysis
四、模块方法详解
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """
requests.api
~~~~~~~~~~~~ This module implements the Requests API. :copyright: (c) 2012 by Kenneth Reitz.
:license: Apache2, see LICENSE for more details.
""" from . import sessions def request(method, url, **kwargs):
"""Constructs and sends a :class:`Request <Request>`. :param method: method for the new :class:`Request` object.
:param url: URL for the new :class:`Request` object.
:param params: (optional) Dictionary, list of tuples or bytes to send
in the body of the :class:`Request`.
:param data: (optional) Dictionary, list of tuples, bytes, or file-like
object to send in the body of the :class:`Request`.
:param json: (optional) A JSON serializable Python object to send in the body of the :class:`Request`.
:param headers: (optional) Dictionary of HTTP Headers to send with the :class:`Request`.
:param cookies: (optional) Dict or CookieJar object to send with the :class:`Request`.
:param files: (optional) Dictionary of ``'name': file-like-objects`` (or ``{'name': file-tuple}``) for multipart encoding upload.
``file-tuple`` can be a 2-tuple ``('filename', fileobj)``, 3-tuple ``('filename', fileobj, 'content_type')``
or a 4-tuple ``('filename', fileobj, 'content_type', custom_headers)``, where ``'content-type'`` is a string
defining the content type of the given file and ``custom_headers`` a dict-like object containing additional headers
to add for the file.
:param auth: (optional) Auth tuple to enable Basic/Digest/Custom HTTP Auth.
:param timeout: (optional) How many seconds to wait for the server to send data
before giving up, as a float, or a :ref:`(connect timeout, read
timeout) <timeouts>` tuple.
:type timeout: float or tuple
:param allow_redirects: (optional) Boolean. Enable/disable GET/OPTIONS/POST/PUT/PATCH/DELETE/HEAD redirection. Defaults to ``True``.
:type allow_redirects: bool
:param proxies: (optional) Dictionary mapping protocol to the URL of the proxy.
:param verify: (optional) Either a boolean, in which case it controls whether we verify
the server's TLS certificate, or a string, in which case it must be a path
to a CA bundle to use. Defaults to ``True``.
:param stream: (optional) if ``False``, the response content will be immediately downloaded.
:param cert: (optional) if String, path to ssl client cert file (.pem). If Tuple, ('cert', 'key') pair.
:return: :class:`Response <Response>` object
:rtype: requests.Response Usage:: >>> import requests
>>> req = requests.request('GET', 'https://httpbin.org/get')
<Response [200]>
""" # By using the 'with' statement we are sure the session is closed, thus we
# avoid leaving sockets open which can trigger a ResourceWarning in some
# cases, and look like a memory leak in others.
with sessions.Session() as session:
return session.request(method=method, url=url, **kwargs) def get(url, params=None, **kwargs):
r"""Sends a GET request. :param url: URL for the new :class:`Request` object.
:param params: (optional) Dictionary, list of tuples or bytes to send
in the body of the :class:`Request`.
:param \*\*kwargs: Optional arguments that ``request`` takes.
:return: :class:`Response <Response>` object
:rtype: requests.Response
""" kwargs.setdefault('allow_redirects', True)
return request('get', url, params=params, **kwargs) def options(url, **kwargs):
r"""Sends an OPTIONS request. :param url: URL for the new :class:`Request` object.
:param \*\*kwargs: Optional arguments that ``request`` takes.
:return: :class:`Response <Response>` object
:rtype: requests.Response
""" kwargs.setdefault('allow_redirects', True)
return request('options', url, **kwargs) def head(url, **kwargs):
r"""Sends a HEAD request. :param url: URL for the new :class:`Request` object.
:param \*\*kwargs: Optional arguments that ``request`` takes.
:return: :class:`Response <Response>` object
:rtype: requests.Response
""" kwargs.setdefault('allow_redirects', False)
return request('head', url, **kwargs) def post(url, data=None, json=None, **kwargs):
r"""Sends a POST request. :param url: URL for the new :class:`Request` object.
:param data: (optional) Dictionary, list of tuples, bytes, or file-like
object to send in the body of the :class:`Request`.
:param json: (optional) json data to send in the body of the :class:`Request`.
:param \*\*kwargs: Optional arguments that ``request`` takes.
:return: :class:`Response <Response>` object
:rtype: requests.Response
""" return request('post', url, data=data, json=json, **kwargs) def put(url, data=None, **kwargs):
r"""Sends a PUT request. :param url: URL for the new :class:`Request` object.
:param data: (optional) Dictionary, list of tuples, bytes, or file-like
object to send in the body of the :class:`Request`.
:param json: (optional) json data to send in the body of the :class:`Request`.
:param \*\*kwargs: Optional arguments that ``request`` takes.
:return: :class:`Response <Response>` object
:rtype: requests.Response
""" return request('put', url, data=data, **kwargs) def patch(url, data=None, **kwargs):
r"""Sends a PATCH request. :param url: URL for the new :class:`Request` object.
:param data: (optional) Dictionary, list of tuples, bytes, or file-like
object to send in the body of the :class:`Request`.
:param json: (optional) json data to send in the body of the :class:`Request`.
:param \*\*kwargs: Optional arguments that ``request`` takes.
:return: :class:`Response <Response>` object
:rtype: requests.Response
""" return request('patch', url, data=data, **kwargs) def delete(url, **kwargs):
r"""Sends a DELETE request. :param url: URL for the new :class:`Request` object.
:param \*\*kwargs: Optional arguments that ``request`` takes.
:return: :class:`Response <Response>` object
:rtype: requests.Response
""" return request('delete', url, **kwargs)
五、范例
'''
GET 请求获取URL位置的资源
HEAD 请求获取URL位置资源的响应消息报告,即获得该资源的头部信息
POST 请求向URL位置的资源后附加新的数据
PUT 请求向URL位置存储一个资源,覆盖原URL位置的资源
PATCH 请求局部更新URL位置的资源,即改变该处资源的部分内容
DELETE 请求删除URL位置存储的资源
HTTP协议方法于requests库方法是一一对应的。
requests库的7个主要方法
requests.request() 构造一个请求,支撑以下各方法的基础方法
requests.get() 获取HTML网页的主要方法,对应于HTTP的GET
requests.head() 获取HTML网页头信息的方法,对应于HTTP的HEAD
requests.post() 向HTML网页提交POST请求的方法,对应于HTTP的POST
requests.put() 向HTML网页提交PUT请求的方法,对应于HTTP的PUT
requests.patch() 向HTML网页提交局部修改请求,对应于HTTP的PATCH
requests.delete() 向HTML页面提交删除请求,对应于HTTP的DELETE
1) head()方法示例
>>> r = requests.head('http://httpbin.org/get')
>>> r.headers
{'Content‐Length': '238', 'Access‐Control‐Allow‐Origin': '*', 'Access‐
Control‐Allow‐Credentials': 'true', 'Content‐Type':
'application/json', 'Server': 'nginx', 'Connection': 'keep‐alive',
'Date': 'Sat, 18 Feb 2017 12:07:44 GMT'}
>>> r.text
'' 2) post()方法示例
>>> payload = {'key1': 'value1', 'key2': 'value2'}
>>> r = requests.post('http://httpbin.org/post', data = payload)
>>> print(r.text)
{ ...
"form": {
"key2": "value2",
"key1": "value1"
},
}
向URL POST一个字典,自动编码为form(表单)。
post字典,默认存到form表单中。
>>> r = requests.post('http://httpbin.org/post', data = 'ABC')
>>> print(r.text)
{ ...
"data": "ABC"
"form": {},
}
向URL POST一个字符串,自动编码为data。
post字符串,默认存到data中。 3) put()方法示例
>>> payload = {'key1': 'value1', 'key2': 'value2'}
>>> r = requests.put('http://httpbin.org/put', data = payload)
>>> print(r.text)
{ ...
"form": {
"key2": "value2",
"key1": "value1"
},
} 4) request方法
requsets库的request方法,是所有方法的基础方法。
request方法的完整使用方法
requests.request(method, url, **kwargs)
method : 请求方式,对应get/put/post等7种
url : 拟获取页面的url链接
**kwargs: 控制访问的参数,共13个
methed:request的请求方式(7种)
r = requests.request('GET', url, **kwargs)
r = requests.request('HEAD', url, **kwargs)
r = requests.request('POST', url, **kwargs)
r = requests.request('PUT', url, **kwargs)
r = requests.request('PATCH', url, **kwargs)
r = requests.request('delete', url, **kwargs)
r = requests.request('OPTIONS', url, **kwargs) http协议的请求参数设置。
OPTIONS是向服务器获取一些服务器和客户端能够打交道的参数。
**kwargs: 控制访问的参数,均为可选项
params : 字典或字节序列,作为参数增加到url中
>>> kv = {'key1': 'value1', 'key2': 'value2'}
>>> r = requests.request('GET', 'http://python123.io/ws', params=kv)
>>> print(r.url)
http://python123.io/ws?key1=value1&key2=value2 data : 字典、字节序列或文件对象,作为Request的内容
>>> kv = {'key1': 'value1', 'key2': 'value2'}
>>> r = requests.request('POST', 'http://python123.io/ws', data=kv)
>>> body = '主体内容'
>>> r = requests.request('POST', 'http://python123.io/ws', data=body) json : JSON格式的数据,作为Request的内容
>>> kv = {'key1': 'value1'}
>>> r = requests.request('POST', 'http://python123.io/ws', json=kv) headers : 字典,HTTP定制头
>>> hd = {'user‐agent': 'Chrome/10'}
>>> r = requests.request('POST', 'http://python123.io/ws', headers=hd) cookies : 字典或CookieJar,Request中的cookie
import requests
cookie = "23F5D5F299F9FF7F7541095DA115EFCFADFDF127695462AF30E653A38F03998376B7FA69"
header = {'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/53.0.2785.143 Safari/537.36',
'Connection': 'keep-alive',
'accept': 'text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,*/*;q=0.8',
'Cookie': cookie}
r = requests.get("https://www.cnblogs.com/windyrainy/p/10593806.html",headers=header)
r.encoding = "utf-8"
print(r.text) auth : 元组,支持HTTP认证功能 files : 字典类型,传输文件
>>> fs = {'file': open('data.xls', 'rb')}
>>> r = requests.request('POST', 'http://python123.io/ws', files=fs)
timeout : 设定超时时间,秒为单位
>>> r = requests.request('GET', 'http://www.baidu.com', timeout=10)
proxies : 字典类型,设定访问代理服务器,可以增加登录认证
>>> pxs = { 'http': 'http://user:pass@10.10.10.1:1234'
'https': 'https://10.10.10.1:4321' }
>>> r = requests.request('GET', 'http://www.baidu.com', proxies=pxs) allow_redirects : True/False,默认为True,重定向开关
stream : True/False,默认为True,获取内容立即下载开关
verify : True/False,默认为True,认证SSL证书开关
cert : 本地SSL证书路径
'''
范例
六、关键知识点理解
1、HTTP原理
'''
互联网在传输数据的时候需要遵循一定的规范格式,其中我们在使用浏览器浏览网页的时候就需要遵循HTTP协议,中文名称为超文本传输协议。HTTP协议主要用来传输超文本(网页等)数据。类似的协议还有ftp(主要用来传输文件)等.。 我们需要采集指定计算机中的数据,那么我们怎么才能找到这台计算机呢? HTTP协议使用URL来定位计算机和计算机中的数据资源。例如https://www.cnblogs.com/windyrainy/就是一个URL,在浏览器上输入这串字符,就可以找到博客首页了。https表示协议的名称,https是http协议的加密版本。www.cnblogs.com表示服务器的域名,通过转换可以变成ip地址,可以通过域名在茫茫互联网上定位到博客园的服务器。最后/windyrainy路径是该服务器web站点下的资源。
'''
http原理
2、HTTP请求
'''
我们在浏览器上输入一个URL,按下回车之后很快就看到了页面的内容,这其中包含了很复杂的过程,我们需要了解的是,我们的浏览器向URL指向的服务器发出了http请求request,服务器处理请求之后,返回响应response。浏览器根据response中的源代码等内容进行解析,渲染之后,我们就可以在浏览器上看到丰富多彩的内容了。
'''
http请求
reques主要由以下4部分组成(请求行+请求头+空行+请求体)组成:
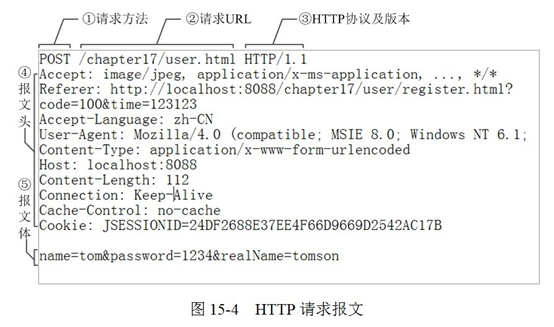
'''
①是请求方法,GET和POST是最常见的HTTP方法,除此以外还包括DELETE、HEAD、OPTIONS、PUT、TRACE。不过,当前的大多数浏览器只支持GET和POST,Spring 3.0提供了一个HiddenHttpMethodFilter,允许你通过“_method”的表单参数指定这些特殊的HTTP方法(实际上还是通过POST提交表单)。服务端配置了HiddenHttpMethodFilter后,Spring会根据_method参数指定的值模拟出相应的HTTP方法,这样,就可以使用这些HTTP方法对处理方法进行映射了。 ②为请求对应的URL地址,它和报文头的Host属性组成完整的请求URL, ③是协议名称及版本号。 ④是HTTP的报文头,报文头包含若干个属性,格式为“属性名:属性值”,服务端据此获取客户端的信息。 ⑤是报文体,它将一个页面表单中的组件值通过param1=value1¶m2=value2的键值对形式编码成一个格式化串,它承载多个请求参数的数据。不但报文体可以传递请求参数,请求URL也可以通过类似于“/chapter15/user.html? param1=value1¶m2=value2”的方式传递请求参数。
'''
报文结构解析
对照上面的请求报文,我们把它进一步分解,你可以看到一幅更详细的结构图:
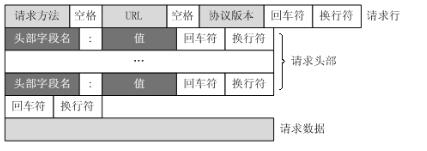
'''
1) 请求行解析
请求行:请求行由三个标记组成:请求方法、请求URI和HTTP版本,它们用空格分隔。
例如:GET /index.html HTTP/1.1
HTTP规范定义了8种可能的请求方法:
GET 检索URI中标识资源的一个简单请求
HEAD 与GET方法相同,服务器只返回状态行和头标,并不返回请求文档
POST 服务器接受被写入客户端输出流中的数据的请求
PUT 服务器保存请求数据作为指定URI新内容的请求
DELETE 服务器删除URI中命名的资源的请求
OPTIONS 关于服务器支持的请求方法信息的请求
TRACE Web服务器反馈Http请求和其头标的请求
CONNECT 已文档化但当前未实现的一个方法,预留做隧道处理 2) 请求头解析
1. Accept:告诉WEB服务器自己接受什么介质类型,*/* 表示任何类型,type/* 表示该类型下的所有子类型,type/sub-type。
2. Accept-Charset: 浏览器申明自己接收的字符集
Accept-Encoding: 浏览器申明自己接收的编码方法,通常指定压缩方法,是否支持压缩,支持什么压缩方法 (gzip,deflate)
Accept-Language::浏览器申明自己接收的语言语言跟字符集的区别:中文是语言,中文有多种字符集,比如big5,gb2312,gbk等等。
3. Accept-Ranges:WEB服务器表明自己是否接受获取其某个实体的一部分(比如文件的一部分)的请求。bytes:表示接受,none:表示不接受。
4. Age:当代理服务器用自己缓存的实体去响应请求时,用该头部表明该实体从产生到现在经过多长时间了。
5. Authorization:当客户端接收到来自WEB服务器的 WWW-Authenticate 响应时,该头部来回应自己的身份验证信息给WEB服务器。
6. Cache-Control:
请求:
no-cache(不要缓存的实体,要求现在从WEB服务器去取)
max-age:(只接受 Age 值小于 max-age 值,并且没有过期的对象)
max-stale:(可以接受过去的对象,但是过期时间必须小于max-stale 值)
min-fresh:(接受其新鲜生命期大于其当前 Age 跟 min-fresh 值之和的缓存对象)
响应:
public:(可以用 Cached 内容回应任何用户)
private:(只能用缓存内容回应先前请求该内容的那个用户)
no-cache:(可以缓存,但是只有在跟WEB服务器验证了其有效后,才能返回给客户端)
max-age:(本响应包含的对象的过期时间)
ALL: no-store:(不允许缓存)
7. Connection:
请求:
close(告诉WEB服务器或者代理服务器,在完成本次请求的响应后,断开连接,不要等待本次连接的后续请求了)。
keepalive(告诉WEB服务器或者代理服务器,在完成本次请求的响应后,保持连接,等待本次连接的后续请求)。
响应:
close(连接已经关闭)。
keepalive(连接保持着,在等待本次连接的后续请求)。
Keep-Alive:如果浏览器请求保持连接,则该头部表明希望 WEB 服务器保持连接多长时间(秒)。
例如:Keep-Alive:300
8. Content-Encoding:WEB服务器表明自己使用了什么压缩方法(gzip,deflate)压缩响应中的对象。
例如:Content-Encoding:gzip
Content-Language:WEB 服务器告诉浏览器自己响应的对象的语言。
Content-Length: WEB 服务器告诉浏览器自己响应的对象的长度。
例如:Content-Length: 26012
Content-Range: WEB 服务器表明该响应包含的部分对象为整个对象的哪个部分。
例如:Content-Range: bytes 21010-47021/47022
Content-Type: WEB 服务器告诉浏览器自己响应的对象的类型。
例如:Content-Type:application/xml
9. ETag:就是一个对象(比如URL)的标志值,就一个对象而言,比如一个 html 文件,如果被修改了,其 Etag 也会别修改, 所以,ETag 的作用跟 Last-Modified 的作用差不多,主要供 WEB 服务器 判断一个对象是否改变了。比如前一次请求某个 html 文件时,获得了其 ETag,当这次又请求这个文件时,浏览器就会把先前获得的 ETag 值发送给 WEB 服务器,然后 WEB 服务器会把这个 ETag 跟该文件的当前 ETag 进行对比,然后就知道这个文件有没有改变了。
10. Expired:WEB服务器表明该实体将在什么时候过期,对于过期了的对象,只有在跟WEB服务器验证了其有效性后,才能用来响应客户请求。是 HTTP/1.0 的头部。
例如:Expires:Sat, 23 May 2009 10:02:12 GMT
11. Host:客户端指定自己想访问的WEB服务器的域名/IP 地址和端口号。
例如:Host:rss.sina.com.cn
12. If-Match:如果对象的 ETag 没有改变,其实也就意味著对象没有改变,才执行请求的动作。
If-None-Match:如果对象的 ETag 改变了,其实也就意味著对象也改变了,才执行请求的动作。
13. If-Modified-Since:如果请求的对象在该头部指定的时间之后修改了,才执行请求的动作(比如返回对象),否则返回代码304,告诉浏览器该对象没有修改。
例如:If-Modified-Since:Thu, 10 Apr 2008 09:14:42 GMT
If-Unmodified-Since:如果请求的对象在该头部指定的时间之后没修改过,才执行请求的动作(比如返回对象)。
14. If-Range:浏览器告诉 WEB 服务器,如果我请求的对象没有改变,就把我缺少的部分给我,如果对象改变了,就把整个对象给我。 浏览器通过发送请求对象的ETag 或者 自己所知道的最后修改时间给 WEB 服务器,让其判断对象是否改变了。总是跟 Range 头部一起使用。
15. Last-Modified:WEB 服务器认为对象的最后修改时间,比如文件的最后修改时间,动态页面的最后产生时间等等。
例如:Last-Modified:Tue, 06 May 2008 02:42:43 GMT
16. Location:WEB 服务器告诉浏览器,试图访问的对象已经被移到别的位置了,到该头部指定的位置去取。
例如:Location:http://i0.sinaimg.cn/dy/deco/2008/0528/sinahome_0803_ws_005_text_0.gif
17. Pramga:主要使用 Pramga: no-cache,相当于 Cache-Control: no-cache。
例如:Pragma:no-cache
18. Proxy-Authenticate: 代理服务器响应浏览器,要求其提供代理身份验证信息。
Proxy-Authorization:浏览器响应代理服务器的身份验证请求,提供自己的身份信息。
19. Range:浏览器(比如 Flashget 多线程下载时)告诉 WEB 服务器自己想取对象的哪部分。
例如:Range: bytes=1173546-
20. Referer:浏览器向 WEB 服务器表明自己是从哪个 网页/URL 获得/点击 当前请求中的网址/URL。
例如:Referer:http://www.sina.com/
21. Server: WEB 服务器表明自己是什么软件及版本等信息。
例如:Server:Apache/2.0.61 (Unix)
22. User-Agent: 浏览器表明自己的身份(是哪种浏览器)。
例如:User-Agent:Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; zh-CN;rv:1.8.1.14) Gecko/20080404 Firefox/2.0.0.14
23. Transfer-Encoding: WEB 服务器表明自己对本响应消息体(不是消息体里面的对象)作了怎样的编码,比如是否分块(chunked)。
例如:Transfer-Encoding: chunked
24. Vary: WEB服务器用该头部的内容告诉 Cache 服务器,在什么条件下才能用本响应所返回的对象响应后续的请求。假如源WEB服务器在接到第一个请求消息时,其响应消息的头部为:Content-Encoding: gzip; Vary: Content-Encoding 那么 Cache 服务器会分析后续请求消息的头部,检查其 Accept-Encoding,是否跟先前响应的 Vary 头部值一致,即是否使用相同的内容编码方法,这样就可以防止 Cache 服务器用自己Cache 里面压缩后的实体响应给不具备解压能力的浏览器。
例如:Vary:Accept-Encoding
25. Via: 列出从客户端到 OCS 或者相反方向的响应经过了哪些代理服务器,他们用什么协议(和版本)发送的请求。当客户端请求到达第一个代理服务器时,该服务器会在自己发出的请求里面添加 Via 头部,并填上自己的相关信息,当下一个代理服务器 收到第一个代理服务器的请求时,会在自己发出的请求里面复制前一个代理服务器的请求的Via头部,并把自己的相关信息加到后面, 以此类推,当 OCS 收到最后一个代理服务器的请求时,检查 Via 头部,就知道该请求所经过的路由。
例如:Via:1.0 236-81.D07071953.sina.com.cn:80 (squid/2.6.STABLE13)
3) 空行解析
空行:最后一个请求头标之后是一个空行,发送回车符和退行,通知服务器以下不再有头标
'''
报文内容解析
HTTP 请求消息头部实例:
'''
Host:rss.sina.com.cn
User-Agent:Mozilla/5.0 (Windows; U; Windows NT 5.1; zh-CN; rv:1.8.1.14) Gecko/20080404 Firefox/2.0.0.14
Accept:text/xml,application/xml,application/xhtml+xml,text/html;q=0.9,text/plain;q=0.8,image/png,*/*;q=0.5
Accept-Language:zh-cn,zh;q=0.5
Accept-Encoding:gzip,deflate
Accept-Charset:gb2312,utf-8;q=0.7,*;q=0.7
Keep-Alive:300
Connection:keep-alive
Cookie:userId=C5bYpXrimdmsiQmsBPnE1Vn8ZQmdWSm3WRlEB3vRwTnRtW <-- Cookie
If-Modified-Since:Sun, 01 Jun 2008 12:05:30 GMT
Cache-Control:max-age=0
'''
HTTP 请求消息头部实例:
3、HTTP响应
HTTP的响应报文也由4部分(响应行+响应头+空行+响应体)组成:

'''
1) 状态行
状态行:状态行由三个标记组成:HTTP版本、响应代码和响应描述。
HTTP版本:向客户端指明其可理解的最高版本。
响应代码:3位的数字代码,指出请求的成功或失败,如果失败则指出原因。
响应描述:为响应代码的可读性解释。
例如:HTTP/1.1 200 OK
HTTP响应码:
1xx 消息,一般是告诉客户端,请求已经收到了,正在处理,别急...
2xx 处理成功,一般表示:请求收悉、我明白你要的、请求已受理、已经处理完成等信息.
3xx 重定向到其它地方。它让客户端再发起一个请求以完成整个处理。
4xx 处理发生错误,责任在客户端,如客户端的请求一个不存在的资源,客户端未被授权,禁止访问等。
5xx 处理发生错误,责任在服务端,如服务端抛出异常,路由出错,HTTP版本不支持等。
继续 101 分组交换协 200 OK 201 被创建 202 被采纳
非授权信息 204 无内容 205 重置内容 206 部分内容
多选项 301 永久地传送 302 找到 303 参见其他
未改动 305 使用代理 307 暂时重定向 400 错误请求
未授权 402 要求付费 403 禁止 404 未找到
不允许的方法 406 不被采纳 407 要求代理授权408 请求超时
冲突 410 过期的 411 要求的长度 412 前提不成立
请求实例太大 414 请求URI太大 415 不支持的媒体类型
无法满足的请求范围 417 失败的预期 500 内部服务器错误
未被使用 502 网关错误 503 不可用的服务 504 网关超时 2) 响应头标
响应头标:像请求头标一样,它们指出服务器的功能,标识出响应数据的细节。 3) 空行
空行:最后一个响应头标之后是一个空行,发送回车符和退行,表明服务器以下不再有头标。 4) 响应数据
响应数据:HTML文档和图像等,也就是HTML本身。
'''
报文结构解析
HTTP 响应消息头部实例:
'''
Status:OK - 200 <-- 响应状态码,表示 web 服务器处理的结果。
Date:Sun, 01 Jun 2008 12:35:47 GMT
Server:Apache/2.0.61 (Unix)
Last-Modified:Sun, 01 Jun 2008 12:35:30 GMT
Accept-Ranges:bytes
Content-Length:18616
Cache-Control:max-age=120
Expires:Sun, 01 Jun 2008 12:37:47 GMT
Content-Type:application/xml
Age:2
X-Cache:HIT from 236-41.D07071951.sina.com.cn <-- 反向代理服务器使用的 HTTP 头部
Via:1.0 236-41.D07071951.sina.com.cn:80 (squid/2.6.STABLE13)
Connection:close
'''
HTTP 响应消息头部实例:
4、Session和Cookies
在浏览一些网站,比如购物的时候,我们常常需要先登陆,登陆过后我们可以连续访问网站,并且可以将我们需要的购买的东西加入购物车。但是有时候我们中途过了一段时间没有操作就需要重新登陆。还有某些网站,打开网页之后就已经登陆了。这些功能看起来来很神奇,其实都是Session和Cookie在发挥作用。
简述
1、无状态HTTP
'''
Http有个特点,即无状态。什么叫无状态呢。Http无状态是指Http协议对事务处理没有记忆能力,当我们向服务器发送请求后,服务器处理请求之后返回结果。这是一个独立的过程,再次向服务器发出请求,服务器做出响应又是一次独立的过程。不会有一条网线一直连着你的电脑和服务器来完成你的所有请求。因此,服务器并不知道收到的两次请求是否来自同一个用户。这种效果并不是我们想要的。为了保持前后的状态,我们需要将前面所有请求中的数据再重传一次,这是非常麻烦和浪费资源的。为了解决这个问题,用于保持HTTP连接状态的Session和Cookies就出现了。
'''
无状态HTTP
2、session与cookies
'''
session是指从我们打开一个网站开始至我们关闭浏览器一系列的请求过程。比如我们打开淘宝网站,淘宝网站的服务器就会为我们创建并保存一个会话对象,会话对象里有用户的一些信息,比如我们登陆之后,会话中就保存着我们的账号信息。会话有一定的生命周期,当我们长时间(超过会话有效期)没有访问该网站或者关闭浏览器,服务器就会删掉该会话对象。 cookies是指网站为了辨别用户身份,进行会话跟踪而储存在本地终端的数据,cookies一般再电脑中的文件里以文本形式储存。cookies其实是有键值对组成的
'''
session、cookies
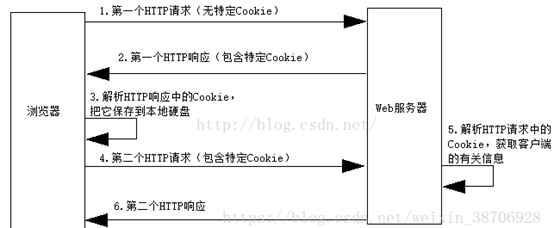
3、会话维持
'''
当客户端浏览器第一次请求服务器时,服务器会再response中设置一个Set-Cookies的字段,用来标记用户的身份,客户端浏览器会把cookies保存起来,cookies中保存的有Session的id信息。当客户端浏览器再次请求该网站时,会把Cookies放在请求头中一起提交给服务器,服务器检查该Cookies即可找到对应的会话是什么,再通过判断会话来辨认用户的状态。 当我们成功登陆网站时,网站会告诉客户端应该设置哪些Cookies信息,以保持登陆状态。如果客户端浏览器传给服务器的cookies无效或者会话过期,可能就会收到错误的响应或者跳转到登陆页面重新登陆。 cookie和session的共同之处在于:cookie和session都是用来跟踪浏览器用户身份的会话方式。
cookie和session的区别是:cookie数据保存在客户端,session数据保存在服务器端。
cookie不是很安全,别人可以分析存放在本地的COOKIE并进行COOKIE欺骗,如果主要考虑到安全应当使用session,当然也没有绝对的安全,只是相对cookie,session更加安全
session会在一定时间内保存在服务器上。当访问增多,会比较占用你服务器的性能,如果主要考虑到减轻服务器性能方面,应当使用COOKIE
cookie和session各有优缺点,所以将登陆信息等重要信息存放为SESSION;其他信息如果需要保留,可以放在COOKIE中
'''
会话维持
Python中第三方模块requests解析的更多相关文章
- Python中第三方库Requests库的高级用法详解
Python中第三方库Requests库的高级用法详解 虽然Python的标准库中urllib2模块已经包含了平常我们使用的大多数功能,但是它的API使用起来让人实在感觉不好.它已经不适合现在的时代, ...
- Python中第三方的用于解析HTML的库:BeautifulSoup
背景 在Python去写爬虫,网页解析等过程中,比如: 如何用Python,C#等语言去实现抓取静态网页+抓取动态网页+模拟登陆网站 常常需要涉及到HTML等网页的解析. 当然,对于简单的HTML中内 ...
- python中zipfile模块实例化解析
文章内容由--“脚本之家“--提供,在此感谢脚本之家的贡献,该网站网址为:https://www.jb51.net/ 简介: zipfile是python里用来做zip格式编码的压缩和解压缩的,由于是 ...
- Python中functools模块函数解析
Python自带的 functools 模块提供了一些常用的高阶函数,也就是用于处理其它函数的特殊函数.换言之,就是能使用该模块对可调用对象进行处理. functools模块函数概览 functool ...
- python中jsonpath模块,解析多层嵌套的json数据
1. jsonpath介绍用来解析多层嵌套的json数据;JsonPath 是一种信息抽取类库,是从JSON文档中抽取指定信息的工具,提供多种语言实现版本,包括:Javascript, Python, ...
- python基础——第三方模块
python基础——第三方模块 在Python中,安装第三方模块,是通过包管理工具pip完成的. 如果你正在使用Mac或Linux,安装pip本身这个步骤就可以跳过了. 如果你正在使用Window ...
- Python中optionParser模块的使用方法[转]
本文以实例形式较为详尽的讲述了Python中optionParser模块的使用方法,对于深入学习Python有很好的借鉴价值.分享给大家供大家参考之用.具体分析如下: 一般来说,Python中有两个内 ...
- Python中的模块介绍和使用
在Python中有一个概念叫做模块(module),这个和C语言中的头文件以及Java中的包很类似,比如在Python中要调用sqrt函数,必须用import关键字引入math这个模块,下面就来了解一 ...
- python中导入模块的本质, 无法导入手写模块的解决办法
最近身边一些朋友发生在项目当中编写自己模块,导入的时候无法导入的问题. 下面我来分享一下关于python中导入模块的一些基本知识. 1 导入模块时寻找路径 在每一个运行的python程序当中,都维护了 ...
随机推荐
- 朱晔的互联网架构实践心得S2E1:业务代码究竟难不难写?
注意,这是我的架构实践心得的第二季的系列文章,第一季有10篇你也可以回顾. 见https://www.cnblogs.com/lovecindywang/category/1296779.html 最 ...
- Jenkins- job之间传参
前言: 本文介绍插件: Parameterized Trigger plugin的具体使用方法. 一.插件介绍 Parameterized Trigger plugin插件可以让你在构建完成时触发新的 ...
- 百度软件开发实习生c++方向面经(一面)
百度2017实习生软件开发(cpp方向) 首先说一下岗位.分为软件开发,开发测试,前端,机器学习数据挖掘,移动开发,据我观察,报的人数来看,软件开发最多,移动开发和开发测试较少.百度前台还准备了吃的喝 ...
- 每周分享之cookie详解
本章从JS方向讲解cookie的使用.(实质上后端代码也是差不多用法,无非读取和设置两块) 基本用法:document.cookie="username=pengpeng"; 修改 ...
- 《梦断代码》Scott Rosenberg著(二)
书中有一段说的是一个闪烁缺陷——在改变某软件中某个窗体的尺寸时,屏幕会闪烁一秒钟左右.虽然该缺陷不会影响程序运行,但它不符合作者的审美观,历时六个多月仍然没能修正.其实在日常的编程中也有许多小bug的 ...
- hadoop:如何运行自带wordcount
1.在linux系统创建文件 vi aa.txt --------i 进行编辑 输入 内容(多个单词例如:aa bb cc aa) 2.在HDFS上面创建文件夹 hdfs dfs -mkdir ...
- Problem 2285 迷宫寻宝
http://acm.fzu.edu.cn/problem.php?pid=2285 Problem Description 洪尼玛今天准备去寻宝,在一个n*n (n行, n列)的迷宫中,存在着一个入 ...
- Java使用Redis实现分布式锁来防止重复提交问题
如何用消息系统避免分布式事务? - 少年阿宾 - BlogJavahttp://www.blogjava.net/stevenjohn/archive/2018/01/04/433004.html [ ...
- WCF上传下载文件
思路:上传时将要上传的文件流提交给服务器端 下载时只需要将服务器上的流返回给客户端即可 1.契约,当需要传递的数量多于一个时就需要通过messagecontract来封装起来 这里分别实现了上传和下载 ...
- babel (三) babel polly-fill
Babel includes a polyfill that includes a custom regenerator runtime and core-js. This will emulate ...
