Spring详解(六)------AspectJ 实现AOP
上一篇博客我们引出了 AOP 的概念,以及 AOP 的具体实现方式。但是为什么要这样实现?以及提出的切入点表达式到底该怎么理解?
这篇博客我们通过对 AspectJ 框架的介绍来详细了解。
1、什么是 AspectJ?
AspectJ是一个面向切面的框架,它扩展了Java语言。AspectJ定义了AOP语法,也可以说 AspectJ 是一个基于 Java 语言的 AOP 框架。通常我们在使用 Spring AOP 的时候,都会导入 AspectJ 的相关 jar 包。

在 spring2.0以后,spring新增了对AspectJ 切点表达式的支持;Aspect1.5新增注解功能,通过 JDK5的注解技术,能直接在类中定义切面;新版本的 spring 框架,也都建议使用 AspectJ 来实现 AOP。所以说在 spring AOP 的核心包 Spring-aop-3.2.jar 里面也有对 AspectJ 的支持。
2、切入点表达式
上一篇博客中,我们在spring配置文件中配置如下:
<!-- 切入点表达式 -->
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.ys.aop.*.*(..))" id="myPointCut"/>
那么它表达的意思是 返回值任意,包名为 com.ys.aop 下的任意类名中的任意方法名,参数任意。那么这到底是什么意思呢?
首先 execution 是 AspectJ 框架定义的一个切入点函数,其语法形式如下:
execution(modifiers-pattern? ref-type-pattern declaring-type-pattern? name-pattern(param-pattern) throws-pattern?)
类修饰符 返回值 方法所在的包 方法名 方法抛出的异常
简单点来说就是:
语法:execution(修饰符 返回值 包.类.方法名(参数) throws异常)
具体解释我们用下面一张思维导图来看:
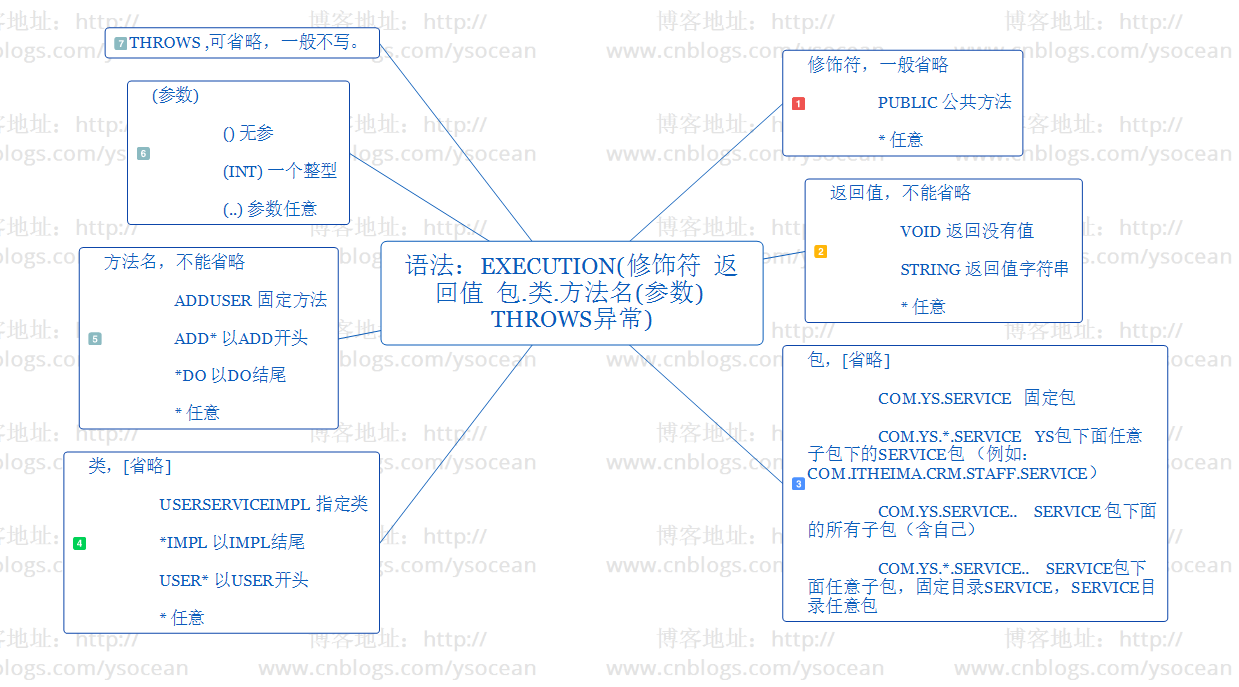
注意:如果切入点表达式有多个不同目录呢? 可以通过 || 来表示或的关系。
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.ys.*Service1.*(..)) ||
execution(* com.ys.*Service2.*(..))" id="myPointCut"/>
表示匹配 com.ys包下的,以 Service1结尾或者以Service2结尾的类的任意方法。
AOP 切入点表达式支持多种形式的定义规则:
1、execution:匹配方法的执行(常用)
execution(public *.*(..))
2.within:匹配包或子包中的方法(了解)
within(com.ys.aop..*)
3.this:匹配实现接口的代理对象中的方法(了解)
this(com.ys.aop.user.UserDAO)
4.target:匹配实现接口的目标对象中的方法(了解)
target(com.ys.aop.user.UserDAO)
5.args:匹配参数格式符合标准的方法(了解)
args(int,int)
6.bean(id) 对指定的bean所有的方法(了解)
bean('userServiceId')
2、Aspect 通知类型
Aspect 通知类型,定义了类型名称以及方法格式。类型如下:
before:前置通知(应用:各种校验)
在方法执行前执行,如果通知抛出异常,阻止方法运行
afterReturning:后置通知(应用:常规数据处理)
方法正常返回后执行,如果方法中抛出异常,通知无法执行
必须在方法执行后才执行,所以可以获得方法的返回值。
around:环绕通知(应用:十分强大,可以做任何事情)
方法执行前后分别执行,可以阻止方法的执行
必须手动执行目标方法
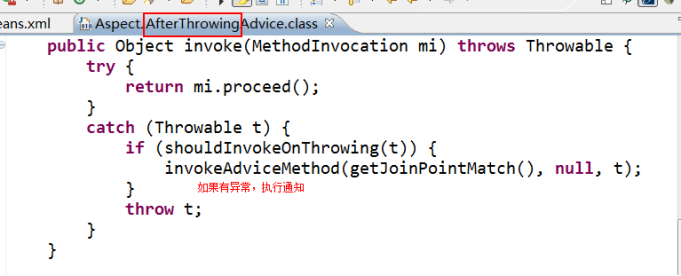
afterThrowing:抛出异常通知(应用:包装异常信息)
方法抛出异常后执行,如果方法没有抛出异常,无法执行
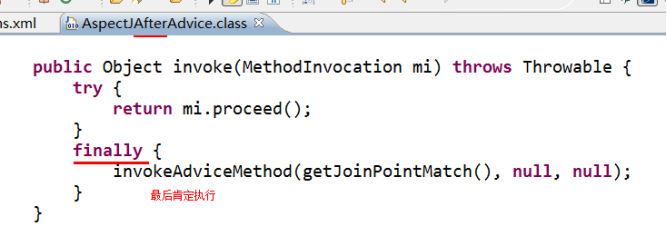
after:最终通知(应用:清理现场)
方法执行完毕后执行,无论方法中是否出现异常
这里最重要的是around,环绕通知,它可以代替上面的任意通知。
在程序中表示的意思如下:
try{
//前置:before
//手动执行目标方法
//后置:afterRetruning
} catch(){
//抛出异常 afterThrowing
} finally{
//最终 after
}
对应的 jar 包如下:
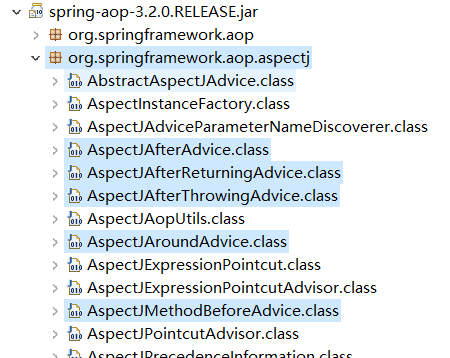
我们可以查看源码:
3、AOP具体实例
①、创建接口
package com.ys.aop;
public interface UserService {
//添加 user
public void addUser();
//删除 user
public void deleteUser();
}
②、创建实现类
package com.ys.aop;
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{
@Override
public void addUser() {
System.out.println("增加 User");
}
@Override
public void deleteUser() {
System.out.println("删除 User");
}
}
③、创建切面类(包含各种通知)
package com.ys.aop;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
public class MyAspect {
/**
* JoinPoint 能获取目标方法的一些基本信息
* @param joinPoint
*/
public void myBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint){
System.out.println("前置通知 : " + joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
}
public void myAfterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object ret){
System.out.println("后置通知 : " + joinPoint.getSignature().getName() + " , -->" + ret);
}
public void myAfter(){
System.out.println("最终通知");
}
}
④、创建spring配置文件applicationContext.xml
我们首先测试前置通知、后置通知、最终通知
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--1、 创建目标类 -->
<bean id="userService" class="com.ys.aop.UserServiceImpl"></bean>
<!--2、创建切面类(通知) -->
<bean id="myAspect" class="com.ys.aop.MyAspect"></bean> <!--3、aop编程
3.1 导入命名空间
3.2 使用 <aop:config>进行配置
proxy-target-class="true" 声明时使用cglib代理
如果不声明,Spring 会自动选择cglib代理还是JDK动态代理
<aop:pointcut> 切入点 ,从目标对象获得具体方法
<aop:advisor> 特殊的切面,只有一个通知 和 一个切入点
advice-ref 通知引用
pointcut-ref 切入点引用
3.3 切入点表达式
execution(* com.ys.aop.*.*(..))
选择方法 返回值任意 包 类名任意 方法名任意 参数任意 -->
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect ref="myAspect">
<!-- 切入点表达式 -->
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.ys.aop.*.*(..))" id="myPointCut"/>
<!-- 3.1 前置通知
<aop:before method="" pointcut="" pointcut-ref=""/>
method : 通知,及方法名
pointcut :切入点表达式,此表达式只能当前通知使用。
pointcut-ref : 切入点引用,可以与其他通知共享切入点。
通知方法格式:public void myBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint){
参数1:org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint 用于描述连接点(目标方法),获得目标方法名等
-->
<aop:before method="myBefore" pointcut-ref="myPointCut"/> <!-- 3.2后置通知 ,目标方法后执行,获得返回值
<aop:after-returning method="" pointcut-ref="" returning=""/>
returning 通知方法第二个参数的名称
通知方法格式:public void myAfterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object ret){
参数1:连接点描述
参数2:类型Object,参数名 returning="ret" 配置的
-->
<aop:after-returning method="myAfterReturning" pointcut-ref="myPointCut" returning="ret" /> <!-- 3.3 最终通知 -->
<aop:after method="myAfter" pointcut-ref="myPointCut"/> </aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
⑤、测试
@Test
public void testAop(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
UserService useService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
useService.addUser();
}
控制台打印:
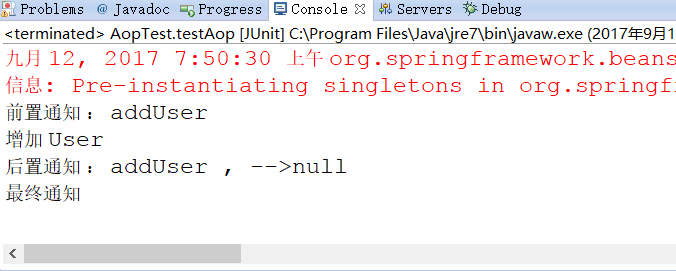
注意,后置通知的返回值为 null,是因为我们的目标方法 addUser() 没有返回值。如果有返回值,这里就是addUser() 的返回值。
4、测试异常通知
目标接口保持不变,目标类我们手动引入异常:
public void addUser() {
int i = 1/0;//显然这里会抛出除数不能为 0
System.out.println("增加 User");
}
接着配置切面:MyAspect.java
public void myAfterThrowing(JoinPoint joinPoint,Throwable e){
System.out.println("抛出异常通知 : " + e.getMessage());
}
接着在 applicationContext.xml 中配置如下:
<!-- 3.4 抛出异常
<aop:after-throwing method="" pointcut-ref="" throwing=""/>
throwing :通知方法的第二个参数名称
通知方法格式:public void myAfterThrowing(JoinPoint joinPoint,Throwable e){
参数1:连接点描述对象
参数2:获得异常信息,类型Throwable ,参数名由throwing="e" 配置
-->
<aop:after-throwing method="myAfterThrowing" pointcut-ref="myPointCut" throwing="e"/>
测试:
@Test
public void testAop(){
String str = "com/ys/execption/applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(str);
UserService useService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
useService.addUser();
}
控制台打印:
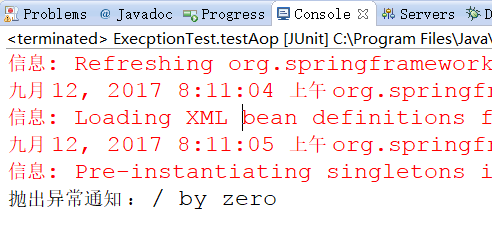
5、测试环绕通知
目标接口和目标类保持不变,切面MyAspect 修改如下:
public class MyAspect {
public Object myAround(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable{
System.out.println("前置通知");
//手动执行目标方法
Object obj = joinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("后置通知");
return obj;
}
}
applicationContext.xml 配置如下:
<!-- 环绕通知
<aop:around method="" pointcut-ref=""/>
通知方法格式:public Object myAround(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable{
返回值类型:Object
方法名:任意
参数:org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint
抛出异常
执行目标方法:Object obj = joinPoint.proceed();
-->
<aop:around method="myAround" pointcut-ref="myPointCut"/>
测试:
@Test
public void testAop(){
String str = "com/ys/around/applicationContext.xml";
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(str);
UserService useService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
useService.addUser();
}
打印结果:
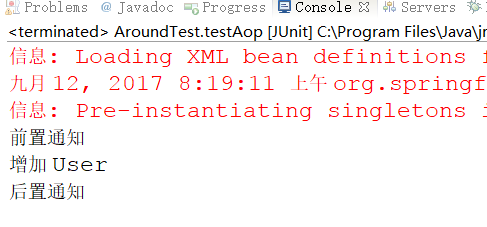
那么至此,通过 xml 配置的方式我们讲解了Spring AOP 的配置。下一章将通过注解的方式来实现。
Spring详解(六)------AspectJ 实现AOP的更多相关文章
- Spring详解(七)------AOP 注解
上一篇博客我们讲解了 AspectJ 框架如何实现 AOP,然后具体的实现方式我们是通过 xml 来进行配置的.xml 方式思路清晰,便于理解,但是书写过于麻烦.这篇博客我们将用 注解 的方式来进行 ...
- Spring 详解(二)------- AOP关键概念以及两种实现方式
目录 1. AOP 关键词 2. AOP 的作用 3. AOP 的通知类型 4. 基于 xml 的配置方式 5. 基于注解的配置方式 6. 切面的优先级 7. 重用切点表达式 8. 两种方式的比较(摘 ...
- Spring详解(五)------AOP
这章我们接着讲 Spring 的核心概念---AOP,这也是 Spring 框架中最为核心的一个概念. PS:本篇博客源码下载链接:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1skZjg7r 密码 ...
- Spring 详解(一)------- AOP前序
目录 1. AOP 简介 2. 示例需求 3. 解决方法一:使用静态代理 4. 解决方法二:使用动态代理 1. AOP 简介 AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming),通常 ...
- Spring详解(六)------AOP 注解
上一篇博客我们讲解了 AspectJ 框架如何实现 AOP,然后具体的实现方式我们是通过 xml 来进行配置的.xml 方式思路清晰,便于理解,但是书写过于麻烦.这篇博客我们将用 注解 的方式来进行 ...
- Spring详解(五)------AspectJ 实现AOP
上一篇博客我们引出了 AOP 的概念,以及 AOP 的具体实现方式.但是为什么要这样实现?以及提出的切入点表达式到底该怎么理解? 这篇博客我们通过对 AspectJ 框架的介绍来详细了解. 1.什么是 ...
- Spring详解(一)------概述
本系列教程我们将对 Spring 进行详解的介绍,相信你在看完后一定能够有所收获. 1.什么是 Spring ? Spring是一个开源框架,Spring是于2003 年兴起的一个轻量级的Java 开 ...
- Spring详解
https://gitee.com/xiaomosheng888老师的码云 1.核心容器:核心容器提供 Spring 框架的基本功能(Spring Core).核心容器的主要组件是 BeanFacto ...
- Spring详解------概述
1.什么是 Spring ? Spring是一个开源框架,Spring是于2003 年兴起的一个轻量级的Java 开发框架,由Rod Johnson 在其著作Expert One-On-One J2E ...
随机推荐
- PlayFramework 一步一步来 之 页面模板引擎
Play的魔板引擎本人认为可以说是为full stack Developers量身打造的功能.在原有的html页面基础上,只需要在html文件名后缀名前面加上”.scala“,就可以在页面上写Scal ...
- 移动端 去除onclick点击事件出现的背景色框
这个特效是实现在移动端点击某个地方的时候,比如说按钮或者超链接的时候,系统会默认加上一些灰色的背景和一些高亮的效果.但是有的时候我们并不想要这些效果.并且希望点击的时候实现神不知鬼不觉的感觉,,这个时 ...
- JavaScript中Object.keys用法
Object.keys()方法会返回一个由一个给定对象的自身可枚举属性组成的数组. var data={a:1,b:2,c:9,d:4,e:5}; console.log(data);//{a: 1, ...
- vue中created、mounted、 computed,watch,method 等方法整理
created:html加载完成之前,执行.执行顺序:父组件-子组件 mounted:html加载完成后执行.执行顺序:子组件-父组件 methods:事件方法执行 watch:watch是去监听一个 ...
- nginx上传文件时 nginx 413 Request Entity Too Large 错误
产生原因: 上传文件的大小超出了 Nginx 允许的最大值,默认是1M: 解决方法: 修改Nginx的配置文件(一般是:nginx/nginx.conf),在 http{} 段中增大nginx上传文件 ...
- redis学习-集合set常用命令
redis学习-集合set常用命令 1.sadd:添加一个元素到集合中(集合中的元素无序的并且唯一) 2.smembers:查看集合中所有的元素(上图事例) 3.srem:删除结合中指定的元素 4 ...
- (29)Why Earth may someday look like Mars
https://www.ted.com/talks/anjali_tripathi_why_earth_may_someday_look_like_mars/transcript00:12So whe ...
- vue-cli入门
这也仅仅是入门而已了☺ 自己也在慢慢学习中,不对的地方希望大佬可以多多指教,请不吝赐教,感激不尽. 这章主要是搭建环境: 1.安装node环境 从官网下载并安装node,傻瓜操作,安装完成之后,命令行 ...
- 逻辑回归 vs 决策树 vs 支持向量机(I)
原文链接:http://www.edvancer.in/logistic-regression-vs-decision-trees-vs-svm-part1/ 分类问题是我们在各个行业的商业业务中遇到 ...
- 行业相关的webgl项目
炼钢厂污水处理http://www.hightopo.com/demo/CirculatingWaterPump/index.html智能idc机房http://www.hightopo.com/de ...
