C程序编译过程
- 1.1程序被其他程序翻译成不同的格式
1.hello.c
- #include <stdio.h>
- int main()
- {
- printf("hello world\n");
- }
2.编译过程
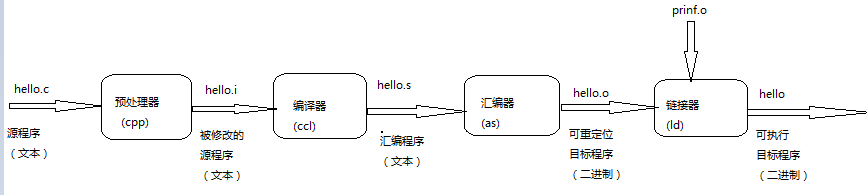
3.编译系统
预处理器、编译器、汇编器和链接器一起构成了编译系统
预处理阶段。预处理器(cpp)根据以字符#开通的命令,修改原始的C程序。比如hello.c中第1行的#include<stdio.h>命令告诉预处理器读取系统头文件stdio.h的内容,并把它直接插入到程序的文本中。结果就得到了另一个C程序,通常是以.i作为文件扩展名
预处理的过程主要处理包括以下过程:
- 将所有的#define删除,并且展开所有的宏定义
- 处理所有的条件预编译指令,比如#if #ifdef #elif #else #endif等
- 处理#include 预编译指令,将被包含的文件插入到该预编译指令的位置。
- 删除所有注释 “//”和”/* */”.
- 添加行号和文件标识,以便编译时产生调试用的行号及编译错误警告行号。
- 保留所有的#pragma编译器指令,因为编译器需要使用它们
通常使用以下命令来进行预处理:
gcc -E hello.c -o hello.i
参数-E表示只进行预处理 或者也可以使用以下指令完成预处理过程
cpp hello.c > hello.i /* cpp – The C Preprocessor */
- # "hello.c"
- # "<built-in>"
- # "<command-line>"
- # "hello.c"
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- # "/usr/include/features.h"
- # "/usr/include/features.h"
- # "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/predefs.h"
- # "/usr/include/features.h"
- # "/usr/include/features.h"
- # "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/sys/cdefs.h"
- # "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/sys/cdefs.h"
- # "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/wordsize.h"
- # "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/sys/cdefs.h"
- # "/usr/include/features.h"
- # "/usr/include/features.h"
- # "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/gnu/stubs.h"
- # "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/wordsize.h"
- # "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/gnu/stubs.h"
- # "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/gnu/stubs-64.h"
- # "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/gnu/stubs.h"
- # "/usr/include/features.h"
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- # "/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-linux-gnu/4.6/include/stddef.h"
- # "/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-linux-gnu/4.6/include/stddef.h"
- typedef long unsigned int size_t;
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- # "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/types.h"
- # "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/types.h"
- # "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/wordsize.h"
- # "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/types.h"
- typedef unsigned char __u_char;
- typedef unsigned short int __u_short;
- typedef unsigned int __u_int;
- typedef unsigned long int __u_long;
- typedef signed char __int8_t;
- typedef unsigned char __uint8_t;
- typedef signed short int __int16_t;
- typedef unsigned short int __uint16_t;
- typedef signed int __int32_t;
- typedef unsigned int __uint32_t;
- typedef signed long int __int64_t;
- typedef unsigned long int __uint64_t;
- typedef long int __quad_t;
- typedef unsigned long int __u_quad_t;
- # "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/types.h"
- # "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/typesizes.h"
- # "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/types.h"
- typedef unsigned long int __dev_t;
- typedef unsigned int __uid_t;
- typedef unsigned int __gid_t;
- typedef unsigned long int __ino_t;
- typedef unsigned long int __ino64_t;
- typedef unsigned int __mode_t;
- typedef unsigned long int __nlink_t;
- typedef long int __off_t;
- typedef long int __off64_t;
- typedef int __pid_t;
- typedef struct { int __val[]; } __fsid_t;
- typedef long int __clock_t;
- typedef unsigned long int __rlim_t;
- typedef unsigned long int __rlim64_t;
- typedef unsigned int __id_t;
- typedef long int __time_t;
- typedef unsigned int __useconds_t;
- typedef long int __suseconds_t;
- typedef int __daddr_t;
- typedef long int __swblk_t;
- typedef int __key_t;
- typedef int __clockid_t;
- typedef void * __timer_t;
- typedef long int __blksize_t;
- typedef long int __blkcnt_t;
- typedef long int __blkcnt64_t;
- typedef unsigned long int __fsblkcnt_t;
- typedef unsigned long int __fsblkcnt64_t;
- typedef unsigned long int __fsfilcnt_t;
- typedef unsigned long int __fsfilcnt64_t;
- typedef long int __ssize_t;
- typedef __off64_t __loff_t;
- typedef __quad_t *__qaddr_t;
- typedef char *__caddr_t;
- typedef long int __intptr_t;
- typedef unsigned int __socklen_t;
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- struct _IO_FILE;
- typedef struct _IO_FILE FILE;
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- typedef struct _IO_FILE __FILE;
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- # "/usr/include/libio.h"
- # "/usr/include/libio.h"
- # "/usr/include/_G_config.h"
- # "/usr/include/_G_config.h"
- # "/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-linux-gnu/4.6/include/stddef.h"
- # "/usr/include/_G_config.h"
- # "/usr/include/wchar.h"
- # "/usr/include/wchar.h"
- typedef struct
- {
- int __count;
- union
- {
- unsigned int __wch;
- char __wchb[];
- } __value;
- } __mbstate_t;
- # "/usr/include/_G_config.h"
- typedef struct
- {
- __off_t __pos;
- __mbstate_t __state;
- } _G_fpos_t;
- typedef struct
- {
- __off64_t __pos;
- __mbstate_t __state;
- } _G_fpos64_t;
- # "/usr/include/_G_config.h"
- typedef int _G_int16_t __attribute__ ((__mode__ (__HI__)));
- typedef int _G_int32_t __attribute__ ((__mode__ (__SI__)));
- typedef unsigned int _G_uint16_t __attribute__ ((__mode__ (__HI__)));
- typedef unsigned int _G_uint32_t __attribute__ ((__mode__ (__SI__)));
- # "/usr/include/libio.h"
- # "/usr/include/libio.h"
- # "/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-linux-gnu/4.6/include/stdarg.h"
- # "/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-linux-gnu/4.6/include/stdarg.h"
- typedef __builtin_va_list __gnuc_va_list;
- # "/usr/include/libio.h"
- # "/usr/include/libio.h"
- struct _IO_jump_t; struct _IO_FILE;
- # "/usr/include/libio.h"
- typedef void _IO_lock_t;
- struct _IO_marker {
- struct _IO_marker *_next;
- struct _IO_FILE *_sbuf;
- int _pos;
- # "/usr/include/libio.h"
- };
- enum __codecvt_result
- {
- __codecvt_ok,
- __codecvt_partial,
- __codecvt_error,
- __codecvt_noconv
- };
- # "/usr/include/libio.h"
- struct _IO_FILE {
- int _flags;
- char* _IO_read_ptr;
- char* _IO_read_end;
- char* _IO_read_base;
- char* _IO_write_base;
- char* _IO_write_ptr;
- char* _IO_write_end;
- char* _IO_buf_base;
- char* _IO_buf_end;
- char *_IO_save_base;
- char *_IO_backup_base;
- char *_IO_save_end;
- struct _IO_marker *_markers;
- struct _IO_FILE *_chain;
- int _fileno;
- int _flags2;
- __off_t _old_offset;
- unsigned short _cur_column;
- signed char _vtable_offset;
- char _shortbuf[];
- _IO_lock_t *_lock;
- # "/usr/include/libio.h"
- __off64_t _offset;
- # "/usr/include/libio.h"
- void *__pad1;
- void *__pad2;
- void *__pad3;
- void *__pad4;
- size_t __pad5;
- int _mode;
- char _unused2[ * sizeof (int) - * sizeof (void *) - sizeof (size_t)];
- };
- typedef struct _IO_FILE _IO_FILE;
- struct _IO_FILE_plus;
- extern struct _IO_FILE_plus _IO_2_1_stdin_;
- extern struct _IO_FILE_plus _IO_2_1_stdout_;
- extern struct _IO_FILE_plus _IO_2_1_stderr_;
- # "/usr/include/libio.h"
- typedef __ssize_t __io_read_fn (void *__cookie, char *__buf, size_t __nbytes);
- typedef __ssize_t __io_write_fn (void *__cookie, __const char *__buf,
- size_t __n);
- typedef int __io_seek_fn (void *__cookie, __off64_t *__pos, int __w);
- typedef int __io_close_fn (void *__cookie);
- # "/usr/include/libio.h"
- extern int __underflow (_IO_FILE *);
- extern int __uflow (_IO_FILE *);
- extern int __overflow (_IO_FILE *, int);
- # "/usr/include/libio.h"
- extern int _IO_getc (_IO_FILE *__fp);
- extern int _IO_putc (int __c, _IO_FILE *__fp);
- extern int _IO_feof (_IO_FILE *__fp) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
- extern int _IO_ferror (_IO_FILE *__fp) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
- extern int _IO_peekc_locked (_IO_FILE *__fp);
- extern void _IO_flockfile (_IO_FILE *) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
- extern void _IO_funlockfile (_IO_FILE *) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
- extern int _IO_ftrylockfile (_IO_FILE *) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
- # "/usr/include/libio.h"
- extern int _IO_vfscanf (_IO_FILE * __restrict, const char * __restrict,
- __gnuc_va_list, int *__restrict);
- extern int _IO_vfprintf (_IO_FILE *__restrict, const char *__restrict,
- __gnuc_va_list);
- extern __ssize_t _IO_padn (_IO_FILE *, int, __ssize_t);
- extern size_t _IO_sgetn (_IO_FILE *, void *, size_t);
- extern __off64_t _IO_seekoff (_IO_FILE *, __off64_t, int, int);
- extern __off64_t _IO_seekpos (_IO_FILE *, __off64_t, int);
- extern void _IO_free_backup_area (_IO_FILE *) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- typedef __gnuc_va_list va_list;
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- typedef __off_t off_t;
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- typedef __ssize_t ssize_t;
- typedef _G_fpos_t fpos_t;
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- # "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/stdio_lim.h"
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- extern struct _IO_FILE *stdin;
- extern struct _IO_FILE *stdout;
- extern struct _IO_FILE *stderr;
- extern int remove (__const char *__filename) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
- extern int rename (__const char *__old, __const char *__new) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
- extern int renameat (int __oldfd, __const char *__old, int __newfd,
- __const char *__new) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
- extern FILE *tmpfile (void) ;
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- extern char *tmpnam (char *__s) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
- extern char *tmpnam_r (char *__s) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- extern char *tempnam (__const char *__dir, __const char *__pfx)
- __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) __attribute__ ((__malloc__)) ;
- extern int fclose (FILE *__stream);
- extern int fflush (FILE *__stream);
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- extern int fflush_unlocked (FILE *__stream);
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- extern FILE *fopen (__const char *__restrict __filename,
- __const char *__restrict __modes) ;
- extern FILE *freopen (__const char *__restrict __filename,
- __const char *__restrict __modes,
- FILE *__restrict __stream) ;
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- extern FILE *fdopen (int __fd, __const char *__modes) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- extern FILE *fmemopen (void *__s, size_t __len, __const char *__modes)
- __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
- extern FILE *open_memstream (char **__bufloc, size_t *__sizeloc) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
- extern void setbuf (FILE *__restrict __stream, char *__restrict __buf) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
- extern int setvbuf (FILE *__restrict __stream, char *__restrict __buf,
- int __modes, size_t __n) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
- extern void setbuffer (FILE *__restrict __stream, char *__restrict __buf,
- size_t __size) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
- extern void setlinebuf (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
- extern int fprintf (FILE *__restrict __stream,
- __const char *__restrict __format, ...);
- extern int printf (__const char *__restrict __format, ...);
- extern int sprintf (char *__restrict __s,
- __const char *__restrict __format, ...) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__));
- extern int vfprintf (FILE *__restrict __s, __const char *__restrict __format,
- __gnuc_va_list __arg);
- extern int vprintf (__const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg);
- extern int vsprintf (char *__restrict __s, __const char *__restrict __format,
- __gnuc_va_list __arg) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__));
- extern int snprintf (char *__restrict __s, size_t __maxlen,
- __const char *__restrict __format, ...)
- __attribute__ ((__nothrow__)) __attribute__ ((__format__ (__printf__, , )));
- extern int vsnprintf (char *__restrict __s, size_t __maxlen,
- __const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg)
- __attribute__ ((__nothrow__)) __attribute__ ((__format__ (__printf__, , )));
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- extern int vdprintf (int __fd, __const char *__restrict __fmt,
- __gnuc_va_list __arg)
- __attribute__ ((__format__ (__printf__, , )));
- extern int dprintf (int __fd, __const char *__restrict __fmt, ...)
- __attribute__ ((__format__ (__printf__, , )));
- extern int fscanf (FILE *__restrict __stream,
- __const char *__restrict __format, ...) ;
- extern int scanf (__const char *__restrict __format, ...) ;
- extern int sscanf (__const char *__restrict __s,
- __const char *__restrict __format, ...) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- extern int fscanf (FILE *__restrict __stream, __const char *__restrict __format, ...) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_fscanf")
- ;
- extern int scanf (__const char *__restrict __format, ...) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_scanf")
- ;
- extern int sscanf (__const char *__restrict __s, __const char *__restrict __format, ...) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_sscanf") __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__))
- ;
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- extern int vfscanf (FILE *__restrict __s, __const char *__restrict __format,
- __gnuc_va_list __arg)
- __attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, , ))) ;
- extern int vscanf (__const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg)
- __attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, , ))) ;
- extern int vsscanf (__const char *__restrict __s,
- __const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg)
- __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) __attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, , )));
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- extern int vfscanf (FILE *__restrict __s, __const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_vfscanf")
- __attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, , ))) ;
- extern int vscanf (__const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_vscanf")
- __attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, , ))) ;
- extern int vsscanf (__const char *__restrict __s, __const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_vsscanf") __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__))
- __attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, , )));
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- extern int fgetc (FILE *__stream);
- extern int getc (FILE *__stream);
- extern int getchar (void);
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- extern int getc_unlocked (FILE *__stream);
- extern int getchar_unlocked (void);
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- extern int fgetc_unlocked (FILE *__stream);
- extern int fputc (int __c, FILE *__stream);
- extern int putc (int __c, FILE *__stream);
- extern int putchar (int __c);
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- extern int fputc_unlocked (int __c, FILE *__stream);
- extern int putc_unlocked (int __c, FILE *__stream);
- extern int putchar_unlocked (int __c);
- extern int getw (FILE *__stream);
- extern int putw (int __w, FILE *__stream);
- extern char *fgets (char *__restrict __s, int __n, FILE *__restrict __stream)
- ;
- extern char *gets (char *__s) ;
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- extern __ssize_t __getdelim (char **__restrict __lineptr,
- size_t *__restrict __n, int __delimiter,
- FILE *__restrict __stream) ;
- extern __ssize_t getdelim (char **__restrict __lineptr,
- size_t *__restrict __n, int __delimiter,
- FILE *__restrict __stream) ;
- extern __ssize_t getline (char **__restrict __lineptr,
- size_t *__restrict __n,
- FILE *__restrict __stream) ;
- extern int fputs (__const char *__restrict __s, FILE *__restrict __stream);
- extern int puts (__const char *__s);
- extern int ungetc (int __c, FILE *__stream);
- extern size_t fread (void *__restrict __ptr, size_t __size,
- size_t __n, FILE *__restrict __stream) ;
- extern size_t fwrite (__const void *__restrict __ptr, size_t __size,
- size_t __n, FILE *__restrict __s);
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- extern size_t fread_unlocked (void *__restrict __ptr, size_t __size,
- size_t __n, FILE *__restrict __stream) ;
- extern size_t fwrite_unlocked (__const void *__restrict __ptr, size_t __size,
- size_t __n, FILE *__restrict __stream);
- extern int fseek (FILE *__stream, long int __off, int __whence);
- extern long int ftell (FILE *__stream) ;
- extern void rewind (FILE *__stream);
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- extern int fseeko (FILE *__stream, __off_t __off, int __whence);
- extern __off_t ftello (FILE *__stream) ;
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- extern int fgetpos (FILE *__restrict __stream, fpos_t *__restrict __pos);
- extern int fsetpos (FILE *__stream, __const fpos_t *__pos);
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- extern void clearerr (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
- extern int feof (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
- extern int ferror (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
- extern void clearerr_unlocked (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
- extern int feof_unlocked (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
- extern int ferror_unlocked (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
- extern void perror (__const char *__s);
- # "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/sys_errlist.h"
- # "/usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu/bits/sys_errlist.h"
- extern int sys_nerr;
- extern __const char *__const sys_errlist[];
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- extern int fileno (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
- extern int fileno_unlocked (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- extern FILE *popen (__const char *__command, __const char *__modes) ;
- extern int pclose (FILE *__stream);
- extern char *ctermid (char *__s) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- extern void flockfile (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
- extern int ftrylockfile (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
- extern void funlockfile (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
- # "/usr/include/stdio.h"
- # "hello.c"
- int main()
- {
- printf("hello world!\n");
- }
hello.i
编译阶段。编译器(ccl)将文本文件hello.i翻译成文本文件hello.s,它包含一个汇编语言程序。汇编语言程序中的每条语句都以一种标准的文本格式确切地描述了一条低级机器语言指令。汇编语言是非常有用的,因为他为不同高级语言的不同编译器提供了通用的输出语言。例如,C编译器和Fortran编译器产生的输出文件用的都是一样的汇编语言。
编译过程就是把预处理完的文件进行一系列的词法分析,语法分析,语义分析及优化后生成相应的汇编代码。
gcc –S hello.i –o hello.s
- .file "hello.c"
- .section .rodata
- .LC0:
- .string "hello world!"
- .text
- .globl main
- .type main, @function
- main:
- .LFB0:
- .cfi_startproc
- pushq %rbp
- .cfi_def_cfa_offset
- .cfi_offset , -
- movq %rsp, %rbp
- .cfi_def_cfa_register
- movl $.LC0, %edi
- call puts
- popq %rbp
- .cfi_def_cfa ,
- ret
- .cfi_endproc
- .LFE0:
- .size main, .-main
- .ident "GCC: (Ubuntu/Linaro 4.6.3-1ubuntu5) 4.6.3"
- .section .note.GNU-stack,"",@progbits
hello.s
汇编阶段。汇编器(as)将hello.s翻译成机器语言指令,并把这些指令打包成一种叫做可充定位目标程序(relocatable object program)的格式,并将结果保存在目标文件hello.o中,hello.o文件是一个二进制文件,它的字节编码是机器语言指令而不是字符。如果我们在文本编辑器中打开hello.o文件,看到的将是一堆乱码。
汇编器是将汇编代码转变成机器可以执行的命令,每一个汇编语句几乎都对应一条机器指令。汇编相对于编译过程比较简单,根据汇编指令和机器指令的对照表一一翻译即可。
$ gcc –c hello.c –o hello.o
或者
$ as hello.s –o hello.co
由于hello.o的内容为机器码,不能以普通文本形式的查看
连接阶段。请注意,hello程序调用了printf函数,他是每个C编译器都会提供的标准C库中的一个函数。printf函数存在于一个名为printf.o程序中。链接器(ld)就负责处理这种合并。结果就得到hello文件,他是一个可执行目标文件(或者简称可执行文件),可以被加载到内存,由系统执行。
通过调用链接器ld来链接程序运行需要的一大堆目标文件,以及所依赖的其它库文件,最后生成可执行文件。
参考:
书籍:《深入理解计算机系统》
博客:http://blog.csdn.net/koudaidai/article/details/8092647
C程序编译过程的更多相关文章
- 李洪强漫谈iOS开发[C语言-004]-开发概述程序设计语言程序编译过程
汇编语言 指令用特定的名字来标记,这就是汇编语言 人比较容易看懂汇编语言 汇编直接和程序一一对应的 有汇编器把程序翻译成机器码 把高级语言编译成计算机识别的语言 程序编译过程 命令行 UNIX 系统中 ...
- C程序编译过程浅析
前几天看了<程序员的自我修养——链接.装载与库>中的第二章“编译和链接”,主要根据其中的内容简单总结一下C程序编译的过程吧. 我现在一般都是用gcc,所以自然以GCC编译hellworld ...
- C程序编译过程浅析(转)
前几天看了<程序员的自我修养——链接.装载与库>中的第二章“编译和链接”,主要根据其中的内容简单总结一下C程序编译的过程吧. 我现在一般都是用gcc,所以自然以GCC编译hellworld ...
- C程序编译过程浅析【转】
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/koudaidai/article/details/8092647 前几天看了<程序员的自我修养——链接.装载与库>中的第二章“编译和链接” ...
- Linux 程序编译过程的来龙去脉
大家肯定都知道计算机程序设计语言通常分为机器语言.汇编语言和高级语言三类.高级语言需要通过翻译成机器语言才能执行,而翻译的方式分为两种,一种是编译型,另一种是解释型,因此我们基本上将高级语言分为两大类 ...
- linux程序编译过程
大家肯定都知道计算机程序设计语言通常分为机器语言.汇编语言和高级语言三类.高级语言需要通过翻译成机器语言才能执行,而翻译的方式分为两种,一种是编译型,另一种是解释型,因此我们基本上将高级语言分为两大类 ...
- 后台程序编译过程报错PCC-F-02104, Unable to connect to Oracle
偶然重新编译了一下后台程序,发现编译过程报错无法连接数据库.但通过sqlplus登录数据库是正常的.后台程序改动中也做了详细的分析,没有改动相关数据库的参数和配置. 最后通过浏览器查看了很多相关问题的 ...
- 【转】android程序编译过程
现在很多人想对Android工程的编译和打包进行自动化,比如建立每日构建系统.自动生成发布文件等等.这些都需要我们对Android工程的编译和打包有一个深入的理解,至少要知道它的每一步都做了什么,需要 ...
- unix 网路编程(卷一)第一个程序编译过程
unix卷一去年暑假买的到现在才开始看无比惭愧,而且惭愧第一个程序就断断续续弄了几天,要好好写程序了,马上要找工作了,下面介绍下把本书第一个程序跑起来的过程: 搜各种博客 我用系统的是ubuntu 1 ...
随机推荐
- NuGet学习笔记(1) 初识NuGet及快速安装使用
关于NuGet园子里已经有不少介绍及使用经验,本文仅作为自己研究学习NuGet一个记录. 初次认识NuGet是在去年把项目升级为MVC3的时候,当时看到工具菜单多一项Library Package M ...
- 函数调用关于从Ring3转到Ring0 ESP堆栈变化
在ring0堆栈获取ring3堆栈方式 第一种方式 [esp+4] == [esp+参数个数*4+4] 如果这里不相等就需要用第二种方式 [[esp+参数个数*4+8]] 这里面的值就是Ring3的堆 ...
- JSON详解以及可以把javabean转换成json串的json-lib应用
JSON 1. json是什么 它是js提供的一种数据交换格式! 2. json的语法 {}:是对象! 属性名必须使用双引号括起来!单引不行!!! 属性值:null,数值,字符串,数组:使用[]括起来 ...
- 【jQuery 区别】attr()和prop()的区别
1>>> 今天实现一个 点击更新按钮 ,可以勾选上本行的的checkbox的功能: 使用代码: /** * updateproduct.htmls 更新 产品信息 */ $(docu ...
- Loadrunner中参数化实战(9)-Unique+Once
参数化数据30条: 脚本如下,演示登录,投资,退出操作是,打印手机号: 首先验证Vugen中迭代: Unique+Once 设置迭代4次Action 结果如下:
- java jdbc sqlhelper
package com.shop.util; import java.sql.*; //SqlHelper类 //定义了数据库连接函数,关闭查询结果集,关闭Statement对象,关闭数据库连接 // ...
- SPOJ SUBST1 后缀数组
题目链接:http://www.spoj.com/problems/SUBST1/en/ 题意:给定一个字符串,求不相同的子串个数. 思路:直接根据09年oi论文<<后缀数组——出来字符串 ...
- 用Python做自然语言处理必知的八个工具【转载】
Python以其清晰简洁的语法.易用和可扩展性以及丰富庞大的库深受广大开发者喜爱.其内置的非常强大的机器学习代码库和数学库,使Python理所当然成为自然语言处理的开发利器. 那么使用Python进行 ...
- [工作中的设计模式]策略模式stategy
一.模式解析 策略模式定义了一系列的算法,并将每一个算法封装起来,而且使它们还可以相互替换.策略模式让算法独立于使用它的客户而独立变化. 策略模式的关键点为: 1.多种算法存在 2.算法继承同样的接口 ...
- js-错误处理与调试,JSON
错误处理与调试: 1.try-catch try{ window.someNoneXistentFunction(); }catch(error){ alert(error.message) } 2. ...
