平衡二叉树(Balanced Binary Tree 或 Height-Balanced Tree)又称AVL树
平衡二叉树(Balanced Binary Tree 或 Height-Balanced Tree)又称AVL树
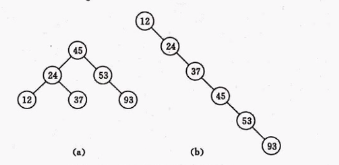
(a)和(b)都是排序二叉树,但是查找(b)的93节点就需要查找6次,查找(a)的93节点就需要查找3次,所以(b)的效率不高。
平衡二叉树(Balanced Binary Tree 或 Height-Balanced Tree)又称AVL树。它或者是一颗空树,或者是具有下列性质的二叉树:它的左子树和右子树的深度只差的绝对值不超过1。若将二叉树上节点的平衡因子BF(Balance Factor)定义为该节点的左子树的深度减去它右子树的深度,则平衡二叉树上所有节点的平衡因子只可能是-1,0,1。只要二叉树上有一个节点的平衡因子的绝对值大于1,则该二叉树就是不平衡的。
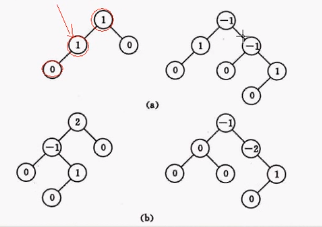
上图(a)是平衡二叉树,(b)不是平衡二叉树,因为有的节点的平衡因子大于1了。
插入节点的大致思路:
- 首先找到插入节点的位置,插入节点
- 插入节点后,调整相关节点的平衡因子
- 调整平衡因子后,如果发现树不平衡了,就要进行节点的调整(单左旋转,或单右旋转,或双旋转(先左后又,或者先右后左)。
avl_tree.h
#ifndef __AVLTREE__
#define __AVLTREE__
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include "nodestack.h"
#define Type int
#define FALSE 0
#define TRUE 1
#define BOOL int
typedef struct AVLNode{
Type data;
struct AVLNode* left;
struct AVLNode* right;
int bf;//平衡因子
}AVLNode;
typedef struct AVLTree{
struct AVLNode* root;
}AVLTree;
void init_avl_tree(AVLTree* avl);
//插入节点
BOOL insert_avl(AVLTree* avl, Type t);
#endif
avl_tree.c
#include "avl_tree.h"
void init_avl_tree(AVLTree* avl){
avl->root = NULL;
}
AVLNode* malNode(Type x){
AVLNode* t = (AVLNode*)malloc(sizeof(AVLNode));
assert(NULL != t);
t->data = x;
t->left = NULL;
t->right = NULL;
t->bf = 0;
return t;
}
//右旋转
void rotateR(AVLNode** t){
AVLNode* subR = *t;
*t = (*t)->left;
subR->left = (*t)->right;
(*t)->right = subR;
(*t)->bf = 0;
subR->bf = 0;
}
//左旋转
void rotateL(AVLNode** t){
AVLNode* subL = *t;
*t = (*t)->right;
subL->right = (*t)->left;
(*t)->left = subL;
(*t)->bf = 0;
subL->bf = 0;
}
//左右旋转
void rotateLR(AVLNode** t){
AVLNode* subR = *t;
AVLNode* subL = subR->left;
*t = subL->right;
subL->right = (*t)->left;
(*t)->left = subL;
if((*t)->bf <= 0){///??
subL->bf = 0;
}
else{
subL->bf = -1;
}
subR->left = (*t)->right;
(*t)->right = subR;
if((*t)->bf == -1){
subR->bf = 1;//???
}
else{
subR->bf = 0;//???
}
(*t)->bf = 0;
}
//右左旋转
void rotateRL(AVLNode** t){
AVLNode* subL = *t;
AVLNode* subR = subL->right;
*t = subR->left;
subR->left = (*t)->right;
(*t)->right = subR;
if((*t)->bf >= 0){
subR->bf = 0;
}
else{
subR->bf = 1;
}
subL->right = (*t)->left;
(*t)->left = subL;
if((*t)->bf == 1){
subL->bf = -1;
}
else{
subL->bf = 0;
}
(*t)->bf = 0;
}
//插入树的节点
BOOL insert_avl_node(AVLNode** t, Type x){
AVLNode* p = *t;
AVLNode* parent = NULL;
nodestack st;
init(&st);
while(p != NULL){
if(x == p->data)
return FALSE;
parent = p;
push(&st, parent);
if(x < p->data)
p = p->left;
else
p = p->right;
}
p = malNode(x);
//插入节点为root节点
if(parent == NULL){
*t = p;
return TRUE;
}
//插入节点不是root节点
if(x < parent->data)
parent->left = p;
else
parent->right = p;
//调整BF
while(length(&st) != 0){
parent = getTop(&st);
pop(&st);
if(parent->left == p){
parent->bf--;
}
else{
parent->bf++;
}
if(parent->bf == 0){
break;
}
if(parent->bf == 1 || parent->bf == -1){
p = parent;
}
else{
//旋转树,让树变成平衡树
int flag = (parent->bf < 0) ? -1 : 1;
//符号相同,说明是一条直线,不是折线,所以单旋转
if(p->bf == flag){
//因为是撇/,所以右旋转
if(flag == -1){
rotateR(&parent);
}
//因为是捺\,所以左旋转
else{
rotateL(&parent);
}
}
//符号不同,说明是折线,所以双旋转
else{
//折线的角指向右>
if(flag == 1){
rotateRL(&parent);
}
//折线的角指向左<
else{
rotateLR(&parent);
}
}
break;
}
}
if(length(&st) == 0){
*t = parent;
}
else{
AVLNode* q = getTop(&st);
if(q->data > parent->data){
q->left = parent;
}
else{
q->right = parent;
}
}
clear(&st);
return TRUE;
}
//插入节点
BOOL insert_avl(AVLTree* avl, Type t){
return insert_avl_node(&avl->root, t);
}
avl_treemain.c
#include "avl_tree.h"
int main(){
AVLTree avl;
init_avl_tree(&avl);
//Type ar[] = {13,24,37,90,53};
//Type ar[] = {30,20,10};
//Type ar[] = {30,20,40,10,25,5,22,28,21};
//Type ar[] = {30,20,10};
//Type ar[] = {50,40,60,10,45,70,5,30,20,12};
Type ar[] = {30,20,50,10,40,70,60,80,55};
int n = sizeof(ar) / sizeof(Type);
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
insert_avl(&avl, ar[i]);
}
return 0;
}
编译方法:g++ -g nodestack.c avl_tree.c avl_treemain.c
平衡二叉树(Balanced Binary Tree 或 Height-Balanced Tree)又称AVL树的更多相关文章
- 数据结构与算法——平衡二叉树(AVL树)
目录 二叉排序树存在的问题 基本介绍 单旋转(左旋转) 树高度计算 旋转 右旋转 双旋转 完整代码 二叉排序树存在的问题 一个数列 {1,2,3,4,5,6},创建一颗二叉排序树(BST) 创建完成的 ...
- C++版 - 剑指offer 面试题39:判断平衡二叉树(LeetCode 110. Balanced Binary Tree) 题解
剑指offer 面试题39:判断平衡二叉树 提交网址: http://www.nowcoder.com/practice/8b3b95850edb4115918ecebdf1b4d222?tpId= ...
- [CareerCup] 4.1 Balanced Binary Tree 平衡二叉树
4.1 Implement a function to check if a binary tree is balanced. For the purposes of this question, a ...
- 平衡二叉树(Balanced Binary Tree)
平衡二叉树(Balanced Binary Tree)/AVL树:
- [Algorithm] Find Max Items and Max Height of a Completely Balanced Binary Tree
A balanced binary tree is something that is used very commonly in analysis of computer science algor ...
- LeetCode 110. 平衡二叉树(Balanced Binary Tree) 15
110. 平衡二叉树 110. Balanced Binary Tree 题目描述 给定一个二叉树,判断它是否是高度平衡的二叉树. 本题中,一棵高度平衡二叉树定义为: 一个二叉树每个节点的左右两个子树 ...
- AVL平衡二叉树的各种问题(Balanced Binary Tree)
AVL树或者是一棵空树,或者是具有以下性质的非空二叉搜索树: 1. 任一结点的左.右子树均为AVL树: 2.根结点左.右子树高度差的绝对值不超过1. 1.声明 #include<iostream ...
- [LeetCode] 110. Balanced Binary Tree ☆(二叉树是否平衡)
Balanced Binary Tree [数据结构和算法]全面剖析树的各类遍历方法 描述 解析 递归分别判断每个节点的左右子树 该题是Easy的原因是该题可以很容易的想到时间复杂度为O(n^2)的方 ...
- 110. Balanced Binary Tree - LeetCode
Question 110. Balanced Binary Tree Solution 题目大意:判断一个二叉树是不是平衡二叉树 思路:定义个boolean来记录每个子节点是否平衡 Java实现: p ...
随机推荐
- 【ASP.NET MVC系列】浅谈jqGrid 在ASP.NET MVC中增删改查
ASP.NET MVC系列文章 [01]浅谈Google Chrome浏览器(理论篇) [02]浅谈Google Chrome浏览器(操作篇)(上) [03]浅谈Google Chrome浏览器(操作 ...
- JavaScript基础回顾一(类型、值和变量)
请看代码并思考输出结果 var scope = 'global'; function f(){ console.log(scope); var scope = 'local'; console.log ...
- TensorFlow的图切割模块——Graph Partitioner
背景 [作者:DeepLearningStack,阿里巴巴算法工程师,开源TensorFlow Contributor] 在经过TensorFlow的Placer策略模块调整之后,下一步就是根据Pla ...
- [PKUWC2018] Slay the spire
Description 现在有 \(n\) 张强化牌和 \(n\) 张攻击牌: 攻击牌:打出后对对方造成等于牌上的数字的伤害. 强化牌:打出后,假设该强化牌上的数字为 \(x\),则其他剩下的攻击牌的 ...
- 第1章 Linux文件类基础命令
1. 关于路径和通配符 Linux中分绝对路径和相对路径,绝对路径一定是从/开始写的,相对路径不从根开始写,还可能使用路径符号. 路径展开符号: . :(一个点)表示当前目录 .. :(两个点)表示上 ...
- Python函数属性和PyCodeObject
函数属性 python中的函数是一种对象,它有属于对象的属性.除此之外,函数还可以自定义自己的属性.注意,属性是和对象相关的,和作用域无关. 自定义属性 自定义函数自己的属性方式很简单.假设函数名称为 ...
- go基础系列:结构struct
Go语言不是一门面向对象的语言,没有对象和继承,也没有面向对象的多态.重写相关特性. Go所拥有的是数据结构,它可以关联方法.Go也支持简单但高效的组合(Composition),请搜索面向对象和组合 ...
- C语言学习之assert
C语言学习之assert assert (编程术语) 编写代码时,我们总是会做出一些假设,断言就是用于在代码中捕捉这些假设,可以将断言看作是异常处理的一种高级形式.断言表示为一些布尔表达式,程序员相信 ...
- [转]virtualBox实现主机和虚拟机相互ping通,配置静态IP地址
本文转自:https://blog.csdn.net/u010486658/article/details/70871940 背景: 需要在linux上安装软件用来练习,但是需要将安装包发送到linu ...
- [转]RPA流程自动化-Blueprism认证考试介绍
本文转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/digod/p/9190186.html RPA流程自动化-Blueprism认证考试介绍 接触RPA有一段时间了,几种RPA相关工具也都试用 ...
