kubeadm安装Kubernetes V1.10集群详细文档
https://www.kubernetes.org.cn/3808.html?tdsourcetag=s_pcqq_aiomsg
1:服务器信息以及节点介绍
系统信息:centos1708 minimal 只修改IP地址
| 主机名称 | IP | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| node01 | 192.168.150.181 | master and etcd |
| rode02 | 192.168.150.182 | master and etcd |
| node03 | 192.168.150.183 | master and etcd |
| node04 | 192.168.150.184 | node |
| VIP | 192.168.150.186 |
软件版本:
docker17.03.2-ce
socat-1.7.3.2-2.el7.x86_64
kubelet-1.10.0-0.x86_64
kubernetes-cni-0.6.0-0.x86_64
kubectl-1.10.0-0.x86_64
kubeadm-1.10.0-0.x86_64
1:环境初始化
1:分别在4台主机设置主机名称
hostnamectl set-hostname node01
hostnamectl set-hostname node02
hostnamectl set-hostname node03
hostnamectl set-hostname node04
2:配置主机映射
cat <<EOF > /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
192.168.150.181 node01
192.168.150.182 node02
192.168.150.183 node03
192.168.150.184 node04
EOF
3:node01上执行ssh免密码登陆配置
ssh-keygen #一路回车即可
ssh-copy-id node02
ssh-copy-id node03
ssh-copy-id node04
4:四台主机配置、停防火墙、关闭Swap、关闭Selinux、设置内核、K8S的yum源、安装依赖包、配置ntp(配置完后建议重启一次)
systemctl stop firewalld
systemctl disable firewalld swapoff -a
sed -i 's/.*swap.*/#&/' /etc/fstab setenforce 0
sed -i "s/^SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=disabled/g" /etc/sysconfig/selinux
sed -i "s/^SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=disabled/g" /etc/selinux/config
sed -i "s/^SELINUX=permissive/SELINUX=disabled/g" /etc/sysconfig/selinux
sed -i "s/^SELINUX=permissive/SELINUX=disabled/g" /etc/selinux/config modprobe br_netfilter
cat <<EOF > /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1
EOF
sysctl -p /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf
ls /proc/sys/net/bridge cat <<EOF > /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo
[kubernetes]
name=Kubernetes
baseurl=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64/
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
repo_gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg
EOF yum install -y epel-release
yum install -y yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2 net-tools conntrack-tools wget vim ntpdate libseccomp libtool-ltdl systemctl enable ntpdate.service
echo '*/30 * * * * /usr/sbin/ntpdate time7.aliyun.com >/dev/null 2>&1' > /tmp/crontab2.tmp
crontab /tmp/crontab2.tmp
systemctl start ntpdate.service echo "* soft nofile 65536" >> /etc/security/limits.conf
echo "* hard nofile 65536" >> /etc/security/limits.conf
echo "* soft nproc 65536" >> /etc/security/limits.conf
echo "* hard nproc 65536" >> /etc/security/limits.conf
echo "* soft memlock unlimited" >> /etc/security/limits.conf
echo "* hard memlock unlimited" >> /etc/security/limits.conf
2:安装、配置keepalived(主节点)
1:安装keepalived
yum install -y keepalived
systemctl enable keepalived
node01的keepalived.conf
cat <<EOF > /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf
global_defs {
router_id LVS_k8s
} vrrp_script CheckK8sMaster {
script "curl -k https://192.168.150.186:6443"
interval 3
timeout 9
fall 2
rise 2
} vrrp_instance VI_1 {
state MASTER
interface ens160
virtual_router_id 61
priority 100
advert_int 1
mcast_src_ip 192.168.150.181
nopreempt
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass sqP05dQgMSlzrxHj
}
unicast_peer {
192.168.150.182
192.168.150.183
}
virtual_ipaddress {
192.168.150.186/24
}
track_script {
CheckK8sMaster
} }
EOF
node02的keepalived.conf
cat <<EOF > /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf
global_defs {
router_id LVS_k8s
} global_defs {
router_id LVS_k8s
} vrrp_script CheckK8sMaster {
script "curl -k https://192.168.150.186:6443"
interval 3
timeout 9
fall 2
rise 2
} vrrp_instance VI_1 {
state BACKUP
interface ens160
virtual_router_id 61
priority 90
advert_int 1
mcast_src_ip 192.168.150.182
nopreempt
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass sqP05dQgMSlzrxHj
}
unicast_peer {
192.168.150.181
192.168.150.183
}
virtual_ipaddress {
192.168.150.186/24
}
track_script {
CheckK8sMaster
} }
EOF
node03的keepalived.conf
cat <<EOF > /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf
global_defs {
router_id LVS_k8s
} global_defs {
router_id LVS_k8s
} vrrp_script CheckK8sMaster {
script "curl -k https://192.168.150.186:6443"
interval 3
timeout 9
fall 2
rise 2
} vrrp_instance VI_1 {
state BACKUP
interface ens160
virtual_router_id 61
priority 80
advert_int 1
mcast_src_ip 192.168.150.183
nopreempt
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass sqP05dQgMSlzrxHj
}
unicast_peer {
192.168.150.181
192.168.150.182
}
virtual_ipaddress {
192.168.150.186/24
}
track_script {
CheckK8sMaster
} }
EOF
2:启动keepalived
systemctl restart keepalived
可以看到VIP已经绑定到node01上面了
ens160: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP qlen 1000
link/ether 00:50:56:b2:09:6a brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.150.181/24 brd 192.168.150.255 scope global ens160
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet 192.168.150.186/24 scope global secondary ens160
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::e3d1:55df:2f64:8571/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
3:创建etcd证书(node01上执行即可)
1:设置cfssl环境
wget https://pkg.cfssl.org/R1.2/cfssl_linux-amd64
wget https://pkg.cfssl.org/R1.2/cfssljson_linux-amd64
wget https://pkg.cfssl.org/R1.2/cfssl-certinfo_linux-amd64
chmod +x cfssl_linux-amd64
mv cfssl_linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/cfssl
chmod +x cfssljson_linux-amd64
mv cfssljson_linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/cfssljson
chmod +x cfssl-certinfo_linux-amd64
mv cfssl-certinfo_linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/cfssl-certinfo
export PATH=/usr/local/bin:$PATH
2:创建 CA 配置文件(下面配置的IP为etc节点的IP)
mkdir /root/ssl
cd /root/ssl
cat > ca-config.json <<EOF
{
"signing": {
"default": {
"expiry": "8760h"
},
"profiles": {
"kubernetes-Soulmate": {
"usages": [
"signing",
"key encipherment",
"server auth",
"client auth"
],
"expiry": "8760h"
}
}
}
}
EOF cat > ca-csr.json <<EOF
{
"CN": "kubernetes-Soulmate",
"key": {
"algo": "rsa",
"size": 2048
},
"names": [
{
"C": "CN",
"ST": "shanghai",
"L": "shanghai",
"O": "k8s",
"OU": "System"
}
]
}
EOF cfssl gencert -initca ca-csr.json | cfssljson -bare ca cat > etcd-csr.json <<EOF
{
"CN": "etcd",
"hosts": [
"127.0.0.1",
"192.168.150.181",
"192.168.150.182",
"192.168.150.183"
],
"key": {
"algo": "rsa",
"size": 2048
},
"names": [
{
"C": "CN",
"ST": "shanghai",
"L": "shanghai",
"O": "k8s",
"OU": "System"
}
]
}
EOF cfssl gencert -ca=ca.pem \
-ca-key=ca-key.pem \
-config=ca-config.json \
-profile=kubernetes-Soulmate etcd-csr.json | cfssljson -bare etcd
3:node01分发etcd证书到node02、node03上面
mkdir -p /etc/etcd/ssl
cp etcd.pem etcd-key.pem ca.pem /etc/etcd/ssl/
ssh -n node02 "mkdir -p /etc/etcd/ssl && exit"
ssh -n node03 "mkdir -p /etc/etcd/ssl && exit"
scp -r /etc/etcd/ssl/*.pem node02:/etc/etcd/ssl/
scp -r /etc/etcd/ssl/*.pem node03:/etc/etcd/ssl/
4:安装配置etcd (三主节点)
1:安装etcd
yum install etcd -y
mkdir -p /var/lib/etcd
node01的etcd.service
cat <<EOF >/etc/systemd/system/etcd.service
[Unit]
Description=Etcd Server
After=network.target
After=network-online.target
Wants=network-online.target
Documentation=https://github.com/coreos [Service]
Type=notify
WorkingDirectory=/var/lib/etcd/
ExecStart=/usr/bin/etcd \
--name node01 \
--cert-file=/etc/etcd/ssl/etcd.pem \
--key-file=/etc/etcd/ssl/etcd-key.pem \
--peer-cert-file=/etc/etcd/ssl/etcd.pem \
--peer-key-file=/etc/etcd/ssl/etcd-key.pem \
--trusted-ca-file=/etc/etcd/ssl/ca.pem \
--peer-trusted-ca-file=/etc/etcd/ssl/ca.pem \
--initial-advertise-peer-urls https://192.168.150.181:2380 \
--listen-peer-urls https://192.168.150.181:2380 \
--listen-client-urls https://192.168.150.181:2379,http://127.0.0.1:2379 \
--advertise-client-urls https://192.168.150.181:2379 \
--initial-cluster-token etcd-cluster-0 \
--initial-cluster node01=https://192.168.150.181:2380,node02=https://192.168.150.182:2380,node03=https://192.168.150.183:2380 \
--initial-cluster-state new \
--data-dir=/var/lib/etcd
Restart=on-failure
RestartSec=5
LimitNOFILE=65536 [Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
EOF
node02的etcd.service
cat <<EOF >/etc/systemd/system/etcd.service
[Unit]
Description=Etcd Server
After=network.target
After=network-online.target
Wants=network-online.target
Documentation=https://github.com/coreos [Service]
Type=notify
WorkingDirectory=/var/lib/etcd/
ExecStart=/usr/bin/etcd \
--name node02 \
--cert-file=/etc/etcd/ssl/etcd.pem \
--key-file=/etc/etcd/ssl/etcd-key.pem \
--peer-cert-file=/etc/etcd/ssl/etcd.pem \
--peer-key-file=/etc/etcd/ssl/etcd-key.pem \
--trusted-ca-file=/etc/etcd/ssl/ca.pem \
--peer-trusted-ca-file=/etc/etcd/ssl/ca.pem \
--initial-advertise-peer-urls https://192.168.150.182:2380 \
--listen-peer-urls https://192.168.150.182:2380 \
--listen-client-urls https://192.168.150.182:2379,http://127.0.0.1:2379 \
--advertise-client-urls https://192.168.150.182:2379 \
--initial-cluster-token etcd-cluster-0 \
--initial-cluster node01=https://192.168.150.181:2380,node02=https://192.168.150.182:2380,node03=https://192.168.150.183:2380 \
--initial-cluster-state new \
--data-dir=/var/lib/etcd
Restart=on-failure
RestartSec=5
LimitNOFILE=65536 [Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
EOF
node03的etcd.service
cat <<EOF >/etc/systemd/system/etcd.service
[Unit]
Description=Etcd Server
After=network.target
After=network-online.target
Wants=network-online.target
Documentation=https://github.com/coreos [Service]
Type=notify
WorkingDirectory=/var/lib/etcd/
ExecStart=/usr/bin/etcd \
--name node03 \
--cert-file=/etc/etcd/ssl/etcd.pem \
--key-file=/etc/etcd/ssl/etcd-key.pem \
--peer-cert-file=/etc/etcd/ssl/etcd.pem \
--peer-key-file=/etc/etcd/ssl/etcd-key.pem \
--trusted-ca-file=/etc/etcd/ssl/ca.pem \
--peer-trusted-ca-file=/etc/etcd/ssl/ca.pem \
--initial-advertise-peer-urls https://192.168.150.183:2380 \
--listen-peer-urls https://192.168.150.183:2380 \
--listen-client-urls https://192.168.150.183:2379,http://127.0.0.1:2379 \
--advertise-client-urls https://192.168.150.183:2379 \
--initial-cluster-token etcd-cluster-0 \
--initial-cluster node01=https://192.168.150.181:2380,node02=https://192.168.150.182:2380,node03=https://192.168.150.183:2380 \
--initial-cluster-state new \
--data-dir=/var/lib/etcd
Restart=on-failure
RestartSec=5
LimitNOFILE=65536 [Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
EOF
2:添加自启动(etc集群最少2个节点才能启动,启动报错看mesages日志)
mv etcd.service /usr/lib/systemd/system/
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl enable etcd
systemctl start etcd
systemctl status etcd
3:在三个etcd节点执行一下命令检查
etcdctl --endpoints=https://192.168.150.181:2379,https://192.168.150.182:2379,https://192.168.150.183:2379 \
--ca-file=/etc/etcd/ssl/ca.pem \
--cert-file=/etc/etcd/ssl/etcd.pem \
--key-file=/etc/etcd/ssl/etcd-key.pem cluster-health
5:所有节点安装配置docker
1:安装docker(kubeadm目前支持docker最高版本是17.03.x)
yum install https://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/7/x86_64/stable/Packages/docker-ce-selinux-17.03.2.ce-1.el7.centos.noarch.rpm -y
yum install https://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/7/x86_64/stable/Packages/docker-ce-17.03.2.ce-1.el7.centos.x86_64.rpm -y
修改配置文件 vim /usr/lib/systemd/system/docker.service
ExecStart=/usr/bin/dockerd -H tcp://0.0.0.0:2375 -H unix:///var/run/docker.sock --registry-mirror=https://ms3cfraz.mirror.aliyuncs.com
启动docker
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl restart docker
systemctl enable docker
systemctl status docker
6: 安装、配置kubeadm
1:所有节点安装kubelet kubeadm kubectl
yum install -y kubelet kubeadm kubectl
systemctl enable kubelet
2: 所有节点修改kubelet配置文件
/etc/systemd/system/kubelet.service.d/10-kubeadm.conf
#修改这一行
Environment="KUBELET_CGROUP_ARGS=--cgroup-driver=cgroupfs"
#添加这一行
Environment="KUBELET_EXTRA_ARGS=--v=2 --fail-swap-on=false --pod-infra-container-image=registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/k8sth/pause-amd64:3.0"
3:所有节点修改完配置文件一定要重新加载配置
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl enable kubelet
4: 命令补全
yum install -y bash-completion
source /usr/share/bash-completion/bash_completion
source <(kubectl completion bash)
echo "source <(kubectl completion bash)" >> ~/.bashrc
7:初始化集群
1:node01、node02、node03添加集群初始配置文件(集群配置文件一样)
cat <<EOF > config.yaml
apiVersion: kubeadm.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: MasterConfiguration
etcd:
endpoints:
- https://192.168.150.181:2379
- https://192.168.150.182:2379
- https://192.168.150.183:2379
caFile: /etc/etcd/ssl/ca.pem
certFile: /etc/etcd/ssl/etcd.pem
keyFile: /etc/etcd/ssl/etcd-key.pem
dataDir: /var/lib/etcd
networking:
podSubnet: 10.244.0.0/16
kubernetesVersion: 1.10.0
api:
advertiseAddress: "192.168.150.186"
token: "b99a00.a144ef80536d4344"
tokenTTL: "0s"
apiServerCertSANs:
- node01
- node02
- node03
- 192.168.150.181
- 192.168.150.182
- 192.168.150.183
- 192.168.150.184
- 192.168.150.186
featureGates:
CoreDNS: true
imageRepository: "registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/k8sth"
EOF
2:首先node01初始化集群
配置文件定义podnetwork是10.244.0.0/16
kubeadmin init –hlep可以看出,service默认网段是10.96.0.0/12
/etc/systemd/system/kubelet.service.d/10-kubeadm.conf默认dns地址cluster-dns=10.96.0.10
kubeadm init --config config.yaml
初始化失败后处理办法
kubeadm reset
#或
rm -rf /etc/kubernetes/*.conf
rm -rf /etc/kubernetes/manifests/*.yaml
docker ps -a |awk '{print $1}' |xargs docker rm -f
systemctl stop kubelet
初始化正常的结果如下
Your Kubernetes master has initialized successfully! To start using your cluster, you need to run the following as a regular user: mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config You should now deploy a pod network to the cluster.
Run "kubectl apply -f [podnetwork].yaml" with one of the options listed at:
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/addons/ You can now join any number of machines by running the following on each node
as root: kubeadm join 192.168.150.186:6443 --token b99a00.a144ef80536d4344 --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:f79b68fb698c92b9336474eb3bf184e847f967dc58a6296911892662b98b1315
3:node01上面执行如下命令
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
4:kubeadm生成证书密码文件分发到node02和node03上面去
scp -r /etc/kubernetes/pki node03:/etc/kubernetes/
scp -r /etc/kubernetes/pki node02:/etc/kubernetes/
5:部署flannel网络,只需要在node01执行就行
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/coreos/flannel/master/Documentation/kube-flannel.yml
#版本信息:quay.io/coreos/flannel:v0.10.0-amd64 kubectl create -f kube-flannel.yml
执行命令
[root@node01 ~]# kubectl get node
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
node01 Ready master 31m v1.10.0
[root@node01 ~]# kubectl get pods --all-namespaces
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kube-system coredns-7997f8864c-4x7mg 1/1 Running 0 29m
kube-system coredns-7997f8864c-zfcck 1/1 Running 0 29m
kube-system kube-apiserver-node01 1/1 Running 0 29m
kube-system kube-controller-manager-node01 1/1 Running 0 30m
kube-system kube-flannel-ds-hw2xb 1/1 Running 0 1m
kube-system kube-proxy-s265b 1/1 Running 0 29m
kube-system kube-scheduler-node01 1/1 Running 0 30m
6:部署dashboard
kubectl create -f kubernetes-dashboard.yaml
获取token,通过令牌登陆
kubectl -n kube-system describe secret $(kubectl -n kube-system get secret | grep admin-user | awk '{print $1}')
通过firefox访问dashboard,输入token,即可登陆
https://192.168.150.181:30000/#!/login
kubernetes-dashboard.yaml文件内容如下
# Copyright 2017 The Kubernetes Authors.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License. # Configuration to deploy release version of the Dashboard UI compatible with
# Kubernetes 1.8.
#
# Example usage: kubectl create -f <this_file> # ------------------- Dashboard Secret ------------------- # apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
name: kubernetes-dashboard-certs
namespace: kube-system
type: Opaque ---
# ------------------- Dashboard Service Account ------------------- # apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
name: kubernetes-dashboard
namespace: kube-system ---
# ------------------- Dashboard Role & Role Binding ------------------- # kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: kubernetes-dashboard-minimal
namespace: kube-system
rules:
# Allow Dashboard to create 'kubernetes-dashboard-key-holder' secret.
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["secrets"]
verbs: ["create"]
# Allow Dashboard to create 'kubernetes-dashboard-settings' config map.
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["configmaps"]
verbs: ["create"]
# Allow Dashboard to get, update and delete Dashboard exclusive secrets.
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["secrets"]
resourceNames: ["kubernetes-dashboard-key-holder", "kubernetes-dashboard-certs"]
verbs: ["get", "update", "delete"]
# Allow Dashboard to get and update 'kubernetes-dashboard-settings' config map.
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["configmaps"]
resourceNames: ["kubernetes-dashboard-settings"]
verbs: ["get", "update"]
# Allow Dashboard to get metrics from heapster.
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["services"]
resourceNames: ["heapster"]
verbs: ["proxy"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["services/proxy"]
resourceNames: ["heapster", "http:heapster:", "https:heapster:"]
verbs: ["get"] ---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: kubernetes-dashboard-minimal
namespace: kube-system
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: kubernetes-dashboard-minimal
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: kubernetes-dashboard
namespace: kube-system ---
# ------------------- Dashboard Deployment ------------------- # kind: Deployment
apiVersion: apps/v1beta2
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
name: kubernetes-dashboard
namespace: kube-system
spec:
replicas: 1
revisionHistoryLimit: 10
selector:
matchLabels:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
template:
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
spec:
nodeSelector:
node-role.kubernetes.io/master: ""
containers:
- name: kubernetes-dashboard
image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/k8sth/kubernetes-dashboard-amd64:v1.8.3
ports:
- containerPort: 8443
protocol: TCP
args:
- --auto-generate-certificates
# Uncomment the following line to manually specify Kubernetes API server Host
# If not specified, Dashboard will attempt to auto discover the API server and connect
# to it. Uncomment only if the default does not work.
# - --apiserver-host=http://my-address:port
volumeMounts:
- name: kubernetes-dashboard-certs
mountPath:/certs
# Create on-disk volume to store exec logs
- mountPath: /tmp
name: tmp-volume
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
scheme: HTTPS
path:/
port: 8443
initialDelaySeconds: 30
timeoutSeconds: 30
volumes:
- name: kubernetes-dashboard-certs
secret:
secretName: kubernetes-dashboard-certs
- name: tmp-volume
emptyDir: {}
serviceAccountName: kubernetes-dashboard
# Comment the following tolerations if Dashboard must not be deployed on master
tolerations:
- key: node-role.kubernetes.io/master
effect:NoSchedule---# ------------------- Dashboard Service ------------------- # kind:Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
name: kubernetes-dashboard
namespace: kube-system
spec:
type:NodePort
ports:- port:443
targetPort:8443
nodePort:30000
selector:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard ---
apiVersion: v1
kind:ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: admin-user
namespace: kube-system ---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind:ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: admin-user
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind:ClusterRole
name: cluster-admin
subjects:- kind:ServiceAccount
name: admin-user
namespace: kube-system
7:安装heapster
[root@node01 ~]# kubectl create -f kube-heapster/influxdb/
deployment.extensions "monitoring-grafana" created
service "monitoring-grafana" created
serviceaccount "heapster" created
deployment.extensions "heapster" created
service "heapster" created
deployment.extensions "monitoring-influxdb" created
service "monitoring-influxdb" created
[root@node01 ~]# kubectl create -f kube-heapster/rbac/
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io "heapster" created
[root@node01 ~]# kubectl get pods --all-namespaces
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kube-system coredns-7997f8864c-4x7mg 1/1 Running 0 1h
kube-system coredns-7997f8864c-zfcck 1/1 Running 0 1h
kube-system heapster-647b89cd4b-wmvmw 1/1 Running 0 39s
kube-system kube-apiserver-node01 1/1 Running 0 1h
kube-system kube-controller-manager-node01 1/1 Running 0 1h
kube-system kube-flannel-ds-hw2xb 1/1 Running 0 49m
kube-system kube-proxy-s265b 1/1 Running 0 1h
kube-system kube-scheduler-node01 1/1 Running 0 1h
kube-system kubernetes-dashboard-7b44ff9b77-26fkj 1/1 Running 0 44m
kube-system monitoring-grafana-74bdd98b7d-szvqg 1/1 Running 0 40s
kube-system monitoring-influxdb-55bbd4b96-95tw7 1/1 Running 0 40s
访问https://192.168.150.181:30000/#!/login即可看到监控信息
heapster文件信息
[root@node01 ~]# tree kube-heapster/
kube-heapster/
├── influxdb
│ ├── grafana.yaml
│ ├── heapster.yaml
│ └── influxdb.yaml
└── rbac
└── heapster-rbac.yaml
grafana.yaml
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: monitoring-grafana
namespace: kube-system
spec:
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
task: monitoring
k8s-app: grafana
spec:
nodeSelector:
node-role.kubernetes.io/master: ""
containers:
- name: grafana
image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/k8sth/heapster-grafana-amd64:v4.4.3
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
ports:
- containerPort: 3000
protocol: TCP
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /etc/ssl/certs
name: ca-certificates
readOnly: true
- mountPath: /var
name: grafana-storage
env:
- name: INFLUXDB_HOST
value: monitoring-influxdb
- name: GF_SERVER_HTTP_PORT
value: "3000"
# The following env variables are required to make Grafana accessible via
# the kubernetes api-server proxy. On production clusters, we recommend
# removing these env variables, setup auth for grafana, and expose the grafana
# service using a LoadBalancer or a public IP.
- name: GF_AUTH_BASIC_ENABLED
value: "false"
- name: GF_AUTH_ANONYMOUS_ENABLED
value: "true"
- name: GF_AUTH_ANONYMOUS_ORG_ROLE
value: Admin
- name: GF_SERVER_ROOT_URL
# If you're only using the API Server proxy, set this value instead:
# value: /api/v1/namespaces/kube-system/services/monitoring-grafana/proxy
value: /
volumes:
- name: ca-certificates
hostPath:
path: /etc/ssl/certs
- name: grafana-storage
emptyDir: {}
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
# For use as a Cluster add-on (https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/tree/master/cluster/addons)
# If you are NOT using this as an addon, you should comment out this line.
kubernetes.io/cluster-service: 'true'
kubernetes.io/name: monitoring-grafana
name: monitoring-grafana
namespace: kube-system
spec:
# In a production setup, we recommend accessing Grafana through an external Loadbalancer
# or through a public IP.
# type: LoadBalancer
# You could also use NodePort to expose the service at a randomly-generated port
# type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 3000
selector:
k8s-app: grafana
heapster.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: heapster
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: heapster
namespace: kube-system
spec:
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
task: monitoring
k8s-app: heapster
spec:
serviceAccountName: heapster
nodeSelector:
node-role.kubernetes.io/master: ""
containers:
- name: heapster
image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/k8sth/heapster-amd64:v1.4.2
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
command:
- /heapster
- --source=kubernetes:https://kubernetes.default
- --sink=influxdb:http://monitoring-influxdb.kube-system.svc:8086
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
task: monitoring
# For use as a Cluster add-on (https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/tree/master/cluster/addons)
# If you are NOT using this as an addon, you should comment out this line.
kubernetes.io/cluster-service: 'true'
kubernetes.io/name: Heapster
name: heapster
namespace: kube-system
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 8082
selector:
k8s-app: heapster
influxdb.yaml
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: monitoring-influxdb
namespace: kube-system
spec:
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
task: monitoring
k8s-app: influxdb
spec:
nodeSelector:
node-role.kubernetes.io/master: ""
containers:
- name: influxdb
image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/k8sth/heapster-influxdb-amd64:v1.3.3
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /data
name: influxdb-storage
volumes:
- name: influxdb-storage
emptyDir: {}
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
task: monitoring
# For use as a Cluster add-on (https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/tree/master/cluster/addons)
# If you are NOT using this as an addon, you should comment out this line.
kubernetes.io/cluster-service: 'true'
kubernetes.io/name: monitoring-influxdb
name: monitoring-influxdb
namespace: kube-system
spec:
ports:
- port: 8086
targetPort: 8086
selector:
k8s-app: influxdb
heapster-rbac.yaml
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
name: heapster
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: system:heapster
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: heapster
namespace: kube-system
9:在node02和node03上面分别执行初始化
kubeadm init --config config.yaml
#初始化的结果和node01的结果完全一样
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
10:查看节点信息
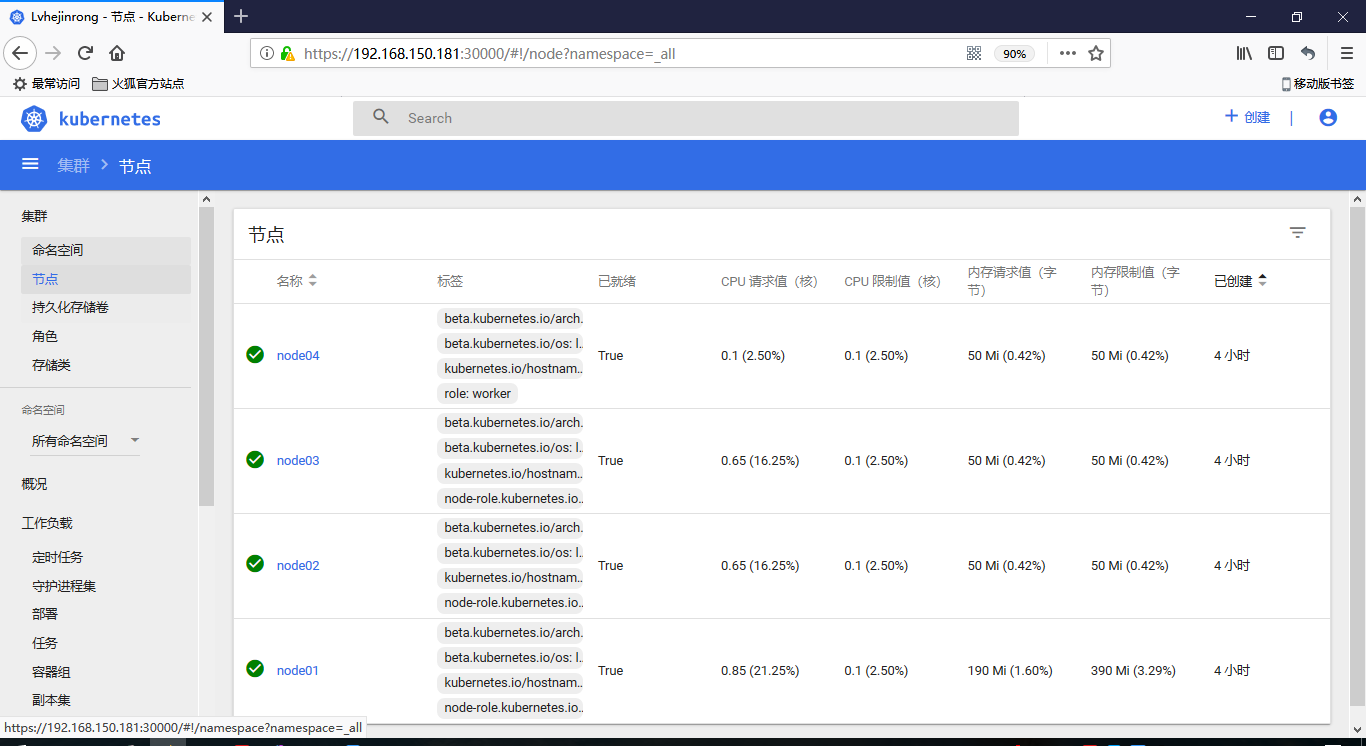
[root@node01 ~]# kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
node01 Ready master 1h v1.10.0
node02 Ready master 1h v1.10.0
node03 Ready master 1h v1.10.0
[root@node01 ~]# kubectl get pods --all-namespaces -o wide
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE
kube-system coredns-7997f8864c-lwtfl 1/1 Running 0 1h 10.244.2.2 node03
kube-system coredns-7997f8864c-q2z9d 1/1 Running 0 1h 10.244.2.3 node03
kube-system kube-apiserver-node01 1/1 Running 0 36m 192.168.150.181 node01
kube-system kube-apiserver-node02 1/1 Running 0 36m 192.168.150.182 node02
kube-system kube-apiserver-node03 1/1 Running 0 1h 192.168.150.183 node03
kube-system kube-controller-manager-node01 1/1 Running 0 36m 192.168.150.181 node01
kube-system kube-controller-manager-node02 1/1 Running 0 36m 192.168.150.182 node02
kube-system kube-controller-manager-node03 1/1 Running 0 1h 192.168.150.183 node03
kube-system kube-flannel-ds-2xrbm 1/1 Running 0 40m 192.168.150.181 node01
kube-system kube-flannel-ds-7gf89 1/1 Running 0 40m 192.168.150.182 node02
kube-system kube-flannel-ds-fmk5z 1/1 Running 0 40m 192.168.150.183 node03
kube-system kube-proxy-dj4c7 1/1 Running 0 1h 192.168.150.181 node01
kube-system kube-proxy-lsg47 1/1 Running 0 1h 192.168.150.183 node03
kube-system kube-proxy-s5wrf 1/1 Running 0 1h 192.168.150.182 node02
kube-system kube-scheduler-node01 1/1 Running 0 36m 192.168.150.181 node01
kube-system kube-scheduler-node02 1/1 Running 0 36m 192.168.150.182 node02
kube-system kube-scheduler-node03 1/1 Running 0 1h 192.168.150.183 node03
11:让master也运行pod(默认master不运行pod)
kubectl taint nodes --all node-role.kubernetes.io/master-
八:添加node04节点到集群
在node04节点执行如下命令,即可将节点添加进集群
kubeadm join 192.168.150.186:6443 --token b99a00.a144ef80536d4344 --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:f79b68fb698c92b9336474eb3bf184e847f967dc58a6296911892662b98b1315
[root@node01 ~]# kubectl get node
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
node01 Ready master 45m v1.10.0
node02 Ready master 15m v1.10.0
node03 Ready master 14m v1.10.0
node04 Ready <none> 13m v1.10.0
参考文档:https://github.com/cookeem/kubeadm-ha/blob/master/README_CN.md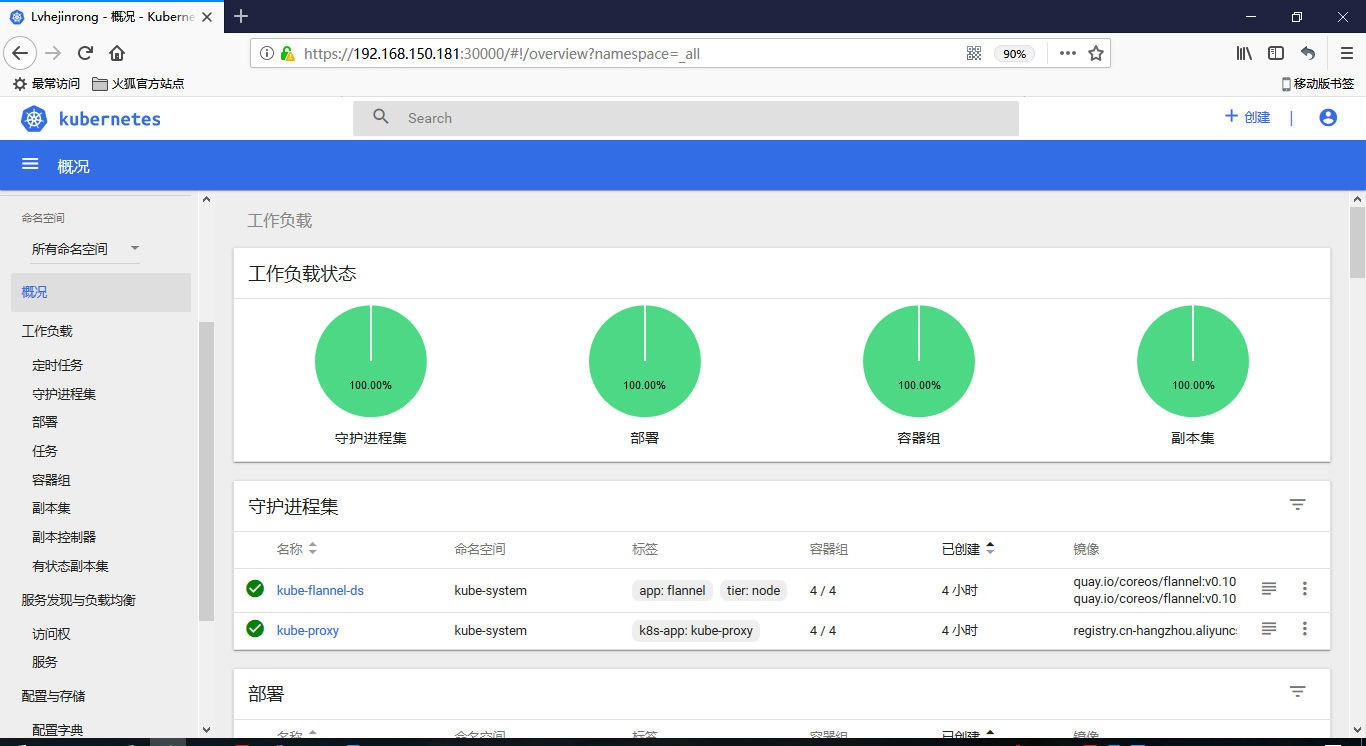
kubeadm安装Kubernetes V1.10集群详细文档的更多相关文章
- 使用kubeadm安装kubernetes高可用集群
kubeadm安装kubernetes高可用集群搭建 第一步:首先搭建etcd集群 yum install -y etcd 配置文件 /etc/etcd/etcd.confETCD_NAME=inf ...
- 使用kubeadm安装Kubernetes v1.10
关于K8S: Kubernetes是Google开源的容器集群管理系统.它构建于docker技术之上,为容器化的应用提供资源调度.部署运行.服务发现.扩 容缩容等整一套功能,本质上可看作是基于容器技术 ...
- kubernetes之kubeadm 安装kubernetes 高可用集群
1. 架构信息 系统版本:CentOS 7.6 内核:3.10.0-957.el7.x86_64 Kubernetes: v1.14.1 Docker-ce: 18.09.5 推荐硬件配置:4核8G ...
- kubeadm安装kubernetes V1.11.1 集群
之前测试了离线环境下使用二进制方法安装配置Kubernetes集群的方法,安装的过程中听说 kubeadm 安装配置集群更加方便,因此试着折腾了一下.安装过程中,也有一些坑,相对来说操作上要比二进制方 ...
- 使用kubeadm安装kubernetes v1.14.1
使用kubeadm安装kubernetes v1.14.1 一.环境准备 操作系统:Centos 7.5 ⼀ 一台或多台运⾏行行着下列列系统的机器器: Ubuntu 16.04+ Debi ...
- 使用 kubeadm 安装 kubernetes v1.16.0
近日通过kubeadm 安装 kubernetes v1.16.0,踩过不少坑,现记录下安装过程. 安装环境: 系 统:CentOS Linux release 7.6 Docke ...
- Redis集群部署文档(Ubuntu15.10系统)
Redis集群部署文档(Ubuntu15.10系统)(要让集群正常工作至少需要3个主节点,在这里我们要创建6个redis节点,其中三个为主节点,三个为从节点,对应的redis节点的ip和端口对应关系如 ...
- HP DL160 Gen9服务器集群部署文档
HP DL160 Gen9服务器集群部署文档 硬件配置=======================================================Server Memo ...
- redis多机集群部署文档
redis多机集群部署文档(centos6.2) (要让集群正常工作至少需要3个主节点,在这里我们要创建6个redis节点,其中三个为主节点,三个为从节点,对应的redis节点的ip和端口对应关系如下 ...
随机推荐
- 【python练习题】程序7
#题目:将一个列表的数据复制到另一个列表中. l = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8] m = [] m = l[:] print (m)
- codeforces24D
CF24D Broken robot 题目背景 小小迪带你吃瓜 题目描述 给出一个 n×m 的矩阵区域,一个机器人初始在第 x 行第 y 列,每一步机器人会等概率 的选择停在原地,左移一步,右移一步, ...
- 红米Note 7 Pro在印度首销迅速售罄
3月13日消息,红米Note 7 Pro在印度率先发售. 小米印度业务负责人Manu Kumar Jain发推特表示,红米Note 7 Pro开售几秒钟就被抢光,我们的工厂正在加班加点工作,全力以赴提 ...
- ☆ [POJ2559] Largest Rectangle in a Histogram 「单调栈」
类型:单调栈 传送门:>Here< 题意:给出若干宽度相同的矩形的高度(条形统计图),求最大子矩形面积 解题思路 单调栈的经典题 显然,最终的子矩形高度一定和某一个矩形相等(反证).因此一 ...
- 【XSY2707】snow 线段树 并查集
题目描述 有\(n\)个人和一条长度为\(t\)的线段,每个人还有一个工作范围(是一个区间).最开始整条线段都是白的.定义每个人的工作长度是这个人的工作范围中白色部分的长度(会随着线段改变而改变).每 ...
- 【BZOJ3813】【清华集训2014】奇数国 线段树 数学
题目描述 给你一个长度为\(n\)的数列,第\(i\)个数为\(a_i\).每个数的质因子都只有前\(60\)个质数.有\(q\)个询问,每次给你\(l,r\),求\(\varphi(\prod_{i ...
- 【hdu 6172】Array Challenge(数列、找规律)
多校10 1002 HDU 6172 Array Challenge 题意 There's an array that is generated by following rule. \(h_0=2, ...
- 「HDU - 2857」Mirror and Light(点关于直线的对称点)
题目链接 Mirror and Light 题意 一条直线代表镜子,一个入射光线上的点,一个反射光线上的点,求反射点.(都在一个二维平面内) 题解 找出入射光线关于镜子直线的对称点,然后和反射光线连边 ...
- Codeforces Bubble Cup 11 J. Moonwalk challenge加强版
题意 有一棵 \(n\) 个节点的树,每条边上有一个字符,有 \(m\) 次询问. 每次会选定两个点 \(u, v\) , \(u\) 到 \(v\) 的路径上的字符形成了一个字符串 \(T\) ,再 ...
- Leetcode 345. 反转字符串中的元音字母 By Python
编写一个函数,以字符串作为输入,反转该字符串中的元音字母. 示例 1: 输入: "hello" 输出: "holle" 示例 2: 输入: "leet ...
