Python爬虫:requests 库详解,cookie操作与实战
第三方库 requests是基于urllib编写的。比urllib库强大,非常适合爬虫的编写。
安装: pip install requests
简单的爬百度首页的例子:
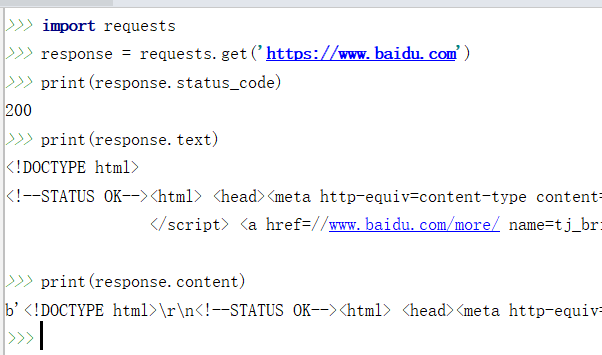
response.text 和 response.content的区别:
- response.text是解过码的字符串。比较容易出现乱码
- response.content 未解码的二进制格式(bytes). 适用于文本,图片和音乐。如果是文本,可以使用 response.content.decode('utf-8') 解码
requests 库支持的请求方法:
import requests
requests.get("http://xxxx.com/")
requests.post("http://xxxx.com/post", data = {'key':'value'})
requests.put("http://xxxx.com/put", data = {'key':'value'})
requests.delete("http://xxxx.com/delete")
requests.head("http://xxxx.com/get")
requests.options("http://xxxx.com/get")
发送带参数的get 请求:
在get方法里设置字典格式的params参数即可。requests 方法会自动完成url的拼接
import requests
params = {
"wd": "python", "pn": 10,
}
response = requests.get('https://www.baidu.com/s', params=params)
print(response.url)
print(response.text)
'''
需要设置header,百度会进行反爬验证
'''
发送带数据的post 请求:
只需要在post方法里设置data参数即可。 raise_for_status()会表示成功或失败
import requests
post_data = {'username': 'value1', 'password': 'value2'}
response = requests.post("http://xxx.com/login/", data=post_data)
response.raise_for_status()
post 文件的例子:
>>> import requests
>>> url = 'http://httpbin.org/post'
>>> files = {'file': open('report.xls', 'rb')}
>>> r = requests.post(url, files=files)
设置与查看请求头(headers):
很多网站有反爬机制,如果一个请求不携带请求头headers,很可能被禁止访问。
import requests
headers = { "User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_12_4) AppleWebKit/"
"537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/58.0.3029.110 Safari/537.36"
} response1 =requests.get("https://www.baidu.com", headers=headers)
response2 =requests.post("https://www.xxxx.com", data={"key": "value"},
headers=headers) print(response1.headers)
print(response1.headers['Content-Type'])
print(response2.text)
设置代理Proxy:
有的网站反爬机制会限制单位时间内同一IP的请求次数,我们可以通过设置 IP proxy代理来应对这个反爬机制。
import requests
proxies = {
"http": "http://10.10.1.10:3128",
"https": "http://10.10.1.10:1080",
}
requests.get("http://example.org", proxies=proxies)
Cookie的获取和添加:
有时候我们需要爬取登录后才能访问的页面,这时我们就需要借助cookie来实现模拟登陆和会话维持了。
当用户首次发送请求时,服务器端一般会生成并存储一小段信息,包含在response数据里。如果这一小段信息存储在客户端(浏览器或磁盘),我们称之为cookie.如果这一小段信息存储在服务器端,我们称之为session(会话).这样当用户下次发送请求到不同页面时,请求自动会带上cookie,这样服务器就制定用户之前已经登录访问过了。
可以通过打印 response.cookies来获取查看cookie内容,从而知道首次请求后服务器是否生成了cookie.
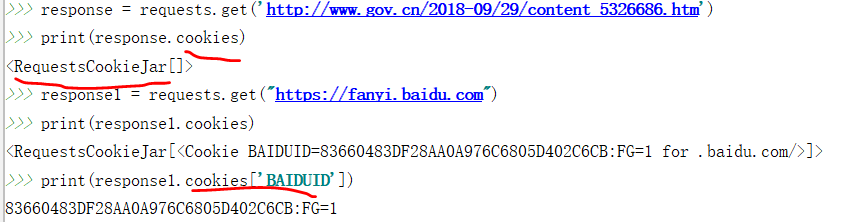
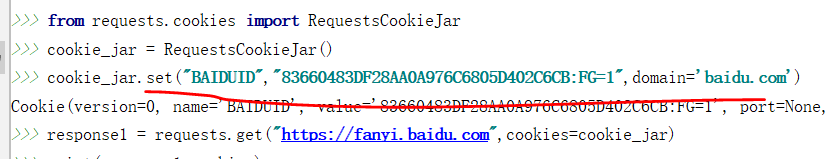
发送请求时添加cookie的方法:
- 设置cookies参数
import requests headers = {
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_12_4) AppleWebKit/"
"537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/58.0.3029.110 Safari/537.36"
} cookies = {"cookie_name": "cookie_value", }
response = requests.get("https://www.baidu.com", headers=headers, cookies=cookies) - 先实例化一个 RequestCookieJar的类,然后把值set进去,最后在get,post方法里面指定cookie参数
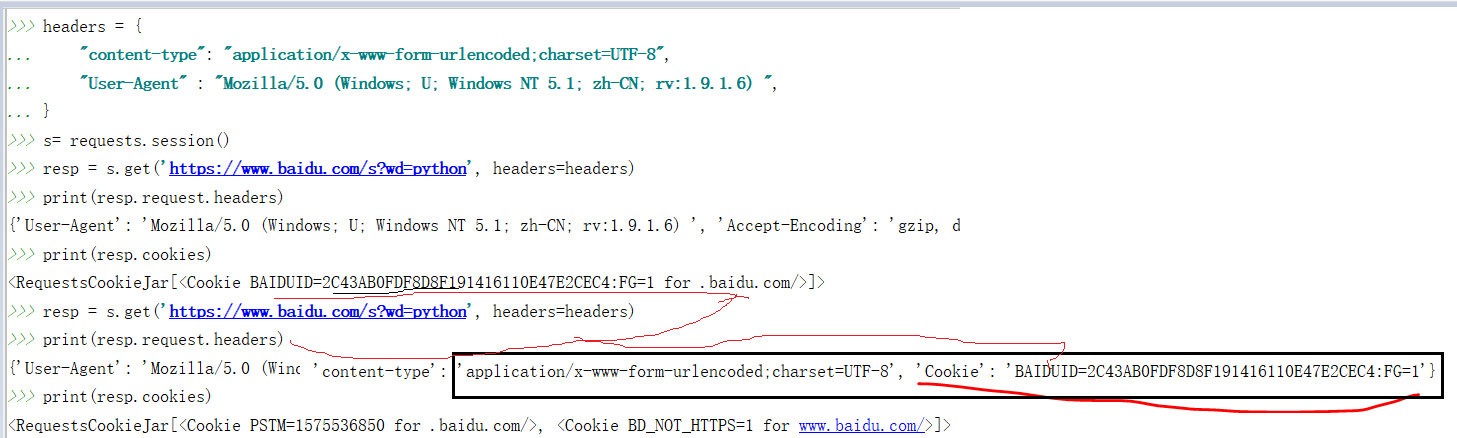
Session会话的维持:
session 与cookie不同,因为session一般存储在服务器端。session对象能够帮我们跨请求保持某些参数,也会在同一个session实例发出的所有请求之间保持cookies.
为了保持会话的连续,我们最好的办法是先创建一个session对象,用它打开一个url,而不是直接使用 request.get方法打开一个url.
每当我们使用这个session对象重新打开一个url时,请求头都会带上首次产生的cookie,实现了会话的延续。
例子:
爬百度前20条搜索记录。(结果还是有点问题的,因为跳转的太多了,搜出不是对应的大条目)
#coding: utf-8
'''
爬取百度搜索前20个搜索页面的标题和链接
'''
import requests
import sys
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup as bs
import re
import chardet headers = {
'Accept': 'text/javascript, application/javascript, application/ecmascript, application/x-ecmascript, */*; q=0.01',
'Accept-Encoding': 'gzip, deflate, br',
'Accept-Language':'zh-CN,zh;q=0.9',
'Connection': 'keep-alive',
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/73.0.3683.86 Safari/537.36',
'X-Requested-With': 'XMLHttpRequest'
} def main(keyword):
file_name = "{}.txt".format(keyword)
f = open(file_name,'w+', encoding='utf-8')
f.close()
for pn in range(0,20,10):
params = {'wd':keyword,'pn':pn}
response = requests.get("https://www.baidu.com/s",params=params,headers=headers)
soup = bs(response.content,'html.parser')
urls = soup.find_all(name='a',attrs={"href": re.compile('.')})
for i in urls:
if 'http://www.baidu.com/link?url=' in i.get('href'):
a = requests.get(url=i.get('href'),headers=headers)
print(i.get('href'))
soup1 = bs(a.content,'html.parser')
title = soup1.title.string
with open(keyword+'.txt','r',encoding='utf-8') as f:
if a.url not in f.read():
f = open(keyword+'.txt','a',encoding='utf-8')
f.write(title + '\n')
f.write(a.url + '\n')
f.close() if __name__ == '__main__':
keyword ='Django'
main(keyword)
print("下载完成")
Python爬虫:requests 库详解,cookie操作与实战的更多相关文章
- python的requests库详解
快速上手 迫不及待了吗?本页内容为如何入门 Requests 提供了很好的指引.其假设你已经安装了 Requests.如果还没有,去安装一节看看吧. 首先,确认一下: Requests 已安装 Req ...
- python的requests用法详解
Requests是一个Python语言写的http相关设置或者请求的一个库 安装:pip install Requests或者pip3 install requests 使用的时候要import re ...
- Python爬虫—requests库get和post方法使用
目录 Python爬虫-requests库get和post方法使用 1. 安装requests库 2.requests.get()方法使用 3.requests.post()方法使用-构造formda ...
- Python爬虫学习==>第八章:Requests库详解
学习目的: request库比urllib库使用更加简洁,且更方便. 正式步骤 Step1:什么是requests requests是用Python语言编写,基于urllib,采用Apache2 Li ...
- python WEB接口自动化测试之requests库详解
由于web接口自动化测试需要用到python的第三方库--requests库,运用requests库可以模拟发送http请求,再结合unittest测试框架,就能完成web接口自动化测试. 所以笔者今 ...
- python接口自动化测试之requests库详解
前言 说到python发送HTTP请求进行接口自动化测试,脑子里第一个闪过的可能就是requests库了,当然python有很多模块可以发送HTTP请求,包括原生的模块http.client,urll ...
- 爬虫学习--Requests库详解 Day2
什么是Requests Requests是用python语言编写,基于urllib,采用Apache2 licensed开源协议的HTTP库,它比urllib更加方便,可以节约我们大量的工作,完全满足 ...
- Python爬虫 requests库基础
requests库简介 requests是使用Apache2 licensed 许可证的HTTP库. 用python编写. 比urllib2模块更简洁. Request支持HTTP连接保持和连接池,支 ...
- Python爬虫--Requests库
Requests Requests是用python语言基于urllib编写的,采用的是Apache2 Licensed开源协议的HTTP库,requests是python实现的最简单易用的HTTP库, ...
随机推荐
- 以php中的自增自自减运算符操作(整型,浮点型,字符串型,布尔型,空类型)数据
// 环境 // // php版本 // PHP 7.0.33-0+deb9u1 (cli) (built: Dec 7 2018 11:36:49) ( NTS ) // Copyright (c) ...
- 接口缓存--把接口放在redis数据库中,减少访问量
针对访问量大,且数据较固定的接口,建议建立接口缓存,建立了缓存之后,不会再直接去访问接口了. 比如下面的轮播图接口,每刷新一下首页都会访问一下轮播图接口,所以我们用接口缓存来处理,减少访问量. 视图模 ...
- HTML 标签入门
HTML 简介 定义: 超文本标记语言(html)是标准通用标记语言下的一个应用,也是一种规范,一种标准 它通过标记符号来表示网页中的各个部分,网页文件本身是一种文本文件,通过在文本文件中添加标记符, ...
- centos+docker+jenkins
1.直接运行jenkins镜像,无该镜像会直接下载 docker run -p 8080:8080 -p 50000:50000 -d -v /home/jenkins-home-docker:/va ...
- JS中浏览器的数据存储机制
一.JS中的三种数据存储方式 cookie.sessionStorage.localStorage 二.cookie 1.cookie的定义: cookie是存储在浏览器上的一小段数据,用来记录某些当 ...
- Python 使用gevent实现多任务
import gevent import time # 如果需要默认的 time.sleep(0.5) 需要打补丁 from gevent import monkey monkey.patch_all ...
- Linux Exploit系列之三 Off-By-One 漏洞 (基于栈)
Off-By-One 漏洞 (基于栈) 原文地址:https://bbs.pediy.com/thread-216954.htm 什么是off by one? 将源字符串复制到目标缓冲区可能会导致of ...
- ios设备app作为蓝牙外设端
苹果手机可以作为蓝牙外设端,被蓝牙中央端来扫描连接交互数据,实现模拟蓝牙外设硬件.通过阅读CoreBluetooth库,可以找到一个CBPeripheralManager的类,该类主要的作用就是允许你 ...
- Linux 磁盘、分区、文件系统、挂载
磁盘 Linux所有设备都被抽象成为一个文件,保存在/dev目录下. 设备名称一般为hd[a-z]或sd[a-z].如果电脑中有多硬盘,则设备名依次为sda.adb.sdc...以此类推 IDE设备的 ...
- Linux命令——ls
15 Interview Questions on Linux “ls” Command – Part 1 10 Useful ‘ls’ Command Interview Questions – P ...
