1.Go-copy函数、sort排序、双向链表、list操作和双向循环链表
1.1.copy函数
通过copy函数可以把一个切片内容复制到另一个切片中
(1)把长切片拷贝到短切片中
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
package mainimport "fmt"func main() { s1 := []int {1,2} s2 := []int{3,4,5,6} //copy的是角标,不会增加元切片的长度 copy(s1,s2) fmt.Println(s1) //[3 4] fmt.Println(s2) //[3 4 5 6]} |
(2)把短切片拷贝到长切片中
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
package mainimport "fmt"func main() { s1 := []int {1,2} s2 := []int{3,4,5,6} //copy的是角标,不会增加元切片的长度 copy(s2,s1) fmt.Println(s1) //[1 2] fmt.Println(s2) //[1 2 5 6]} |
(3)把切片片段拷贝到切片中
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
package mainimport "fmt"func main() { s1 := []int {1,2} s2 := []int{3,4,5,6} //copy的是角标,不会增加元切片的长度 copy(s1,s2[1:3]) fmt.Println(s1) //[[4 5] fmt.Println(s2) //[3 4 5 6]} |
1.2.sort排序
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
package mainimport ( "fmt" "sort")func main() { num := []int{1,7,3,5,2} //升序排序 sort.Ints(num) fmt.Println(num) //[1 2 3 5 7] //降序排序 sort.Sort(sort.Reverse(sort.IntSlice(num))) fmt.Println(num) //[7 5 3 2 1]} |
1.3.双向链表
(1)双向链表的结构
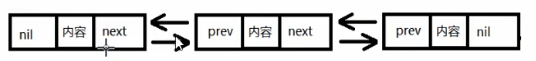
双向链表结构中元素在内存中不是紧邻空间,而是每个元素中存放上一个元素和后一个元素的地址
- 第一个元素称为(头)元素,前连接(前置指针域)为nil
- 最后一个元素称为 尾(foot)元素,后连接(后置指针域)尾nil
双向链表的优点
- 在执行新增元素或删除元素时效率高,获取任意一个元素,可以方便的在这个元素前后插入元素
- 充分利用内存空间,实现内存灵活管理
- 可实现正序和逆序遍历
- 头元素和尾元素新增或删除时效率较高
双向链表的缺点
- 链表增加了元素的指针域,空间开销比较大
- 遍历时跳跃性查找内容,大量数据遍历性能低
(2)双向链表容器List
在Go语言标准库的container/list包提供了双向链表List
List结构体定义如下
- root表示根元素
- len表示链表中有多少元素
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
// List represents a doubly linked list.// The zero value for List is an empty list ready to use.type List struct { root Element // sentinel list element, only &root, root.prev, and root.next are used len int // current list length excluding (this) sentinel element} |
其中Element结构体定义如下
- next表示下一个元素,使用Next()可以获取到
- prev表示上一个元素,使用Prev()可以获取到
- list表示元素属于哪个链表
- Value表示元素的值,interface()在Go语言中表示任意类型
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
// Element is an element of a linked list.type Element struct { // Next and previous pointers in the doubly-linked list of elements. // To simplify the implementation, internally a list l is implemented // as a ring, such that &l.root is both the next element of the last // list element (l.Back()) and the previous element of the first list // element (l.Front()). next, prev *Element // The list to which this element belongs. list *List // The value stored with this element. Value interface{}} |
1.4.操作List
(1)直接使用container/list包下的New()新建一个空的List
添加,遍历,取首尾,取中间元素
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
|
package mainimport ( "container/list" "fmt")func main() { //实例化 mylist := list.New() fmt.Println(mylist) //添加 mylist.PushFront("a") //["a"] mylist.PushBack("b") //["a","b"] mylist.PushBack("c") //["a","b","c"] //在最后一个元素的前面添加 mylist.InsertBefore("d",mylist.Back()) //["a","b","d","c"] mylist.InsertAfter("e",mylist.Front()) //["a","e","b","d","c"] //遍历 for e := mylist.Front(); e != nil; e = e.Next(){ fmt.Print(e.Value, " ") //a e b d c } fmt.Println("") //取首尾 fmt.Println(mylist.Front().Value) //a fmt.Println(mylist.Back().Value) //c //取中间的元素,通过不断的Next() n := 3 var curr *list.Element if n > 0 && n <= mylist.Len(){ if n == 1 { curr = mylist.Front() }else if n == mylist.Len(){ curr = mylist.Back() }else { curr = mylist.Front() for i := 1; i < n; i++{ curr = curr.Next() } } }else { fmt.Println("n的数值不对") } fmt.Println(curr.Value) //b} |
(2)移动元素
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
package mainimport ( "container/list" "fmt")func main() { //实例化 mylist := list.New() fmt.Println(mylist) //添加 mylist.PushFront("a") //["a"] mylist.PushBack("b") //["a","b"] mylist.PushBack("c") //["a","b","c"] //在最后一个元素的前面添加 mylist.InsertBefore("d",mylist.Back()) //["a","b","d","c"] mylist.InsertAfter("e",mylist.Front()) //["a","e","b","d","c"] //移动,把第一个元素一道最后一个元素的前面 mylist.MoveBefore(mylist.Front(),mylist.Back()) //mylist.MoveAfter(mylist.Back(),mylist.Front()) //把最后一个元素移动到最前面 //mylist.MoveToFront(mylist.Back()) //把第一个元素移动到最后面 //mylist.MoveToBack(mylist.Front()) for e := mylist.Front(); e != nil; e = e.Next(){ fmt.Print(e.Value, " ") //e b d a c }} |
(3)删除
|
1
|
mylist.Remove(mylist.Front()) |
1.5.双向循环列表
(1)循环链表特点是没有节点的指针域为nil,通过任何一个元素都可以找到其它元素
环形链表结构如下
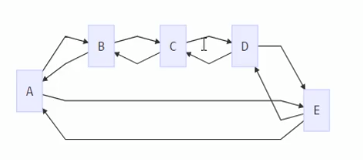
双向循环链表和双向链表区别
- 双向循环链表没有严格意义上的头元素和尾元素
- 没有元素的前连接和后连接为nil
- 一个长度为n的双向循环链表,通过某个元素向某个方向移动,在查找最多n-1次,一定会找到另一个元素
(2)在container/ring包下结构体Ring源码如下
- 官方明确说明了Ring是循环链表的元素,又是环形链表
- 实际使用时Ring遍历就是环形链表第一个元素
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
// A Ring is an element of a circular list, or ring.// Rings do not have a beginning or end; a pointer to any ring element// serves as reference to the entire ring. Empty rings are represented// as nil Ring pointers. The zero value for a Ring is a one-element// ring with a nil Value.//type Ring struct { next, prev *Ring Value interface{} // for use by client; untouched by this library} |
(3)创建和查看
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
package mainimport ( "container/ring" "fmt")func main() { //r代表整个循环链表,又代表第一个元素 r := ring.New(5) r.Value = 0 r.Next().Value = 1 r.Next().Next().Value = 2 //r.Next().Next().Next().Value = 3 //r.Next().Next().Next().Next().Value = 4 r.Prev().Value = 4 r.Prev().Prev().Value = 3 //查看元素内容 //循环链表有几个元素,func就执行几次,i当前执行元素的内容 r.Do(func(i interface{}) { fmt.Print(i, " ") //0 1 2 3 4 }) fmt.Println("") //取中间元素,用移动 fmt.Println(r.Move(3).Value) //3} |
(4)增加
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
package mainimport ( "container/ring" "fmt")func main() { //r代表整个循环链表,又代表第一个元素 r := ring.New(5) r.Value = 0 r.Next().Value = 1 r.Next().Next().Value = 2 //r.Next().Next().Next().Value = 3 //r.Next().Next().Next().Next().Value = 4 r.Prev().Value = 4 r.Prev().Prev().Value = 3 //增加 r1 := ring.New(2) r1.Value = 5 r1.Next().Value = 6 r.Link(r1) r.Do(func(i interface{}) { fmt.Print(i, " ") //0 5 6 1 2 3 4 })} |
(5)删除
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
package mainimport ( "container/ring" "fmt")func main() { //r代表整个循环链表,又代表第一个元素 r := ring.New(5) r.Value = 0 r.Next().Value = 1 r.Next().Next().Value = 2 //r.Next().Next().Next().Value = 3 //r.Next().Next().Next().Next().Value = 4 r.Prev().Value = 4 r.Prev().Prev().Value = 3 //删除 r.Unlink(1) r.Do(func(i interface{}) { fmt.Print(i, " ") //0 2 3 4 })} |
删除后面两个
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
//删除 r.Unlink(2) r.Do(func(i interface{}) { fmt.Print(i, " ") //0 3 4 }) |
r.Next()删除
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
//删除 r.Next().Unlink(2) r.Do(func(i interface{}) { fmt.Print(i, " ") //0 1 4 })qu |
超出范围,取5的余数
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
//删除 r.Unlink(6) r.Do(func(i interface{}) { fmt.Print(i, " ") //0 2 3 4 }) |
来源地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/derek1184405959/
1.Go-copy函数、sort排序、双向链表、list操作和双向循环链表的更多相关文章
- 1.Go语言copy函数、sort排序、双向链表、list操作和双向循环链表
1.1.copy函数 通过copy函数可以把一个切片内容复制到另一个切片中 (1)把长切片拷贝到短切片中 package main import "fmt" func main() ...
- C++排序函数sort/qsort使用
问题描述: C++排序函数sort/qsort的使用 问题解决: (1)sort函数使用 注: sort函数,参数1为数组首地址,参数2是数组 ...
- C++ 排序函数 sort(),qsort()的使用方法
想起来自己天天排序排序,冒泡啊,二分查找啊,结果在STL中就自带了排序函数sort,qsort,总算把自己解脱了~ 所以自己总结了一下,首先看sort函数见下表: 函数名 功能描写叙述 sort 对给 ...
- linux makefile字符串操作函数 替换subst、模式替换patsubst、去首尾空格strip、查找字符串findstring、过滤filter、反过滤filter-out、排序函数sort、取单词word、取单词串wordlist、个数统计words
1.1 字符操作函数使用 在Makefile中可以使用函数来处理变量,从而让我们的命令或是规则更为的灵活和具有智能.make所支持的函数也不算很多,不过已经足够我们的操作了.函数调用后,函 ...
- FCL源码中数组类型的学习及排序函数Sort函数的分析
Array 是所有数组的基类ArrayList 解决了所有Array 类的缺点 能动态扩容, 但是类型不安全的,而是会有装箱与拆箱的性能开销List<T> 则是解决了ArrayLis ...
- 使用sort函数进行排序
介绍 C++的一个重要组成部分STL(Standard Template Library),即标准模板库,是一些高级数据结构和算法的集合:高级数据结构(容器)主要包括list.set.vector.m ...
- python排序函数sort()与sorted()区别
sort是容器的函数:sort(cmp=None, key=None, reverse=False) sorted是python的内建函数:sorted(iterable, cmp=None, key ...
- STL源代码分析——STL算法sort排序算法
前言 因为在前文的<STL算法剖析>中,源代码剖析许多,不方便学习,也不方便以后复习.这里把这些算法进行归类,对他们单独的源代码剖析进行解说.本文介绍的STL算法中的sort排序算法,SG ...
- 标准模板库(STL)学习指南之sort排序
对于程序员来说,数据结构是必修的一门课.从查找到排序,从链表到二叉树,几乎所有的算法和原理都需要理解,理解不了也要死记硬背下来.幸运的是这些理论都已经比较成熟,算法也基本固定下来,不需要你再去花费心思 ...
随机推荐
- ScrollView设置了ContentSize高度为0,仍然能滑动的问题
你有没有遇到过这样的情况: 对于ScrollView的不能上下滑动,设置了以下代码: _scrollViewTitle=[[UIScrollView alloc]initWithFrame:CGRec ...
- python中接受上一条命令执行的结果----subprocess.check_output()
subprocess.call 是不能作为赋值的,需要用到 subprocess.check_output 函数,而且如果要引用赋值就必须使用subprocess.call(['echo',line] ...
- gin框架教程:代码系列demo地址
gin框架教程代码地址: https://github.com/jiujuan/gin-tutorial demo目录: 01quickstart 02parameter 03route 04midd ...
- convert.ToInt32和int.parse区别
前者适合将object类类型转换成int类型 int.Parse适合将string类类型转换成int类型 1)这两个方法的最大不同是它们对null值的处理方法:Convert.ToInt32(null ...
- sqlalchemy orm 层面删除数据注意
#encoding: utf-8 from sqlalchemy import create_engine,Column,Integer,String,Float,func,and_,or_,Text ...
- grep与正则表达式:
1.grep程序 Linux下有文本处理三剑客 -- grep sed awk grep:文本 行过滤工具 sed: 文本 行编辑器(流编辑器) awk:报告生成器(做文本输出格式化) grep ...
- 【转贴】GS464/GS464E
GS464/GS464E GS464为四发射64位结构,采用动态流水线.其1.0版本(简称GS464)为9级流水线结构,在龙芯3A.3B.2H中使用.其2.0版本(简称GS464E)为12级动态流水线 ...
- 【Vue高级知识】细谈Vue 中三要素(响应式+模板+render函数)
[Vue高级知识]细谈Vue 中三要素(响应式+模板+render函数):https://blog.csdn.net/m0_37981569/article/details/93304809
- 12306 的架构也太 "牛X" 了吧!
每到节假日期间,一二线城市返乡.外出游玩的人们几乎都面临着一个问题:抢火车票! 虽然现在大多数情况下都能订到票,但是放票瞬间即无票的场景,相信大家都深有体会.尤其是春节期间,大家不仅使用12306,还 ...
- Type类的使用
Type类的使用(类反射)通过类获得Type: Type t = typeof(Person)通过实例对象获得类的Type: Type t = p.GetType()获取Type的方法:MethodI ...
