P4747 [CERC2017] Intrinsic Interval 题解
题目链接:Intrinsic Interval
讲讲析合树如何解决这种问题,其实这题很接近析合树的板题的应用。
增量法进行析合树建树时,需要用 ST 表预处理出 \(max\) 和 \(min\) 以便 \(O(1)\) 查询极差,然后线段树去维护 \([l,r]\) 上的极差减区间端点做差即 \(diff-(r-l)\),当这玩意等于 \(0\) 时容易知道,\([l,r]\) 就是一个连续段,而我们观察到这个东西是 \(\ge 0\) 的,很容易证的,区间极差一定大于等于端点做差。因为这个是排列,所以一定最多有 \(r-l\) 个连续的数,这样使得极差至少都是 \(r-l\),不会小于它。所以我们线段树维护个区间最小值,当然因为还有增量变化,所以再维护个区间加操作,这玩意是单调不升的,就能线段树上二分出 \(L_i\),这个 \(L_i\) 是使得 \([L_i,curr]\) 为连续段的最左边的点,显而易见的,我们需要用当前节点 \(curr\) 不断向左合并一直到这个节点为止。
考虑每次加入一个节点对线段树维护有何影响,容易观察到如果 \(max\) 变大了,那么显然需要去掉原来的 \(max\) 加入新的 \(max\),\(min\) 只有可能变小,那么很显然原来极差是 \(max-min\),此时应该加上原来的 \(min\) 减去新的 \(min\) 即可。这个最大最小值变化只需要维护单调栈就行了,维护单调递增和递减栈。相邻的栈节点他们的最大或者最小值是相同的,加入了新的节点使得被弹出了,这个时候就更改了相邻节点的最大最小值,这个时候就需要更改它们的线段树贡献了。
加入这个节点构成析合森林就老规矩,三种情况分讨:
这个栈顶节点是合点,且可以和它的最右儿子的左端点区间形成连续段,符合合点性质,直接作为这个栈顶节点的右儿子。
本身可以和它作为一个连续段,那就构造一个新的节点作为合点,作为它俩的父亲就行了。
这个时候需要一堆节点合并成一个新的连续段,新搞一个根,然后不断地弹栈找到这个形成连续段的点,这一堆点不符合合点相邻形成连续段的性质,所以这一堆连续段合并起来的新节点是一个析点。
注意往右添加移动 \([l,r]\) 中的 \(r\),时,显然 \(diff-(r-l)\) 整体会 \(-1\),注意去掉就行。
这样一来析合树就建完了。
本题做法
很显然的是,查询区间的两个端点的 \(lca\) 即是满足的一个连续段,但它不一定是答案说的包含这个区间的 “最小” 连续段。具体的分讨:
如果这个 \(lca\) 是析点,显然析点对应的区间就是答案了,因为析点的相邻子节点并不能拼成连续段,只能由所有节点拼凑。
如果这个 \(lca\) 是合点,显然根据合点的性质,它的任意相邻儿子可以拼成连续段,我们只需要找到这两个对应的到 \(lca\) 链上的两个相邻子区间形成的连续段更小。
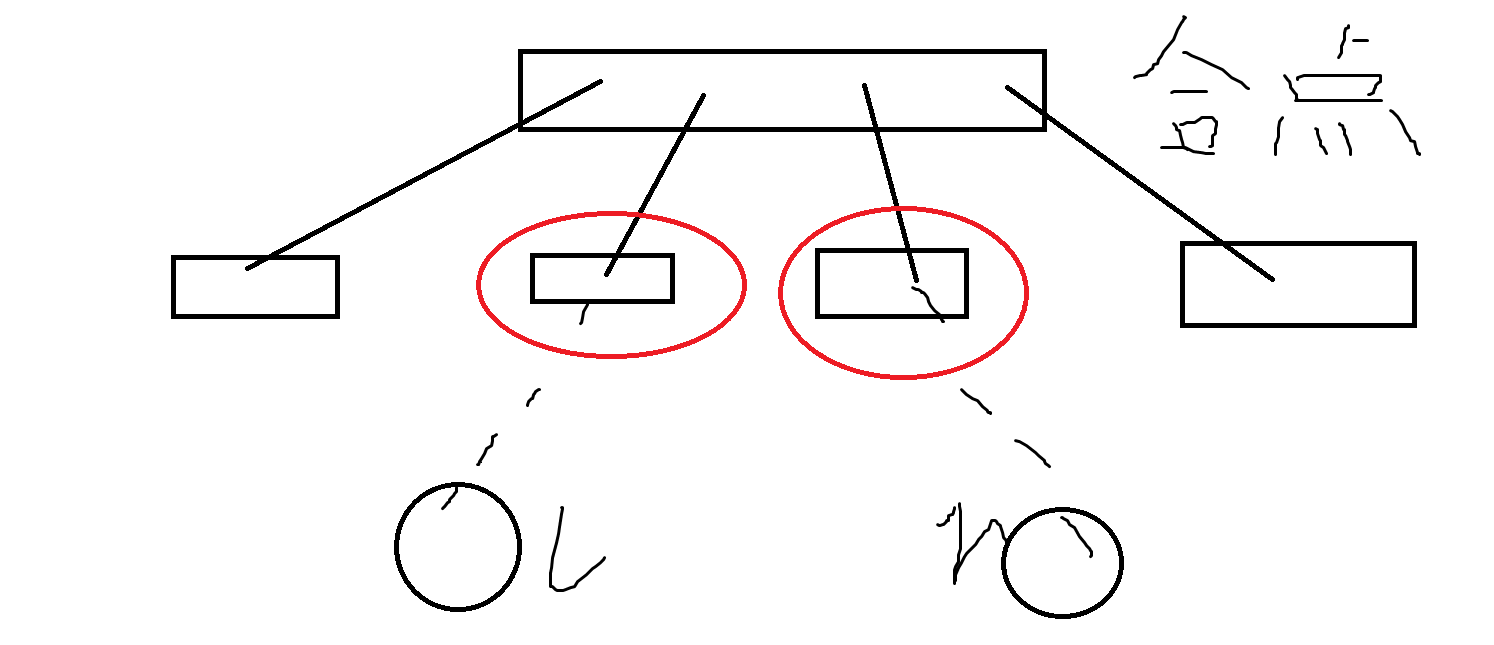
如图,\(l\) 和 \(r\) 对应的最小连续段应该为红色圆圈两个连续段的组合才是答案。所以倍增找到 \(lca\) 深度 \(+1\) 的那个点就行了,具体的相当于找 \(k\) 级祖先,找到 \(deep[l/r]-deep[lca]-1\) 级祖先即是这个点。
参照代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
// #pragma GCC optimize("Ofast,unroll-loops")
// #pragma GCC optimize(2)
// #define isPbdsFile
#ifdef isPbdsFile
#include <bits/extc++.h>
#else
#include <ext/pb_ds/priority_queue.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/hash_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/tree_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/trie_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/tag_and_trait.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/hash_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/list_update_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/exception.hpp>
#include <ext/rope>
#endif
using namespace std;
using namespace __gnu_cxx;
using namespace __gnu_pbds;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef pair<ll, ll> pll;
typedef tuple<int, int, int> tii;
typedef tuple<ll, ll, ll> tll;
typedef unsigned int ui;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef __int128 i128;
#define hash1 unordered_map
#define hash2 gp_hash_table
#define hash3 cc_hash_table
#define stdHeap std::priority_queue
#define pbdsHeap __gnu_pbds::priority_queue
#define sortArr(a, n) sort(a+1,a+n+1)
#define all(v) v.begin(),v.end()
#define yes cout<<"YES"
#define no cout<<"NO"
#define Spider ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
#define MyFile freopen("..\\input.txt", "r", stdin),freopen("..\\output.txt", "w", stdout);
#define forn(i, a, b) for(int i = a; i <= b; i++)
#define forv(i, a, b) for(int i=a;i>=b;i--)
#define ls(x) (x<<1)
#define rs(x) (x<<1|1)
#define endl '\n'
//用于Miller-Rabin
[[maybe_unused]] static int Prime_Number[13] = {0, 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37};
template <typename T>
int disc(T* a, int n)
{
return unique(a + 1, a + n + 1) - (a + 1);
}
template <typename T>
T lowBit(T x)
{
return x & -x;
}
template <typename T>
T Rand(T l, T r)
{
static mt19937 Rand(time(nullptr));
uniform_int_distribution<T> dis(l, r);
return dis(Rand);
}
template <typename T1, typename T2>
T1 modt(T1 a, T2 b)
{
return (a % b + b) % b;
}
template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3>
T1 qPow(T1 a, T2 b, T3 c)
{
a %= c;
T1 ans = 1;
for (; b; b >>= 1, (a *= a) %= c)if (b & 1)(ans *= a) %= c;
return modt(ans, c);
}
template <typename T>
void read(T& x)
{
x = 0;
T sign = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while (!isdigit(ch))
{
if (ch == '-')sign = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while (isdigit(ch))
{
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (ch ^ 48);
ch = getchar();
}
x *= sign;
}
template <typename T, typename... U>
void read(T& x, U&... y)
{
read(x);
read(y...);
}
template <typename T>
void write(T x)
{
if (typeid(x) == typeid(char))return;
if (x < 0)x = -x, putchar('-');
if (x > 9)write(x / 10);
putchar(x % 10 ^ 48);
}
template <typename C, typename T, typename... U>
void write(C c, T x, U... y)
{
write(x), putchar(c);
write(c, y...);
}
template <typename T11, typename T22, typename T33>
struct T3
{
T11 one;
T22 tow;
T33 three;
bool operator<(const T3 other) const
{
if (one == other.one)
{
if (tow == other.tow)return three < other.three;
return tow < other.tow;
}
return one < other.one;
}
T3() { one = tow = three = 0; }
T3(T11 one, T22 tow, T33 three) : one(one), tow(tow), three(three)
{
}
};
template <typename T1, typename T2>
void uMax(T1& x, T2 y)
{
if (x < y)x = y;
}
template <typename T1, typename T2>
void uMin(T1& x, T2 y)
{
if (x > y)x = y;
}
constexpr int N = 2e5 + 10;
constexpr int T = 25;
int a[N], n;
//查询极差
struct
{
int stMin[N][T], stMax[N][T];
int LOG2[N];
void build()
{
forn(i, 2, n)LOG2[i] = LOG2[i >> 1] + 1;
const int k = LOG2[n] + 1;
forn(i, 1, n)stMax[i][0] = stMin[i][0] = a[i];
forn(j, 1, k)
{
forn(i, 1, n-(1<<j)+1)
{
stMin[i][j] = min(stMin[i][j - 1], stMin[i + (1 << j - 1)][j - 1]);
stMax[i][j] = max(stMax[i][j - 1], stMax[i + (1 << j - 1)][j - 1]);
}
}
}
int queryRange(const int l, const int r) const
{
const int k = LOG2[r - l + 1];
return max(stMax[l][k], stMax[r - (1 << k) + 1][k]) - min(stMin[l][k], stMin[r - (1 << k) + 1][k]);
}
} ST;
//是否是连续段
inline bool isContinue(const int l, const int r)
{
return ST.queryRange(l, r) == r - l;
}
//维护Diff-(r-l)最小值(单调递增),线段树上二分找第一个为0的点,即为最近第一个满足点
struct
{
struct Node
{
int Min, Add;
} node[N << 2];
#define Min(x) node[x].Min
#define Add(x) node[x].Add
void push_up(const int curr)
{
Min(curr) = min(Min(ls(curr)),Min(rs(curr)));
}
void push_down(const int curr)
{
if (Add(curr))
{
Min(ls(curr)) += Add(curr), Min(rs(curr)) += Add(curr);
Add(ls(curr)) += Add(curr), Add(rs(curr)) += Add(curr);
Add(curr) = 0;
}
}
void add(const int curr, const int l, const int r, const int val, const int s = 1, const int e = n)
{
if (l <= s and e <= r)
{
Min(curr) += val, Add(curr) += val;
return;
}
const int mid = s + e >> 1;
push_down(curr);
if (l <= mid)add(ls(curr), l, r, val, s, mid);
if (r > mid)add(rs(curr), l, r, val, mid + 1, e);
push_up(curr);
}
int query(const int curr = 1, const int l = 1, const int r = n)
{
const int mid = l + r >> 1;
if (l == r)return l;
push_down(curr);
if (!Min(ls(curr)))return query(ls(curr), l, mid);
return query(rs(curr), mid + 1, r);
}
} Seg;
//析合树节点
struct DCT
{
int type, left, right, rightL; //0是析点,1是合点
DCT() = default;
DCT(const int left, const int right, const int type = 0, const int rightL = 0)
: type(type),
left(left),
right(right), rightL(rightL)
{
}
} dct[N];
int dctRoot;
#define left(x) dct[x].left
#define right(x) dct[x].right
#define type(x) dct[x].type
#define rightL(x) dct[x].rightL
int cnt;
int stMax[N], stMin[N], maxCnt, minCnt; //两种单调栈
stack<int> st; //析合森林节点
#define maxTop a[stMax[maxCnt]]
#define minTop a[stMin[minCnt]]
#define root st.top()
vector<int> child[N]; //析合树邻接表
int node[N]; //每个点所在析合树节点编号
//维护为(Max-Min)-(r-l)>=0,去Max需要减,取Min则是加
inline void build()
{
forn(i, 1, n)
{
while (maxCnt and a[i] >= maxTop)Seg.add(1, stMax[maxCnt - 1] + 1, stMax[maxCnt], -maxTop), maxCnt--;
while (minCnt and a[i] <= minTop)Seg.add(1, stMin[minCnt - 1] + 1, stMin[minCnt], minTop), minCnt--;
Seg.add(1, stMax[maxCnt] + 1, i, a[i]), Seg.add(1, stMin[minCnt] + 1, i, -a[i]);
stMax[++maxCnt] = stMin[++minCnt] = i;
dct[node[i] = ++cnt] = DCT(i, i);
const int L = Seg.query();
int curr = cnt;
//需要将这个连续段的所有本原连续段的节点解决了
while (!st.empty() and left(root) >= L)
{
if (type(root) and isContinue(rightL(root), i))
{
//合点且最后一个点可以和当前点形成连续段,所以做儿子
right(root) = i;
rightL(root) = left(curr);
child[root].push_back(curr);
curr = root;
st.pop();
}
else if (isContinue(left(root), i))
{
//本身和它连续就合并节点成为合点
dct[++cnt] = DCT(left(root), i, 1,left(curr)); //构造新的合点,当前节点就是最右节点,栈顶则是左节点
child[cnt].push_back(root);
child[cnt].push_back(curr);
st.pop();
curr = cnt;
}
else
{
//不断合并往左找连续段
child[++cnt].push_back(curr);
do child[cnt].push_back(root), st.pop();
while (!isContinue(left(root), i));
dct[cnt] = DCT(left(root), i); //作为一个析点
child[cnt].push_back(root);
st.pop();
curr = cnt;
}
}
st.push(curr);
Seg.add(1, 1, i, -1); //因为r+1,所以max-min-(r-l)整体-1
}
dctRoot = root; //析合树的根也即是析点
}
int fa[N][T + 1];
int deep[N];
inline void dfs(const int curr, const int pa)
{
deep[curr] = deep[pa] + 1;
fa[curr][0] = pa;
forn(i, 1, T)fa[curr][i] = fa[fa[curr][i - 1]][i - 1];
for (const auto nxt : child[curr])dfs(nxt, curr);
}
inline int LCA(int x, int y)
{
if (deep[x] < deep[y])swap(x, y);
forv(i, T, 0)if (deep[fa[x][i]] >= deep[y])x = fa[x][i];
if (x == y)return x;
forv(i, T, 0)if (fa[x][i] != fa[y][i])x = fa[x][i], y = fa[y][i];
return fa[x][0];
}
//k级祖先
inline int kthRoot(int curr, int k)
{
while (k)
{
const int step = ST.LOG2[k];
curr = fa[curr][step];
k -= 1 << step;
}
return curr;
}
int ansL, ansR;
//查找答案
inline void query(const int l, const int r)
{
const int L = node[l], R = node[r];
const int lca = LCA(L, R);
//如果是lca是合点应该跳到合点下面一个点上的两个连续段依旧可以拼成连续段,析点自然是左右两边了
if (type(lca))ansL = left(kthRoot(L,deep[L]-deep[lca]-1)), ansR = right(kthRoot(R,deep[R]-deep[lca]-1));
else ansL = left(lca), ansR = right(lca);
cout << ansL << " " << ansR << endl;
}
int q;
inline void solve()
{
cin >> n;
forn(i, 1, n)cin >> a[i];
ST.build(); //建ST表
build(); //建析合树
dfs(dctRoot, 0);
cin >> q;
forn(i, 1, q)
{
int l, r;
cin >> l >> r;
query(l, r);
}
}
signed int main()
{
// MyFile
Spider
//------------------------------------------------------
// clock_t start = clock();
int test = 1;
// read(test);
// cin >> test;
forn(i, 1, test)solve();
// while (cin >> n, n)solve();
// while (cin >> test)solve();
// clock_t end = clock();
// cerr << "time = " << double(end - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC << "s" << endl;
}
\]
P4747 [CERC2017] Intrinsic Interval 题解的更多相关文章
- 洛谷 P4747 [CERC2017]Intrinsic Interval 线段树维护连续区间
题目描述 题目传送门 分析 考虑对于 \([l,r]\),如何求出包住它的长度最短的好区间 做法就是用一个指针从 \(r\) 向右扫,每次查询以当前指针为右端点的最短的能包住 \([l,r]\) 的好 ...
- [CERC2017]Intrinsic Interval——扫描线+转化思想+线段树
[CERC2017]Intrinsic Interval https://www.luogu.org/blog/ywycasm/solution-p4747# 这种“好的区间”,见得还是比较多的了. ...
- [CERC2017]Intrinsic Interval(神仙+线段树)
题目大意:给一个1-n的排列,有一堆询问区间,定义一个好的区间为它的值域区间长度等于它的区间长度,求包这个询问区间的最小好的区间. 题解 做法太神了,根本想不到. %%%i207m. 结论:当一个区间 ...
- [CERC2017] Intrinsic Interval
首先理清这奇葩题意表述 给出一个\(1\)到\(n\)的排列\(p[]\)和\(m\)次询问,每次询问覆盖区间\([l,r]\)的最小区间\([a,b]\),满足\([a,b]\)内的元素排序后是连续 ...
- [CERC2017]Intrinsic Interval[scc+线段树优化建图]
题意 给定一个长度为 \(n\) 的排列,有 \(q\) 次询问,每次询问一个区间 \([l,r]\) ,找到最小的包含 \([l,r]\) 的区间,满足这个区间包含了一段连续的数字. \(n\leq ...
- BZOJ5259/洛谷P4747: [Cerc2017]区间
BZOJ5259/洛谷P4747: [Cerc2017]区间 2019.8.5 [HZOI]NOIP模拟测试13 C.优美序列 思维好题,然而当成NOIP模拟题↑真的好吗... 洛谷和BZOJ都有,就 ...
- Gym - 101620I Intrinsic Interval
题面在这里! 首先一个非常重要的性质是,两个好的区间的交依然是好的区间. 有了这个性质,我们只要找到包含某个区间的右端点最小的好区间,然后就是这个区间的答案拉. 至于找右端点最小的好区间就是一个扫描线 ...
- [luogu4747]Intrinsic Interval
有一个结论,答案一定是所有包含其合法区间中$l$最大且$r$最小的 证明比较容易,考虑两个合法区间有交,那么交必然合法,同时交也必然包含该区间,因此这个区间一定是合法的(取$l$最大的和$r$最小的两 ...
- JZOJ 2022.07.18【提高组A】模拟
\(\text{T1}\) 很容易想到用 \(f_1 f_2 ... f_k\) 来表示第 \(n\) 项 发现重点关注指数即可,即我们要递推 \(f_1 ... f_k\) 对应的指数 递推涉及 \ ...
- bzoj5000+的洛谷题号
前言 闲得没事把 bzoj5000+ 在 Luogu 上可找到的题面整理了一下-- 对于我,bzoj 连账号都没有,所以肯定是不清楚 bzoj 题目总数的--因此其实就是手动翻查. 工作量很大,基本不 ...
随机推荐
- 前端科普系列(4):Babel —— 把 ES6 送上天的通天塔
本文首发于 vivo互联网技术 微信公众号 链接: https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/plJewhUd0xDXh3Ce4CGpHg作者:Morrain 一.前言 在上一节 < ...
- 5、SpringBoot连接数据库引入mybatis
系列导航 springBoot项目打jar包 1.springboot工程新建(单模块) 2.springboot创建多模块工程 3.springboot连接数据库 4.SpringBoot连接数据库 ...
- 动态给div赋值高,使页面高度100%
import { ref, onMounted, onUnmounted, computed, nextTick } from 'vue' const boxRef = ref() const sea ...
- MaxListenersExceededWarning:Possible EventEmitter memory leak detected.
打包出现内存溢出 解决办法:
- vue动态组件使用
- 介绍几种OPTIONS检测的方法
概述 日常的VOIP开发中,OPTIONS检测是常用的网络状态检测工具. OPTIONS原本是作为获取对方能力的消息,也可以检测当前服务状态.正常情况下,UAS收到OPTIONS心跳,直接回复200即 ...
- C++17 解构绑定
在python中,加入我们有一个函数返回了两个数值,如: def getData(x, y): return x,y 那么我们在使用这个函数时只需要使用两个新变量去接收函数返回值就可以: a,b = ...
- 第二章 VB.NET 绘图基础
GDI+( Graphics Device Interface Plus)是 Windows操作系统用来执行绘画及其他相关图形操作的一套子系统,是由. Net Framework中的System.Dr ...
- Chrome显示和更改显示网页字符集的方法
Chrome显示和更改显示网页字符集的方法 背景 前段时间学习和总结了unicode和utf8的一些知识. 当时想到应该学习和整理一下网站网页的编码格式字符集相关的内容 想着既然给自己立了flag, ...
- [转帖]缓存与存储的一致性策略:从 CPU 到分布式系统
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/151745863 在计算机系统设计实践中,我们常常会遇到下图所示架构: 为了解决单个存储器读吞吐无法满足要求的问题,常常需要在存储器上面增加 ...
