【lombok】lombok---帮你简化生成必要但臃肿的java代码工具 【映射注解和lombok注解同时使用 以及 映射注解放在属性和get方法上的区别】
官方地址:https://projectlombok.org/
GitHub:https://github.com/rzwitserloot/lombok
指导说明文档:http://jnb.ociweb.com/jnb/jnbJan2010.html
===============================================================================================================
本来来说,lombok作为一个目前为止【2017-11-27】java并未将其作为标准来推广。还有很多人问使用它是否合适。
这里不做这种讨论!!!
===============================================================================================================
在使用之前,要明确一点,在开发过程中,一般情况下,仅使用@Data 即可满足生成entity类的大部分情况。
摘自指导文档:
Essentially, using @Data on a class is the same as annotating the class with a default @ToString and @EqualsAndHashCode as well as annotating each field with both @Getter and @Setter.
实质上,在一个类上使用@Data与用默认的@ToString和@EqualsAndHashCode注释这个类以及用@Getter和@Setter注释每个字段是一样的。
===============================================================================================================
使用起来:
一.安装lombok插件【idea使用为例】
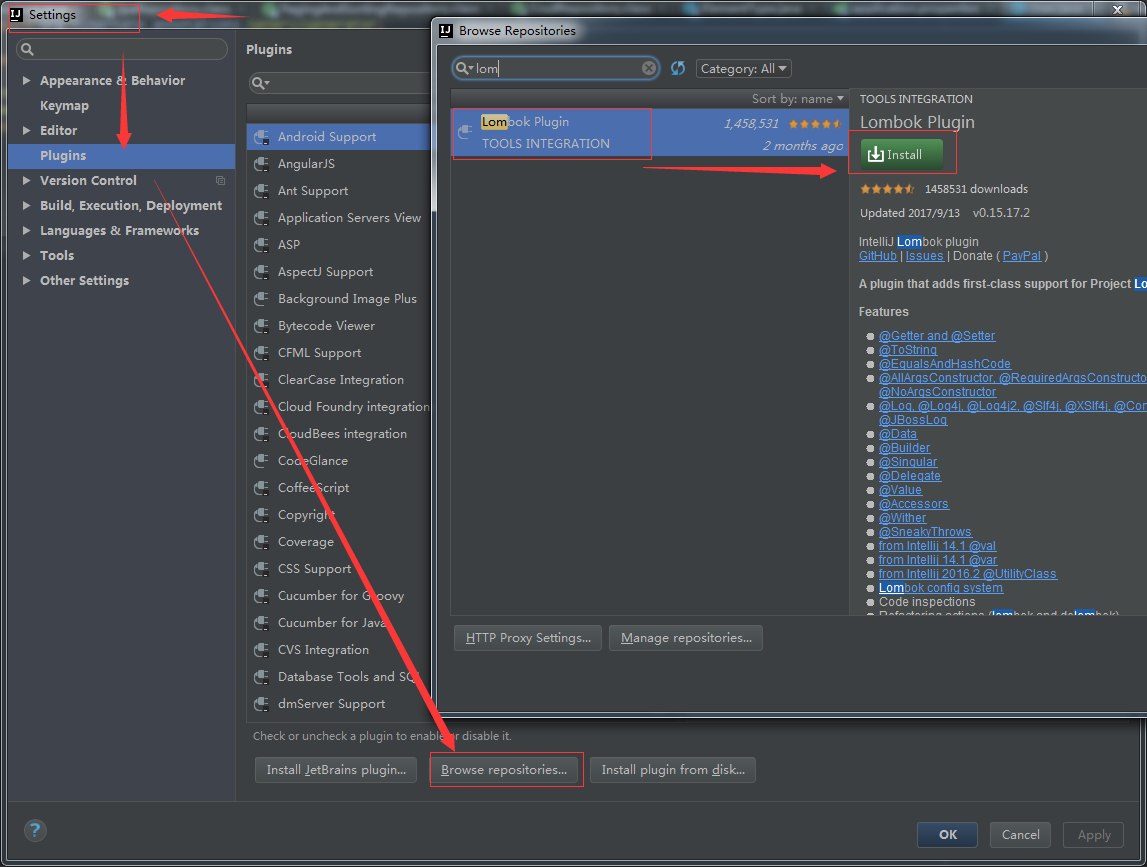
二.项目引入lombok依赖
<!--lombok-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
版本这里不给了,想使用最新版本的,可以自己加上。
三.lombok注解使用详解
在上面安装插件的时候,可以看到有很多的注解是被支持的:

官方的指导文档,时间久远。所以就找到下面的注解进行详解。
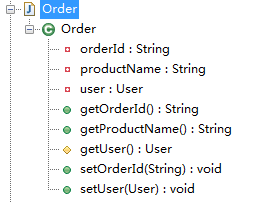
@Getter and @Setter
【属性级别,生成本属性的get和set方法】
AccessLevel.PROTECTED 默认生成的方法为public,此属性可以设置生成方法的访问修饰符【非必须】
转化前:
package com.sxd.entity; import lombok.AccessLevel;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter; public class Order { @Getter @Setter private String orderId;
@Getter(AccessLevel.PROTECTED) @Setter private User user;
@Getter @Setter(AccessLevel.NONE) private String productName; }
编译后:
package com.sxd.entity; public class Order
{
private String orderId;
private User user;
private String productName; public void setOrderId(String orderId)
{
this.orderId = orderId;
} public String getOrderId()
{
return this.orderId;
} public void setUser(User user)
{
this.user = user;
} protected User getUser()
{
return this.user;
} public String getProductName()
{
return this.productName;
}
}
=============================================================================
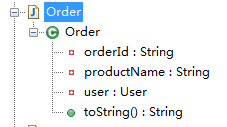
@ToString
【类级别,生成自定义的toString()方法】
exclude="{字段1,字段2}" 生成的toString()不包含哪些字段【非必须】
callSuper=true 如果继承的有父类的话,可以设置callSuper 让其调用父类的toString()方法【非必须】
转化前:
package com.sxd.entity;
import lombok.ToString;
@ToString(exclude = {"orderId","user"},callSuper = false)
public class Order {
private String orderId;
private User user;
private String productName;
}
编译后:
package com.sxd.entity; public class Order
{
private String orderId;
private User user;
private String productName; public String toString()
{
return "Order(productName=" + this.productName + ")";
}
}
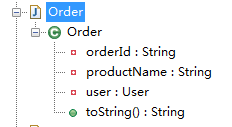
不使用上述属性值的话:
转化前:
package com.sxd.entity; import lombok.ToString; @ToString
public class Order { private String orderId;
private User user;
private String productName; }
编译后:
package com.sxd.entity; public class Order
{
private String orderId;
private User user;
private String productName; public String toString()
{
return "Order(orderId=" + this.orderId + ", user=" + this.user + ", productName=" + this.productName + ")";
}
}
===================================================================================
@EqualsAndHashCode
【类级别,生成自定义的equals()方法和HashCode()方法】
exclude="{字段1,字段2}" 生成的方法不包含哪些字段【非必须】
callSuper=true 如果继承的有父类的话,可以设置callSuper 让其调用父类的方法【非必须】
转化前:
package com.sxd.entity;
import lombok.EqualsAndHashCode;
@EqualsAndHashCode(exclude = {"orderId","user"},callSuper = false)
public class Order {
private String orderId;
private User user;
private String productName;
}
编译后:
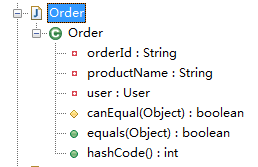
package com.sxd.entity; public class Order
{
private String orderId;
private User user;
private String productName; public int hashCode()
{
int PRIME = 59;int result = 1;Object $productName = this.productName;result = result * 59 + ($productName == null ? 43 : $productName.hashCode());return result;
} protected boolean canEqual(Object other)
{
return other instanceof Order;
} public boolean equals(Object o)
{
if (o == this) {
return true;
}
if (!(o instanceof Order)) {
return false;
}
Order other = (Order)o;
if (!other.canEqual(this)) {
return false;
}
Object this$productName = this.productName;Object other$productName = other.productName;return this$productName == null ? other$productName == null : this$productName.equals(other$productName);
}
}
=====================================================================================
@NonNull
【属性级别,验证不能为null的注解,如果执行加了这个注解的setter方法时设置为Null,抛异常java.lang.NullPointerException】
转化前:
package com.sxd.entity; import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.NonNull;
import lombok.Setter; public class Order { private String orderId;
private User user;
@NonNull @Getter @Setter private String productName; public Order() { } }
编译后:
package com.sxd.entity; import lombok.NonNull; public class Order
{
private String orderId;
private User user;
@NonNull
private String productName; public void setProductName(@NonNull String productName)
{
if (productName == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("productName");
}
this.productName = productName;
} @NonNull
public String getProductName()
{
return this.productName;
}
}
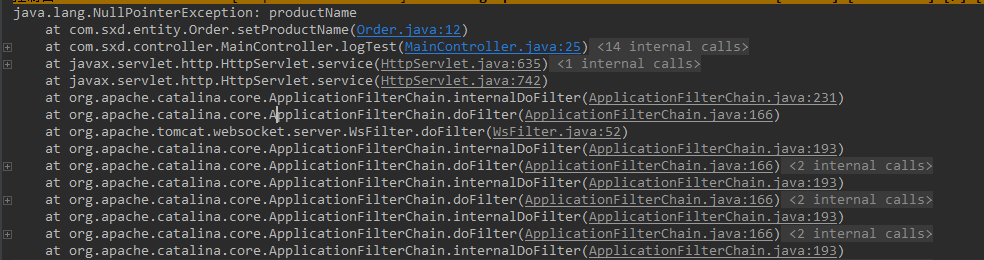
如果去执行setter方法并赋值Null,则报错:

注意报错行数:
===========================================================================================
@NoArgsConstructor
【类级别,生成无参构造方法】
focus=true 当类中有final字段没有被初始化时,编译器会报错,此时可用@NoArgsConstructor(force = true),然后就会为没有初始化的final字段设置默认值 0 / false / null。对于具有约束的字段(例如@NonNull字段),不会生成检查或分配,因此请注意,正确初始化这些字段之前,这些约束无效。 转化前:
package com.sxd.entity; import lombok.NoArgsConstructor; @NoArgsConstructor(force = true)
public class Order {
private String orderId;
private User user;
private String productName; }
编译后:
package com.sxd.entity; public class Order
{
private String orderId;
private User user;
private String productName;
}
=====================================================================================
@RequiredArgsConstructor
【类级别,生成有 或 无参的静态方法,用于获取本对象】
staticName = "自定义静态方法名"
转化前:
package com.sxd.entity; import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor; @RequiredArgsConstructor(staticName = "build")
public class Order {
private String orderId;
private User user;
private String productName; }
转化后:
package com.sxd.entity; public class Order
{
private String orderId;
private User user;
private String productName; public static Order build()
{
return new Order();
}
}

===============================================================================
@AllArgsConstructor
【类级别,生成全参构造方法】
转化前:
package com.sxd.entity; import lombok.AllArgsConstructor; @AllArgsConstructor
public class Order {
private String orderId;
private User user;
private String productName; }
编译后:
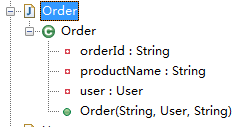
package com.sxd.entity; import java.beans.ConstructorProperties; public class Order
{
private String orderId;
private User user;
private String productName; @ConstructorProperties({"orderId", "user", "productName"})
public Order(String orderId, User user, String productName)
{
this.orderId = orderId;this.user = user;this.productName = productName;
}
}
================================================================================
@Data
【类级别,此注解为lombok中最常用注解】
【@Data 包含了@ToString,@EqualsAndHashCode,@Getter / @Setter和@RequiredArgsConstructor的功能】
staticConstructor="静态实例化方法名"
转化前:
package com.sxd.entity; import lombok.Data; @Data(staticConstructor = "build")
public class Order {
private String orderId;
private User user;
private String productName; }
编译后:
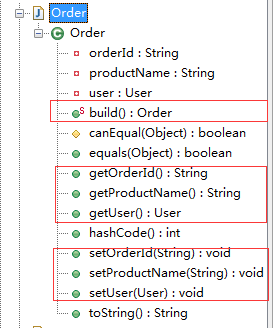
package com.sxd.entity; public class Order
{
private String orderId;
private User user;
private String productName; public static Order build()
{
return new Order();
} public int hashCode()
{
int PRIME = 59;int result = 1;Object $orderId = getOrderId();result = result * 59 + ($orderId == null ? 43 : $orderId.hashCode());Object $user = getUser();result = result * 59 + ($user == null ? 43 : $user.hashCode());Object $productName = getProductName();result = result * 59 + ($productName == null ? 43 : $productName.hashCode());return result;
} protected boolean canEqual(Object other)
{
return other instanceof Order;
} public boolean equals(Object o)
{
if (o == this) {
return true;
}
if (!(o instanceof Order)) {
return false;
}
Order other = (Order)o;
if (!other.canEqual(this)) {
return false;
}
Object this$orderId = getOrderId();Object other$orderId = other.getOrderId();
if (this$orderId == null ? other$orderId != null : !this$orderId.equals(other$orderId)) {
return false;
}
Object this$user = getUser();Object other$user = other.getUser();
if (this$user == null ? other$user != null : !this$user.equals(other$user)) {
return false;
}
Object this$productName = getProductName();Object other$productName = other.getProductName();return this$productName == null ? other$productName == null : this$productName.equals(other$productName);
} public void setOrderId(String orderId)
{
this.orderId = orderId;
} public void setUser(User user)
{
this.user = user;
} public void setProductName(String productName)
{
this.productName = productName;
} public String toString()
{
return "Order(orderId=" + getOrderId() + ", user=" + getUser() + ", productName=" + getProductName() + ")";
} public String getOrderId()
{
return this.orderId;
} public User getUser()
{
return this.user;
} public String getProductName()
{
return this.productName;
}
}
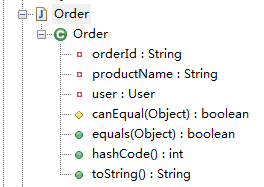
@Accessors
【类级别,控制get、set方法】
- fluent boolean值,默认为false。此字段主要为控制生成的getter和setter方法前面是否带get/set;false带,true不带
- chain boolean值,默认false。如果设置为true,setter返回的是此对象,方便链式调用方法
- prefix 设置前缀 例如:@Accessors(prefix = "abc") private String abcAge 当生成get/set方法时,会把此前缀去掉
转化前:【注意三个属性设值以及生成】
package com.sxd.entity; import lombok.Data;
import lombok.experimental.Accessors; @Data
@Accessors(fluent = false,chain = false,prefix = "aaa")
public class Order {
private String orderId;
private User user;
private String productName; }
编译后:
package com.sxd.entity; public class Order
{
private String orderId;
private User user;
private String productName; public String toString()
{
return "Order(orderId=" + this.orderId + ", user=" + this.user + ", productName=" + this.productName + ")";
} public int hashCode()
{
int PRIME = 59;int result = 1;Object $orderId = this.orderId;result = result * 59 + ($orderId == null ? 43 : $orderId.hashCode());Object $user = this.user;result = result * 59 + ($user == null ? 43 : $user.hashCode());Object $productName = this.productName;result = result * 59 + ($productName == null ? 43 : $productName.hashCode());return result;
} protected boolean canEqual(Object other)
{
return other instanceof Order;
} public boolean equals(Object o)
{
if (o == this) {
return true;
}
if (!(o instanceof Order)) {
return false;
}
Order other = (Order)o;
if (!other.canEqual(this)) {
return false;
}
Object this$orderId = this.orderId;Object other$orderId = other.orderId;
if (this$orderId == null ? other$orderId != null : !this$orderId.equals(other$orderId)) {
return false;
}
Object this$user = this.user;Object other$user = other.user;
if (this$user == null ? other$user != null : !this$user.equals(other$user)) {
return false;
}
Object this$productName = this.productName;Object other$productName = other.productName;return this$productName == null ? other$productName == null : this$productName.equals(other$productName);
}
}
===========================================================
转化前:【注意fluent】
package com.sxd.entity; import lombok.Data;
import lombok.experimental.Accessors; @Data
@Accessors(fluent = true,chain = false)
public class Order {
private String orderId;
private User user;
private String productName; }
编译后:
package com.sxd.entity; public class Order
{
private String orderId;
private User user;
private String productName; public void productName(String productName)
{
this.productName = productName;
} public int hashCode()
{
int PRIME = 59;int result = 1;Object $orderId = orderId();result = result * 59 + ($orderId == null ? 43 : $orderId.hashCode());Object $user = user();result = result * 59 + ($user == null ? 43 : $user.hashCode());Object $productName = productName();result = result * 59 + ($productName == null ? 43 : $productName.hashCode());return result;
} protected boolean canEqual(Object other)
{
return other instanceof Order;
} public void orderId(String orderId)
{
this.orderId = orderId;
} public void user(User user)
{
this.user = user;
} public String toString()
{
return "Order(orderId=" + orderId() + ", user=" + user() + ", productName=" + productName() + ")";
} public boolean equals(Object o)
{
if (o == this) {
return true;
}
if (!(o instanceof Order)) {
return false;
}
Order other = (Order)o;
if (!other.canEqual(this)) {
return false;
}
Object this$orderId = orderId();Object other$orderId = other.orderId();
if (this$orderId == null ? other$orderId != null : !this$orderId.equals(other$orderId)) {
return false;
}
Object this$user = user();Object other$user = other.user();
if (this$user == null ? other$user != null : !this$user.equals(other$user)) {
return false;
}
Object this$productName = productName();Object other$productName = other.productName();return this$productName == null ? other$productName == null : this$productName.equals(other$productName);
} public String orderId()
{
return this.orderId;
} public User user()
{
return this.user;
} public String productName()
{
return this.productName;
}
}

==============================================================================
转化前:【注意chain】
package com.sxd.entity; import lombok.Data;
import lombok.experimental.Accessors; @Data
@Accessors(fluent = false,chain = true)
public class Order {
private String orderId;
private User user;
private String productName; }
编译后:
package com.sxd.entity; public class Order
{
private String orderId;
private User user;
private String productName; public Order setProductName(String productName)
{
this.productName = productName;return this;
} public int hashCode()
{
int PRIME = 59;int result = 1;Object $orderId = getOrderId();result = result * 59 + ($orderId == null ? 43 : $orderId.hashCode());Object $user = getUser();result = result * 59 + ($user == null ? 43 : $user.hashCode());Object $productName = getProductName();result = result * 59 + ($productName == null ? 43 : $productName.hashCode());return result;
} protected boolean canEqual(Object other)
{
return other instanceof Order;
} public Order setOrderId(String orderId)
{
this.orderId = orderId;return this;
} public Order setUser(User user)
{
this.user = user;return this;
} public String toString()
{
return "Order(orderId=" + getOrderId() + ", user=" + getUser() + ", productName=" + getProductName() + ")";
} public boolean equals(Object o)
{
if (o == this) {
return true;
}
if (!(o instanceof Order)) {
return false;
}
Order other = (Order)o;
if (!other.canEqual(this)) {
return false;
}
Object this$orderId = getOrderId();Object other$orderId = other.getOrderId();
if (this$orderId == null ? other$orderId != null : !this$orderId.equals(other$orderId)) {
return false;
}
Object this$user = getUser();Object other$user = other.getUser();
if (this$user == null ? other$user != null : !this$user.equals(other$user)) {
return false;
}
Object this$productName = getProductName();Object other$productName = other.getProductName();return this$productName == null ? other$productName == null : this$productName.equals(other$productName);
} public String getOrderId()
{
return this.orderId;
} public User getUser()
{
return this.user;
} public String getProductName()
{
return this.productName;
}
}
===================================================================
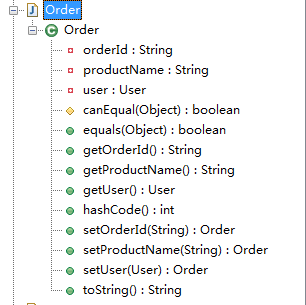
转化前:【注意prefix】
package com.sxd.entity; import lombok.Data;
import lombok.experimental.Accessors; @Data
@Accessors(fluent = false,chain = true,prefix = "product")
public class Order {
private String orderId;
private User user;
private String productName; }
编译后:
package com.sxd.entity; public class Order
{
private String orderId;
private User user;
private String productName; public String toString()
{
return "Order(orderId=" + this.orderId + ", user=" + this.user + ", productName=" + getName() + ")";
} public int hashCode()
{
int PRIME = 59;int result = 1;Object $orderId = this.orderId;result = result * 59 + ($orderId == null ? 43 : $orderId.hashCode());Object $user = this.user;result = result * 59 + ($user == null ? 43 : $user.hashCode());Object $productName = getName();result = result * 59 + ($productName == null ? 43 : $productName.hashCode());return result;
} protected boolean canEqual(Object other)
{
return other instanceof Order;
} public boolean equals(Object o)
{
if (o == this) {
return true;
}
if (!(o instanceof Order)) {
return false;
}
Order other = (Order)o;
if (!other.canEqual(this)) {
return false;
}
Object this$orderId = this.orderId;Object other$orderId = other.orderId;
if (this$orderId == null ? other$orderId != null : !this$orderId.equals(other$orderId)) {
return false;
}
Object this$user = this.user;Object other$user = other.user;
if (this$user == null ? other$user != null : !this$user.equals(other$user)) {
return false;
}
Object this$productName = getName();Object other$productName = other.getName();return this$productName == null ? other$productName == null : this$productName.equals(other$productName);
} public Order setName(String productName)
{
this.productName = productName;return this;
} public String getName()
{
return this.productName;
}
}

=========================================================================
@Cleanup
【代码级别,清理资源/关闭资源注解】
转化前:
public void testCleanUp() {
try {
@Cleanup ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
baos.write(new byte[] {'Y','e','s'});
System.out.println(baos.toString());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
编译后:
public void testCleanUp() {
try {
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
try {
baos.write(new byte[]{'Y', 'e', 's'});
System.out.println(baos.toString());
} finally {
baos.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
=========================================================================
@Synchronized
【方法级别,同步/线程安全注解】
转化前:
private DateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("MM-dd-YYYY");
@Synchronized
public String synchronizedFormat(Date date) {
return format.format(date);
}
编译后:
private final java.lang.Object $lock = new java.lang.Object[0];
private DateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("MM-dd-YYYY"); public String synchronizedFormat(Date date) {
synchronized ($lock) {
return format.format(date);
}
}
=========================================================================
@Wither
【属性级别,提供了给final字段赋值的一种方法】
转化前:
import lombok.AccessLevel;
import lombok.NonNull;
import lombok.experimental.Wither;
public class WitherExample {
@Wither private final int age;
@Wither(AccessLevel.PROTECTED) @NonNull private final String name; public WitherExample(String name, int age) {
if (name == null) throw new NullPointerException();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
编译后:
import lombok.NonNull;
public class WitherExample {
private final int age;
private @NonNull final String name; public WitherExample(String name, int age) {
if (name == null) throw new NullPointerException();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
} public WitherExample withAge(int age) {
return this.age == age ? this : new WitherExample(age, name);
} protected WitherExample withName(@NonNull String name) {
if (name == null) throw new java.lang.NullPointerException("name");
return this.name == name ? this : new WitherExample(age, name);
}
}
==================================================================================
@Builder
【类级别,为你的类生成复杂的构建器API】
转化前:
package com.sxd.entity; import lombok.Builder; @Builder
public class Order {
private String orderId;
private User user;
private String productName; }
编译后:
package com.sxd.entity; import java.beans.ConstructorProperties; public class Order
{
private String orderId;
private User user;
private String productName; public static class OrderBuilder
{
private String orderId;
private User user;
private String productName; public String toString()
{
return "Order.OrderBuilder(orderId=" + this.orderId + ", user=" + this.user + ", productName=" + this.productName + ")";
} public Order build()
{
return new Order(this.orderId, this.user, this.productName);
} public OrderBuilder productName(String productName)
{
this.productName = productName;return this;
} public OrderBuilder user(User user)
{
this.user = user;return this;
} public OrderBuilder orderId(String orderId)
{
this.orderId = orderId;return this;
}
} public static OrderBuilder builder()
{
return new OrderBuilder();
} @ConstructorProperties({"orderId", "user", "productName"})
Order(String orderId, User user, String productName)
{
this.orderId = orderId;this.user = user;this.productName = productName;
}
}
==============================================================
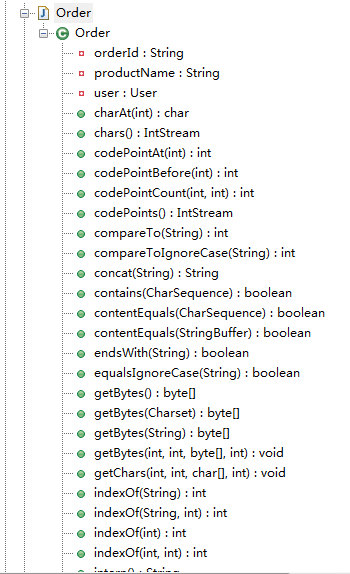
@Delegate
【属性级别,同化所在属性的类型的方法到本类中】
转化前:【本属性类型为String】
package com.sxd.entity;
import lombok.experimental.Delegate;
public class Order {
private String orderId;
private User user;
@Delegate private String productName;
}
编译后:
package com.sxd.entity; import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.util.Locale;
import java.util.stream.IntStream; public class Order
{
private String orderId;
private User user;
private String productName; public IntStream codePoints()
{
return this.productName.codePoints();
} public IntStream chars()
{
return this.productName.chars();
} public String intern()
{
return this.productName.intern();
} public char[] toCharArray()
{
return this.productName.toCharArray();
} public String trim()
{
return this.productName.trim();
} public String toUpperCase()
{
return this.productName.toUpperCase();
} public String toUpperCase(Locale arg0)
{
return this.productName.toUpperCase(arg0);
} public String toLowerCase()
{
return this.productName.toLowerCase();
} public String toLowerCase(Locale arg0)
{
return this.productName.toLowerCase(arg0);
} public String[] split(String arg0)
{
return this.productName.split(arg0);
} public String[] split(String arg0, int arg1)
{
return this.productName.split(arg0, arg1);
} public String replace(CharSequence arg0, CharSequence arg1)
{
return this.productName.replace(arg0, arg1);
} public String replaceAll(String arg0, String arg1)
{
return this.productName.replaceAll(arg0, arg1);
} public String replaceFirst(String arg0, String arg1)
{
return this.productName.replaceFirst(arg0, arg1);
} public boolean contains(CharSequence arg0)
{
return this.productName.contains(arg0);
} public boolean matches(String arg0)
{
return this.productName.matches(arg0);
} public String replace(char arg0, char arg1)
{
return this.productName.replace(arg0, arg1);
} public String concat(String arg0)
{
return this.productName.concat(arg0);
} public CharSequence subSequence(int arg0, int arg1)
{
return this.productName.subSequence(arg0, arg1);
} public String substring(int arg0, int arg1)
{
return this.productName.substring(arg0, arg1);
} public String substring(int arg0)
{
return this.productName.substring(arg0);
} public int lastIndexOf(String arg0, int arg1)
{
return this.productName.lastIndexOf(arg0, arg1);
} public int lastIndexOf(String arg0)
{
return this.productName.lastIndexOf(arg0);
} public int indexOf(String arg0, int arg1)
{
return this.productName.indexOf(arg0, arg1);
} public int indexOf(String arg0)
{
return this.productName.indexOf(arg0);
} public int lastIndexOf(int arg0, int arg1)
{
return this.productName.lastIndexOf(arg0, arg1);
} public int lastIndexOf(int arg0)
{
return this.productName.lastIndexOf(arg0);
} public int indexOf(int arg0, int arg1)
{
return this.productName.indexOf(arg0, arg1);
} public int indexOf(int arg0)
{
return this.productName.indexOf(arg0);
} public boolean endsWith(String arg0)
{
return this.productName.endsWith(arg0);
} public boolean startsWith(String arg0)
{
return this.productName.startsWith(arg0);
} public boolean startsWith(String arg0, int arg1)
{
return this.productName.startsWith(arg0, arg1);
} public boolean regionMatches(boolean arg0, int arg1, String arg2, int arg3, int arg4)
{
return this.productName.regionMatches(arg0, arg1, arg2, arg3, arg4);
} public boolean regionMatches(int arg0, String arg1, int arg2, int arg3)
{
return this.productName.regionMatches(arg0, arg1, arg2, arg3);
} public int compareToIgnoreCase(String arg0)
{
return this.productName.compareToIgnoreCase(arg0);
} public int compareTo(String arg0)
{
return this.productName.compareTo(arg0);
} public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String arg0)
{
return this.productName.equalsIgnoreCase(arg0);
} public boolean contentEquals(CharSequence arg0)
{
return this.productName.contentEquals(arg0);
} public boolean contentEquals(StringBuffer arg0)
{
return this.productName.contentEquals(arg0);
} public byte[] getBytes()
{
return this.productName.getBytes();
} public byte[] getBytes(Charset arg0)
{
return this.productName.getBytes(arg0);
} public byte[] getBytes(String arg0)
throws UnsupportedEncodingException
{
return this.productName.getBytes(arg0);
} @Deprecated
public void getBytes(int arg0, int arg1, byte[] arg2, int arg3)
{
this.productName.getBytes(arg0, arg1, arg2, arg3);
} public void getChars(int arg0, int arg1, char[] arg2, int arg3)
{
this.productName.getChars(arg0, arg1, arg2, arg3);
} public int offsetByCodePoints(int arg0, int arg1)
{
return this.productName.offsetByCodePoints(arg0, arg1);
} public int codePointCount(int arg0, int arg1)
{
return this.productName.codePointCount(arg0, arg1);
} public int codePointBefore(int arg0)
{
return this.productName.codePointBefore(arg0);
} public int codePointAt(int arg0)
{
return this.productName.codePointAt(arg0);
} public char charAt(int arg0)
{
return this.productName.charAt(arg0);
} public boolean isEmpty()
{
return this.productName.isEmpty();
} public int length()
{
return this.productName.length();
}
}
==========================================================================
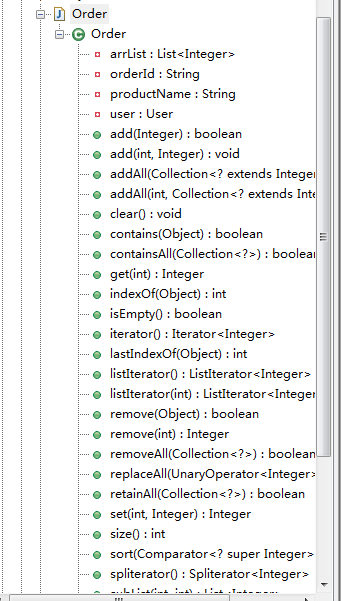
转化前:【所在属性类型为List】
package com.sxd.entity;
import lombok.experimental.Delegate;
import java.util.List;
public class Order {
private String orderId;
private User user;
private String productName;
@Delegate private List<Integer> arrList;
}
编译后:
package com.sxd.entity; import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ListIterator;
import java.util.Spliterator;
import java.util.function.UnaryOperator; public class Order
{
private String orderId;
private User user;
private String productName;
private List<Integer> arrList; public Spliterator<Integer> spliterator()
{
return this.arrList.spliterator();
} public List<Integer> subList(int arg0, int arg1)
{
return this.arrList.subList(arg0, arg1);
} public ListIterator<Integer> listIterator(int arg0)
{
return this.arrList.listIterator(arg0);
} public ListIterator<Integer> listIterator()
{
return this.arrList.listIterator();
} public int lastIndexOf(Object arg0)
{
return this.arrList.lastIndexOf(arg0);
} public int indexOf(Object arg0)
{
return this.arrList.indexOf(arg0);
} public Integer remove(int arg0)
{
return (Integer)this.arrList.remove(arg0);
} public void add(int arg0, Integer arg1)
{
this.arrList.add(arg0, arg1);
} public Integer set(int arg0, Integer arg1)
{
return (Integer)this.arrList.set(arg0, arg1);
} public Integer get(int arg0)
{
return (Integer)this.arrList.get(arg0);
} public void clear()
{
this.arrList.clear();
} public void sort(Comparator<? super Integer> arg0)
{
this.arrList.sort(arg0);
} public void replaceAll(UnaryOperator<Integer> arg0)
{
this.arrList.replaceAll(arg0);
} public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> arg0)
{
return this.arrList.retainAll(arg0);
} public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> arg0)
{
return this.arrList.removeAll(arg0);
} public boolean addAll(int arg0, Collection<? extends Integer> arg1)
{
return this.arrList.addAll(arg0, arg1);
} public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends Integer> arg0)
{
return this.arrList.addAll(arg0);
} public boolean containsAll(Collection<?> arg0)
{
return this.arrList.containsAll(arg0);
} public boolean remove(Object arg0)
{
return this.arrList.remove(arg0);
} public boolean add(Integer arg0)
{
return this.arrList.add(arg0);
} public <T> T[] toArray(T[] arg0)
{
return this.arrList.toArray(arg0);
} public Object[] toArray()
{
return this.arrList.toArray();
} public Iterator<Integer> iterator()
{
return this.arrList.iterator();
} public boolean contains(Object arg0)
{
return this.arrList.contains(arg0);
} public boolean isEmpty()
{
return this.arrList.isEmpty();
} public int size()
{
return this.arrList.size();
}
}
============================================================================
@SneakyThrows
【异常处理注解,这里不做详细解释】
转化前:
@SneakyThrows
public void testSneakyThrows() {
throw new IllegalAccessException();
}
编译后:
public void testSneakyThrows() {
try {
throw new IllegalAccessException();
} catch (java.lang.Throwable $ex) {
throw lombok.Lombok.sneakyThrow($ex);
}
}
============================================================================
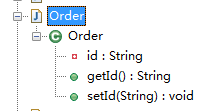
@_({注解1,注解2})或@_(注解) 配合onMethod=使用
【属性级别,用于将注解放在注解中使用】
转化前:
package com.sxd.entity; import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter; import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Id; public class Order { @Getter(onMethod = @_({@Column,@Id}))
@Setter
private String id;
}
编译后:
package com.sxd.entity; import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Id; public class Order
{
private String id; @Column
@Id
public String getId()
{
return this.id;
} public void setId(String id)
{
this.id = id;
}
}
【注意:这个时而有用,时而报错,具体问题依旧找不到~~~~~~~~~~~~具体看附录2】
============================================================================================================
最后,如果使用了lombok的话,如何在实体类上声明实体对数据表的映射?
注意:@Column等注解是可以直接放在字段上而不用放在get方法上
例如:创建不同包下同名的实体类User.java
自己写get/set方法的User类如下:
package com.sxd.entity; import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; import javax.persistence.*; @Entity
@GenericGenerator(name = "uuid2", strategy = "org.hibernate.id.UUIDGenerator" )
public class User {
private String id;
private String username;
private String password;
private Integer age; @Id
@GeneratedValue(generator = "uuid2")
public String getId() {
return id;
} public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
} @Column(nullable = false)
public String getUsername() {
return username;
} public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
} @Column(nullable = false)
public String getPassword() {
return password;
} public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
} @Column(nullable = false)
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
} public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
} public User() { } public User(String id, String username, String password, Integer age) {
this.id = id;
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
this.age = age;
} @Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id='" + id + '\'' +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
编译完是:
package com.sxd.entity; import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; @Entity
@GenericGenerator(name="uuid2", strategy="org.hibernate.id.UUIDGenerator")
public class User
{
private String id;
private String username;
private String password;
private Integer age; @Id
@GeneratedValue(generator="uuid2")
public String getId()
{
return this.id;
} public void setId(String id)
{
this.id = id;
} @Column(nullable=false)
public String getUsername()
{
return this.username;
} public void setUsername(String username)
{
this.username = username;
} @Column(nullable=false)
public String getPassword()
{
return this.password;
} public void setPassword(String password)
{
this.password = password;
} @Column(nullable=false)
public Integer getAge()
{
return this.age;
} public void setAge(Integer age)
{
this.age = age;
} public User() {} public User(String id, String username, String password, Integer age)
{
this.id = id;
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
this.age = age;
} public String toString()
{
return "User{id='" + this.id + '\'' + ", username='" + this.username + '\'' + ", password='" + this.password + '\'' + ", age=" + this.age + '}';
}
}
=================== ==================================
使用lombok之后如下:
package com.sxd.controller; import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import lombok.experimental.Accessors;
import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id; @Entity
@GenericGenerator(name = "uuid2", strategy = "org.hibernate.id.UUIDGenerator" )
@Data(staticConstructor = "of")
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Accessors(chain = true)
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(generator = "uuid2")private String id;
private String username; @Column(nullable = false)
private String password; @Column(nullable = false)
private Integer age; }
编译完是:
package com.sxd.controller; import java.beans.ConstructorProperties;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; @Entity
@GenericGenerator(name="uuid2", strategy="org.hibernate.id.UUIDGenerator")
public class User
{
@Id
@GeneratedValue(generator="uuid2")
private String id;
private String username;
@Column(nullable=false)
private String password;
@Column(nullable=false)
private Integer age; public User setAge(Integer age)
{
this.age = age;return this;
} public String toString()
{
return "User(id=" + getId() + ", username=" + getUsername() + ", password=" + getPassword() + ", age=" + getAge() + ")";
} public int hashCode()
{
int PRIME = 59;int result = 1;Object $id = getId();result = result * 59 + ($id == null ? 43 : $id.hashCode());Object $username = getUsername();result = result * 59 + ($username == null ? 43 : $username.hashCode());Object $password = getPassword();result = result * 59 + ($password == null ? 43 : $password.hashCode());Object $age = getAge();result = result * 59 + ($age == null ? 43 : $age.hashCode());return result;
} protected boolean canEqual(Object other)
{
return other instanceof User;
} public User setId(String id)
{
this.id = id;return this;
} public User setUsername(String username)
{
this.username = username;return this;
} public User setPassword(String password)
{
this.password = password;return this;
} public boolean equals(Object o)
{
if (o == this) {
return true;
}
if (!(o instanceof User)) {
return false;
}
User other = (User)o;
if (!other.canEqual(this)) {
return false;
}
Object this$id = getId();Object other$id = other.getId();
if (this$id == null ? other$id != null : !this$id.equals(other$id)) {
return false;
}
Object this$username = getUsername();Object other$username = other.getUsername();
if (this$username == null ? other$username != null : !this$username.equals(other$username)) {
return false;
}
Object this$password = getPassword();Object other$password = other.getPassword();
if (this$password == null ? other$password != null : !this$password.equals(other$password)) {
return false;
}
Object this$age = getAge();Object other$age = other.getAge();return this$age == null ? other$age == null : this$age.equals(other$age);
} @ConstructorProperties({"id", "username", "password", "age"})
public User(String id, String username, String password, Integer age)
{
this.id = id;this.username = username;this.password = password;this.age = age;
} public String getId()
{
return this.id;
} public String getUsername()
{
return this.username;
} public String getPassword()
{
return this.password;
} public Integer getAge()
{
return this.age;
} public User() {}
}
有一个疑问,映射注解放在属性上和放在get方法上有什么区别???【看附录3】
===============================================================附录1:equals()方法和hashCode()方法的意义==========================================================
摘录:
1.hashcode是用来查找的,如果你学过数据结构就应该知道,在查找和排序这一章有
例如内存中有这样的位置
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
而我有个类,这个类有个字段叫ID,我要把这个类存放在以上8个位置之一,如果不用hashcode而任意存放,那么当查找时就需要到这八个位置里挨个去找,或者用二分法一类的算法。
但如果用hashcode那就会使效率提高很多。
我们这个类中有个字段叫ID,那么我们就定义我们的hashcode为ID%8,然后把我们的类存放在取得得余数那个位置。比如我们的ID为9,9除8的余数为1,那么我们就把该类存在1这个位置,如果ID是13,求得的余数是5,那么我们就把该类放在5这个位置。这样,以后在查找该类时就可以通过ID除 8求余数直接找到存放的位置了。 2.但是如果两个类有相同的hashcode怎么办那(我们假设上面的类的ID不是唯一的),例如9除以8和17除以8的余数都是1,那么这是不是合法的,
回答是:可以这样。那么如何判断呢?在这个时候就需要定义 equals了。
也就是说,我们先通过 hashcode来判断两个类是否存放某个桶里,但这个桶里可能有很多类,那么我们就需要再通过 equals 来在这个桶里找到我们要的类。
那么。重写了equals(),为什么还要重写hashCode()呢?
想想,你要在一个桶里找东西,你必须先要找到这个桶啊,你不通过重写hashcode()来找到桶,光重写equals()有什么用啊
==============================================================附录2:@Getter()等lombok注解配合hibernate的映射注解怎么使用===========================================================
如果在项目中真的使用lombok的注解的话,映射注解应该如何处理呢?
寥寥无几的资料中有大概类似于如下的写法:
@Getter(onMethod = @_({@Id,@Column(name="id",nullable=false),@GeneratedValue(strategy= GenerationType.AUTO)}))
@Setter
private Integer id;
亲自试了一下,
如下:
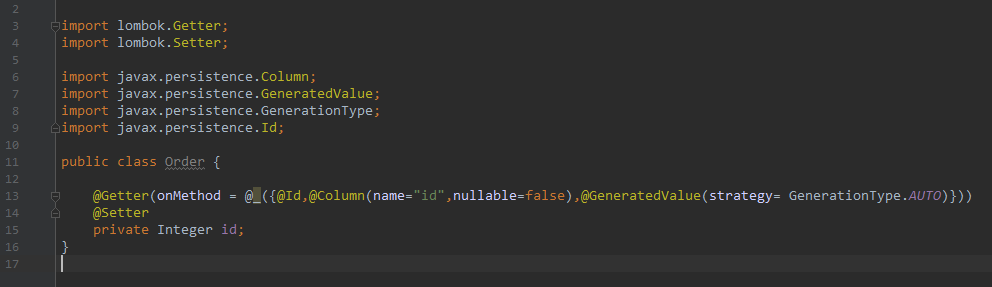
报错如下:

其实在@Getter()注解接口中定义如下:
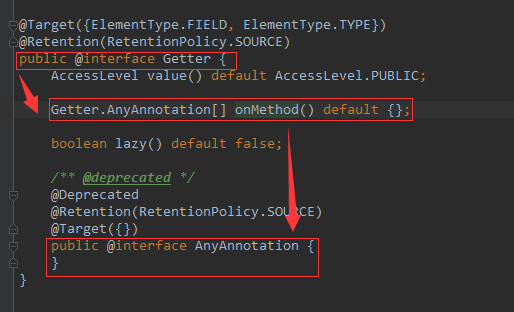
但是具体怎么去写,还没有研究出来。
【如有解决方法,不吝赐教!!】
所以,最终按照并列将注解写在属性上,而不是在@Getter()注解中写@Column()注解。
如下:
@Data(staticConstructor = "of")
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Accessors(chain = true)
@Entity
@GenericGenerator(name = "uuid2", strategy = "org.hibernate.id.UUIDGenerator" )
public class Member { @Id
@GeneratedValue(generator = "uuid2")
@Column(name = "memberId")
private String memberId; @OneToOne(cascade = {CascadeType.MERGE,CascadeType.REFRESH},fetch = FetchType.EAGER)
private User user; @Column(name="memberGrade",nullable = false)
@NonNull
private Integer memberGrade;
}
编译完成如下:
package com.sxd.entity; import java.beans.ConstructorProperties;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.FetchType;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.OneToOne;
import lombok.NonNull;
import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; @Entity
@GenericGenerator(name="uuid2", strategy="org.hibernate.id.UUIDGenerator")
public class Member
{
@Id
@GeneratedValue(generator="uuid2")
@Column(name="memberId")
private String memberId;
@OneToOne(cascade={javax.persistence.CascadeType.MERGE, javax.persistence.CascadeType.REFRESH}, fetch=FetchType.EAGER)
private User user;
@Column(name="memberGrade", nullable=false)
@NonNull
private Integer memberGrade; public String toString()
{
return "Member(memberId=" + getMemberId() + ", user=" + getUser() + ", memberGrade=" + getMemberGrade() + ")";
} public int hashCode()
{
int PRIME = 59;int result = 1;Object $memberId = getMemberId();result = result * 59 + ($memberId == null ? 43 : $memberId.hashCode());Object $user = getUser();result = result * 59 + ($user == null ? 43 : $user.hashCode());Object $memberGrade = getMemberGrade();result = result * 59 + ($memberGrade == null ? 43 : $memberGrade.hashCode());return result;
} public Member setMemberId(String memberId)
{
this.memberId = memberId;return this;
} public Member setUser(User user)
{
this.user = user;return this;
} public Member setMemberGrade(@NonNull Integer memberGrade)
{
if (memberGrade == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("memberGrade");
}
this.memberGrade = memberGrade;return this;
} protected boolean canEqual(Object other)
{
return other instanceof Member;
} public boolean equals(Object o)
{
if (o == this) {
return true;
}
if (!(o instanceof Member)) {
return false;
}
Member other = (Member)o;
if (!other.canEqual(this)) {
return false;
}
Object this$memberId = getMemberId();Object other$memberId = other.getMemberId();
if (this$memberId == null ? other$memberId != null : !this$memberId.equals(other$memberId)) {
return false;
}
Object this$user = getUser();Object other$user = other.getUser();
if (this$user == null ? other$user != null : !this$user.equals(other$user)) {
return false;
}
Object this$memberGrade = getMemberGrade();Object other$memberGrade = other.getMemberGrade();return this$memberGrade == null ? other$memberGrade == null : this$memberGrade.equals(other$memberGrade);
} @ConstructorProperties({"memberId", "user", "memberGrade"})
public Member(String memberId, User user, @NonNull Integer memberGrade)
{
if (memberGrade == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("memberGrade");
}
this.memberId = memberId;this.user = user;this.memberGrade = memberGrade;
} public String getMemberId()
{
return this.memberId;
} public User getUser()
{
return this.user;
} @NonNull
public Integer getMemberGrade()
{
return this.memberGrade;
} public Member() {}
}

那么最后看 附录3,了解最后一个问题,映射注解放在属性上和放在get方法上有什么区别?
=======================================================================附录3:映射注解放在属性上和放在get()方法上有什么区别======================================================================
摘录自:http://blog.csdn.net/most_rabbitfishes/article/details/70904949
对于属性字段和表的字段关系对应的注解属性的位置,一般我们采用以下两种方式:
第一种:
是把注解@Column(name ="xx")放在field上,一种是把注解放在get方法上一般放在field上看起来比较集中、清晰;
第二种:
是把注解@Column(name= "xx")放在get方法上,这种方式看起来比较散漫、不很清楚;
但是第一种方式这样做实际上破坏了java面向对象的封装性,原因是一般我们写javaBean,成员变量通常定义为private,目的就是不让别人来直接访问的私有属性,而我们把注解放在私有成员的变量上,就是默认hibernate可以直接访问我们的私有的成员变量,所以我们定义属性为private,就实际没有多大意义,至于hibernate为什么能访问,hibernate采用java的反射机制完全可以访问私有成员变量!所以应该放在get方法上,第二种方式这个时候就显得更加合理。
随即,我采用了附录2中实体用于hibernate自动生成数据表的表结构:

Hibernate自动帮我们建表:
如果我们采用注解的方式在我们的实体Bean上,又想通过扫描这些注解的Bean,通过Hibernate自动帮我们建表,那么你就会发现字段注解的位置不同甚至会影响到建表的结构,尤其是大字段、外键约束的生成效果。
如果采用第一种方式注解到私有字段上,这种帮我们建立表结构、约束条件和大字段Lob类型这些都是非常正常的,而通过第二种方式注解到get方法上,这种帮我们的建立的表大部分正常字段正常,而外键关联的和大字段就会出现问题.
虽然项目的开发我们不采用hibernate帮我们自动建表,通常我们还是要手动的建表,所以这一些是对于通过Hibernate帮我们自动建表要考虑的!而实际开发中,已注解在get方法上为多数!
结论:如上 将注解建立在属性上,生成的表结构,约束条件,外键等都正常,所以,如果你要使用hibernate的生成策略,在你建立好实体之后自动去建立数据表的话,同时使用lombok的注解和映射注解都放在属性上是合适的!!!
【lombok】lombok---帮你简化生成必要但臃肿的java代码工具 【映射注解和lombok注解同时使用 以及 映射注解放在属性和get方法上的区别】的更多相关文章
- JAVA 自动生成对应数据库表的JPA代码工具
http://blog.csdn.net/zheng2008hua/article/details/6274659 关键词:JPA 数据库表代码自动生成,JPA代码生成 自动生成对应数据库表的 ...
- 使用maven插件生成grpc所需要的Java代码
1.首先需要编写自己需要的.proto文件,本文重点不在这里,.proto可以参考grpc官方例子 https://grpc.io/docs/quickstart/java.html 2.创建自己的J ...
- 使用 Lombok 简化项目中无谓的Java代码
在写使用Java时,难免会有一些模板代码要写,不然get/set,toString, hashCode, close 资源,定义构造函数等等.代码会显得很冗余,很长.Lombok项目可以是我们摆脱这些 ...
- IDEAL葵花宝典:java代码开发规范插件 lombok 插件
前言: lombok简介: lombok是暑假来到公司实习的时候发现的一个非常好用的小工具,刚见到的时候就感觉非常惊艳,有一种相见恨晚的感觉,用了一段时间之后感觉的确挺不错,所以特此来推荐一下. 那么 ...
- Lombok 安装、入门 - 消除冗长的 java 代码(转)
前言: 逛开源社区的时候无意发现的,用了一段时间,觉得还可以,特此推荐一下. lombok 提供了简单的注解的形式来帮助我们简化消除一些必须有但显得很臃肿的 java 代码.特别是相对于 ...
- 八:Lombok 安装、入门 - 消除冗长的 java 代码
Lombok 安装.入门 - 消除冗长的 java 代码 前言: 逛开源社区的时候无意发现的,用了一段时间,觉得还可以,特此推荐一下. lombok 提供了简单的注解的形式来帮助我们简化消 ...
- Lombok 安装、入门 - 消除冗长的 java 代码
lombok 提供了简单的注解的形式来帮助我们简化消除一些必须有但显得很臃肿的 java 代码. lombok 的官方网址:http://projectlombok.org/ lombok 安装1. ...
- Lombok - 消除冗长的 java 代码
前言: 逛开源社区的时候无意发现的,用了一段时间,觉得还可以,特此推荐一下. lombok 提供了简单的注解的形式来帮助我们简化消除一些必须有但显得很臃肿的 java 代码.特别是相对于 ...
- 【转】Lombok 安装、入门 - 消除冗长的 java 代码
前言: 逛开源社区的时候无意发现的,用了一段时间,觉得还可以,特此推荐一下. lombok 提供了简单的注解的形式来帮助我们简化消除一些必须有但显得很臃肿的 java 代码.特别是相对于 ...
随机推荐
- net user
net user 编辑 Net User命令是一个DOS命令,必须在Windows nt以上系统的MS-DOS模式下运行,所以首先要进入MS-DOS模式:选择“开始”菜单的“附件”选项的子选项“命令提 ...
- MongoDB快速入门学习笔记8 MongoDB的java驱动操作
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.regex.Pattern; import org.bson.D ...
- ACM-ICPC 2018 南京赛区网络预赛
轻轻松松也能拿到区域赛名额,CCPC真的好难 An Olympian Math Problem 问答 只看题面 54.76% 1000ms 65536K Alice, a student of g ...
- easyui 右键绑定事件
$(function(){ $('#hospitalTree').bind('contextmenu', function(e) { e.preventDefault(); ...
- PAT1034
本题要求编写程序,计算2个有理数的和.差.积.商. 输入格式: # include<iostream> # include<algorithm> # include<st ...
- POJ-1087 二分图匹配,最大流。
A Plug for UNIX 题意很迷,不过很水. 题意:一个房间有m个插座,每个插座有一个型号, ...
- Web进程被kill掉后线程还在运行怎么办?
目录 背景描述 原因分析 处理方案 参考 背景描述 系统有一个配置表,系统在启动后会启动一个线程,每隔5分钟将配置表里所有的数据更新到内存中. 系统是通过jenkins构建(直接kill掉Web进程, ...
- xstream+dom4j比较对象
package com.brmoney.util.obj2xml; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.List; import org.dom ...
- springboot使用restTemplate post提交值 restTemplate post值
post提交有 FormData和Payload 两种形式: 第一种是formdata形式,在header参数里可以直接看到 payload则封装成json格式post过去,获取以后需要再解析 ...
- webpack简单使用
1 首先npm init 建立package.json文件 npm init 2 然后全局安装webpack npm install webpack -g ...

