【Ray Tracing The Next Week 超详解】 光线追踪2-8 Volume
Preface
今天有两个东东,一个是体积烟雾,一个是封面图
下一篇我们总结项目代码
Chapter 8:Volumes
我们需要为我们的光线追踪器添加新的物体——烟、雾,也称为participating media。 我们还需要补充一个材质——次表面散射材质,它有点像物体内的浓雾。
体渲染通常的做法是,在体的内部有很多随机表面,来实现散射的效果。比如一束烟可以表示为,在这束烟的内部任意位置,都可以存在一个面,以此来实现烟、雾
对于一个恒定密度体,一条光线通过其中的时候,在烟雾体中传播的时候也会发生散射,光线在烟雾体中能传播多远,也是由烟雾体的密度决定的,密度越高,光线穿透性越差,光线传播的距离也越短。从而实现烟雾的透光性。
引用书中一张图(光线可穿透可散射)
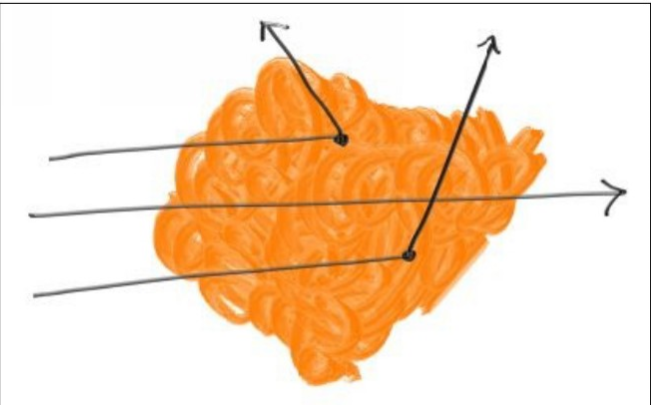
当光线通过体积时,它可能在任何点散射。 光线在任何小距离dL中散射的概率为:
概率= C * dL,其中C与体积的光密度成比例。
对于恒定体积,我们只需要密度C和边界。
/// isotropic.hpp // -----------------------------------------------------
// [author] lv
// [begin ] 2019.1
// [brief ] the isotropic-class for the ray-tracing project
// from the 《ray tracing the next week》
// ----------------------------------------------------- #pragma once namespace rt
{ class isotropic :public material
{
public:
isotropic(texture* tex) :_albedo(tex) { } virtual bool scatter(const ray& InRay, const hitInfo& info, rtvec& attenuation, ray& scattered)const override
{
scattered = ray(info._p, lvgm::random_unit_sphere());
attenuation = _albedo->value(info._u, info._v, info._p);
return true;
} private:
texture * _albedo;
}; } // rt namespace
这个材质的散射原理和漫反射磨砂材质的大同小异,均属于碰撞点转换为新视点,沿任意方向发射新的视线,只不过漫反射的视线方向向量指向外相切球体表面,而isotropic的视线方向指向以碰撞点为球心的单位球体表面
区别就在于
漫反射的散射光线不可能指到物体内部,它一定是散射到表面外部(视线方向指向外切球体表面)
isotropic材质的散射光线可以沿原来的方向一往前,以此视线透光性
因为烟雾内部只是颗粒而不存在真正不可穿透的几何实体,所以漫反射实体不可穿透,只能散射到表面外部,而烟雾可穿透
接下来我们看一下烟雾体
/// constant_medium.hpp // -----------------------------------------------------
// [author] lv
// [begin ] 2019.1
// [brief ] the constant_dedium-class for the ray-tracing project
// from the 《ray tracing the next week》
// ----------------------------------------------------- #pragma once namespace rt
{ class constant_medium :public intersect
{
public:
constant_medium(intersect* p, rtvar d, texture* tex); virtual bool hit(const ray& sight, rtvar t_min, rtvar t_max, hitInfo& info)const override; virtual aabb getbox()const override; private:
intersect* _item; rtvar _density; //烟雾密度 material* _materialp;
}; inline constant_medium::constant_medium(intersect* p, rtvar d, texture* tex)
:_item(p)
,_density(d)
,_materialp(new isotropic(tex))
{
} aabb constant_medium::getbox()const
{
return _item->getbox();
} bool constant_medium::hit(const ray& sight, rtvar t_min, rtvar t_max, hitInfo& info)const
{
hitInfo info1, info2;
if (_item->hit(sight, -rtInf(), rtInf(), info1)) {
if (_item->hit(sight, info1._t + 0.0001, rtInf(), info2)) {
if (info1._t < t_min)
info1._t = t_min;
if (info2._t > t_max)
info2._t = t_max;
if (info1._t >= info2._t)
return false;
if (info1._t < )
info1._t = ;
float distance_inside_boundary = (info2._t - info1._t)*sight.direction().normal();
float hit_distance = -( / _density)*log(lvgm::rand01());
if (hit_distance < distance_inside_boundary) {
info._t = info1._t + hit_distance / sight.direction().normal();
info._p = sight.go(info._t);
info._n = rtvec(, , ); // arbitrary
info._materialp = _materialp;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
} } // rt namespace
hit函数里面是一些边界合法性检测
场景测试代码
intersect* cornell_smoke()
{
intersect ** list = new intersect*[]; int cnt = ;
material* red = new lambertian(new constant_texture(rtvec(0.65, 0.05, 0.05)));
material * blue = new lambertian(new constant_texture(rtvec(0.05, 0.05, 0.73)));
material* white = new lambertian(new constant_texture(rtvec(0.73, 0.73, 0.73)));
material* green = new lambertian(new constant_texture(rtvec(0.12, 0.45, 0.15)));
material* light = new areaLight(new constant_texture(rtvec(, , ))); list[cnt++] = new xz_rect(, , , , , light);
list[cnt++] = new flip_normal(new xz_rect(, , , , , light));
list[cnt++] = new flip_normal(new yz_rect(, , , , , green));
list[cnt++] = new yz_rect(, , , , , red);
list[cnt++] = new flip_normal(new xz_rect(, , , , , white));
list[cnt++] = new xz_rect(, , , , , white);
list[cnt++] = new flip_normal(new xy_rect(, , , , , blue)); intersect* box1 = new translate(new rotate_y(new box(rtvec(), rtvec(, , ), white), -), rtvec(, , ));
intersect* box2 = new translate(new rotate_y(new box(rtvec(), rtvec(, , ), white), ), rtvec(, , )); list[cnt++] = new constant_medium(box2, 0.006, new constant_texture(rtvec(0.8, 0.58, .)));
list[cnt++] = new constant_medium(box1, 0.008, new constant_texture(rtvec(0.9, 0.2, 0.72))); return new intersections(list, cnt);
}
下面是效果:sample -> 1000

注释 // arbitrary处为随机方向,之前为(1,0,0)
我觉得改为(rand01(),rand01(),rand01())较为合适,下面是改之后的效果

Chapter 9:A Scene Testing All New Features
最后的封面图是这样一个场景:
体积雾:有一个蓝色的次表面散射球体,但是这个东西并没有单独实现,而是把它包裹在了一个玻璃球内。
体积雾:整个场景是由层薄薄的雾气笼盖着的
长方体:地面是一堆随机长方体
玻璃球:一个作为蓝色烟雾的容器,一个是单纯的玻璃球
映射纹理:地球纹理球体
过程纹理:柏林噪声纹理球体
运动模糊球体:有一个棕色的运动球体
镜面球体:银白色的镜面球
区域光照:顶部是一个长方形的区域光源
其他未说明材质的都是漫反射
渲染器中剩下的最大缺陷是没有阴影射线,但这就是为什么我们容易获得焦散和次表面散射效果的原因。
下面是渲染代码,关于相机参数设置还需等待渲染结果出来才能公布
VS四开,渲染了一天还没完,我也实属无奈
intersect* finalScene()
{
int nb = ;
intersect ** list = new intersect*[];
intersect ** boxlist = new intersect*[];
intersect ** boxlist2 = new intersect*[]; material * white = new lambertian(new constant_texture(rtvec(0.73, 0.73, 0.73)));
material * ground = new lambertian(new constant_texture(rtvec(0.48, 0.83, 0.53))); int b = ;
for (int i = ; i < nb; ++i)
for (int j = ; j < nb; ++j)
{
rtvar w = ;
rtvar x0 = - + i*w;
rtvar z0 = - + j*w;
rtvar y0 = ;
rtvar x1 = x0 + w;
rtvar y1 = * (lvgm::rand01() + 0.01);
rtvar z1 = z0 + w;
boxlist[b++] = new box(rtvec(x0, y0, z0), rtvec(x1, y1, z1), ground);
} int l = ;
list[l++] = new bvh_node(boxlist, b, , );
material * light = new areaLight(new constant_texture(rtvec(, , )));
list[l++] = new xz_rect(, , , , , light);
rtvec center(, , );
list[l++] = new moving_sphere(center, center + rtvec(, , ), , , , new lambertian(new constant_texture(rtvec(0.7, 0.3, 0.1))));
list[l++] = new sphere(rtvec(, , ), , new dielectric(1.5));
list[l++] = new sphere(rtvec(, , ), , new metal(new constant_texture(rtvec(0.8, 0.8, 0.9)), 10.0)); intersect * boundary = new sphere(rtvec(, , ), , new dielectric(1.5));
list[l++] = boundary;
list[l++] = new constant_medium(boundary, 0.2, new constant_texture(rtvec(0.2, 0.4, 0.9)));
boundary = new sphere(rtvec(), , new dielectric(1.5));
list[l++] = new constant_medium(boundary, 0.0011, new constant_texture(rtvec(., ., .))); int x, y, n;
unsigned char * tex = stbi_load("earthmap.jpg", &x, &y, &n, );
material * emat = new lambertian(new image_texture(tex, x, y));
list[l++] = new sphere(rtvec(, , ), , emat);
texture * pertext = new noise_texture(0.1);
list[l++] = new sphere(rtvec(, , ), , new lambertian(pertext));
int ns = ;
for (int j = ; j < ns; ++j)
boxlist2[j] = new sphere(rtvec( * lvgm::rand01(), * lvgm::rand01(), lvgm::rand01()), , white); list[l++] = new translate(new rotate_y(new bvh_node(boxlist2, ns, , ), ), rtvec(-, , )); return new intersections(list, l);
}
/-----------------------更新线-------------------------------/
对应的相机参数
效果

其中,薄雾效果太重了,雾气参数应该小一点,大约在1e-4左右较好
vfov可能太大了,45°应该更好一点吧
镜头应该更靠近些
感谢您的阅读,生活愉快~
【Ray Tracing The Next Week 超详解】 光线追踪2-8 Volume的更多相关文章
- 【Ray Tracing The Next Week 超详解】 光线追踪2-9
我们来整理一下项目的代码 目录 ----include --hit --texture --material ----RTdef.hpp ----ray.hpp ----camera.hpp ---- ...
- 【Ray Tracing The Next Week 超详解】 光线追踪2-6 Cornell box
Chapter 6:Rectangles and Lights 今天,我们来学习长方形区域光照 先看效果 light 首先我们需要设计一个发光的材质 /// light.hpp // ------- ...
- 【Ray Tracing in One Weekend 超详解】 光线追踪1-4
我们上一篇写了Chapter5 的第一个部分表面法线,那么我们来学剩下的部分,以及Chapter6. Chapter5:Surface normals and multiple objects. 我们 ...
- 【Ray Tracing The Next Week 超详解】 光线追踪2-7 任意长方体 && 场景案例
上一篇比较简单,很久才发是因为做了一些好玩的场景,后来发现这一章是专门写场景例子的,所以就安排到了这一篇 Preface 这一篇要介绍的内容有: 1. 自己做的光照例子 2. Cornell box画 ...
- 【Ray Tracing The Next Week 超详解】 光线追踪2-5
Chapter 5:Image Texture Mapping 先看效果: 我们之前的纹理是利用的是撞击点p处的位置信息,比如大理石纹理 而我们今天的图片映射纹理采用2D(u,v)纹理坐标来进行. 在 ...
- 【Ray Tracing in One Weekend 超详解】 光线追踪1-8 自定义相机设计
今天,我们来学习如何设计自定义位置的相机 ready 我们只需要了解我们之前的坐标体系,或者说是相机位置 先看效果 Chapter10:Positionable camera 这一章我们直接用概念 ...
- 【Ray Tracing The Next Week 超详解】 光线追踪2-4 Perlin noise
Preface 为了得到更好的纹理,很多人采用各种形式的柏林噪声(该命名来自于发明人 Ken Perlin) 柏林噪声是一种比较模糊的白噪声的东西:(引用书中一张图) 柏林噪声是用来生成一些看似杂乱 ...
- 【Ray Tracing The Next Week 超详解】 光线追踪2-3
Preface 终于到了激动人心的纹理章节了 然鹅,看了下,并不激动 因为我们之前就接触过 当初有一个 attenuation 吗? 对了,这就是我们的rgb分量过滤器,我们画出的红色.蓝色.绿色等 ...
- 【Ray Tracing The Next Week 超详解】 光线追踪2-2
Chapter 2:Bounding Volume Hierarchies 今天我们来讲层次包围盒,乍一看比较难,篇幅也多,但是咱们一步一步来,相信大家应该都能听懂 BVH 和 Perlin text ...
随机推荐
- 2018-2019-2 网络对抗技术 20165227 Exp4 恶意代码分析
2018-2019-2 网络对抗技术 20165227 Exp4 恶意代码分析 实验步骤: 使用的设备:Win7(虚拟机).kali(虚拟机) 实验一:使用如计划任务,每隔一分钟记录自己的电脑有哪些程 ...
- xcode查找当前程序的沙盒
随意在程序中添加一个断点,当程序命中断点的时候,控制台中会出现一个"lldb" 此时在"lldb"后面添加上 po NSHomeDirectory() 回车 ...
- Mysql 插入中文错误:Incorrect string value: '\xE7\xA8\x8B\xE5\xBA\x8F...' for column 'course' at row 1
create table my_user ( id tinyint(4) not null auto_increment, account varchar(255) default nul ...
- 复制vmware主机修改网卡
https://blog.csdn.net/gui951753/article/details/79491092
- python顺序执行多个py文件
python顺序执行多个py文件 假如我要执行code目录下的python程序,假设该目录下有1.py,2.py,3.py,4.py四个文件,但是我想执行1.py,2.py,4.py,则可在该目录下创 ...
- shell script中read的用法
1.read基本读取 #!/bin/bash #testing the read command echo -n "Enter you name:" #echo -n 让用户直接在 ...
- eclipse自动添加注释
自动添加注释 快捷键:alt shift jwindows-->preference Java-->Code Style-->Code Templates code-->new ...
- CAS 策略已被 .NET Framework 弃用
背景 本来想这里有啥写的,就算了吧.突然看到dev了,我的天啊,这个.net大神,坑了多少开发人员了.功能太强大,以至于后来很长时间我都不知道jquery.当时为了操作dev,为了实现一个功能,都把官 ...
- python操作haproxy.cfg文件
需求 1.查 输入:www.oldboy.org 获取当前backend下的所有记录 2.新建 输入: arg = { 'bakend': 'www.oldboy.org', 'record':{ ' ...
- Spring整合strus2简单应用总结
本身strus2没接触过,所以这块学的一知半解,正常不整合的还没学(接着学) step: 1.创建web工程 2.在/WEB-INF/lib引入jar包 asm-3.3.jarasm-commons- ...
