[JS] ECMAScript 6 - Class : compare with c#
Ref: Class 的基本语法
Ref: Class 的基本继承
许多面向对象的语言都有修饰器(Decorator)函数,用来修改类的行为。目前,有一个提案将这项功能,引入了 ECMAScript。
Ref: JavaScript 中的 this 用法以及 call(apply) 的理解
Ref: JavaScript Object-Oriented Programming Tutorial - OOP with E6【简单介绍引入了类后,带来的简单写法】
基础概念
Class关键字
(1) 传统写法
function Point(x, y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
Point.prototype.toString = function () {
return '(' + this.x + ', ' + this.y + ')';
};
var p = new Point(1, 2);
(2) ES6 提供了更接近传统语言的写法,引入了 Class(类)这个概念,作为对象的模板。通过class关键字,可以定义类。
类的数据类型就是函数,类本身就指向构造函数。
class Point {
constructor(x, y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
toString() {
return '(' + this.x + ', ' + this.y + ')';
}
}
类的方法
class Point {
constructor() { // 都定义在类的prototype属性上面
// ...
}
toString() { // 都定义在类的prototype属性上面
// ...
}
toValue() { // 都定义在类的prototype属性上面
// ...
}
}
类的所有方法都定义在类的prototype属性上面。也就是等同于:
Point.prototype = {
constructor() {},
toString() {},
toValue() {},
};
也就是等价:
在类的实例上面调用方法,其实就是调用原型上的方法。
class B {}
let b = new B();
b.constructor === B.prototype.constructor // true ----> 其实就是调用原型上的方法。
扩展技巧:
Object.assign方法可以很方便地一次向类添加多个方法。
class Point {
constructor(){
// ...
}
}
Object.assign(Point.prototype, {
toString(){},
toValue(){}
});
内部属性方法不可枚举:
可枚举:
var Point = function (x, y) {
// ...
}; Point.prototype.toString = function() {
// ...
}; Object.keys(Point.prototype)
// ["toString"]
Object.getOwnPropertyNames(Point.prototype)
// ["constructor","toString"] ---------------------------------------------------------------------
不可枚举:
class Point {
constructor(x, y) {
// ...
} toString() {
// ...
}
} Object.keys(Point.prototype)
// []
Object.getOwnPropertyNames(Point.prototype)
// ["constructor","toString"]
严格模式:
类和模块的内部,默认就是严格模式,所以不需要使用use strict指定运行模式。只要你的代码写在类或模块之中,就只有严格模式可用。
考虑到未来所有的代码,其实都是运行在模块之中,所以 ES6 实际上把整个语言升级到了严格模式。
Goto: [JS] Why "strict mode" here
类的实例对象
定义了一个空的类Point,JavaScript 引擎会自动为它添加一个空的constructor方法。Constructor返回this,也就是指向自己。
class Point {
// ...
}
// 报错
var point = Point(2, 3);
// 正确
var point = new Point(2, 3); // 只能new,这样才更为接近“类”
对象方法调动的实际上都是prototype上的类型。
//定义类
class Point { constructor(x, y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
} toString() { // 要注意:其实是定义在原型prototype上
return '(' + this.x + ', ' + this.y + ')';
} }
----------------------------------------------------
var point = new Point(2, 3); point.toString() // (2, 3) point.hasOwnProperty('x') // true,因为上面给 this.x赋值
point.hasOwnProperty('y') // true,因为上面给 this.y赋值
point.hasOwnProperty('toString') // false
point.__proto__.hasOwnProperty('toString') // true
Class 表达式
使用表达式的形式定义。
// 类的名字是MyClass
const MyClass = class Me { // Me只在class内部代码中可用;如果类的内部没用到的话,可以省略Me。
getClassName() {
return Me.name; // Me指代当前类
}
};
这么下,可用写成一个立即执行的类(函数):
let person = new class {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
sayName() {
console.log(this.name);
}
}('张三');
person.sayName(); // "张三"
不存在变量提升
如果class被提升到代码头部,而let命令是不提升的,将导致Bar继承Foo的时候,Foo还没有定义。
{
let Foo = class {};
class Bar extends Foo { // <---- 如果class提升,也就是提升到let Foo之前,返回会引来麻烦
}
}
私有方法和私有属性
方法一:
私有方法是常见需求,但 ES6 不提供。【自己通过命名约定】
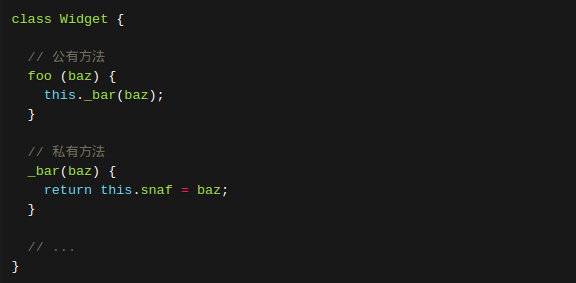
方法二:
将私有方法移出模块,因为模块内部的所有方法都是对外可见的。
class Widget {
foo (baz) { // foo是公有方法
bar.call(this, baz); // 这使得bar实际上成为了当前模块的私有方法
}
// ...
}
-----------------------------------------------------
function bar(baz) {
return this.snaf = baz;
}
方法三:
将私有方法的名字命名为一个Symbol值。
const bar = Symbol('bar');
const snaf = Symbol('snaf');
export default class myClass{
// 公有方法
foo(baz) {
this[bar](baz);
}
// 私有方法
[bar](baz) {
return this[snaf] = baz;
}
// ...
};
私有属性当前只是提案 - 暂略
this 的指向
这里主要是讲如何绑定this的问题,让this的指向比较可控。
(1) 这里找不到print,因为运行时this变为了全局环境。
class Logger {
printName(name = 'there') {
this.print(`Hello ${name}`); // 这里的this,默认指向Logger类的实例
}
print(text) {
console.log(text);
}
}
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
const logger = new Logger();
const { printName } = logger;
printName(); // 将这个方法提取出来单独使用了
// TypeError: Cannot read property 'print' of undefined
(2) 改进:在构造方法中绑定this,这样就不会找不到print方法了。
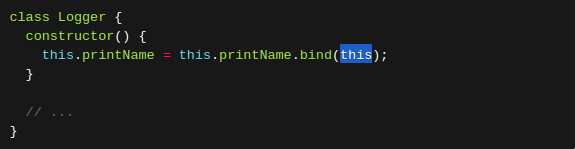
(3) 使用箭头函数,使this只跟定义时的位置有关。
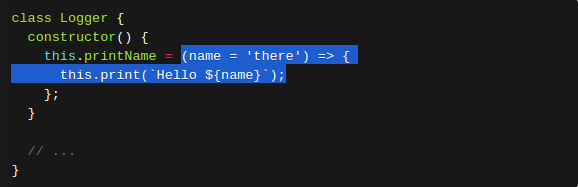
(4) 使用Proxy,获取方法的时候,自动绑定this。【暂时不懂】
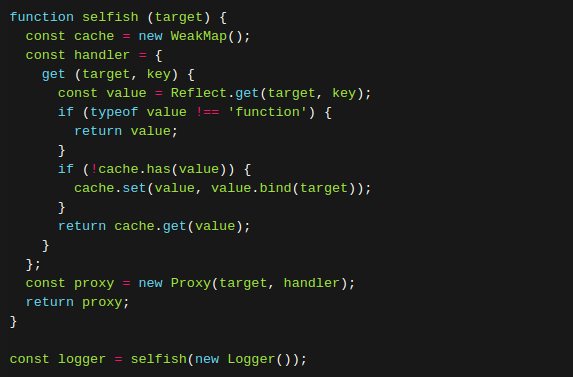
name 属性
ES6 的类只是 ES5 的构造函数的一层包装,所以函数的许多特性都被Class继承,包括name属性。
class Point {}
Point.name // "Point"
取值函数(getter)和存值函数(setter)
class MyClass {
constructor() {
// ...
}
-----------------------------------------------
get prop() {
return 'getter';
}
set prop(value) { // value是属性的value,通过__.prop = 123 等号的方式传过来的
console.log('setter: '+value);
}
}
-----------------------------------------------
let inst = new MyClass();
inst.prop = 123;
// setter: 123
inst.prop
// 'getter'
Generator 方法
静态方法
(1) 加上static关键字,就表示该方法不会被实例继承,而是直接通过类来调用。而不是生成实例后调用。
class Foo {
static classMethod() {
return 'hello';
}
}
Foo.classMethod() // 'hello'
var foo = new Foo();
foo.classMethod() // 生成实例后调用是不行的!
// TypeError: foo.classMethod is not a function
(2) 如果静态方法包含this关键字,这个this指的是类,而不是实例。
class Foo {
static bar () {
this.baz();
}
static baz () {
console.log('hello');
}
baz () { // 静态方法可以与非静态方法重名
console.log('world');
}
}
Foo.bar() // hello
(3) 父类的静态方法,可以被子类继承
class Foo {
static classMethod() {
return 'hello';
}
}
class Bar extends Foo {
}
Bar.classMethod() // 'hello'
(4) 静态方法也是可以从super对象上调用的。
class Foo {
static classMethod() {
return 'hello';
}
}
class Bar extends Foo {
static classMethod() {
return super.classMethod() + ', too';
}
}
Bar.classMethod() // "hello, too"
Class 的静态属性和实例属性
(1)类的实例属性
class MyClass {
myProp = 42; // 使用的是等号
constructor() {
console.log(this.myProp); //
}
}
以前,我们定义实例属性,只能写在类的constructor方法里面。
class ReactCounter extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
count: 0
};
}
}
----------------------------------------------------------------
新的写法,可以不在constructor方法里面定义
class ReactCounter extends React.Component {
state = {
count: 0
};
}
(2)类的静态属性
ES6 明确规定,Class 内部:只有静态方法,没有静态属性。
那就暂时定义在外面:
class Foo {
}
Foo.prop = 1; // 定义在外面,为Foo类定义了一个静态属性prop
Foo.prop // 1
--------------------------------------------------------
// 新写法
class Foo {
static prop = 1;
}new.target 属性
ES6 为new命令引入了一个new.target属性,该属性一般用在构造函数之中,返回new命令作用于的那个构造函数。
这个属性可以用来确定构造函数是怎么调用的。
应用1. 构造函数只能通过new命令调用
function Person(name) {
if (new.target !== undefined) {
this.name = name;
} else {
throw new Error('必须使用 new 命令生成实例');
}
}
// 另一种写法
function Person(name) {
if (new.target === Person) {
this.name = name;
} else {
throw new Error('必须使用 new 命令生成实例');
}
}
--------------------------------------------------------------
var person = new Person('张三'); // 正确
var notAPerson = Person.call(person, '张三'); // 报错
应用2. 不能独立使用、必须继承后才能使用的类
class Shape {
constructor() {
if (new.target === Shape) {
throw new Error('本类不能实例化');
}
}
}
class Rectangle extends Shape {
constructor(length, width) {
super();
// ...
}
}
var x = new Shape(); // 报错
var y = new Rectangle(3, 4); // 正确
注意,在函数外部,使用new.target会报错。
[JS] ECMAScript 6 - Class : compare with c#的更多相关文章
- [JS] ECMAScript 6 - Variable : compare with c#
前言 范围包括:ECMAScript 新功能以及对象. 当前的主要目的就是,JS的学习 --> ECMAScript 6 入门 let 命令 js 因为let, i的范围限制在了循环中. var ...
- [JS] ECMAScript 6 - Inheritance : compare with c#
这一章,估计是js最操蛋的一部分内容. 现代方法: 简介 Object.getPrototypeOf() super 关键字 类的 prototype 属性和__proto__属性 原生构造函数的继承 ...
- [JS] ECMAScript 6 - Prototype : compare with c#
开胃菜 prototype 对象 JavaScript 语言的继承则是通过“原型对象”(prototype). function Cat(name, color) { // <----构造函数 ...
- [JS] ECMAScript 6 - Async : compare with c#
一段引言: Promise 是异步编程的一种解决方案,比传统的解决方案——回调函数和事件——更合理和更强大. 它由社区最早提出和实现,ES6 将其写进了语言标准,统一了用法,原生提供了Promise对 ...
- [JS] ECMAScript 6 - Array : compare with c#
扩展运算符(spread) 先复习下 rest 参数. (1) argument模式,但不够好. // https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_39723544/article/de ...
- [JS] ECMAScript 6 - Object : compare with c#
Ref: 对象的扩展 Outline: 属性的简洁表示法 属性名表达式 方法的 name 属性 Object.is() Object.assign() 属性的可枚举性和遍历 Object.getOwn ...
- [JS] ECMAScript 6 - String, Number, Function : compare with c#
字符串的扩展 正则的扩展 数值的扩展 函数的扩展 字符串的扩展 js 字符的 Unicode 表示法 codePointAt() String.fromCodePoint() 字符串的遍历器接口 at ...
- [JS] ECMAScript 6 - Set & Map : compare with c#
Ref: Set 和 Map 数据结构 Day 0 - 1所学
- [Node.js] ECMAScript 6中的生成器及koa小析
原文地址:http://www.moye.me/2014/11/10/ecmascript-6-generator/ 引子 老听人说 koa大法好,这两天我也赶了把时髦:用 n 安上了node 0.1 ...
随机推荐
- 简单的proxy之TinyHTTPProxy.py
简单的proxy之TinyHTTPProxy.py 如果是在外企工作的话,可以访问美国的机器,这样就可以在美国的机器上为自己装个proxy,然后本地就可以很容易的使用proxy来上网了. TinyHT ...
- 如何在本地搭建一个Android应用crashing跟踪系统-ACRA
https://github.com/bboyfeiyu/android-tech-frontier/tree/master/others/%E5%A6%82%E4%BD%95%E5%9C%A8%E6 ...
- Android ANR Waiting because no window has focus问题分析
转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/MMLoveMeMM/articles/4849667.html 这种问题主要是发生在两个应用页面之间切换的时候,这个临界点的时候,一个页面正在起 ...
- Android Studio下加入百度地图的使用 (一)——环境搭建
最近有学生要做毕业设计,会使用到定位及地图信息的功能,特此研究了一下,供大家参考,百度定位SDK已经更新到了5.0,地图SDK已经更新到了3.5,但是在AndroidStudio中使用还是存在一些不稳 ...
- Android典型界面设计(3)——访网易新闻实现双导航tab切换
一.问题描述 双导航tab切换(底部区块+区域内头部导航),实现方案底部区域使用FragmentTabHost+Fragment, 区域内头部导航使用ViewPager+Fragment,可在之前博客 ...
- LEAPMOTION开发UI专题(1)
非常 抱歉的是,之前说的LEAP/UI框架设计可能仅仅有两篇 由于个人时间实在是不同意 这个问题假设展开去写的话 那么说写本书都是不为过的 且由于内容改动非常是杂乱 所以我第一篇文章用来介绍LEAP预 ...
- 廉价的SUP掌机拆解
最近经常出现的一款山寨sup掌机, 75元包邮入手, 全套配件如下. 看看正面和背面的实拍图, 比较明显的廉价玩具塑料感. 手柄和充电线共用下方的microUSB口, 所以在双打时是不能用电源供电的. ...
- CentOS下网卡启动、配置等ifcfg-eth0教程(转)
步骤1.配置/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 里的文件.it动力的CentOS下的ifcfg-eth0的配置详情: [root@localhost ~ ...
- WebStorm for Mac(Web 前端开发工具)破解版安装
1.软件简介 WebStorm 是 jetbrains 公司旗下一款 JavaScript 开发工具.目前已经被广大中国 JS 开发者誉为 "Web 前端开发神器".&quo ...
- Zookeeper之Zookeeper的Client的分析【转】
Zookeeper之Zookeeper的Client的分析 1)几个重要概念 ZooKeeper:客户端入口 Watcher:客户端注册的callback ZooKeeper.SendThread: ...
