SynchronousQueue 的联想
SynchronousQueue介绍
SynchronousQueue是一种阻塞队列,该队列没有任务的容量。内部实现采用了一种性能更好的无锁算法。
代码实现里的Dual Queue,其中每一个put对应一个take方法。
简单测试代码
public class SynchronousQueueExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
final SynchronousQueue queue = new SynchronousQueue();
new Thread(new QueueProducer(queue)).start();
new Thread(new QueueConsumer(queue)).start();
}
}
public class QueueProducer implements Runnable {
private SynchronousQueue queue;
public QueueProducer(SynchronousQueue queue) {
this.queue = queue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
String event = "FIRST_EVENT";
String another_event = "SECOND_EVENT";
try {
queue.put(event);
System.out.printf("[%s] producer event : %s %n", Thread
.currentThread().getName(), event);
queue.put(another_event);
System.out.printf("[%s] producer event : %s %n", Thread
.currentThread().getName(), another_event);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class QueueConsumer implements Runnable {
private SynchronousQueue queue;
public QueueConsumer(SynchronousQueue queue) {
this.queue = queue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
String event = (String) queue.take();
// thread will block here
System.out.printf("[%s] consumed event : %s %n", Thread
.currentThread().getName(), event);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
--------------------------
[Thread-0] producer event : FIRST_EVENT
[Thread-1] consumed event : FIRST_EVENT
--------------------------
生产者每生产一个,如果没有消费者消费那就发生阻塞上面例子中。结果只打印了FIRST_EVENT ,因为SECOND_EVENT没有调用 queue.take()方法 ,所以没有打印。
绑定 put和take方法
/**
* Puts or takes an item.
*/
Object transfer(Object e, boolean timed, long nanos) {
/*
* Basic algorithm is to loop trying one of three actions:
*
* 1. If apparently empty or already containing nodes of same
* mode, try to push node on stack and wait for a match,
* returning it, or null if cancelled.
*
* 2. If apparently containing node of complementary mode,
* try to push a fulfilling node on to stack, match
* with corresponding waiting node, pop both from
* stack, and return matched item. The matching or
* unlinking might not actually be necessary because of
* other threads performing action 3:
*
* 3. If top of stack already holds another fulfilling node,
* help it out by doing its match and/or pop
* operations, and then continue. The code for helping
* is essentially the same as for fulfilling, except
* that it doesn't return the item.
*/
SNode s = null; // constructed/reused as needed
int mode = (e == null)? REQUEST : DATA;
for (;;) {
SNode h = head;
if (h == null || h.mode == mode) { // empty or same-mode
if (timed && nanos <= 0) { // can't wait
if (h != null && h.isCancelled())
casHead(h, h.next); // pop cancelled node
else
return null;
} else if (casHead(h, s = snode(s, e, h, mode))) {
SNode m = awaitFulfill(s, timed, nanos);
if (m == s) { // wait was cancelled
clean(s);
return null;
}
if ((h = head) != null && h.next == s)
casHead(h, s.next); // help s's fulfiller
return mode == REQUEST? m.item : s.item;
}
} else if (!isFulfilling(h.mode)) { // try to fulfill
if (h.isCancelled()) // already cancelled
casHead(h, h.next); // pop and retry
else if (casHead(h, s=snode(s, e, h, FULFILLING|mode))) {
for (;;) { // loop until matched or waiters disappear
SNode m = s.next; // m is s's match
if (m == null) { // all waiters are gone
casHead(s, null); // pop fulfill node
s = null; // use new node next time
break; // restart main loop
}
SNode mn = m.next;
if (m.tryMatch(s)) {
casHead(s, mn); // pop both s and m
return (mode == REQUEST)? m.item : s.item;
} else // lost match
s.casNext(m, mn); // help unlink
}
}
} else { // help a fulfiller
SNode m = h.next; // m is h's match
if (m == null) // waiter is gone
casHead(h, null); // pop fulfilling node
else {
SNode mn = m.next;
if (m.tryMatch(h)) // help match
casHead(h, mn); // pop both h and m
else // lost match
h.casNext(m, mn); // help unlink
}
}
}
}
说到SynchronousQueue不由的想到LinkedBlockingQueue,ArrayBlockingQueue,PriorityBlockingQueue
根据不同的需要BlockingQueue有4种具体实现:
- (1)ArrayBlockingQueue:规定大小的BlockingQueue,其构造函数必须带一个int参数来指明其大小。其所含的对象是以FIFO(先入先出)顺序排序的。
- (2)LinkedBlockingQueue:大小不定的BlockingQueue,若其构造函数带一个规定大小的参数,生成的BlockingQueue有大小限制, 若不带大小参数,所生成的BlockingQueue的大小由Integer.MAX_VALUE来决定。其所含的对象是以FIFO(先入先出)顺序排序的。LinkedBlockingQueue和ArrayBlockingQueue比较起来,它们背后所用的数据结构不一样, 导致LinkedBlockingQueue的数据吞吐量要大于ArrayBlockingQueue,但在线程数量很大时其性能的可预见性低于ArrayBlockingQueue。
- (3)PriorityBlockingQueue:类似于LinkedBlockingQueue,但其所含对象的排序不是FIFO,而是依据对象的自然排序顺序或者是构造函数所带的Comparator决定的顺序。
- (4)SynchronousQueue:特殊的BlockingQueue,对其的操作必须是放和取交替完成的。
ThreadPoolExecutor
/**
* Creates a new <tt>ThreadPoolExecutor</tt> with the given initial
* parameters and default thread factory.
*
* @param corePoolSize the number of threads to keep in the
* pool, even if they are idle.
* @param maximumPoolSize the maximum number of threads to allow in the
* pool.
* @param keepAliveTime when the number of threads is greater than
* the core, this is the maximum time that excess idle threads
* will wait for new tasks before terminating.
* @param unit the time unit for the keepAliveTime
* argument.
* @param workQueue the queue to use for holding tasks before they
* are executed. This queue will hold only the <tt>Runnable</tt>
* tasks submitted by the <tt>execute</tt> method.
* @param handler the handler to use when execution is blocked
* because the thread bounds and queue capacities are reached.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if corePoolSize or
* keepAliveTime less than zero, or if maximumPoolSize less than or
* equal to zero, or if corePoolSize greater than maximumPoolSize.
* @throws NullPointerException if <tt>workQueue</tt>
* or <tt>handler</tt> are null.
*/
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), handler);
}
上面的每一个参数很详细的介绍了ThreadPoolExecutor的用法,保持线程的数量,最大化线程的数量,调度时间的间隔,用到的线程队列等。
主要的execute方法。
/**
* Executes the given task sometime in the future. The task
* may execute in a new thread or in an existing pooled thread.
*
* If the task cannot be submitted for execution, either because this
* executor has been shutdown or because its capacity has been reached,
* the task is handled by the current <tt>RejectedExecutionHandler</tt>.
*
* @param command the task to execute
* @throws RejectedExecutionException at discretion of
* <tt>RejectedExecutionHandler</tt>, if task cannot be accepted
* for execution
* @throws NullPointerException if command is null
*/
public void execute(Runnable command) {
if (command == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (poolSize >= corePoolSize || !addIfUnderCorePoolSize(command)) {
if (runState == RUNNING && workQueue.offer(command)) {
if (runState != RUNNING || poolSize == 0)
ensureQueuedTaskHandled(command);
}
else if (!addIfUnderMaximumPoolSize(command))
reject(command); // is shutdown or saturated
}
}
在线程池中每一个任务被包装成Runnable 类型,传入到execute方法中 , 该方法中会判断是否超过最大线程,是否有空余线程,当调用停止或者达到最大容量会调用RejectedExecutionHandler。
/**
* Rechecks state after queuing a task. Called from execute when
* pool state has been observed to change after queuing a task. If
* the task was queued concurrently with a call to shutdownNow,
* and is still present in the queue, this task must be removed
* and rejected to preserve shutdownNow guarantees. Otherwise,
* this method ensures (unless addThread fails) that there is at
* least one live thread to handle this task
* @param command the task
*/
private void ensureQueuedTaskHandled(Runnable command) {
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
mainLock.lock();
boolean reject = false;
Thread t = null;
try {
int state = runState;
if (state != RUNNING && workQueue.remove(command))
reject = true;
else if (state < STOP &&
poolSize < Math.max(corePoolSize, 1) &&
!workQueue.isEmpty())
t = addThread(null);
} finally {
mainLock.unlock();
}
if (reject)
reject(command);
else if (t != null)
t.start();
}
/**
* Invokes the rejected execution handler for the given command.
*/
void reject(Runnable command) {
handler.rejectedExecution(command, this);
}
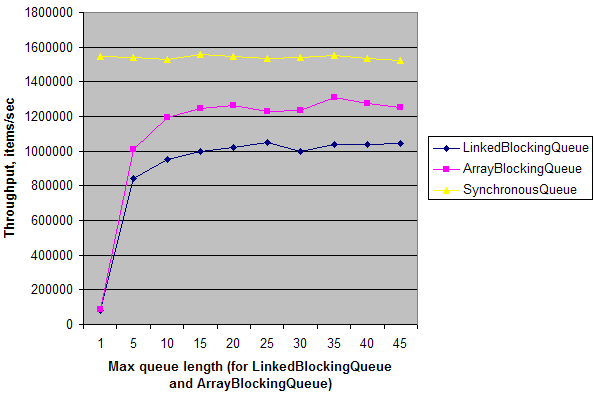
网上的一个测试
public class Test {
static ExecutorService e = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
static int N = 1000000;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
int length = (i == 0) ? 1 : i * 5;
System.out.print(length + "\t");
System.out.print(doTest(new LinkedBlockingQueue<Integer>(length), N) + "\t");
System.out.print(doTest(new ArrayBlockingQueue<Integer>(length), N) + "\t");
System.out.print(doTest(new SynchronousQueue<Integer>(), N));
System.out.println();
}
e.shutdown();
}
private static long doTest(final BlockingQueue<Integer> q, final int n) throws Exception {
long t = System.nanoTime();
e.submit(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
try { q.put(i); } catch (InterruptedException ex) {}
}
});
Long r = e.submit(new Callable<Long>() {
public Long call() {
long sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
try { sum += q.take(); } catch (InterruptedException ex) {}
return sum;
}
}).get();
t = System.nanoTime() - t;
return (long)(1000000000.0 * N / t); // Throughput, items/sec
}
}
具体使用那个一个消息队列要看使用场景,多个生产者一个消费者,多个生产者多个消费者以及并发量的大小。
SynchronousQueue 的联想的更多相关文章
- 设置Fn键 笔记本直接按F1-F12 无须按Fn键 Fn+F12改F12(联想小新300为例)
最近公司给配的笔记本联想小新300 80RT i7-6500U 4G内存 500G机械,后加装120G固态+4G内存 这样就感觉还不错了. 在使用这本子的时候,去了Win10,强行装了Win7.无线 ...
- 联想 Thinkpad X230 SLIC 2.1 Marker
等了好久,终于等到了 X230 的 SLIC 2.1 的 Marker !特发帖备份... 基本情况 笔记本:Lenovo X230(i5+8G+500G) 操作系统:Windows 7 Pro x6 ...
- 萌新笔记——C++里创建 Trie字典树(中文词典)(三)(联想)
萌新做词典第三篇,做得不好,还请指正,谢谢大佬! 今天把词典的联想做好了,也是比较low的,还改了之前的查询.遍历等代码. Orz 一样地先放上运行结果: test1 ID : char : 件 w ...
- ExtJs基础知识总结:自定义弹窗和ComboBox自动联想加载(四)
概述 Extjs弹窗可以分为消息弹窗.对话框,这些弹窗的方式ExtJs自带的Ext.Msg.alert就已经可以满足简单消息提示,但是相对复杂的提示,比如如何将Ext.grid.Panel的控件显示嵌 ...
- 【实战Java高并发程序设计 7】让线程之间互相帮助--SynchronousQueue的实现
[实战Java高并发程序设计 1]Java中的指针:Unsafe类 [实战Java高并发程序设计 2]无锁的对象引用:AtomicReference [实战Java高并发程序设计 3]带有时间戳的对象 ...
- 【JUC】JDK1.8源码分析之SynchronousQueue(九)
一.前言 本篇是在分析Executors源码时,发现JUC集合框架中的一个重要类没有分析,SynchronousQueue,该类在线程池中的作用是非常明显的,所以很有必要单独拿出来分析一番,这对于之后 ...
- 联想A880 DIY 换触摸屏屏幕
今年初入手的Lenovo A880手机,由于摔坏了屏幕不过能正常显示,咨询了联想的售后,说触摸屏和显示屏是分离的,换触摸屏需要280左右 为发挥DIY的精神,准备自己来处理这个屏幕 第一步:购买屏幕, ...
- 利用 lucene.net 实现高效率的 WildcardQuery ,记一次类似百度搜索下拉关键字联想功能的实现。
打开百度输入 站内搜索也要实现类似功能.最基础的做法,写个方法查数据库搜索历史综合表keywordSearch(先将被搜索过的关键字记录到一张表,记录好他们被搜索的次数.上次搜索的有多少结果) 大概 ...
- 玩转AR,联想将在2017年推出第二款Tango AR手机
今年6月份,联想与谷歌合作推出了全球首款消费级AR手机Phab2 Pro,并获得很大的关注.作为谷歌Project Tango的一部分,这款手机的最大亮点是它搭载了三颗后置摄像头和多个传感器,机身背面 ...
随机推荐
- Tomcat服务器的下载及安装
Tomcat服务器的下载及安装 1)到apache官网.www.apache.org http://jakarta.apache.org(产品的主页) 2) 安装版:window (exe.m ...
- 微信公众平台宣布增加接口IP白名单提高安全性
微信公众平台目前已经发布通知在平台接口调用上为了提高安全性需要添加IP白名单并仅允许白名单IP调用. 目前微信公众平台面向开发者主要提供的开发者ID和开发者密钥,在调用时ID和密钥通过检验即可进行调用 ...
- 织梦dede在首页调用留言本
织梦dedecms在首页调用留言本 . {dede:loop table=dede_guestbook sort=dtime row=10 titlelen=36 typeid=40 if=ische ...
- ip 淘宝ip库 精简版
<?php header('Content-type: text/html; charset=utf-8'); //根据ip获取城市.网络运营商等信息 function findCityByIp ...
- Laravel的unique和exists验证规则的优化
本文是Laravel实战:任务管理系统(一)的扩展阅读 原文链接:http://pilishen.com/posts/Improvements-to-the-Laravel-unique-and-ex ...
- python_怎么格式化字符串?
案例: 如何对下面字典的key左对齐 {'dhqbl': 30, 'psfgj': 40, 'ontpqsb': 90, 'mrean': 110, 'klespjtr': 60, 'lprnkqhb ...
- python_如何对迭代器进行切片操作
案例: 对于某个文件,我只想读取到其中100~200行之间的内容,是否可以通过切片的方式进行读取? 我想: f = open() f[100:200] 可行? 如何解决这个问题? 方法1: 全部读取到 ...
- Can’t open /dev/* exclusively. Mounted filesystem?解决
1 错误提示:Can’t open /dev/* exclusively. Mounted filesystem? 做完软件RAID之后,根据鸟哥书上的操作,其实没有真正删除软件RAID,导致出现如下 ...
- MyEclipse中好用的快捷键汇总
MyEclipse中常用的快捷键有很多,合理的使用其中一些快捷键组合,可以有效提高开发的效率和质量. 1.Ctrl + Shift + R:打开资源.可以查找并打开工作区中任何一个文件,且支持使用通配 ...
- JAVA中比较两个文件夹不同的方法
JAVA中比较两个文件夹不同的方法,可以通过两步来完成,首先遍历获取到文件夹下的所有文件夹和文件,再通过文件路径和文件的MD5值来判断文件的异同.具体例子如下: public class TestFo ...