Getting Started with Blocks
本文来源为:developer.apple.com,仅仅是博主练习排版所用。
Getting Started with Blocks
The following sections help you to get started with blocks using practical examples.
Declaring and Using a Block
You use the ^ operator to declare a block variable and to indicate the beginning of a block literal. The body of the block itself is contained within {}, as shown in this example (as usual with C, ; indicates the end of the statement):
int multiplier = 7;
int (^myBlock)(int) = ^(int num) {
return num * multiplier;
};
The example is explained in the following illustration:
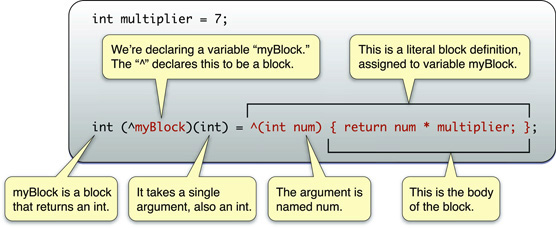
Notice that the block is able to make use of variables from the same scope in which it was defined.
If you declare a block as a variable, you can then use it just as you would a function:
int multiplier = 7;
int (^myBlock)(int) = ^(int num) {
return num * multiplier;
};
printf("%d", myBlock(3));
// prints "21"
Using a Block Directly
In many cases, you don’t need to declare block variables; instead you simply write a block literal inline where it’s required as an argument. The following example uses the qsort_b function. qsort_b is similar to the standard qsort_r function, but takes a block as its final argument.
char *myCharacters[3] = { "TomJohn", "George", "Charles Condomine" };
qsort_b(myCharacters, 3, sizeof(char *), ^(const void *l, const void *r) {
char *left = *(char **)l;
char *right = *(char **)r;
return strncmp(left, right, 1);
});
Blocks with Cocoa
Several methods in the Cocoa frameworks take a block as an argument, typically either to perform an operation on a collection of objects, or to use as a callback after an operation has finished. The following example shows how to use a block with the NSArray method sortedArrayUsingComparator:. The method takes a single argument—the block. For illustration, in this case the block is defined as an NSComparator local variable:
NSArray *stringsArray = @[ @"string 1",
@"String 21",
@"string 12",
@"String 11",
@"String 02" ];
static NSStringCompareOptions comparisonOptions = NSCaseInsensitiveSearch | NSNumericSearch |
NSWidthInsensitiveSearch | NSForcedOrderingSearch;
NSLocale *currentLocale = [NSLocale currentLocale];
NSComparator finderSortBlock = ^(id string1, id string2) {
NSRange string1Range = NSMakeRange(0, [string1 length]);
return [string1 compare:string2 options:comparisonOptions range:string1Range locale:currentLocale];
};
NSArray *finderSortArray = [stringsArray sortedArrayUsingComparator:finderSortBlock];
NSLog(@"finderSortArray: %@", finderSortArray);
/*
Output: NSArray *stringArray = @[ @"string 1", @"string 2", @"string21", @"string 12", @"string 02"];
NSComparator finderSortBlock = ^(id string1, id string2){
NSRange string1Range = NSMakeRange(0, [string1 length]);
return [string1 compare:string2 options:comparisonOptions range:string1Range locale:currentLocale];
};
NSArray *findSortArray = [stringArray sortedArrayUsingComparator:finderSortBlock];
NSLog(@"...:%@",findSortArray);
finderSortArray: (
"string 1",
"String 02",
"String 11",
"string 12",
"String 21"
)
*/
__block Variables
A powerful feature of blocks is that they can modify variables in the same lexical scope. You signal that a block can modify a variable using the __block storage type modifier. Adapting the example shown in Blocks with Cocoa, you could use a block variable to count how many strings are compared as equal as shown in the following example. For illustration, in this case the block is used directly and uses currentLocale as a read-only variable within the block:
NSArray *stringsArray = @[ @"string 1",
@"String 21", // <-
@"string 12",
@"String 11",
@"Strîng 21", // <-
@"Striñg 21", // <-
@"String 02" ];
NSLocale *currentLocale = [NSLocale currentLocale];
__block NSUInteger orderedSameCount = 0;
NSArray *diacriticInsensitiveSortArray = [stringsArray sortedArrayUsingComparator:^(id string1, id string2) {
NSRange string1Range = NSMakeRange(0, [string1 length]);
NSComparisonResult comparisonResult = [string1 compare:string2 options:NSDiacriticInsensitiveSearch range:string1Range locale:currentLocale];
if (comparisonResult == NSOrderedSame) {
orderedSameCount++;
}
return comparisonResult;
}];
NSLog(@"diacriticInsensitiveSortArray: %@", diacriticInsensitiveSortArray);
NSLog(@"orderedSameCount: %d", orderedSameCount);
/*
Output:
diacriticInsensitiveSortArray: (
"String 02",
"string 1",
"String 11",
"string 12",
"String 21",
"Str\U00eeng 21",
"Stri\U00f1g 21"
)
orderedSameCount: 2
*/
This is discussed in greater detail in Blocks and Variables.
Getting Started with Blocks的更多相关文章
- 从Script到Code Blocks、Code Behind到MVC、MVP、MVVM
刚过去的周五(3-14)例行地主持了技术会议,主题正好是<UI层的设计模式——从Script.Code Behind到MVC.MVP.MVVM>,是前一天晚上才定的,中午花了半小时准备了下 ...
- 【POJ-1390】Blocks 区间DP
Blocks Time Limit: 5000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 5252 Accepted: 2165 Descriptio ...
- 开发该选择Blocks还是Delegates
前文:网络上找了很多关于delegation和block的使用场景,发现没有很满意的解释,后来无意中在stablekernel找到了这篇文章,文中作者不仅仅是给出了解决方案,更值得我们深思的是作者独特 ...
- poj 1390 Blocks
poj 1390 Blocks 题意 一排带有颜色的砖块,每一个可以消除相同颜色的砖块,,每一次可以到块数k的平方分数.问怎么消能使分数最大.. 题解 此题在徐源盛<对一类动态规划问题的研究&g ...
- Java 同步代码块 - Synchronized Blocks
java锁实现原理: http://blog.csdn.net/endlu/article/details/51249156 The synchronized keyword can be used ...
- 区块 Blocks
Structure / Blocks / Demonstrate block regions
- 使用Code::blocks在windows下写网络程序
使用Code::blocks在windows下写网络程序 作者 He YiJun – storysnail<at>gmail.com 团队 ls 版权 转载请保留本声明! 本文档包含的原创 ...
- Code::Blocks配置GTK+2和GTK+3
Code::Blocks配置GTK+2和GTK+3 作者 He YiJun – storysnail<at>gmail.com 团队 ls 版权 转载请保留本声明! 本文档包含的原创代码根 ...
- [翻译]理解Ruby中的blocks,Procs和lambda
原文出处:Understanding Ruby Blocks, Procs and Lambdas blocks,Procs和lambda(在编程领域被称为闭包)是Ruby中很强大的特性,也是最容易引 ...
- Java Synchronized Blocks
From http://tutorials.jenkov.com/java-concurrency/synchronized.html By Jakob Jenkov A Java synchro ...
随机推荐
- IPC-----POSIX消息队列
消息队列可以认为是一个链表.进程(线程)可以往里写消息,也可以从里面取出消息.一个进程可以往某个消息队列里写消息,然后终止,另一个进程随时可以从消息队列里取走这些消息.这里也说明了,消息队列具有随内核 ...
- fstream的使用方法介绍
转载自: fstream的使用方法介绍 - saga's blog - C++博客 http://www.cppblog.com/saga/archive/2007/06/19/26652.html ...
- Oracle java.sql.SQLException: 数字溢出
六月 30, 2016 5:47:47 下午 org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader loadBeanDefinit ...
- Linux下安装Nginx服务器
安装Nginx之前,首先要安装好编译环境gcc和g++,然后以CentOS为例安装Nginx,安装Nginx需要PRCE库.zlib库和ssl的支持,除了ssl外其他的我们都是去官网下载: Nginx ...
- FastReport中文网
FastReport中文网 http://www.fastreportcn.com/Article/2.html
- nyoj138 找球号(二)_离散化
找球号(二) 时间限制:1000 ms | 内存限制:65535 KB 难度:5 描述 在某一国度里流行着一种游戏.游戏规则为:现有一堆球中,每个球上都有一个整数编号i(0<=i< ...
- VB兼容问题
window7 64位无法显示打印窗问题 在Windows7 64位和VS2008环境下,PrintDialog.ShowDialog不能显示打印对话框 在VS2008中编写?如下代码: PrintD ...
- simpleTree简单使用
SimpleTree使用起来比较方便,它实现了最基本的树形菜单的功能,包括1个JS文件.1个CSS文件和5个图标文件. 使用时只要将相关文件复制到项目中,并在相应的页面引用它就行,例如: <!D ...
- 【leetcode】Text Justification(hard) ☆
Given an array of words and a length L, format the text such that each line has exactly L characters ...
- object实现小老鼠交互
直接使用 <p style="text-align: center; "> <object type="application/x-shockwave- ...
