kube-scheduler源码分析(2)-核心处理逻辑分析
kube-scheduler源码分析(2)-核心处理逻辑分析
kube-scheduler简介
kube-scheduler组件是kubernetes中的核心组件之一,主要负责pod资源对象的调度工作,具体来说,kube-scheduler组件负责根据调度算法(包括预选算法和优选算法)将未调度的pod调度到合适的最优的node节点上。
kube-scheduler架构图
kube-scheduler的大致组成和处理流程如下图,kube-scheduler对pod、node等对象进行了list/watch,根据informer将未调度的pod放入待调度pod队列,并根据informer构建调度器cache(用于快速获取需要的node等对象),然后sched.scheduleOne方法为kube-scheduler组件调度pod的核心处理逻辑所在,从未调度pod队列中取出一个pod,经过预选与优选算法,最终选出一个最优node,然后更新cache并异步执行bind操作,也就是更新pod的nodeName字段,至此一个pod的调度工作完成。
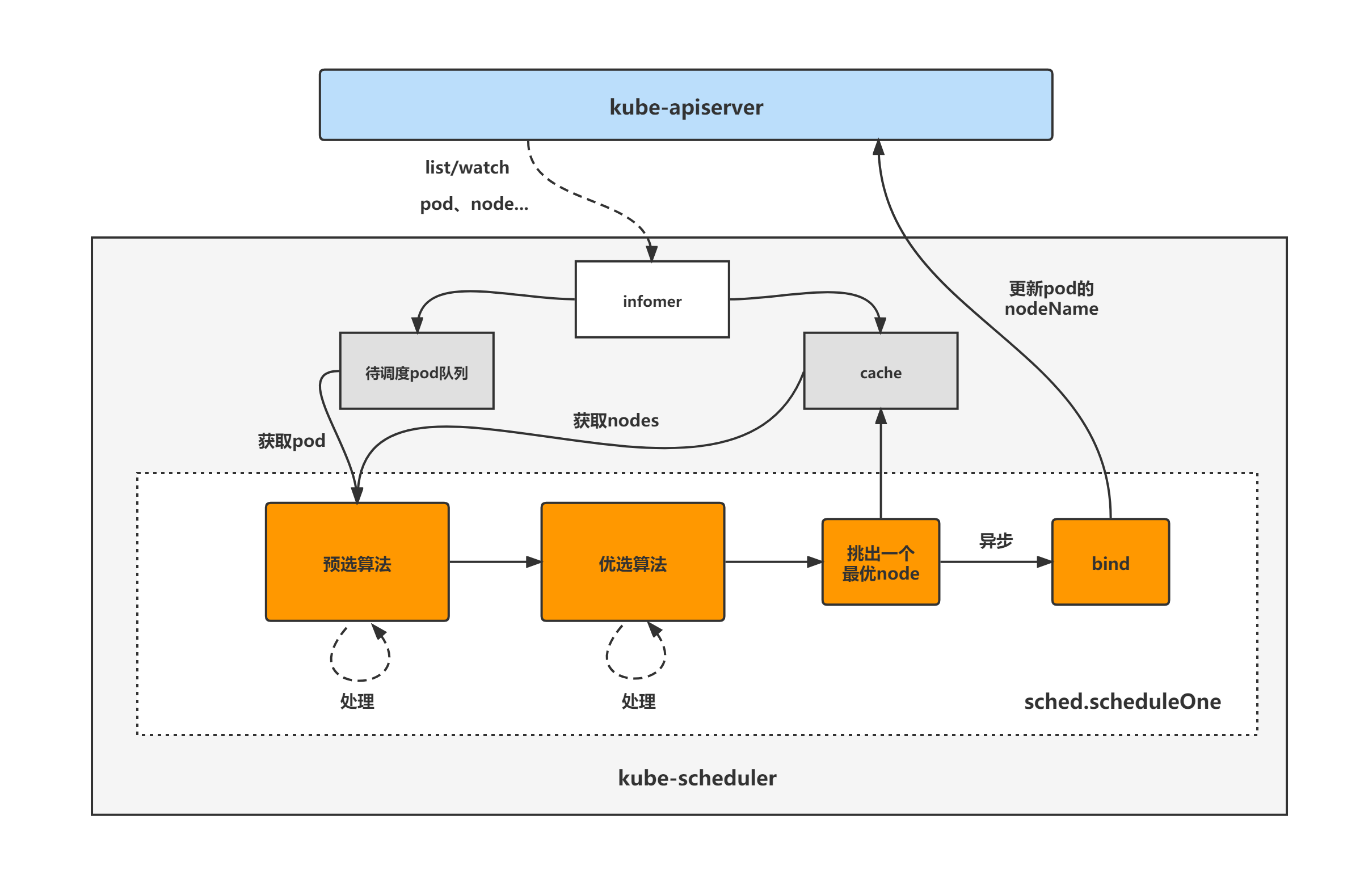
kube-scheduler组件的分析将分为两大块进行,分别是:
(1)kube-scheduler初始化与启动分析;
(2)kube-scheduler核心处理逻辑分析。
上一篇进行了kube-scheduler组件的初始化与启动分析,本篇进行核心处理逻辑分析。
2.kube-scheduler核心处理逻辑分析
基于tag v1.17.4
https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/releases/tag/v1.17.4
直接看到kube-scheduler核心处理方法sched.Run。
sched.Run
sched.Run主要逻辑:
(1)判断informer中的对象cache是否同步完成;
(2)循环调用sched.scheduleOne调度pod。
// pkg/scheduler/scheduler.go
func (sched *Scheduler) Run(ctx context.Context) {
// 1.判断informer中的对象cache是否同步完成
if !cache.WaitForCacheSync(ctx.Done(), sched.scheduledPodsHasSynced) {
return
}
// 2.循环调用sched.scheduleOne调度pod
wait.UntilWithContext(ctx, sched.scheduleOne, 0)
}
sched.scheduleOne
sched.scheduleOne方法作用是调度一个pod到合适的node节点,主要逻辑如下:
(1)从scheduler的待调度pod队列中取出一个pod,如果该pod的deletetimestamp不为空(代表处于删除状态)则跳过该pod的调度工作;
(2)调用sched.Algorithm.Schedule执行调度算法,返回通过预算及优选算法算出的nodo节点;
(3)当执行调度算法失败时,上报调度失败event,更新pod的status;
(4)当没有找到合适的节点时,判断scheduler是否开启了抢占调度机制,是则调用sched.preempt执行抢占逻辑;
(5)调用sched.VolumeBinder.Binder.AssumePodVolumes,更新cache,判断关联pvc是否都已bound;
(6)执行调用 "reserve" plugins(有印象即可,后面会对该类plugins进行讲解);
(7)调用sched.assume,在scheduler的cache中记录这个pod已经调度了,因为更新pod的nodeName是异步操作,防止pod被重复调度;
(8)起一个goroutine,异步执行pod的binding操作:
(8.1)执行调用 "permit" plugins(有印象即可,后面会对该类plugins进行讲解);
(8.2)调用sched.bindVolumes,绑定volumes;
(8.3)执行调用 "prebind" plugins(有印象即可,后面会对该类plugins进行讲解);
(8.4)更新pod的nodeName,写入etcd;
(8.5)执行调用 "postbind" plugins(有印象即可,后面会对该类plugins进行讲解),该pod调度结束。
// pkg/scheduler/scheduler.go
func (sched *Scheduler) scheduleOne(ctx context.Context) {
fwk := sched.Framework
// 1.从scheduler的待调度pod队列中取出一个pod
podInfo := sched.NextPod()
// pod could be nil when schedulerQueue is closed
if podInfo == nil || podInfo.Pod == nil {
return
}
pod := podInfo.Pod
// 如果该pod的deletetimestamp不为空(代表处于删除状态)则跳过该pod的调度工作
if pod.DeletionTimestamp != nil {
sched.Recorder.Eventf(pod, nil, v1.EventTypeWarning, "FailedScheduling", "Scheduling", "skip schedule deleting pod: %v/%v", pod.Namespace, pod.Name)
klog.V(3).Infof("Skip schedule deleting pod: %v/%v", pod.Namespace, pod.Name)
return
}
klog.V(3).Infof("Attempting to schedule pod: %v/%v", pod.Namespace, pod.Name)
// 2.调用sched.schedule执行调度算法,返回通过预算及优选算法算出的nodo节点
// Synchronously attempt to find a fit for the pod.
start := time.Now()
state := framework.NewCycleState()
state.SetRecordFrameworkMetrics(rand.Intn(100) < frameworkMetricsSamplePercent)
schedulingCycleCtx, cancel := context.WithCancel(ctx)
defer cancel()
scheduleResult, err := sched.Algorithm.Schedule(schedulingCycleCtx, state, pod)
if err != nil {
// 3.当执行调度算法失败时,上报调度失败event,更新pod的status
sched.recordSchedulingFailure(podInfo.DeepCopy(), err, v1.PodReasonUnschedulable, err.Error())
// Schedule() may have failed because the pod would not fit on any host, so we try to
// preempt, with the expectation that the next time the pod is tried for scheduling it
// will fit due to the preemption. It is also possible that a different pod will schedule
// into the resources that were preempted, but this is harmless.
if fitError, ok := err.(*core.FitError); ok {
// 4.当没有找到合适的节点时,判断scheduler是否开启了抢占调度机制,是则调用sched.preempt执行抢占逻辑
if sched.DisablePreemption {
klog.V(3).Infof("Pod priority feature is not enabled or preemption is disabled by scheduler configuration." +
" No preemption is performed.")
} else {
preemptionStartTime := time.Now()
sched.preempt(schedulingCycleCtx, state, fwk, pod, fitError)
metrics.PreemptionAttempts.Inc()
metrics.SchedulingAlgorithmPreemptionEvaluationDuration.Observe(metrics.SinceInSeconds(preemptionStartTime))
metrics.DeprecatedSchedulingAlgorithmPreemptionEvaluationDuration.Observe(metrics.SinceInMicroseconds(preemptionStartTime))
metrics.SchedulingLatency.WithLabelValues(metrics.PreemptionEvaluation).Observe(metrics.SinceInSeconds(preemptionStartTime))
metrics.DeprecatedSchedulingLatency.WithLabelValues(metrics.PreemptionEvaluation).Observe(metrics.SinceInSeconds(preemptionStartTime))
}
// Pod did not fit anywhere, so it is counted as a failure. If preemption
// succeeds, the pod should get counted as a success the next time we try to
// schedule it. (hopefully)
metrics.PodScheduleFailures.Inc()
} else {
klog.Errorf("error selecting node for pod: %v", err)
metrics.PodScheduleErrors.Inc()
}
return
}
metrics.SchedulingAlgorithmLatency.Observe(metrics.SinceInSeconds(start))
metrics.DeprecatedSchedulingAlgorithmLatency.Observe(metrics.SinceInMicroseconds(start))
// Tell the cache to assume that a pod now is running on a given node, even though it hasn't been bound yet.
// This allows us to keep scheduling without waiting on binding to occur.
assumedPodInfo := podInfo.DeepCopy()
assumedPod := assumedPodInfo.Pod
// 5.更新cache,判断关联pvc是否都已bound
// Assume volumes first before assuming the pod.
//
// If all volumes are completely bound, then allBound is true and binding will be skipped.
//
// Otherwise, binding of volumes is started after the pod is assumed, but before pod binding.
//
// This function modifies 'assumedPod' if volume binding is required.
allBound, err := sched.VolumeBinder.Binder.AssumePodVolumes(assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost)
if err != nil {
sched.recordSchedulingFailure(assumedPodInfo, err, SchedulerError,
fmt.Sprintf("AssumePodVolumes failed: %v", err))
metrics.PodScheduleErrors.Inc()
return
}
// 6.执行调用 "reserve" plugins
// Run "reserve" plugins.
if sts := fwk.RunReservePlugins(schedulingCycleCtx, state, assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost); !sts.IsSuccess() {
sched.recordSchedulingFailure(assumedPodInfo, sts.AsError(), SchedulerError, sts.Message())
metrics.PodScheduleErrors.Inc()
return
}
// 7.调用sched.assume,在scheduler的cache中记录这个pod已经调度了,因为更新pod的nodeName是异步操作,防止pod被重复调度
// assume modifies `assumedPod` by setting NodeName=scheduleResult.SuggestedHost
err = sched.assume(assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost)
if err != nil {
// This is most probably result of a BUG in retrying logic.
// We report an error here so that pod scheduling can be retried.
// This relies on the fact that Error will check if the pod has been bound
// to a node and if so will not add it back to the unscheduled pods queue
// (otherwise this would cause an infinite loop).
sched.recordSchedulingFailure(assumedPodInfo, err, SchedulerError, fmt.Sprintf("AssumePod failed: %v", err))
metrics.PodScheduleErrors.Inc()
// trigger un-reserve plugins to clean up state associated with the reserved Pod
fwk.RunUnreservePlugins(schedulingCycleCtx, state, assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost)
return
}
// 8.起一个goroutine,异步执行pod的binding操作
// bind the pod to its host asynchronously (we can do this b/c of the assumption step above).
go func() {
bindingCycleCtx, cancel := context.WithCancel(ctx)
defer cancel()
metrics.SchedulerGoroutines.WithLabelValues("binding").Inc()
defer metrics.SchedulerGoroutines.WithLabelValues("binding").Dec()
// Run "permit" plugins.
permitStatus := fwk.RunPermitPlugins(bindingCycleCtx, state, assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost)
if !permitStatus.IsSuccess() {
var reason string
if permitStatus.IsUnschedulable() {
metrics.PodScheduleFailures.Inc()
reason = v1.PodReasonUnschedulable
} else {
metrics.PodScheduleErrors.Inc()
reason = SchedulerError
}
if forgetErr := sched.Cache().ForgetPod(assumedPod); forgetErr != nil {
klog.Errorf("scheduler cache ForgetPod failed: %v", forgetErr)
}
// trigger un-reserve plugins to clean up state associated with the reserved Pod
fwk.RunUnreservePlugins(bindingCycleCtx, state, assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost)
sched.recordSchedulingFailure(assumedPodInfo, permitStatus.AsError(), reason, permitStatus.Message())
return
}
// Bind volumes first before Pod
if !allBound {
err := sched.bindVolumes(assumedPod)
if err != nil {
sched.recordSchedulingFailure(assumedPodInfo, err, "VolumeBindingFailed", err.Error())
metrics.PodScheduleErrors.Inc()
// trigger un-reserve plugins to clean up state associated with the reserved Pod
fwk.RunUnreservePlugins(bindingCycleCtx, state, assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost)
return
}
}
// Run "prebind" plugins.
preBindStatus := fwk.RunPreBindPlugins(bindingCycleCtx, state, assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost)
if !preBindStatus.IsSuccess() {
var reason string
metrics.PodScheduleErrors.Inc()
reason = SchedulerError
if forgetErr := sched.Cache().ForgetPod(assumedPod); forgetErr != nil {
klog.Errorf("scheduler cache ForgetPod failed: %v", forgetErr)
}
// trigger un-reserve plugins to clean up state associated with the reserved Pod
fwk.RunUnreservePlugins(bindingCycleCtx, state, assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost)
sched.recordSchedulingFailure(assumedPodInfo, preBindStatus.AsError(), reason, preBindStatus.Message())
return
}
err := sched.bind(bindingCycleCtx, assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost, state)
metrics.E2eSchedulingLatency.Observe(metrics.SinceInSeconds(start))
metrics.DeprecatedE2eSchedulingLatency.Observe(metrics.SinceInMicroseconds(start))
if err != nil {
metrics.PodScheduleErrors.Inc()
// trigger un-reserve plugins to clean up state associated with the reserved Pod
fwk.RunUnreservePlugins(bindingCycleCtx, state, assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost)
sched.recordSchedulingFailure(assumedPodInfo, err, SchedulerError, fmt.Sprintf("Binding rejected: %v", err))
} else {
// Calculating nodeResourceString can be heavy. Avoid it if klog verbosity is below 2.
if klog.V(2) {
klog.Infof("pod %v/%v is bound successfully on node %q, %d nodes evaluated, %d nodes were found feasible.", assumedPod.Namespace, assumedPod.Name, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost, scheduleResult.EvaluatedNodes, scheduleResult.FeasibleNodes)
}
metrics.PodScheduleSuccesses.Inc()
metrics.PodSchedulingAttempts.Observe(float64(podInfo.Attempts))
metrics.PodSchedulingDuration.Observe(metrics.SinceInSeconds(podInfo.InitialAttemptTimestamp))
// Run "postbind" plugins.
fwk.RunPostBindPlugins(bindingCycleCtx, state, assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost)
}
}()
}
2.1 sched.Algorithm.Schedule
sched.Algorithm.Schedule主要作用是执行预选算法和优选算法,给pod算出一个合适的node,其主要逻辑为:
(1)对pod使用到的pvc进行检查,检查其是否处于删除状态;
(2)调用g.snapshot,获取当前的所有node节点信息快照,用于本轮调度,包括下面执行的预算算法与优选算法都将使用该node快照;
(3)执行调用 "prefilter" plugins(有印象即可,后面会对该类plugins进行讲解);
(4)调用g.findNodesThatFit,执行预选算法,筛选出符合该pod运行条件的合适node节点;
(5)执行调用 "postfilter" plugins(有印象即可,后面会对该类plugins进行讲解);
(6)判断合适的node节点数,如果为0直接返回失败;
(7)判断合适的node节点数,如果为1则直接返回该node节点,不往下执行优选算法;
(8)调用g.prioritizeNodes,执行优选算法,给合适的所有node节点打分;
(9)调用g.selectHost,从优选算法打分过后的node节点中选择最佳(即得分最高)的node节点并返回。
// pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go
func (g *genericScheduler) Schedule(ctx context.Context, state *framework.CycleState, pod *v1.Pod) (result ScheduleResult, err error) {
trace := utiltrace.New("Scheduling", utiltrace.Field{Key: "namespace", Value: pod.Namespace}, utiltrace.Field{Key: "name", Value: pod.Name})
defer trace.LogIfLong(100 * time.Millisecond)
// 1.对pod使用到的pvc进行检查,检查其是否处于删除状态
if err := podPassesBasicChecks(pod, g.pvcLister); err != nil {
return result, err
}
trace.Step("Basic checks done")
// 2.调用g.snapshot,获取当前的所有node节点信息快照,用于本轮调度,包括下面执行的预算算法与优选算法都将使用该node快照
if err := g.snapshot(); err != nil {
return result, err
}
trace.Step("Snapshoting scheduler cache and node infos done")
if len(g.nodeInfoSnapshot.NodeInfoList) == 0 {
return result, ErrNoNodesAvailable
}
// Run "prefilter" plugins.
preFilterStatus := g.framework.RunPreFilterPlugins(ctx, state, pod)
if !preFilterStatus.IsSuccess() {
return result, preFilterStatus.AsError()
}
trace.Step("Running prefilter plugins done")
// 4.调用g.findNodesThatFit,执行预选算法,筛选出符合该pod运行条件的合适node节点
startPredicateEvalTime := time.Now()
filteredNodes, failedPredicateMap, filteredNodesStatuses, err := g.findNodesThatFit(ctx, state, pod)
if err != nil {
return result, err
}
trace.Step("Computing predicates done")
// Run "postfilter" plugins.
postfilterStatus := g.framework.RunPostFilterPlugins(ctx, state, pod, filteredNodes, filteredNodesStatuses)
if !postfilterStatus.IsSuccess() {
return result, postfilterStatus.AsError()
}
// 6.判断合适的node节点数,如果为0直接返回失败
if len(filteredNodes) == 0 {
return result, &FitError{
Pod: pod,
NumAllNodes: len(g.nodeInfoSnapshot.NodeInfoList),
FailedPredicates: failedPredicateMap,
FilteredNodesStatuses: filteredNodesStatuses,
}
}
trace.Step("Running postfilter plugins done")
metrics.SchedulingAlgorithmPredicateEvaluationDuration.Observe(metrics.SinceInSeconds(startPredicateEvalTime))
metrics.DeprecatedSchedulingAlgorithmPredicateEvaluationDuration.Observe(metrics.SinceInMicroseconds(startPredicateEvalTime))
metrics.SchedulingLatency.WithLabelValues(metrics.PredicateEvaluation).Observe(metrics.SinceInSeconds(startPredicateEvalTime))
metrics.DeprecatedSchedulingLatency.WithLabelValues(metrics.PredicateEvaluation).Observe(metrics.SinceInSeconds(startPredicateEvalTime))
// 7.判断合适的node节点数,如果为1则直接返回该node节点,不往下执行优选算法
startPriorityEvalTime := time.Now()
// When only one node after predicate, just use it.
if len(filteredNodes) == 1 {
metrics.SchedulingAlgorithmPriorityEvaluationDuration.Observe(metrics.SinceInSeconds(startPriorityEvalTime))
metrics.DeprecatedSchedulingAlgorithmPriorityEvaluationDuration.Observe(metrics.SinceInMicroseconds(startPriorityEvalTime))
return ScheduleResult{
SuggestedHost: filteredNodes[0].Name,
EvaluatedNodes: 1 + len(failedPredicateMap) + len(filteredNodesStatuses),
FeasibleNodes: 1,
}, nil
}
// 8.调用g.prioritizeNodes,执行优选算法,给合适的所有node节点打分
metaPrioritiesInterface := g.priorityMetaProducer(pod, filteredNodes, g.nodeInfoSnapshot)
priorityList, err := g.prioritizeNodes(ctx, state, pod, metaPrioritiesInterface, filteredNodes)
if err != nil {
return result, err
}
metrics.SchedulingAlgorithmPriorityEvaluationDuration.Observe(metrics.SinceInSeconds(startPriorityEvalTime))
metrics.DeprecatedSchedulingAlgorithmPriorityEvaluationDuration.Observe(metrics.SinceInMicroseconds(startPriorityEvalTime))
metrics.SchedulingLatency.WithLabelValues(metrics.PriorityEvaluation).Observe(metrics.SinceInSeconds(startPriorityEvalTime))
metrics.DeprecatedSchedulingLatency.WithLabelValues(metrics.PriorityEvaluation).Observe(metrics.SinceInSeconds(startPriorityEvalTime))
// 9.调用g.selectHost,从合适的node节点中选择最佳(即得分最高)的node节点并返回
host, err := g.selectHost(priorityList)
trace.Step("Prioritizing done")
return ScheduleResult{
SuggestedHost: host,
EvaluatedNodes: len(filteredNodes) + len(failedPredicateMap) + len(filteredNodesStatuses),
FeasibleNodes: len(filteredNodes),
}, err
}
2.1.1 g.snapshot
g.snapshot方法主要是获取当前的所有node节点信息快照,用于本轮调度,包括后面执行的预算算法与优选算法都将使用该node快照。当node节点信息没有变化时(根据node节点的generation大小判断),该方法直接返回现有node节点信息快照,无需更新,当node节点信息有变化时才更新快照并返回最新快照。
// pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go
func (g *genericScheduler) snapshot() error {
// Used for all fit and priority funcs.
return g.cache.UpdateNodeInfoSnapshot(g.nodeInfoSnapshot)
}
// pkg/scheduler/internal/cache/cache.go
func (cache *schedulerCache) UpdateNodeInfoSnapshot(nodeSnapshot *nodeinfosnapshot.Snapshot) error {
cache.mu.Lock()
defer cache.mu.Unlock()
balancedVolumesEnabled := utilfeature.DefaultFeatureGate.Enabled(features.BalanceAttachedNodeVolumes)
// Get the last generation of the snapshot.
snapshotGeneration := nodeSnapshot.Generation
// 增加和更新node节点快照
// Start from the head of the NodeInfo doubly linked list and update snapshot
// of NodeInfos updated after the last snapshot.
for node := cache.headNode; node != nil; node = node.next {
if node.info.GetGeneration() <= snapshotGeneration {
// all the nodes are updated before the existing snapshot. We are done.
break
}
if balancedVolumesEnabled && node.info.TransientInfo != nil {
// Transient scheduler info is reset here.
node.info.TransientInfo.ResetTransientSchedulerInfo()
}
if np := node.info.Node(); np != nil {
nodeSnapshot.NodeInfoMap[np.Name] = node.info.Clone()
}
}
// Update the snapshot generation with the latest NodeInfo generation.
if cache.headNode != nil {
nodeSnapshot.Generation = cache.headNode.info.GetGeneration()
}
// 删除多余的node节点快照
if len(nodeSnapshot.NodeInfoMap) > len(cache.nodes) {
for name := range nodeSnapshot.NodeInfoMap {
if _, ok := cache.nodes[name]; !ok {
delete(nodeSnapshot.NodeInfoMap, name)
}
}
}
// Take a snapshot of the nodes order in the tree
nodeSnapshot.NodeInfoList = make([]*schedulernodeinfo.NodeInfo, 0, cache.nodeTree.numNodes)
nodeSnapshot.HavePodsWithAffinityNodeInfoList = make([]*schedulernodeinfo.NodeInfo, 0, cache.nodeTree.numNodes)
for i := 0; i < cache.nodeTree.numNodes; i++ {
nodeName := cache.nodeTree.next()
if n := nodeSnapshot.NodeInfoMap[nodeName]; n != nil {
nodeSnapshot.NodeInfoList = append(nodeSnapshot.NodeInfoList, n)
if len(n.PodsWithAffinity()) > 0 {
nodeSnapshot.HavePodsWithAffinityNodeInfoList = append(nodeSnapshot.HavePodsWithAffinityNodeInfoList, n)
}
} else {
klog.Errorf("node %q exist in nodeTree but not in NodeInfoMap, this should not happen.", nodeName)
}
}
return nil
}
2.1.2 g.findNodesThatFit 执行预选算法
g.findNodesThatFit方法是执行预选算法的地方。主要逻辑如下:
(1)调用g.numFeasibleNodesToFind,根据一定的算法,计算并返回预选算法要筛选的node节点数量;
(2)定义checkNode函数,用于筛选合适的node节点;
(3)起16个goroutine,并行的对所有node执行checkNode函数,返回合适的node节点列表,列表长度小于等于g.numFeasibleNodesToFind方法返回值;
(4)遍历scheduler-extender(kube-scheduler的一种webhook扩展机制),对已经过滤过的node再来执行extender的Filter,即执行http扩展的预选算法;
(5)最后返回filtered(预选通过的node列表)、failedPredicateMap(预选失败的node和失败原因)等。
// pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go
func (g *genericScheduler) findNodesThatFit(ctx context.Context, state *framework.CycleState, pod *v1.Pod) ([]*v1.Node, FailedPredicateMap, framework.NodeToStatusMap, error) {
var filtered []*v1.Node
failedPredicateMap := FailedPredicateMap{}
filteredNodesStatuses := framework.NodeToStatusMap{}
if len(g.predicates) == 0 && !g.framework.HasFilterPlugins() {
filtered = g.nodeInfoSnapshot.ListNodes()
} else {
allNodes := len(g.nodeInfoSnapshot.NodeInfoList)
numNodesToFind := g.numFeasibleNodesToFind(int32(allNodes))
// Create filtered list with enough space to avoid growing it
// and allow assigning.
filtered = make([]*v1.Node, numNodesToFind)
errCh := util.NewErrorChannel()
var (
predicateResultLock sync.Mutex
filteredLen int32
)
ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(ctx)
// We can use the same metadata producer for all nodes.
meta := g.predicateMetaProducer(pod, g.nodeInfoSnapshot)
state.Write(migration.PredicatesStateKey, &migration.PredicatesStateData{Reference: meta})
checkNode := func(i int) {
// We check the nodes starting from where we left off in the previous scheduling cycle,
// this is to make sure all nodes have the same chance of being examined across pods.
nodeInfo := g.nodeInfoSnapshot.NodeInfoList[(g.nextStartNodeIndex+i)%allNodes]
fits, failedPredicates, status, err := g.podFitsOnNode(
ctx,
state,
pod,
meta,
nodeInfo,
g.alwaysCheckAllPredicates,
)
if err != nil {
errCh.SendErrorWithCancel(err, cancel)
return
}
if fits {
length := atomic.AddInt32(&filteredLen, 1)
if length > numNodesToFind {
cancel()
atomic.AddInt32(&filteredLen, -1)
} else {
filtered[length-1] = nodeInfo.Node()
}
} else {
predicateResultLock.Lock()
if !status.IsSuccess() {
filteredNodesStatuses[nodeInfo.Node().Name] = status
}
if len(failedPredicates) != 0 {
failedPredicateMap[nodeInfo.Node().Name] = failedPredicates
}
predicateResultLock.Unlock()
}
}
// Stops searching for more nodes once the configured number of feasible nodes
// are found.
workqueue.ParallelizeUntil(ctx, 16, allNodes, checkNode)
processedNodes := int(filteredLen) + len(filteredNodesStatuses) + len(failedPredicateMap)
g.nextStartNodeIndex = (g.nextStartNodeIndex + processedNodes) % allNodes
filtered = filtered[:filteredLen]
if err := errCh.ReceiveError(); err != nil {
return []*v1.Node{}, FailedPredicateMap{}, framework.NodeToStatusMap{}, err
}
}
if len(filtered) > 0 && len(g.extenders) != 0 {
for _, extender := range g.extenders {
if !extender.IsInterested(pod) {
continue
}
filteredList, failedMap, err := extender.Filter(pod, filtered, g.nodeInfoSnapshot.NodeInfoMap)
if err != nil {
if extender.IsIgnorable() {
klog.Warningf("Skipping extender %v as it returned error %v and has ignorable flag set",
extender, err)
continue
}
return []*v1.Node{}, FailedPredicateMap{}, framework.NodeToStatusMap{}, err
}
for failedNodeName, failedMsg := range failedMap {
if _, found := failedPredicateMap[failedNodeName]; !found {
failedPredicateMap[failedNodeName] = []predicates.PredicateFailureReason{}
}
failedPredicateMap[failedNodeName] = append(failedPredicateMap[failedNodeName], predicates.NewFailureReason(failedMsg))
}
filtered = filteredList
if len(filtered) == 0 {
break
}
}
}
return filtered, failedPredicateMap, filteredNodesStatuses, nil
}
g.numFeasibleNodesToFind
g.numFeasibleNodesToFind方法根据一定的算法计算并返回预选算法要筛选的node节点数量。
返回值node节点数量将根据一定的算法来计算得出:
(1)当node节点数量小于100,或配置参数percentageOfNodesToScore大于等于100时,返回值为node节点的数量;
(2)当配置参数percentageOfNodesToScore小于等于0时,将启用以下自带算法算出返回的node节点数量值:
返回的node节点数量值=node节点数量*(50-node节点数量/125)/100;
(3)当配置参数percentageOfNodesToScore大于0时,返回的node节点数量值=node节点数量*percentageOfNodesToScore/100;
(4)当计算得出的node节点数量小于100时,任然返回最小值100。
配置参数percentageOfNodesToScore说明:该参数用于kube-scheduler调度器性能调优,允许执行调度预选算法时在找到一定数量的可行node节点后停止寻找更多的节点,提高了调度器在大型集群中的性能。
// pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go
func (g *genericScheduler) numFeasibleNodesToFind(numAllNodes int32) (numNodes int32) {
if numAllNodes < minFeasibleNodesToFind || g.percentageOfNodesToScore >= 100 {
return numAllNodes
}
adaptivePercentage := g.percentageOfNodesToScore
if adaptivePercentage <= 0 {
basePercentageOfNodesToScore := int32(50)
adaptivePercentage = basePercentageOfNodesToScore - numAllNodes/125
if adaptivePercentage < minFeasibleNodesPercentageToFind {
adaptivePercentage = minFeasibleNodesPercentageToFind
}
}
numNodes = numAllNodes * adaptivePercentage / 100
if numNodes < minFeasibleNodesToFind {
return minFeasibleNodesToFind
}
return numNodes
}
checkNode
checkNode函数主要逻辑如下:
(1)从nodes快照中取出一个node;
(2)调用g.podFitsOnNode,对该pod在该node上执行所有的已注册的预选算法;
(3)当已经找到的合适的node节点数量已经大于要筛选的node节点数量时,调用cacel函数,不再继续找。
checkNode := func(i int) {
// (1)从nodes快照中取出一个node
nodeInfo := g.nodeInfoSnapshot.NodeInfoList[(g.nextStartNodeIndex+i)%allNodes]
// (2)对该pod在该node上执行所有的已注册的预选算法
fits, failedPredicates, status, err := g.podFitsOnNode(
ctx,
state,
pod,
meta,
nodeInfo,
g.alwaysCheckAllPredicates,
)
if err != nil {
errCh.SendErrorWithCancel(err, cancel)
return
}
if fits {
length := atomic.AddInt32(&filteredLen, 1)
// (3)当已经找到的合适的node节点数量已经大于要筛选的node节点数量时,调用cacel函数,不再继续找
if length > numNodesToFind {
cancel()
atomic.AddInt32(&filteredLen, -1)
} else {
filtered[length-1] = nodeInfo.Node()
}
} else {
predicateResultLock.Lock()
if !status.IsSuccess() {
filteredNodesStatuses[nodeInfo.Node().Name] = status
}
if len(failedPredicates) != 0 {
failedPredicateMap[nodeInfo.Node().Name] = failedPredicates
}
predicateResultLock.Unlock()
}
}
执行预算算法时将根据预定义的顺序依次执行,并根据配置参数alwaysCheckAllPredicates是否为true,决定当一个预选算法执行失败时要不要继续往下执行剩余的预选算法。
// pkg/scheduler/algorithm/predicates/predicates.go
var (
predicatesOrdering = []string{CheckNodeUnschedulablePred,
GeneralPred, HostNamePred, PodFitsHostPortsPred,
MatchNodeSelectorPred, PodFitsResourcesPred, NoDiskConflictPred,
PodToleratesNodeTaintsPred, PodToleratesNodeNoExecuteTaintsPred, CheckNodeLabelPresencePred,
CheckServiceAffinityPred, MaxEBSVolumeCountPred, MaxGCEPDVolumeCountPred, MaxCSIVolumeCountPred,
MaxAzureDiskVolumeCountPred, MaxCinderVolumeCountPred, CheckVolumeBindingPred, NoVolumeZoneConflictPred,
EvenPodsSpreadPred, MatchInterPodAffinityPred}
)
g.podFitsOnNode
g.podFitsOnNode方法主要作用是对某个pod在某个node上执行所有的已注册的预选算法,看是否满足预选结果。
g.podFitsOnNode方法只用关注两个点:
(1)for循环跑了两遍;
(2)注意到predicates.Ordering(),定义了预选算法的先后顺序;
(3)调用g.framework.RunFilterPlugins,用于执行“Filter” plugins。
for循环跑了两遍,分别做了什么:
(1)第一遍,kube-scheduler假设需要抢占的pod已经在该节点运行(实际上尚未调度到该节点),执行预选算法;
(2)第二遍,kube-scheduler正常执行预选算法,不考虑抢占的pod。
为什么for循环要跑两遍,即执行两遍预选操作:
(1)第一遍执行预选操作是必须的,因为需要考虑到抢占的pod(更高优先级)调度到该节点,如InterPodAntiAffinity等规则将会考虑所有pod之间的互斥关系;
(2)第二遍执行预选操作也是必须的,因为抢占的pod最终不一定运行在该节点上,然后有一些预选算法比如pod亲和性,在抢占的pod没有成功跑到该节点的情况下可能会不满足,所以需要不考虑抢占的pod去正常执行一遍预选算法。
func (g *genericScheduler) podFitsOnNode(
ctx context.Context,
state *framework.CycleState,
pod *v1.Pod,
meta predicates.Metadata,
info *schedulernodeinfo.NodeInfo,
alwaysCheckAllPredicates bool,
) (bool, []predicates.PredicateFailureReason, *framework.Status, error) {
var failedPredicates []predicates.PredicateFailureReason
var status *framework.Status
podsAdded := false
...
// 执行两遍预选操作
for i := 0; i < 2; i++ {
metaToUse := meta
stateToUse := state
nodeInfoToUse := info
if i == 0 {
//处理抢占pod(优先级更高的pod)的逻辑
var err error
// 在addNominatedPods中,会将node上的nominatedPod列举出来,即将抢占pod考虑到其中,然后后面再执行预选算法
podsAdded, metaToUse, stateToUse, nodeInfoToUse, err = g.addNominatedPods(ctx, pod, meta, state, info)
if err != nil {
return false, []predicates.PredicateFailureReason{}, nil, err
}
} else if !podsAdded || len(failedPredicates) != 0 || !status.IsSuccess() {
break
}
for _, predicateKey := range predicates.Ordering() {
var (
fit bool
reasons []predicates.PredicateFailureReason
err error
)
if predicate, exist := g.predicates[predicateKey]; exist {
fit, reasons, err = predicate(pod, metaToUse, nodeInfoToUse)
if err != nil {
return false, []predicates.PredicateFailureReason{}, nil, err
}
if !fit {
// eCache is available and valid, and predicates result is unfit, record the fail reasons
failedPredicates = append(failedPredicates, reasons...)
// if alwaysCheckAllPredicates is false, short circuit all predicates when one predicate fails.
if !alwaysCheckAllPredicates {
klog.V(5).Infoln("since alwaysCheckAllPredicates has not been set, the predicate " +
"evaluation is short circuited and there are chances " +
"of other predicates failing as well.")
break
}
}
}
}
status = g.framework.RunFilterPlugins(ctx, stateToUse, pod, nodeInfoToUse)
if !status.IsSuccess() && !status.IsUnschedulable() {
return false, failedPredicates, status, status.AsError()
}
}
return len(failedPredicates) == 0 && status.IsSuccess(), failedPredicates, status, nil
}
predicates.Ordering(),包含了全部预选算法的列表,并定义了预选算法的先后顺序,所以当需要扩展预选算法的时候必须要记得将其名称添加到此列表中。
// pkg/scheduler/algorithm/predicates/predicates.go
var (
predicatesOrdering = []string{CheckNodeUnschedulablePred,
GeneralPred, HostNamePred, PodFitsHostPortsPred,
MatchNodeSelectorPred, PodFitsResourcesPred, NoDiskConflictPred,
PodToleratesNodeTaintsPred, PodToleratesNodeNoExecuteTaintsPred, CheckNodeLabelPresencePred,
CheckServiceAffinityPred, MaxEBSVolumeCountPred, MaxGCEPDVolumeCountPred, MaxCSIVolumeCountPred,
MaxAzureDiskVolumeCountPred, MaxCinderVolumeCountPred, CheckVolumeBindingPred, NoVolumeZoneConflictPred,
EvenPodsSpreadPred, MatchInterPodAffinityPred}
)
// Ordering returns the ordering of predicates.
func Ordering() []string {
return predicatesOrdering
}
2.1.3 g.prioritizeNodes 执行优选算法
g.prioritizeNodes方法是执行优选算法的地方,每个节点执行所有优选算法过后,将会得到一个分数,最低分0分,最高分100分(v1.17.4版本是100分,旧版本可能是10分)。
// pkg/scheduler/framework/v1alpha1/interface.go
const (
// MaxNodeScore is the maximum score a Score plugin is expected to return.
MaxNodeScore int64 = 100
// MinNodeScore is the minimum score a Score plugin is expected to return.
MinNodeScore int64 = 0
...
)
g.prioritizeNodes方法主要逻辑如下:
(1)如果没有注册优选算法,则所有node节点的得分都为1分;
(2)对nodes执行优选算法,这里使用了MapReduce的思想(Map与Reduce函数在优选算法注册时定义);
(2.1)启动16个goroutine并发为node节点执行优选算法的Map,并记录每个节点的每个优选算法的打分;
(2.2)对每个优选算法,都起一个goroutine来执行Reduce;
(3)执行调用"Score" plugins;
(4)汇总每个node节点的分数(node节点的分数=每个优选算法的得分*该优选算法的权重);
(5)遍历scheduler-extender(kube-scheduler的一种webhook扩展机制),执行extender的Prioritize,即执行http扩展的优选算法,执行完毕后再统计一遍每个node节点的分数。
关于Map-Reduce:一个优选算法的Map函数计算1个node的Score,在有需要时,定义Reduce函数,根据一定的规则策略(收缩分数、反转分数等等)将这个Score进行归约到[0-100],更多关于Map-Reduce的介绍,可自行查看其他资料了解,这里不展开介绍。
// pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go
func (g *genericScheduler) prioritizeNodes(
ctx context.Context,
state *framework.CycleState,
pod *v1.Pod,
meta interface{},
nodes []*v1.Node,
) (framework.NodeScoreList, error) {
// If no priority configs are provided, then all nodes will have a score of one.
// This is required to generate the priority list in the required format
if len(g.prioritizers) == 0 && len(g.extenders) == 0 && !g.framework.HasScorePlugins() {
result := make(framework.NodeScoreList, 0, len(nodes))
for i := range nodes {
result = append(result, framework.NodeScore{
Name: nodes[i].Name,
Score: 1,
})
}
return result, nil
}
var (
mu = sync.Mutex{}
wg = sync.WaitGroup{}
errs []error
)
appendError := func(err error) {
mu.Lock()
defer mu.Unlock()
errs = append(errs, err)
}
results := make([]framework.NodeScoreList, len(g.prioritizers))
for i := range g.prioritizers {
results[i] = make(framework.NodeScoreList, len(nodes))
}
workqueue.ParallelizeUntil(context.TODO(), 16, len(nodes), func(index int) {
nodeInfo := g.nodeInfoSnapshot.NodeInfoMap[nodes[index].Name]
for i := range g.prioritizers {
var err error
results[i][index], err = g.prioritizers[i].Map(pod, meta, nodeInfo)
if err != nil {
appendError(err)
results[i][index].Name = nodes[index].Name
}
}
})
for i := range g.prioritizers {
if g.prioritizers[i].Reduce == nil {
continue
}
wg.Add(1)
go func(index int) {
metrics.SchedulerGoroutines.WithLabelValues("prioritizing_mapreduce").Inc()
defer func() {
metrics.SchedulerGoroutines.WithLabelValues("prioritizing_mapreduce").Dec()
wg.Done()
}()
if err := g.prioritizers[index].Reduce(pod, meta, g.nodeInfoSnapshot, results[index]); err != nil {
appendError(err)
}
if klog.V(10) {
for _, hostPriority := range results[index] {
klog.Infof("%v -> %v: %v, Score: (%d)", util.GetPodFullName(pod), hostPriority.Name, g.prioritizers[index].Name, hostPriority.Score)
}
}
}(i)
}
// Wait for all computations to be finished.
wg.Wait()
if len(errs) != 0 {
return framework.NodeScoreList{}, errors.NewAggregate(errs)
}
// Run the Score plugins.
state.Write(migration.PrioritiesStateKey, &migration.PrioritiesStateData{Reference: meta})
scoresMap, scoreStatus := g.framework.RunScorePlugins(ctx, state, pod, nodes)
if !scoreStatus.IsSuccess() {
return framework.NodeScoreList{}, scoreStatus.AsError()
}
// Summarize all scores.
result := make(framework.NodeScoreList, 0, len(nodes))
for i := range nodes {
result = append(result, framework.NodeScore{Name: nodes[i].Name, Score: 0})
for j := range g.prioritizers {
result[i].Score += results[j][i].Score * g.prioritizers[j].Weight
}
for j := range scoresMap {
result[i].Score += scoresMap[j][i].Score
}
}
if len(g.extenders) != 0 && nodes != nil {
combinedScores := make(map[string]int64, len(g.nodeInfoSnapshot.NodeInfoList))
for i := range g.extenders {
if !g.extenders[i].IsInterested(pod) {
continue
}
wg.Add(1)
go func(extIndex int) {
metrics.SchedulerGoroutines.WithLabelValues("prioritizing_extender").Inc()
defer func() {
metrics.SchedulerGoroutines.WithLabelValues("prioritizing_extender").Dec()
wg.Done()
}()
prioritizedList, weight, err := g.extenders[extIndex].Prioritize(pod, nodes)
if err != nil {
// Prioritization errors from extender can be ignored, let k8s/other extenders determine the priorities
return
}
mu.Lock()
for i := range *prioritizedList {
host, score := (*prioritizedList)[i].Host, (*prioritizedList)[i].Score
if klog.V(10) {
klog.Infof("%v -> %v: %v, Score: (%d)", util.GetPodFullName(pod), host, g.extenders[extIndex].Name(), score)
}
combinedScores[host] += score * weight
}
mu.Unlock()
}(i)
}
// wait for all go routines to finish
wg.Wait()
for i := range result {
// MaxExtenderPriority may diverge from the max priority used in the scheduler and defined by MaxNodeScore,
// therefore we need to scale the score returned by extenders to the score range used by the scheduler.
result[i].Score += combinedScores[result[i].Name] * (framework.MaxNodeScore / extenderv1.MaxExtenderPriority)
}
}
if klog.V(10) {
for i := range result {
klog.Infof("Host %s => Score %d", result[i].Name, result[i].Score)
}
}
return result, nil
}
2.1.4 g.selectHost
g.selectHost方法主要是从所有优选打分过后的节点中,选出得分最高的节点并返回,当有多个得分最高的节点时,将随机返回一个得分最高的node节点。
// pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go
func (g *genericScheduler) selectHost(nodeScoreList framework.NodeScoreList) (string, error) {
if len(nodeScoreList) == 0 {
return "", fmt.Errorf("empty priorityList")
}
maxScore := nodeScoreList[0].Score
selected := nodeScoreList[0].Name
cntOfMaxScore := 1
for _, ns := range nodeScoreList[1:] {
if ns.Score > maxScore {
maxScore = ns.Score
selected = ns.Name
cntOfMaxScore = 1
} else if ns.Score == maxScore {
cntOfMaxScore++
if rand.Intn(cntOfMaxScore) == 0 {
// Replace the candidate with probability of 1/cntOfMaxScore
selected = ns.Name
}
}
}
return selected, nil
}
2.2 sched.preempt
preempt抢占机制:当高优先级的pod没有找到合适的node时,kube-scheduler会将低优先级的pod从所在node驱逐,然后让高优先级的pod调度到该node上,最后被驱逐的pod再进入待调度队列,重新进行调度。抢占机制的代码暂不做具体分析,可以自行查看。
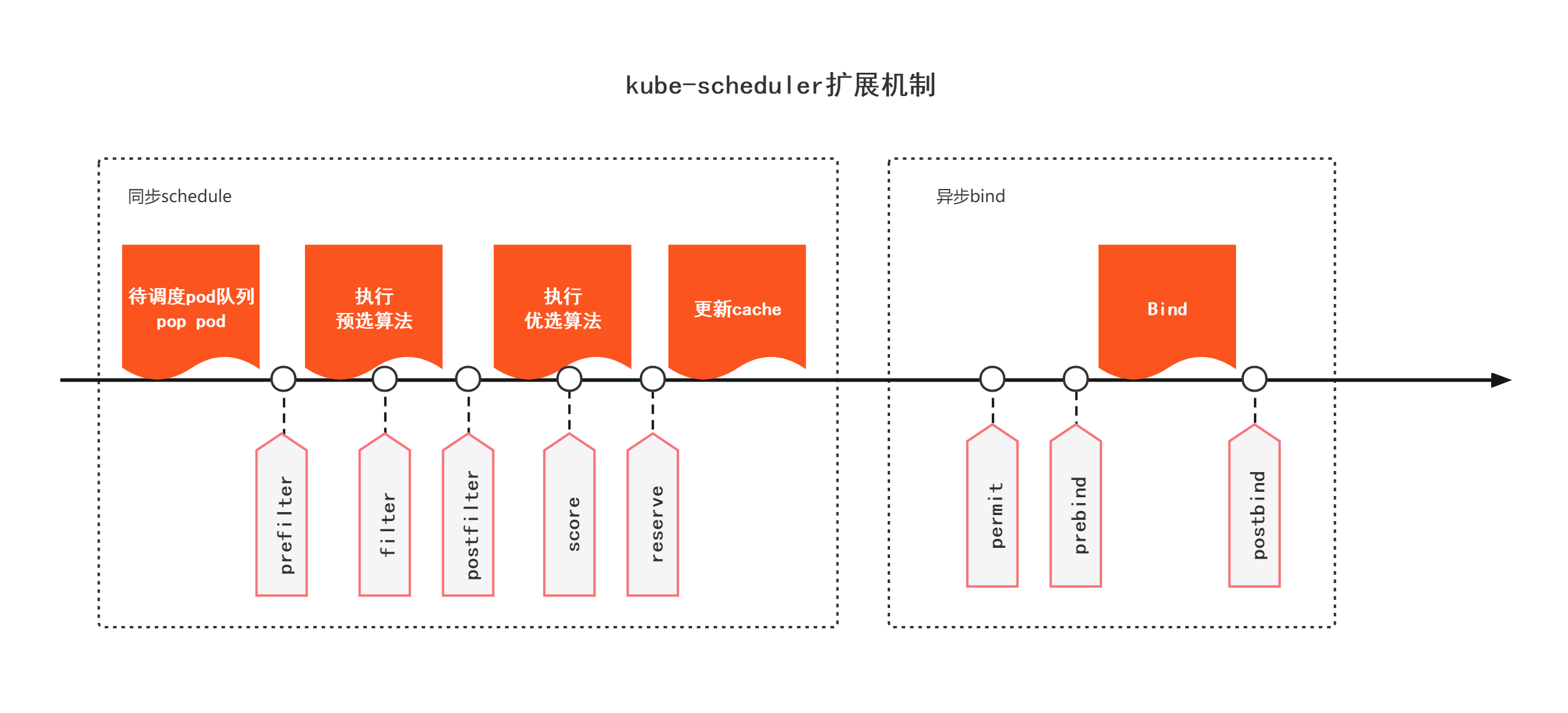
kube-scheduler扩展机制
kube-scheduler当前有两种扩展机制:
(1)scheduler-extender;
(2)scheduler framework。
scheduler-extender
scheduler-extender是以http webhook的形式提供的scheduler扩展形式,在执行预选算法、优选算法和Bind时可以分别进行webhook扩展。
参考:https://liqiang.io/post/kubernetes-scheduler-extender-dd6516a6
scheduler framework
前面代码分析中提到过的执行的filter,都是kube-scheduler的可扩展机制scheduler framework提供的,该机制在调度器生命周期的各个关键点上,向用户暴露可以进行扩展和实现的接口,从而赋予用户自定义调度器的能力。基于篇幅原因,这里不展开介绍kube-scheduler的可扩展机制,可自行进行了解。
目前kube-scheduler的很多内置预选算法和优选算法都是基于scheduler framework机制实现的。
参考:https://cloudnative.to/blog/202003-k8s-scheduling-framework/
总结
kube-scheduler简介
kube-scheduler组件是kubernetes中的核心组件之一,主要负责pod资源对象的调度工作,具体来说,kube-scheduler组件负责根据调度算法(包括预选算法和优选算法)将未调度的pod调度到合适的最优的node节点上。
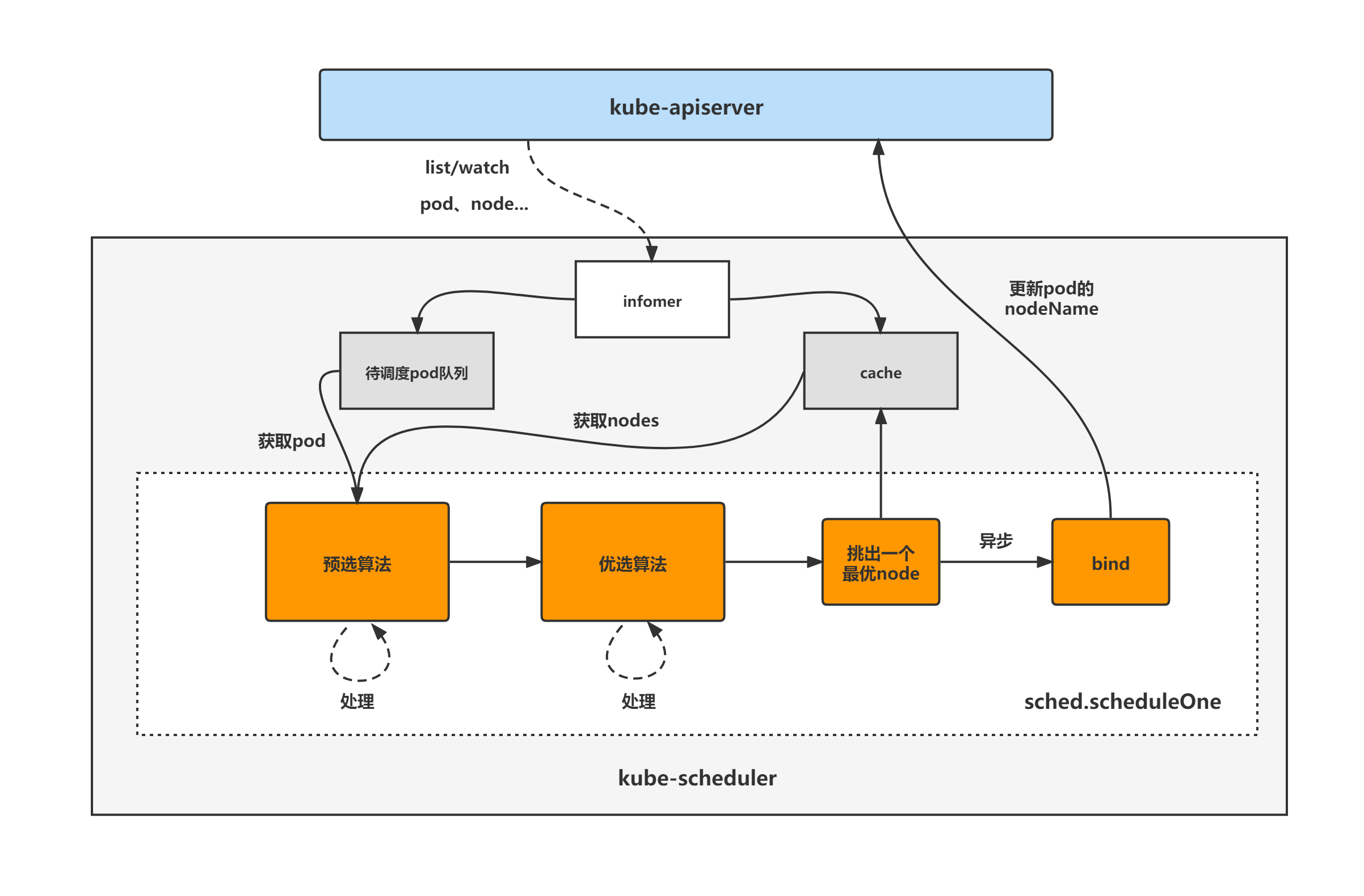
kube-scheduler架构图
kube-scheduler的大致组成和处理流程如下图,kube-scheduler对pod、node等对象进行了list/watch,根据informer将未调度的pod放入待调度pod队列,并根据informer构建调度器cache(用于快速获取需要的node等对象),然后sched.scheduleOne方法为kube-scheduler组件调度pod的核心处理逻辑所在,从未调度pod队列中取出一个pod,经过预选与优选算法,最终选出一个最优node,然后更新cache并异步执行bind操作,也就是更新pod的nodeName字段,至此一个pod的调度工作完成。
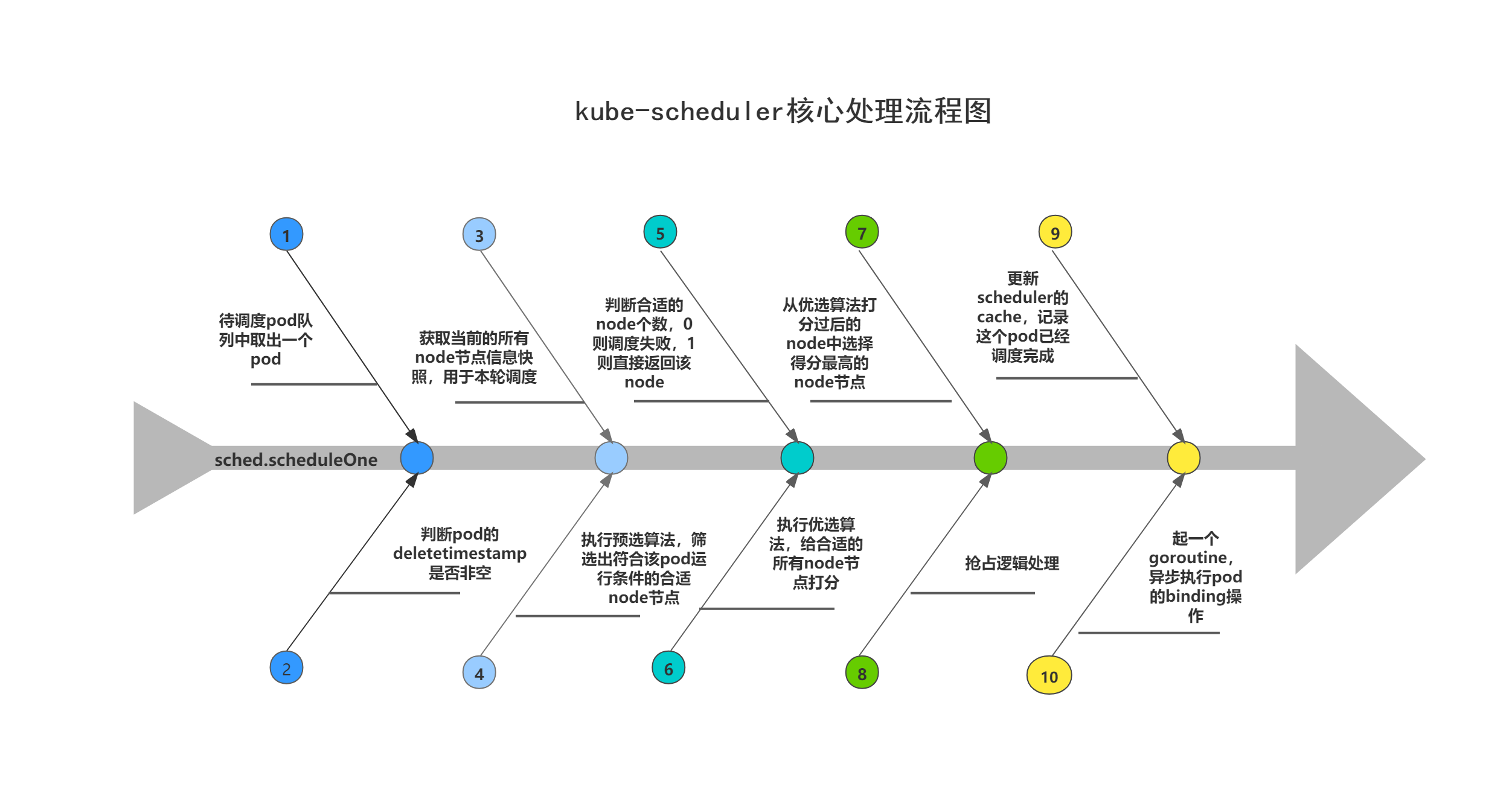
kube-scheduler核心处理流程图
下方处理流程图展示了sched.scheduleOne方法的核心处理步骤,其中kube-scheduler扩展机制相关的步骤未画出。
kube-scheduler源码分析(2)-核心处理逻辑分析的更多相关文章
- external-attacher源码分析(2)-核心处理逻辑分析
kubernetes ceph-csi分析目录导航 基于tag v2.1.1 https://github.com/kubernetes-csi/external-attacher/releases/ ...
- scheduler源码分析——preempt抢占
前言 之前探讨scheduler的调度流程时,提及过preempt抢占机制,它发生在预选调度失败的时候,当时由于篇幅限制就没有展开细说. 回顾一下抢占流程的主要逻辑在DefaultPreemption ...
- 第一篇:Spark SQL源码分析之核心流程
/** Spark SQL源码分析系列文章*/ 自从去年Spark Submit 2013 Michael Armbrust分享了他的Catalyst,到至今1年多了,Spark SQL的贡献者从几人 ...
- scheduler源码分析——调度流程
前言 当api-server处理完一个pod的创建请求后,此时可以通过kubectl把pod get出来,但是pod的状态是Pending.在这个Pod能运行在节点上之前,它还需要经过schedule ...
- Hadoop学习之--Capaycity Scheduler源码分析
Capacity Scheduler调度策略当一个新的job是否允许添加到队列中进行初始化,判断当前队列和用户是否已经达到了初始化数目的上限,下面就从代码层面详细介绍整个的判断逻辑.Capaycity ...
- scrapy-redis(调度器Scheduler源码分析)
settings里面的配置:'''当下面配置了这个(scrapy-redis)时候,下面的调度器已经配置在scrapy-redis里面了'''##########连接配置######## REDIS_ ...
- MyBatis源码分析之核心处理层
目录 1 传统方式源码剖析 1.1 初始化流程 1.2 执行SQL流程 1.2.1 获取SqlSession 1.2.2 执行SqlSession接口 1.2.3 执行Executor接口 1.2.4 ...
- flappy pig小游戏源码分析(4)——核心pig模块(未完待续)
热身之后,我们要动点真格的了,游戏叫flappy pig,我们的pig终于要出场了. 老规矩,看看目录结构,读者对着目录结构好好回想我们已经讲解的几个模块: 其中game.js是游戏主程序,optio ...
- 源码分析 | 手写mybait-spring核心功能(干货好文一次学会工厂bean、类代理、bean注册的使用)
作者:小傅哥 博客:https://bugstack.cn - 汇总系列原创专题文章 沉淀.分享.成长,让自己和他人都能有所收获! 一.前言介绍 一个知识点的学习过程基本分为:运行helloworld ...
- apiserver源码分析——启动流程
前言 apiserver是k8s控制面的一个组件,在众多组件中唯一一个对接etcd,对外暴露http服务的形式为k8s中各种资源提供增删改查等服务.它是RESTful风格,每个资源的URI都会形如 / ...
随机推荐
- xargs、管道、exec区别
作者:ilexwg链接:https://www.zhihu.com/question/27452459/answer/170834758来源:知乎著作权归作者所有.商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转 ...
- 【webpack4.0】---webpack的基本使用(二)
一.什么是plugins plugins可以使webpack在运行到某个时刻的时候,帮你做一些事情,类似于生命周期一样 plugins,它就是一个扩展器,它丰富了wepack本身,针对是loader结 ...
- 人工智能与智能系统2-> 机器人学2 | 时间与运动
<Robotics, Vision and Control>学习到第三章,我才发现这本书是有配套视频的,第二章看的好辛苦,很多地方生硬理解了一下,现在打算把视频再好好看一看,作为补充,也会 ...
- LeetCode673
LeetCode每日一题2021.9.20 LeetCode673. 最长递增子序列的个数 思路 在最长上升子序列的转移时,维护一个 cnt 数组,表示 以 i 结尾的最长上升子序列个数 f[i] 表 ...
- VUE3 之 作用域插槽 - 这个系列的教程通俗易懂,适合新手
1. 概述 破窗效应告诉我们: 当一个建筑物窗户的玻璃完好无损时,很少有人想去破坏它,当有一个人破坏了一块窗户的玻璃,其他窗户的玻璃也很快会被人破坏. 同理,一个很干净的地方,人们不好意思去丢垃圾,但 ...
- 解决死锁之路3 - 常见 SQL 语句的加锁分析 (转)
出处:https://www.aneasystone.com/archives/2017/12/solving-dead-locks-three.html 这篇博客将对一些常见的 SQL 语句进行加锁 ...
- 常见消息处理api
面试:子线程一定不能更新UI? SurfaceView :多媒体视频播放 ,可以在子线程中更新UI: Progress(进度)相关的控件:也是可以在子线程中更新Ui;审计机制:activity完全显示 ...
- Android 三种菜单(Menu)的实现
感谢大佬:https://blog.csdn.net/chileme/article/details/82944764 一.常用方法 java onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu men ...
- drop、delete和truncate三者的区别
相同点:1.truncate和不带where子句的delete.以及drop都会删除表内的数据.2.drop.truncate都是DDL语句(数据定义语言),执行后会自动提交.不同点:1. trunc ...
- Mybatis返回插入数据的主键的两种方式
方式一: 需要在映射文件中添加如下片段: <insert id="insertProduct" parameterType="domain.model.Produc ...
