k8s replicaset controller分析(1)-初始化与启动分析
replicaset controller分析
replicaset controller简介
replicaset controller是kube-controller-manager组件中众多控制器中的一个,是 replicaset 资源对象的控制器,其通过对replicaset、pod 2种资源的监听,当这2种资源发生变化时会触发 replicaset controller 对相应的replicaset对象进行调谐操作,从而完成replicaset期望副本数的调谐,当实际pod的数量未达到预期时创建pod,当实际pod的数量超过预期时删除pod。
replicaset controller主要作用是根据replicaset对象所期望的pod数量与现存pod数量做比较,然后根据比较结果创建/删除pod,最终使得replicaset对象所期望的pod数量与现存pod数量相等。
replicaset controller架构图
replicaset controller的大致组成和处理流程如下图,replicaset controller对pod和replicaset对象注册了event handler,当有事件时,会watch到然后将对应的replicaset对象放入到queue中,然后syncReplicaSet方法为replicaset controller调谐replicaset对象的核心处理逻辑所在,从queue中取出replicaset对象,做调谐处理。
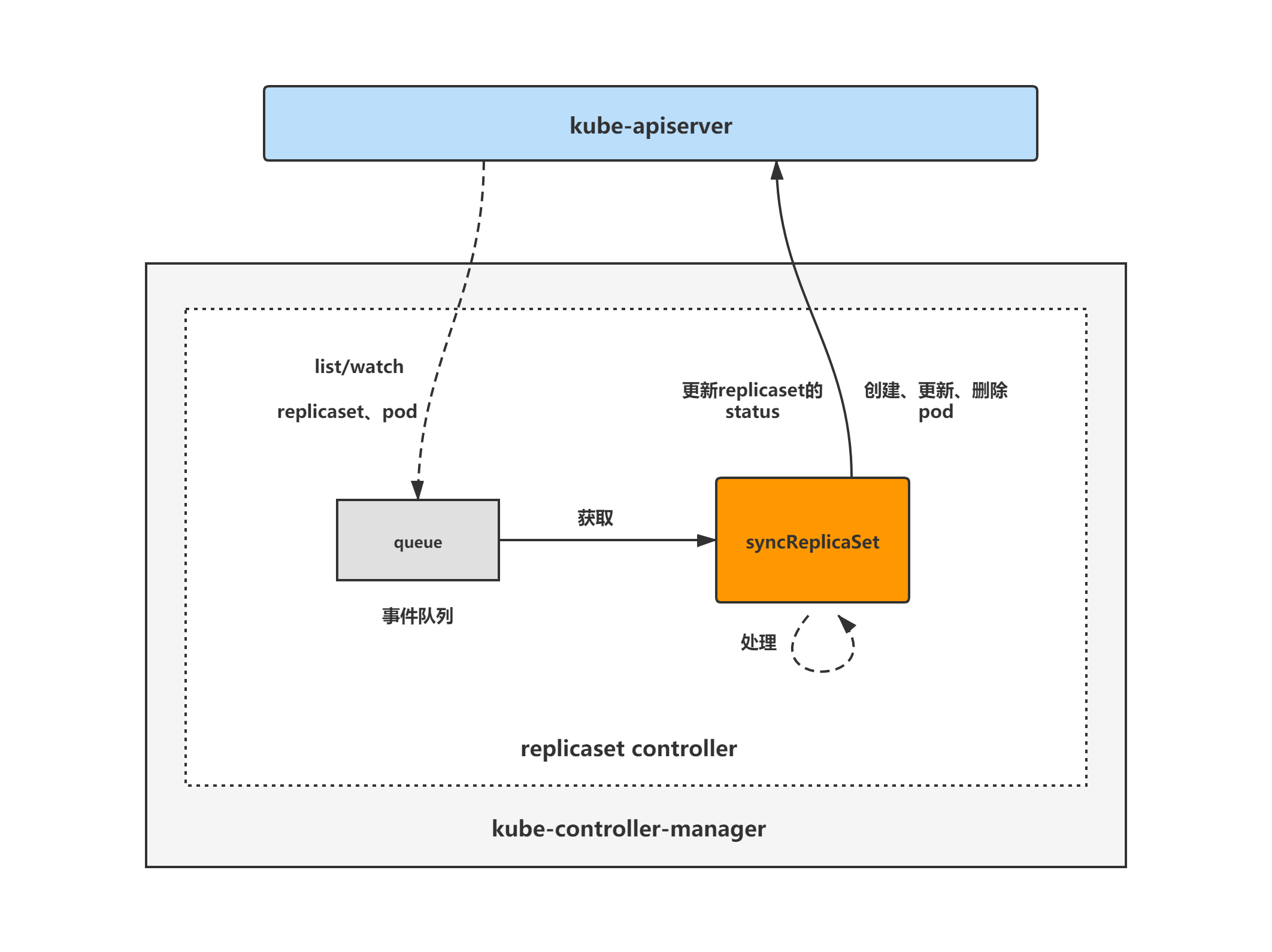
replicaset controller分析将分为3大块进行,分别是:
(1)replicaset controller初始化和启动分析;
(2)replicaset controller核心处理逻辑分析;
(3)replicaset controller expectations机制分析。
本篇博客先进行replicaset controller初始化和启动分析。
ReplicaSetController的初始化与启动分析
基于tag v1.17.4
https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/releases/tag/v1.17.4
直接以startReplicaSetController函数作为garbage collector的初始化与启动源码分析入口。
startReplicaSetController中调用了replicaset.NewReplicaSetController来进行ReplicaSetController的初始化,初始化完成后调用Run进行启动。
这里留意传入Run方法的参数ctx.ComponentConfig.ReplicaSetController.ConcurrentRSSyncs,后面会详细分析。
// cmd/kube-controller-manager/app/apps.go
func startReplicaSetController(ctx ControllerContext) (http.Handler, bool, error) {
if !ctx.AvailableResources[schema.GroupVersionResource{Group: "apps", Version: "v1", Resource: "replicasets"}] {
return nil, false, nil
}
go replicaset.NewReplicaSetController(
ctx.InformerFactory.Apps().V1().ReplicaSets(),
ctx.InformerFactory.Core().V1().Pods(),
ctx.ClientBuilder.ClientOrDie("replicaset-controller"),
replicaset.BurstReplicas,
).Run(int(ctx.ComponentConfig.ReplicaSetController.ConcurrentRSSyncs), ctx.Stop)
return nil, true, nil
}
初始化分析
分析入口 NewReplicaSetController
NewReplicaSetController主要是初始化ReplicaSetController,定义replicaset与pod对象的informer,并注册EventHandler-AddFunc、UpdateFunc与DeleteFunc等,用于监听replicaset与pod对象的变动。
// pkg/controller/replicaset/replica_set.go
// NewReplicaSetController configures a replica set controller with the specified event recorder
func NewReplicaSetController(rsInformer appsinformers.ReplicaSetInformer, podInformer coreinformers.PodInformer, kubeClient clientset.Interface, burstReplicas int) *ReplicaSetController {
eventBroadcaster := record.NewBroadcaster()
eventBroadcaster.StartLogging(klog.Infof)
eventBroadcaster.StartRecordingToSink(&v1core.EventSinkImpl{Interface: kubeClient.CoreV1().Events("")})
return NewBaseController(rsInformer, podInformer, kubeClient, burstReplicas,
apps.SchemeGroupVersion.WithKind("ReplicaSet"),
"replicaset_controller",
"replicaset",
controller.RealPodControl{
KubeClient: kubeClient,
Recorder: eventBroadcaster.NewRecorder(scheme.Scheme, v1.EventSource{Component: "replicaset-controller"}),
},
)
}
// NewBaseController is the implementation of NewReplicaSetController with additional injected
// parameters so that it can also serve as the implementation of NewReplicationController.
func NewBaseController(rsInformer appsinformers.ReplicaSetInformer, podInformer coreinformers.PodInformer, kubeClient clientset.Interface, burstReplicas int,
gvk schema.GroupVersionKind, metricOwnerName, queueName string, podControl controller.PodControlInterface) *ReplicaSetController {
if kubeClient != nil && kubeClient.CoreV1().RESTClient().GetRateLimiter() != nil {
ratelimiter.RegisterMetricAndTrackRateLimiterUsage(metricOwnerName, kubeClient.CoreV1().RESTClient().GetRateLimiter())
}
rsc := &ReplicaSetController{
GroupVersionKind: gvk,
kubeClient: kubeClient,
podControl: podControl,
burstReplicas: burstReplicas,
expectations: controller.NewUIDTrackingControllerExpectations(controller.NewControllerExpectations()),
queue: workqueue.NewNamedRateLimitingQueue(workqueue.DefaultControllerRateLimiter(), queueName),
}
rsInformer.Informer().AddEventHandler(cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
AddFunc: rsc.addRS,
UpdateFunc: rsc.updateRS,
DeleteFunc: rsc.deleteRS,
})
rsc.rsLister = rsInformer.Lister()
rsc.rsListerSynced = rsInformer.Informer().HasSynced
podInformer.Informer().AddEventHandler(cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
AddFunc: rsc.addPod,
// This invokes the ReplicaSet for every pod change, eg: host assignment. Though this might seem like
// overkill the most frequent pod update is status, and the associated ReplicaSet will only list from
// local storage, so it should be ok.
UpdateFunc: rsc.updatePod,
DeleteFunc: rsc.deletePod,
})
rsc.podLister = podInformer.Lister()
rsc.podListerSynced = podInformer.Informer().HasSynced
rsc.syncHandler = rsc.syncReplicaSet
return rsc
}
queue
queue是replicaset controller做sync操作的关键。当replicaset或pod对象发生改变,其对应的EventHandler会把该对象往queue中加入,而replicaset controller的Run方法中调用的rsc.worker(后面再做分析)会从queue中获取对象并做相应的调谐操作。
queue中存放的对象格式:namespace/name
type ReplicaSetController struct {
...
// Controllers that need to be synced
queue workqueue.RateLimitingInterface
}
queue的来源是replicaset与pod对象的EventHandler,下面来一个个分析。
1 rsc.addRS
当发现有新增的replicaset对象,会调用该方法。
主要逻辑:调用rsc.enqueueRS将该对象加入queue中。
// pkg/controller/replicaset/replica_set.go
func (rsc *ReplicaSetController) addRS(obj interface{}) {
rs := obj.(*apps.ReplicaSet)
klog.V(4).Infof("Adding %s %s/%s", rsc.Kind, rs.Namespace, rs.Name)
rsc.enqueueRS(rs)
}
rsc.enqueueRS
组装key,将key加入queue。
func (rsc *ReplicaSetController) enqueueRS(rs *apps.ReplicaSet) {
key, err := controller.KeyFunc(rs)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("couldn't get key for object %#v: %v", rs, err))
return
}
rsc.queue.Add(key)
}
2 rsc.updateRS
当发现replicaset对象有更改,会调用该方法。
主要逻辑:
(1)如果新旧replicaset对象的uid不一致,则调用rsc.deleteRS(rsc.deleteRS在后面分析);
(2)调用rsc.enqueueRS,组装key,将key加入queue。
// pkg/controller/replicaset/replica_set.go
func (rsc *ReplicaSetController) updateRS(old, cur interface{}) {
oldRS := old.(*apps.ReplicaSet)
curRS := cur.(*apps.ReplicaSet)
// TODO: make a KEP and fix informers to always call the delete event handler on re-create
if curRS.UID != oldRS.UID {
key, err := controller.KeyFunc(oldRS)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("couldn't get key for object %#v: %v", oldRS, err))
return
}
rsc.deleteRS(cache.DeletedFinalStateUnknown{
Key: key,
Obj: oldRS,
})
}
// You might imagine that we only really need to enqueue the
// replica set when Spec changes, but it is safer to sync any
// time this function is triggered. That way a full informer
// resync can requeue any replica set that don't yet have pods
// but whose last attempts at creating a pod have failed (since
// we don't block on creation of pods) instead of those
// replica sets stalling indefinitely. Enqueueing every time
// does result in some spurious syncs (like when Status.Replica
// is updated and the watch notification from it retriggers
// this function), but in general extra resyncs shouldn't be
// that bad as ReplicaSets that haven't met expectations yet won't
// sync, and all the listing is done using local stores.
if *(oldRS.Spec.Replicas) != *(curRS.Spec.Replicas) {
klog.V(4).Infof("%v %v updated. Desired pod count change: %d->%d", rsc.Kind, curRS.Name, *(oldRS.Spec.Replicas), *(curRS.Spec.Replicas))
}
rsc.enqueueRS(curRS)
}
3 rsc.deleteRS
当发现replicaset对象被删除,会调用该方法。
主要逻辑:
(1)调用rsc.expectations.DeleteExpectations方法删除该rs的expectations(关于expectations机制,会在后面单独进行分析,这里有个印象就行);
(2)组装key,放入queue中。
// pkg/controller/replicaset/replica_set.go
func (rsc *ReplicaSetController) deleteRS(obj interface{}) {
rs, ok := obj.(*apps.ReplicaSet)
if !ok {
tombstone, ok := obj.(cache.DeletedFinalStateUnknown)
if !ok {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("couldn't get object from tombstone %#v", obj))
return
}
rs, ok = tombstone.Obj.(*apps.ReplicaSet)
if !ok {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("tombstone contained object that is not a ReplicaSet %#v", obj))
return
}
}
key, err := controller.KeyFunc(rs)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("couldn't get key for object %#v: %v", rs, err))
return
}
klog.V(4).Infof("Deleting %s %q", rsc.Kind, key)
// Delete expectations for the ReplicaSet so if we create a new one with the same name it starts clean
rsc.expectations.DeleteExpectations(key)
rsc.queue.Add(key)
}
4 rsc.addPod
当发现有新增的pod对象,会调用该方法。
主要逻辑:
(1)如果pod的DeletionTimestamp属性不为空,则调用rsc.deletePod(后面再做分析),然后返回;
(2)调用metav1.GetControllerOf获取该pod对象的OwnerReference,并判断该pod是否有上层controller,有则再调用rsc.resolveControllerRef查询该pod所属的replicaset是否存在,不存在则直接返回;
(3)调用rsc.expectations.CreationObserved方法,将该rs的expectations期望创建pod数量减1(关于expectations机制,会在后面单独进行分析,这里有个印象就行);
(4)组装key,放入queue中。
注意:pod的eventHandler处理逻辑依然是将pod对应的replicaset对象加入queue中,而不是将pod加入到queue中。
// pkg/controller/replicaset/replica_set.go
func (rsc *ReplicaSetController) addPod(obj interface{}) {
pod := obj.(*v1.Pod)
if pod.DeletionTimestamp != nil {
// on a restart of the controller manager, it's possible a new pod shows up in a state that
// is already pending deletion. Prevent the pod from being a creation observation.
rsc.deletePod(pod)
return
}
// If it has a ControllerRef, that's all that matters.
if controllerRef := metav1.GetControllerOf(pod); controllerRef != nil {
rs := rsc.resolveControllerRef(pod.Namespace, controllerRef)
if rs == nil {
return
}
rsKey, err := controller.KeyFunc(rs)
if err != nil {
return
}
klog.V(4).Infof("Pod %s created: %#v.", pod.Name, pod)
rsc.expectations.CreationObserved(rsKey)
rsc.queue.Add(rsKey)
return
}
// Otherwise, it's an orphan. Get a list of all matching ReplicaSets and sync
// them to see if anyone wants to adopt it.
// DO NOT observe creation because no controller should be waiting for an
// orphan.
rss := rsc.getPodReplicaSets(pod)
if len(rss) == 0 {
return
}
klog.V(4).Infof("Orphan Pod %s created: %#v.", pod.Name, pod)
for _, rs := range rss {
rsc.enqueueRS(rs)
}
}
5 rsc.updatePod
当发现有pod对象发生更改,会调用该方法。
主要逻辑:
(1)判断新旧pod的ResourceVersion,如一致,代表无变化,直接返回;
(2)如果pod的DeletionTimestamp不为空,则调用rsc.deletePod(后面再做分析),然后返回;
(3)...
// pkg/controller/replicaset/replica_set.go
func (rsc *ReplicaSetController) updatePod(old, cur interface{}) {
curPod := cur.(*v1.Pod)
oldPod := old.(*v1.Pod)
if curPod.ResourceVersion == oldPod.ResourceVersion {
// Periodic resync will send update events for all known pods.
// Two different versions of the same pod will always have different RVs.
return
}
labelChanged := !reflect.DeepEqual(curPod.Labels, oldPod.Labels)
if curPod.DeletionTimestamp != nil {
// when a pod is deleted gracefully it's deletion timestamp is first modified to reflect a grace period,
// and after such time has passed, the kubelet actually deletes it from the store. We receive an update
// for modification of the deletion timestamp and expect an rs to create more replicas asap, not wait
// until the kubelet actually deletes the pod. This is different from the Phase of a pod changing, because
// an rs never initiates a phase change, and so is never asleep waiting for the same.
rsc.deletePod(curPod)
if labelChanged {
// we don't need to check the oldPod.DeletionTimestamp because DeletionTimestamp cannot be unset.
rsc.deletePod(oldPod)
}
return
}
curControllerRef := metav1.GetControllerOf(curPod)
oldControllerRef := metav1.GetControllerOf(oldPod)
controllerRefChanged := !reflect.DeepEqual(curControllerRef, oldControllerRef)
if controllerRefChanged && oldControllerRef != nil {
// The ControllerRef was changed. Sync the old controller, if any.
if rs := rsc.resolveControllerRef(oldPod.Namespace, oldControllerRef); rs != nil {
rsc.enqueueRS(rs)
}
}
// If it has a ControllerRef, that's all that matters.
if curControllerRef != nil {
rs := rsc.resolveControllerRef(curPod.Namespace, curControllerRef)
if rs == nil {
return
}
klog.V(4).Infof("Pod %s updated, objectMeta %+v -> %+v.", curPod.Name, oldPod.ObjectMeta, curPod.ObjectMeta)
rsc.enqueueRS(rs)
// TODO: MinReadySeconds in the Pod will generate an Available condition to be added in
// the Pod status which in turn will trigger a requeue of the owning replica set thus
// having its status updated with the newly available replica. For now, we can fake the
// update by resyncing the controller MinReadySeconds after the it is requeued because
// a Pod transitioned to Ready.
// Note that this still suffers from #29229, we are just moving the problem one level
// "closer" to kubelet (from the deployment to the replica set controller).
if !podutil.IsPodReady(oldPod) && podutil.IsPodReady(curPod) && rs.Spec.MinReadySeconds > 0 {
klog.V(2).Infof("%v %q will be enqueued after %ds for availability check", rsc.Kind, rs.Name, rs.Spec.MinReadySeconds)
// Add a second to avoid milliseconds skew in AddAfter.
// See https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/issues/39785#issuecomment-279959133 for more info.
rsc.enqueueRSAfter(rs, (time.Duration(rs.Spec.MinReadySeconds)*time.Second)+time.Second)
}
return
}
// Otherwise, it's an orphan. If anything changed, sync matching controllers
// to see if anyone wants to adopt it now.
if labelChanged || controllerRefChanged {
rss := rsc.getPodReplicaSets(curPod)
if len(rss) == 0 {
return
}
klog.V(4).Infof("Orphan Pod %s updated, objectMeta %+v -> %+v.", curPod.Name, oldPod.ObjectMeta, curPod.ObjectMeta)
for _, rs := range rss {
rsc.enqueueRS(rs)
}
}
}
6 rsc.deletePod
当发现有pod对象被删除,会调用该方法。
主要逻辑:
(1)调用metav1.GetControllerOf获取该pod对象的OwnerReference,并判断是否是controller,是则再调用rsc.resolveControllerRef查询该pod所属的replicaset是否存在,不存在则直接返回;
(2)调用rsc.expectations.DeletionObserved方法,将该rs的expectations期望删除pod数量减1(关于expectations机制,会在后面单独进行分析,这里有个印象就行);
(3)组装key,放入queue中。
// pkg/controller/replicaset/replica_set.go
func (rsc *ReplicaSetController) deletePod(obj interface{}) {
pod, ok := obj.(*v1.Pod)
// When a delete is dropped, the relist will notice a pod in the store not
// in the list, leading to the insertion of a tombstone object which contains
// the deleted key/value. Note that this value might be stale. If the pod
// changed labels the new ReplicaSet will not be woken up till the periodic resync.
if !ok {
tombstone, ok := obj.(cache.DeletedFinalStateUnknown)
if !ok {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("couldn't get object from tombstone %+v", obj))
return
}
pod, ok = tombstone.Obj.(*v1.Pod)
if !ok {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("tombstone contained object that is not a pod %#v", obj))
return
}
}
controllerRef := metav1.GetControllerOf(pod)
if controllerRef == nil {
// No controller should care about orphans being deleted.
return
}
rs := rsc.resolveControllerRef(pod.Namespace, controllerRef)
if rs == nil {
return
}
rsKey, err := controller.KeyFunc(rs)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("couldn't get key for object %#v: %v", rs, err))
return
}
klog.V(4).Infof("Pod %s/%s deleted through %v, timestamp %+v: %#v.", pod.Namespace, pod.Name, utilruntime.GetCaller(), pod.DeletionTimestamp, pod)
rsc.expectations.DeletionObserved(rsKey, controller.PodKey(pod))
rsc.queue.Add(rsKey)
}
启动分析
分析入口 Run
根据workers的值启动相应数量的goroutine,循环调用rsc.worker,从queue中取出一个key做replicaset资源对象的调谐处理。
// pkg/controller/replicaset/replica_set.go
// Run begins watching and syncing.
func (rsc *ReplicaSetController) Run(workers int, stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
defer utilruntime.HandleCrash()
defer rsc.queue.ShutDown()
controllerName := strings.ToLower(rsc.Kind)
glog.Infof("Starting %v controller", controllerName)
defer glog.Infof("Shutting down %v controller", controllerName)
if !controller.WaitForCacheSync(rsc.Kind, stopCh, rsc.podListerSynced, rsc.rsListerSynced) {
return
}
for i := 0; i < workers; i++ {
go wait.Until(rsc.worker, time.Second, stopCh)
}
<-stopCh
}
此处的workers参数由startReplicaSetController方法中传入,值为ctx.ComponentConfig.ReplicaSetController.ConcurrentRSSyncs,它的值实际由kube-controller-manager组件的concurrent-replicaset-syncs启动参数决定,当不配置时,默认值设置为5,代表会起5个goroutine来并行处理和调谐队列中的replicaset对象。
下面来看一下kube-controller-manager组件中replicaset controller相关的concurrent-replicaset-syncs启动参数。
ReplicaSetControllerOptions
// cmd/kube-controller-manager/app/options/replicasetcontroller.go
// ReplicaSetControllerOptions holds the ReplicaSetController options.
type ReplicaSetControllerOptions struct {
*replicasetconfig.ReplicaSetControllerConfiguration
}
// AddFlags adds flags related to ReplicaSetController for controller manager to the specified FlagSet.
func (o *ReplicaSetControllerOptions) AddFlags(fs *pflag.FlagSet) {
if o == nil {
return
}
fs.Int32Var(&o.ConcurrentRSSyncs, "concurrent-replicaset-syncs", o.ConcurrentRSSyncs, "The number of replica sets that are allowed to sync concurrently. Larger number = more responsive replica management, but more CPU (and network) load")
}
// ApplyTo fills up ReplicaSetController config with options.
func (o *ReplicaSetControllerOptions) ApplyTo(cfg *replicasetconfig.ReplicaSetControllerConfiguration) error {
if o == nil {
return nil
}
cfg.ConcurrentRSSyncs = o.ConcurrentRSSyncs
return nil
}
默认值设置
concurrent-replicaset-syncs参数默认值配置为5。
// pkg/controller/apis/config/v1alpha1/register.go
func init() {
// We only register manually written functions here. The registration of the
// generated functions takes place in the generated files. The separation
// makes the code compile even when the generated files are missing.
localSchemeBuilder.Register(addDefaultingFuncs)
}
// pkg/controller/apis/config/v1alpha1/defaults.go
func addDefaultingFuncs(scheme *kruntime.Scheme) error {
return RegisterDefaults(scheme)
}
// pkg/controller/apis/config/v1alpha1/zz_generated.defaults.go
func RegisterDefaults(scheme *runtime.Scheme) error {
scheme.AddTypeDefaultingFunc(&v1alpha1.KubeControllerManagerConfiguration{}, func(obj interface{}) {
SetObjectDefaults_KubeControllerManagerConfiguration(obj.(*v1alpha1.KubeControllerManagerConfiguration))
})
return nil
}
func SetObjectDefaults_KubeControllerManagerConfiguration(in *v1alpha1.KubeControllerManagerConfiguration) {
SetDefaults_KubeControllerManagerConfiguration(in)
SetDefaults_KubeCloudSharedConfiguration(&in.KubeCloudShared)
}
// pkg/controller/apis/config/v1alpha1/defaults.go
func SetDefaults_KubeControllerManagerConfiguration(obj *kubectrlmgrconfigv1alpha1.KubeControllerManagerConfiguration) {
...
// Use the default RecommendedDefaultReplicaSetControllerConfiguration options
replicasetconfigv1alpha1.RecommendedDefaultReplicaSetControllerConfiguration(&obj.ReplicaSetController)
...
}
// pkg/controller/replicaset/config/v1alpha1/defaults.go
func RecommendedDefaultReplicaSetControllerConfiguration(obj *kubectrlmgrconfigv1alpha1.ReplicaSetControllerConfiguration) {
if obj.ConcurrentRSSyncs == 0 {
obj.ConcurrentRSSyncs = 5
}
}
分析完replicaset controller启动参数后,来看一下启动后调用的核心处理方法。
1 rsc.worker
前面提到,在replicaset controller的Run方法中,会根据workers的值启动相应数量的goroutine,循环调用rsc.worker,从queue中取出一个key做replicaset资源对象的调谐处理。
rsc.worker主要逻辑:
(1)从queue中获取一个key;
(2)调用rsc.syncHandler对该key做进一步处理;
(3)从queue中去除该key。
// worker runs a worker thread that just dequeues items, processes them, and marks them done.
// It enforces that the syncHandler is never invoked concurrently with the same key.
func (rsc *ReplicaSetController) worker() {
for rsc.processNextWorkItem() {
}
}
func (rsc *ReplicaSetController) processNextWorkItem() bool {
key, quit := rsc.queue.Get()
if quit {
return false
}
defer rsc.queue.Done(key)
err := rsc.syncHandler(key.(string))
if err == nil {
rsc.queue.Forget(key)
return true
}
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("Sync %q failed with %v", key, err))
rsc.queue.AddRateLimited(key)
return true
}
1.1 rsc.syncHandler
调用rsc.syncHandler实际为调用rsc.syncReplicaSet方法,rsc.syncHandler在NewBaseController中被赋值为rsc.syncReplicaSet,后续分析核心处理逻辑时再具体分析rsc.syncHandler,此处不做深入分析。
// NewBaseController is the implementation of NewReplicaSetController with additional injected
// parameters so that it can also serve as the implementation of NewReplicationController.
func NewBaseController(rsInformer appsinformers.ReplicaSetInformer, podInformer coreinformers.PodInformer, kubeClient clientset.Interface, burstReplicas int,
gvk schema.GroupVersionKind, metricOwnerName, queueName string, podControl controller.PodControlInterface) *ReplicaSetController {
...
rsc.syncHandler = rsc.syncReplicaSet
return rsc
}
总结
replicaset controller是kube-controller-manager组件中众多控制器中的一个,是 replicaset 资源对象的控制器,其通过对replicaset、pod 2种资源的监听,当这2种资源发生变化时会触发 replicaset controller 对相应的replicaset对象进行调谐操作,从而完成replicaset期望副本数的调谐,当实际pod的数量未达到预期时创建pod,当实际pod的数量超过预期时删除pod。
本篇博客对replicaset controller的初始化和启动做了分析,其中对replicaset controller注册的pod和replicaet对象的event handler做了代码分析,以及replicaset controller如何启动,注册了什么方法作为核心处理逻辑方法做了分析与介绍。
replicaset controller架构图
replicaset controller的大致组成和处理流程如下图,replicaset controller对pod和replicaset对象注册了event handler,当有事件时,会watch到然后将对应的replicaset对象放入到queue中,然后syncReplicaSet方法为replicaset controller调谐replicaset对象的核心处理逻辑所在,从queue中取出replicaset对象,做调谐处理。
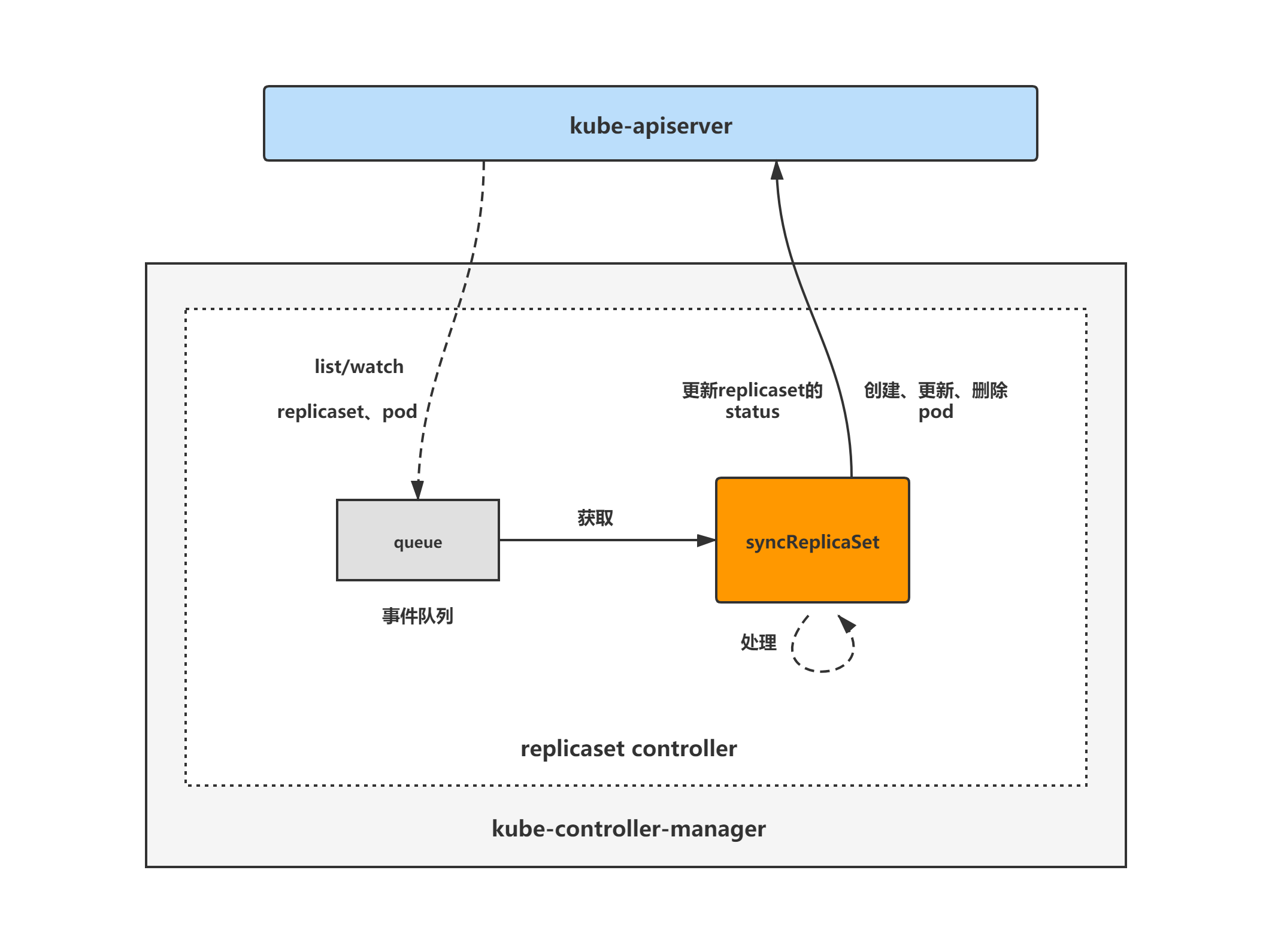
接下来的两篇博客,会依次给大家做replicaset controller的核心处理逻辑以及expectations机制的分析,敬请期待。
k8s replicaset controller分析(1)-初始化与启动分析的更多相关文章
- k8s client-go源码分析 informer源码分析(2)-初始化与启动分析
k8s client-go源码分析 informer源码分析(2)-初始化与启动分析 前面一篇文章对k8s informer做了概要分析,本篇文章将对informer的初始化与启动进行分析. info ...
- k8s replicaset controller分析(2)-核心处理逻辑分析
replicaset controller分析 replicaset controller简介 replicaset controller是kube-controller-manager组件中众多控制 ...
- k8s replicaset controller 分析(3)-expectations 机制分析
replicaset controller分析 replicaset controller简介 replicaset controller是kube-controller-manager组件中众多控制 ...
- k8s garbage collector分析(1)-启动分析
k8s garbage collector分析(1)-启动分析 garbage collector介绍 Kubernetes garbage collector即垃圾收集器,存在于kube-contr ...
- kube-scheduler源码分析(1)-初始化与启动分析
kube-scheduler源码分析(1)-初始化与启动分析 kube-scheduler简介 kube-scheduler组件是kubernetes中的核心组件之一,主要负责pod资源对象的调度工作 ...
- Solr初始化源码分析-Solr初始化与启动
用solr做项目已经有一年有余,但都是使用层面,只是利用solr现有机制,修改参数,然后监控调优,从没有对solr进行源码级别的研究.但是,最近手头的一个项目,让我感觉必须把solrn内部原理和扩展机 ...
- k8s deployment controller源码分析
deployment controller简介 deployment controller是kube-controller-manager组件中众多控制器中的一个,是 deployment 资源对象的 ...
- k8s endpoints controller分析
k8s endpoints controller分析 endpoints controller简介 endpoints controller是kube-controller-manager组件中众多控 ...
- k8s daemonset controller源码分析
daemonset controller分析 daemonset controller简介 daemonset controller是kube-controller-manager组件中众多控制器中的 ...
随机推荐
- kubernetes使用jenkins Pipeline 部署Nginx
文章原文 环境需求 kubernetes 未安装参考使用kubeadm安装kubernetes 1.21 jenkins github/gitee/gitlab 静态页面 镜像仓库(我使用的 hub. ...
- 性能环境之docker操作指南4(全网最全)
容器的常用操作 docker run -i -t /bin/bash 使用image创建container并进入交互模式, login shell是/bin/bash 实例: $ docker ru ...
- js 点击复制文字
复制input里面的文字 html: <input id="content" class="form-control" type="text&q ...
- Tars | 第7篇 TarsJava Subset最终代码的测试方案设计
目录 前言 1. SubsetConf配置项的结构 1.1 SubsetConf 1.2 RatioConfig 1.3 KeyConfig 1.4 KeyRoute 1.5 SubsetConf的结 ...
- go语言游戏服务端开发(二)——网络通信
一.网络层 网络游戏客户端除了全局登录使用http请求外,一般通过socket长连接与服务端保持连接.go语言的net包提供网络socket长连接相关操作. 对于服务端,一般经历 Listen.Acc ...
- Oracle体系结构二
- 一文带你了解.Net读写锁
本文主要讲解.Net基于ReaderWriterLockSlim讲解读写锁 基础概念 读写锁是一个具有特殊用途的线程锁,适用于频繁读取且读取需要一定时间的场景,共享资源的读取操作通常是可以同时执行的, ...
- POJ1741——Tree(树的点分治)
1 /* *********************************************** 2 Author :kuangbin 3 Created Time :2013-11-17 1 ...
- ecshop调用指定栏目下的文章的方法
打开 index.php 添加 fun函数一个,需放在<php与?>中间. /** * 获得指定栏目的文章列表. * @param int $cid 栏目ID * @param int $ ...
- CS:APP Chapter-6 存储器层次系统-读书笔记
存储器层次系统 笔记,应该不是一个大而全的文件,笔记应该是提纲挈领,是对思想的汇总浓缩,如果追求详实的内容反而是丢了初心. 计算机是抽象的,它的设计者努力让计算机变得简单,在设计上高度抽象,而计算机的 ...
