【LeetCode】142. Linked List Cycle II 解题报告(Python & C++)
作者: 负雪明烛
id: fuxuemingzhu
个人博客: http://fuxuemingzhu.cn/
题目地址:https://leetcode.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/description/
题目描述
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null.
To represent a cycle in the given linked list, we use an integer pos which represents the position (0-indexed) in the linked list where tail connects to. If pos is -1, then there is no cycle in the linked list.
Note: Do not modify the linked list.
Example 1:
Input: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
Output: tail connects to node index 1
Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the second node.
Example 2:
Input: head = [1,2], pos = 0
Output: tail connects to node index 0
Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where tail connects to the first node.
Example 3:
Input: head = [1], pos = -1
Output: no cycle
Explanation: There is no cycle in the linked list.
Follow up:
- Can you solve it without using extra space?
题目大意
找出单链表是否有环,如果有环返回环的入口,否则返回None.
解题方法
双指针
做过之前判断一个单链表中是否有环的题,我们知道可以通过一个指针走两步,一个指针走一步的方式,看两者是否相遇即可。这个题是之前的拓展。
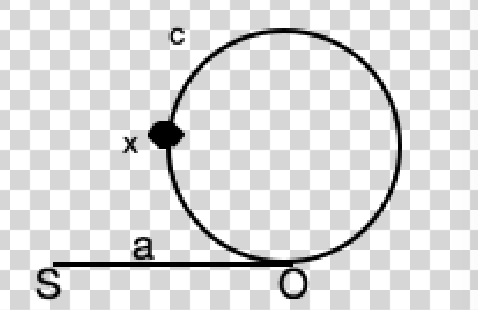
如图所示,两个指针同时从直线起点开始,这个圈是顺时针方向走的,即走的顺序是S-O-x-c-O-x。
感谢评论区指正,如果SO线段的长度a足够长,而圈很小的时候,当两者相遇时,快指针多走的可能不止一圈。下面要证明如果相遇之后,慢指针回到原点继续走再相遇的点在O点。
首先要证明的是,两指针相遇时,慢指针还没有走完整个链表。
- 当慢指针没走完一圈时,显然成立
- 假设慢指针走完了一圈之后相遇,可以假定快指针在O的前一个位置,慢指针走一圈回到了O点,此时快指针走了两圈又回到了O的前一个位置,所以在慢指针走玩一圈之前就已经相遇。
快慢指针在x处第一次汇合,xo之间距离为x,假如快指针走了n圈,快指针走过的路程为a+x+n*(c + x),慢指针走过的路程为a+x,所以a+x+n*(c + x) = 2(a+x),所以a + x = n*(c + x),也就是SOx之间的距离等于n圈的长度,所以令慢指针从起点开始一次一步,快指针从x开始顺时针方向转也一次一步,同时前进,则慢指针走a时,快指针走了n*(c+x) - x的长度,则必会在O处相遇!
同时注意题目中说了,有可能不存在环,所以要进行判断。
二刷的时候提交错误了几次,原因在于判断fast == slow的时候写错位置了。应该写在移动指针之后,而不是在while循环刚开始的时候就判断。因为刚开始就判断的话,那么底下移动之后,可能直接就退出while了,没有做是否相等的判断。
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution(object):
def detectCycle(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
slow, fast = head, head
while fast and fast.next:
fast = fast.next.next
slow = slow.next
if fast == slow:
break
if not fast or not fast.next:
return None
slow = head
while slow != fast:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next
return fast
C++代码如下:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
if (!head) return nullptr;
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* slow = head;
while (fast && fast->next) {
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
if (slow == fast)
break;
}
if (!fast || !fast->next || slow != fast) return nullptr;
slow = head;
while (slow != fast) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return fast;
}
};
set
其实也可以简单一点,如果我们保存走过的每个位置不就好了吗?所以,对于Python来说,可以直接把对象放到set中去,这样,当我们再次遍历到已经访问过的节点时,说明有了环,直接返回该节点即可。
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution(object):
def detectCycle(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
if not head: return None
visited = set()
while head:
if head in visited:
return head
visited.add(head)
head = head.next
return None
对于C++来说,有set和unordered_set两种集合,这里使用unordered_set,里面存放的内容是指向节点的指针,放指针一是可以成功存放,第二是如果已经遍历过了某个节点就相当于遍历过了这个指针。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
if (!head) return nullptr;
unordered_set<ListNode*> visited;
while (head) {
if (visited.count(head))
return head;
visited.insert(head);
head = head->next;
}
return nullptr;
}
};
参考资料:
http://blog.csdn.net/monkeyduck/article/details/50439840
https://blog.csdn.net/l294265421/article/details/50478818
日期
2018 年 3 月 12 日
2019 年 1 月 11 日 —— 小光棍节?
【LeetCode】142. Linked List Cycle II 解题报告(Python & C++)的更多相关文章
- 【算法分析】如何理解快慢指针?判断linked list中是否有环、找到环的起始节点位置。以Leetcode 141. Linked List Cycle, 142. Linked List Cycle II 为例Python实现
引入 快慢指针经常用于链表(linked list)中环(Cycle)相关的问题.LeetCode中对应题目分别是: 141. Linked List Cycle 判断linked list中是否有环 ...
- LeetCode: Linked List Cycle II 解题报告
Linked List Cycle II Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cyc ...
- Java for LeetCode 142 Linked List Cycle II
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null. Foll ...
- [LeetCode] 142. Linked List Cycle II 链表中的环 II
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null. Foll ...
- [LeetCode] 142. Linked List Cycle II 单链表中的环之二
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null. To r ...
- LeetCode 142. Linked List Cycle II 判断环入口的位置 C++/Java
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null. To r ...
- (链表 双指针) leetcode 142. Linked List Cycle II
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null. To r ...
- leetcode 142. Linked List Cycle II
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null. Note ...
- leetcode 142. Linked List Cycle II ----- java
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null. Note ...
随机推荐
- 二进制免编译My SQL
一 下载 MySQL 安装包教程 https://blog.csdn.net/zhan107876/article/details/100701135 ll -h mysql-5.6.47-linux ...
- linux系统中安装JDK
安装之前的准备工作 查看系统中之前安装好的JDK java –version rpm -qa | grep java 卸载JDK (以java-1.7.0-openjdk-1.7.0.45-2.4.3 ...
- Spark(四)【RDD编程算子】
目录 测试准备 一.Value类型转换算子 map(func) mapPartitions(func) mapPartitions和map的区别 mapPartitionsWithIndex(func ...
- 案例 stm32的dma传输过程
首先说一下:DMA_GetCurrDataCounter返回值是什么 返回值是dma缓存里还剩余多少空间. 上面本来应该是,发一下,改变一下.但是这里有一行是特殊的. long : 461,*ff l ...
- 【STM8】STM8S介绍(编程环境、烧录、芯片内容)(Vcap需要一个电容接地)
这篇博客的介绍大纲 [1]我使用的开发板和烧录器 [2]编程环境 [3]烧录软件和界面 [4]芯片内容 [1]我使用的开发板和烧录器 首先,我用的是STM8S003F3P6这款开发板,淘宝上就有了,5 ...
- 转 Android中Activity的启动模式(LaunchMode)和使用场景
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/sinat_14849739/article/details/78072401本文出自Shawpoo的专栏我的简书:简书 一.为什么需要启动模 ...
- Linux基础命令---mysqlimport导入数据库
mysqlimport mysqlimport指令可以用来将文本文件中的数据导入到数据库.在导入文本文件的时候,必须确保数据库中有一张表,而且他的名字和文本文件的名字是一样的. 此命令的适用范围:Re ...
- oracle 预安装命令
yum install oracle-rdbms-server-11gR2-preinstall-1.0-6.el6
- Ruby Gems更换淘宝源方法
官方的 Rubygems 源由于有些资源放在 Amazon S3 上面,所以有时会抽风,在 Linux 下我用 proxychains gem install xxx 实现了指定程序实行 Shadow ...
- 【Linux】【Commands】文件管理工具
文件管理工具:cp, mv, rm cp命令:copy 源文件:目标文件 单源复制:cp [OPTION]... [-T] SOURCE DEST 多源复制:cp [OPTION]... SOURCE ...