【集训笔记】贪心算法【HDOJ1052 【HDOJ2037
FatMouse' Trade
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 38780 Accepted Submission(s): 12797
The warehouse has N rooms. The i-th room contains J[i] pounds of JavaBeans and requires F[i] pounds of cat food. FatMouse does not have to trade for all the JavaBeans in the room, instead, he may get J[i]* a% pounds of JavaBeans if he pays F[i]* a% pounds of cat food. Here a is a real number. Now he is assigning this homework to you: tell him the maximum amount of JavaBeans he can obtain.
31.500
- while(num < m){
- if(flag == n)
- break;
- if(a[flag].f ==){
- flag++;
- }else{
- ans+=a[flag].di;
- a[flag].f-=;
- num++;
- }
- }
Later:
- #include<stdio.h>
- struct sc{
- int f,j;
- double di;
- }a[],temp;
- int main ()
- {
- int num,n,m,i,j,flag;
- double ans;
- while(scanf("%d%d",&m,&n)!=EOF){
- if(m==-&&n==-)
- break;
- ans=;
- num=;
- for(i=;i<n;i++){
- scanf("%d%d",&a[i].j,&a[i].f);
- a[i].di=(double)a[i].j/(double)a[i].f;
- }
- for(i=;i<n;i++){
- for(j=n-;j>=i;j--){
- if(a[j].di > a[j-].di){
- temp=a[j];a[j]=a[j-];a[j-]=temp;
- }
- }
- }
- flag=;
- while(num < m){
- if(flag == n)
- break;
- if(a[flag].f+num<= m){
- ans+=a[flag].j;
- num+=a[flag].f;
- flag++;
- }
- else if(a[flag].f+num > m){
- ans+=a[flag].di;
- num++;
- }
- }
- printf("%.3lf\n",ans);
- }
- return ;
- }
HDOJ2037:(这也是一道上个学期A不了的题目)
今年暑假不AC
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 24701 Accepted Submission(s): 12935
“是的。”
“那你干什么呢?”
“看世界杯呀,笨蛋!”
“@#$%^&*%...”
确实如此,世界杯来了,球迷的节日也来了,估计很多ACMer也会抛开电脑,奔向电视了。
作为球迷,一定想看尽量多的完整的比赛,当然,作为新时代的好青年,你一定还会看一些其它的节目,比如新闻联播(永远不要忘记关心国家大事)、非常6+7、超级女生,以及王小丫的《开心辞典》等等,假设你已经知道了所有你喜欢看的电视节目的转播时间表,你会合理安排吗?(目标是能看尽量多的完整节目)
1 3
3 4
0 7
3 8
15 19
15 20
10 15
8 18
6 12
5 10
4 14
2 9
0
- #include<stdio.h>
- struct sc{
- int s,e;
- }a[],tmp;
- int main ()
- {
- int i,j,t;
- int ti,now,ans;
- while(scanf("%d",&t)!=EOF){
- if(t==)
- break;
- for(i=;i<t;i++)
- scanf("%d%d",&a[i].s,&a[i].e);
- for(i=;i<t;i++){
- for(j=t-;j>=i;j--){
- if(a[j].e < a[j-].e){
- tmp=a[j];a[j]=a[j-];a[j-]=tmp;
- }
- }
- }
- now=;
- ans=;
- int last,flag,min;
- while(){
- //printf("now s= %d e = %d\n",a[now].s,a[now].e);
- flag=;
- for(i=now+;i<t;i++){
- if(a[i].s >= a[now].e)
- flag=;
- }
- if(!flag)
- break;
- last=;
- min=;
- for(i=now+;i<t;i++){
- //printf("%d \n",a[i].s - a[now].e );
- if(a[i].e - a[now].e < min && a[i].s - a[now].e >= ){
- min=a[i].e - a[now].e;
- last=i;
- }
- }
- if(min!=){
- ans++;
- now=last;
- }
- }
- printf("%d\n",ans);
- }
- return ;
- }
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 10334 Accepted Submission(s): 2877
"That was about 2300 years ago. General Tian Ji was a high official in the country Qi. He likes to play horse racing with the king and others."
"Both of Tian and the king have three horses in different classes, namely, regular, plus, and super. The rule is to have three rounds in a match; each of the horses must be used in one round. The winner of a single round takes two hundred silver dollars from the loser."
"Being the most powerful man in the country, the king has so nice horses that in each class his horse is better than Tian's. As a result, each time the king takes six hundred silver dollars from Tian."
"Tian Ji was not happy about that, until he met Sun Bin, one of the most famous generals in Chinese history. Using a little trick due to Sun, Tian Ji brought home two hundred silver dollars and such a grace in the next match."
"It was a rather simple trick. Using his regular class horse race against the super class from the king, they will certainly lose that round. But then his plus beat the king's regular, and his super beat the king's plus. What a simple trick. And how do you think of Tian Ji, the high ranked official in China?"
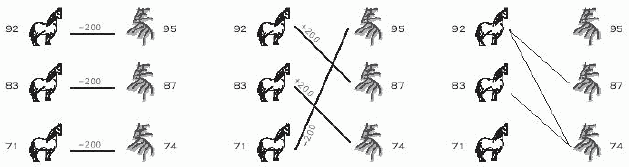
Were Tian Ji lives in nowadays, he will certainly laugh at himself. Even more, were he sitting in the ACM contest right now, he may discover that the horse racing problem can be simply viewed as finding the maximum matching in a bipartite graph. Draw Tian's horses on one side, and the king's horses on the other. Whenever one of Tian's horses can beat one from the king, we draw an edge between them, meaning we wish to establish this pair. Then, the problem of winning as many rounds as possible is just to find the maximum matching in this graph. If there are ties, the problem becomes more complicated, he needs to assign weights 0, 1, or -1 to all the possible edges, and find a maximum weighted perfect matching...
However, the horse racing problem is a very special case of bipartite matching. The graph is decided by the speed of the horses --- a vertex of higher speed always beat a vertex of lower speed. In this case, the weighted bipartite matching algorithm is a too advanced tool to deal with the problem.
In this problem, you are asked to write a program to solve this special case of matching problem.
题意:田忌赛马。田忌和齐王各有n匹马,输入田忌的马的速度和齐王的马的速度。每一轮田忌赢了就得200两银子,平就得0两,输了就失去200两银子。问田忌最多能得到多少。题目的策略是贪心,分析见leokan大牛的blog,这里也转一下,留存根。
http://hi.baidu.com/leokan/blog/item/126da06e1dab5ade80cb4a4f.html
算法可以用DP,或者给每匹马连线赋权变为二分图最佳匹配,还有就是贪心了。
1.当田忌最慢的马比齐王最慢的马快,赢一场先
2.当田忌最慢的马比齐王最慢的马慢,和齐王最快的马比,输一场
3.当田忌最快的马比齐王最快的马快时,赢一场先。
4.当田忌最快的马比齐王最快的马慢时,拿最慢的马和齐王最快的马比,输一场。
5.当田忌最快的马和齐王最快的马相等时,拿最慢的马来和齐王最快的马比.
田忌赛马贪心的正确性证明。
先说简单状况下的证明:
1.当田忌最慢的马比齐王最慢的马快,赢一场先。因为始终要赢齐王最慢的马,不如用最没用的马来赢它。
2.当田忌最慢的马比齐王最慢的马慢,和齐王最快的马比,输一场。因为田忌最慢的马始终要输的,不如用它来消耗齐王最有用的马。
3.当田忌最慢的和齐王最慢的马慢相等时,分4和5讨论。
4.当田忌最快的马比齐王最快的马快时,赢一场先。因为最快的马的用途就是来赢别人快的马,别人慢的马什么马都能赢。
5.当田忌最快的马比齐王最快的马慢时,拿最慢的马和齐王最快的马比,输一场,因为反正要输一场,不如拿最没用的马输。
6.当田忌最快的马和齐王最快的马相等时,这就要展开讨论了,贪心方法是,拿最慢的马来和齐王最快的马比.
前面的证明像公理样的,大家一看都能认同的,没有异议的,就不细说了。
证明:田忌最快的马和齐王最快的马相等时拿最慢的马来和齐王最快的马比有最优解。
1)假设他们有n匹马,看n=2的时候.
a1 a2
b1 b2
因为 田忌最快的马和齐王最快的马相等 所以a1=b1,a2=b2 所以这种情况有2种比赛方式,易得这两种方式得分相等。
2)当数列a和数列b全部相等等时(a1=b1,a2=b2...an=bn),显然最慢的马来和齐王最快的马比有最优解,可以赢n-1长,输1场,找不到更好的方
法了。
3)当数列a和数列b元素全部相等时(a1=b1=a2=b2...=an=bn),无法赢也不输。
现在假设n匹马时拿最慢的马来和齐王最快的马比有最优解,证明有n+1匹马时拿最慢的马来和齐王最快的马比也有最优解。
数列
a1 a2 a3 a4...an an+1
b1 b2 b3 b4...bn bn+1
其中ai>=ai-1,bi>=bi-1
数列a和数列b不全部相等时,拿最慢的马来和齐王最快的马比数列得到数列
(a1) a2 a3 a4...an an+1
b1 b2 b3 b4...bn (bn+1)
分4种情况讨论
1.b1=b2,an=an+1
则有
a2 a3 a4...an
b2 b3 b4...bn
其中a2>=a1,a1=b1,b1=b2,得a2>=b2(此后这种大小关系不再论述),an>=bn.
此时若a2=b1,根据归纳假设,有最优解,否则a2>根据前面“公理”论证有最优解。
当且仅当a数列,b数列元素全部相等时有an+1=b1,已证得,所以an+1>b1,赢回最慢的马来和齐王最快的马比输的那一场。
2.b1<=b2,an=an+1
交换 b1,b2的位置,
数列
(a1) a2 a3 a4...an an+1
b2 b1 b3 b4...bn (bn+1)
此时 a2>=a1,an>=bn,
对于子表
a2 a3 a4...an
b1 b3 b4...bn
根据前面“公理”或归纳假设,有最优解。
an+1>=b2, 当且仅当b2=b3=b4=..=bn+1时有an+1=b2,这种情况,a中其它元素<=b1,b2,b3,b4..bn,对于这部分来说,能赢 x盘(x<=n),假如不拿最慢的马来和齐王最快的马比则拿最快的马来和齐王最快的马比,此时平一盘,能赢x-1盘,而拿最慢的马来和齐王最快的马 比,输一盘能赢x盘,总的来说,还是X这个数,没有亏。
3.b1=b2,an<=an+1
4.b1<=b2,an<=an+1证明方法类似,不再重复。
以证得当有n+1匹马的时候,田忌和齐王最快最慢的马速度相等时,拿最慢的马来和齐王最快的马比有最优解,已知当n=2时成立,所以对于n>2且为整数(废话,马的只数当然是整数)时也成立。当n=1时....这个似乎不用讨论.
AC代码from(http://www.cnblogs.com/Action-/archive/2012/07/03/2574744.html):
- #include <iostream>
- #include<cstdio>
- #include<cstring>
- #include<algorithm>
- using namespace std;
- bool cmp(int a,int b)
- {
- return a>b;
- }
- int main()
- {
- int n,money;
- int a[],b[];
- while(cin>>n)
- {
- if(!n)
- break;
- for(int i=;i<n;i++)
- cin>>a[i];
- for(int i=;i<n;i++)
- cin>>b[i];
- sort(a,a+n,cmp);
- sort(b,b+n,cmp);
- money=;
- for(int i=n-;i>=;i--)
- {
- if(a[i]>b[i])
- {
- money++;
- }
- else if(a[i]<b[i])
- {
- money--;
- for(int j=;j<i;j++)
- b[j]=b[j+];
- }
- else if(a[i]==b[i])
- {
- if(a[]>b[])
- {
- money++;
- for(int j=;j<i;j++)
- {
- a[j]=a[j+];
- b[j]=b[j+];
- }
- }
- else if(a[]<b[])
- {
- money--;
- for(int j=;j<i;j++)
- b[j]=b[j+];
- }
- else
- {
- if(a[i]>b[])
- {
- money++;
- for(int j=;j<i;j++)
- b[j]=b[j+];
- }
- else if(a[i]<b[])
- {
- money--;
- for(int j=;j<i;j++)
- b[j]=b[j+];
- }
- }
- }
- }
- cout<<money*<<endl;
- }
- return ;
- }
【集训笔记】贪心算法【HDOJ1052 【HDOJ2037的更多相关文章
- hdoj2037 贪心算法——今年暑假不AC
所谓“贪心算法”是指:在对问题求解时,总是作出在当前看来是最好的选择.也就是说,不从整体上加以考虑,它所作出的仅仅是在某种意义上的局部最优解(是否是全局最优,需要证明). 经典问题:时间序列问题 ...
- 组合优化学习笔记<之>从贪心算法到子集系统再到拟阵
贪心算法是用的比较多的一种优化算法,因为它过程简洁优美,而且结果有效.有些优化问题如最大权森林(MWF)是可以用贪心问题求解的,由于最小支撑树(MST)问题与MWF是等价的,所以MST也是可以用贪心算 ...
- 贪心算法(Greedy Algorithm)
参考: 五大常用算法之三:贪心算法 算法系列:贪心算法 贪心算法详解 从零开始学贪心算法 一.基本概念: 所谓贪心算法是指,在对问题求解时,总是做出在当前看来是最好的选择.也就是说,不从整体最优上加以 ...
- 算法导论----贪心算法,删除k个数,使剩下的数字最小
先贴问题: 1个n位正整数a,删去其中的k位,得到一个新的正整数b,设计一个贪心算法,对给定的a和k得到最小的b: 一.我的想法:先看例子:a=5476579228:去掉4位,则位数n=10,k=4, ...
- LEETCODE —— Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II [贪心算法]
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II Say you have an array for which the ith element is the price of a ...
- ACM_ICPC hdu-2111(简单贪心算法)
一道非常简单的贪心算法,但是要注意输入的价值是单位体积的价值,并不是这个物品的总价值!#include <iostream> #include <stdio.h> #inclu ...
- 基于贪心算法的几类区间覆盖问题 nyoj 12喷水装置(二) nyoj 14会场安排问题
1)区间完全覆盖问题 问题描述:给定一个长度为m的区间,再给出n条线段的起点和终点(注意这里是闭区间),求最少使用多少条线段可以将整个区间完全覆盖 样例: 区间长度8,可选的覆盖线段[2,6],[1, ...
- 增强学习贪心算法与Softmax算法
(一) 这个算法是基于一个概率来对探索和利用进行折中:每次尝试时,以概率进行探索,即以均匀概率随机选取一个摇臂,以的概率进行利用,即以这个概率选择当前平均奖赏最高的摇臂(如有多个,则随机选取). 其中 ...
- 【九度OJ】题目1434贪心算法
题目 本题的贪心算法策略需要深入思考一下 看到题目,最初没有理解题目的要求:看尽量多的完整的节目.尽量多是指数量多,自己理解成观看的时间最长.这样想其实简化了这道题. 正确理解题意后,首先想到的想法是 ...
- 题目1437:To Fill or Not to Fill:贪心算法解决加油站选择问题(未解决)
//贪心算法解决加油站选择问题 //# include<iostream> # include<stdio.h> using namespace std; # include& ...
随机推荐
- 理解Python的with as语句
简单的说, with open(filepath, 'wb') as file: file.write("something") 等价于: file = open(filepath ...
- Lotus Sametime 服务器的安装和配置
IBM Lotus Sametime 是一款强大的实时协作软件,目前最新版本是 7.5.1.通过它,您不仅能够进行网络聊天,而且可以方便地召开网络会议.在网络社区中与其他人进行沟通.了解更多关于 Lo ...
- Spring RESTful服务接收和返回JSON最佳实践
http://blog.csdn.net/prince_hua/article/details/12103501
- cocos2dx中的精灵CCSprite
什么是精灵(CCSprite),在官网文档中是这么定义的 Sprites A cocos2d CCSprite is similar to sprites you find in other game ...
- 基于Visual C++2013拆解世界五百强面试题--题1-定义各种类型指针
用变量a给出下面的定义 a)一个整型数 b)一个指向整型数的指针 c)一个指向指针的指针,它指向的指针是指向一个整型数 d)一个有10个整型数的数组 e)一个有10个指针 ...
- 用Visual C++设计“精灵”窗体
随着Microsoft凭借Windows在操作系统上取得的巨大成绩,Windows用户界面也日益成为业界标准.统一的界面给广大用户对应用软件的学习与使用带来了很大方便.但每天都面对同一副面孔,日久天长 ...
- 变脸不变质的桥梁模式(Bridge Pattern)
有一哥们是搞山寨货的,什么流行就搞什么.自己有个厂子,前些时间服装挣钱,就生产衣服,如今搞手机挣钱,搞手机,这哥们非常聪明,就换了个产品,工人,厂房都不变.他是怎么做到的?用类图来模拟一下: 由类图能 ...
- .c和.h文件的区别(头文件与之实现文件的的关系~ )
.c和.h文件的区别 一个简单的问题:.c和.h文件的区别 学了几个月的C语言,反而觉得越来越不懂了.同样是子程序,可以定义在.c文件中,也可以定义在.h文件中,那这两个文件到底在用法上有什么区别呢 ...
- SQL数据库语句练习题目
一. 设有一数据库,包括四个表:学生表(Student).课程表(Course).成绩表(Score)以及教师信息表(Teacher).四个表的结构分别如表1-1的表(一)~表( ...
- 一个简单二叉树的C++实现(一)
很久没有接触二叉树了,写这个当作练手,接下来会比较详细地实现二叉树的各个功能及应用. /* * BinaryTree.cpp * Author: Qiang Xiao * Time: 2015-07- ...
