JavaSE学习总结第17天_集合框架3
17.01 ArrayList集合的toString()方法源码解析
代码:
Collection c = new ArrayList();
c.add("hello");
c.add("world");
c.add("java");
System.out.println(c);
输出c时默认调用的是c的toString()方法
A:Collection c = new ArrayList();
这是多态,所以输出c的 toString()方法,其实是输出ArrayList的toString()方法
B:看 ArrayList 的 toString()方法
在ArrayList里面却没有发现toString()。应该去父类查找→ AbstractList → AbstractCollection
C:toString()的方法源码
- public String toString()
- {
- Iterator<E> it = iterator(); //集合本身调用迭代器方法,得到集合迭代器
- if (! it.hasNext())
- return "[]";
- StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
- sb.append('[');
- for (;;)
- {
- E e = it.next(); //e=hello,world,java
- sb.append(e == this ? "(this Collection)" : e);
- if (! it.hasNext())
- //[hello, world, java]
- return sb.append(']').toString();
- sb.append(',').append(' ');
- }
- }
17.02 Set集合概述及特点
Set接口概述:一个不包含重复元素的 collection
特点:
无序(存入与取出的顺序不一致)
唯一(存入集合的元素唯一)
17.03 HashSet存储字符串并遍历
HashSet类概述:不保证 set 的迭代顺序,特别是它不保证该顺序恒久不变。此类允许使用 null 元素。
例:
- public class Practice
- {
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- HashSet<String> hs = new HashSet<String>();
- hs.add("hello");
- hs.add("world");
- hs.add("world");
- hs.add("java");
- for (String s : hs)
- {
- System.out.println(s);
- }
- }
- }
运行结果:
- hello
- java
- world
17.04 HashSet保证元素唯一性的源码解析
- interface Collection
- {...}
- interface Set extends Collection
- {...}
- class HashSet implements Set
- {
- private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();
- private transient HashMap<E,Object> map;
- public HashSet()
- {
- map = new HashMap<>();
- }
- public boolean add(E e)
- { //e=hello,world
- return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
- }
- }
- class HashMap implements Map
- {
- public V put(K key, V value)
- { //key=e=hello,world
- //看哈希表是否为空,如果空,就开辟空间
- if (table == EMPTY_TABLE)
- {
- inflateTable(threshold);
- }
- //判断对象是否为null
- if (key == null)
- return putForNullKey(value);
- int hash = hash(key); //和对象的hashCode()方法相关
- //在哈希表中查找hash值
- int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
- for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next)
- {
- //这次的e其实是第一次的world
- Object k;
- if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k)))
- {
- V oldValue = e.value;
- e.value = value;
- e.recordAccess(this);
- return oldValue;
- //走这里其实是没有添加元素
- }
- }
- modCount++;
- addEntry(hash, key, value, i); //把元素添加
- return null;
- }
- transient int hashSeed = 0;
- final int hash(Object k)
- { //k=key=e=hello,
- int h = hashSeed;
- if (0 != h && k instanceof String)
- {
- return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k);
- }
- h ^= k.hashCode(); //这里调用的是对象的hashCode()方法
- // This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by
- // constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded
- // number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor).
- h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
- return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
- }
- }
通过查看add方法的源码,知道这个方法底层依赖两个方法:hashCode()和equals()。
判断元素唯一性的方式:通过对象的hashCode和equals方法来完成元素唯一性
如果对象的hashCode值不同,那么不用判断equals方法,就直接存储到哈希表中。
如果对象的hashCode值相同,那么要再次判断对象的equals方法是否为true。
如果为true,视为相同元素,不存。如果为false,那么视为不同元素,就进行存储。
如果类没有重写这两个方法,默认使用的Object()。一般来说不会相同。
17.05 HashSet存储自定义对象并遍历
- public class Practice
- {
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- HashSet<Student> hs = new HashSet<Student>();
- hs.add(new Student("小明",23));
- hs.add(new Student("旺财",12));
- hs.add(new Student("旺财",12));
- hs.add(new Student("小强",24));
- hs.add(new Student("小明",22));
- hs.add(new Student("小红",22));
- for(Student s : hs)
- {
- System.out.println(s.getName()+":"+s.getAge());
- }
- }
- }
17.06 HashSet保证元素唯一性的代码体现
上例中重复元素被存入到了集合中,因为Student没有重写hashCode和equals方法,默认使用的Object()的hashCode和equals方法,一般来说结果不会相同,所以存入到了集合中,Student类应重写hashCode和equals方法(自动生成)。
- @Override
- public int hashCode()
- {
- final int prime = 31;
- int result = 1;
- result = prime * result + age;
- result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
- return result;
- }
- @Override
- public boolean equals(Object obj)
- {
- if (this == obj)
- return true;
- if (obj == null)
- return false;
- if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
- return false;
- Student other = (Student) obj;
- if (age != other.age)
- return false;
- if (name == null)
- {
- if (other.name != null)
- return false;
- } else if (!name.equals(other.name))
- return false;
- return true;
- }
17.07 LinkedHashSet的概述和使用
LinkedHashSet类概述:
元素有序唯一:由链表保证元素有序、由哈希表保证元素唯一
例:
- public class Practice
- {
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- LinkedHashSet<String> hs = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
- hs.add("hello");
- hs.add("world");
- hs.add("world");
- hs.add("java");
- for(String s : hs)
- {
- System.out.println(s);
- }
- }
- }
运行结果:
- hello
- world
- java
17.08 TreeSet存储Integer类型的元素并遍历
TreeSet类概述:使用元素的自然顺序对元素进行排序,或者根据创建 set 时提供的 Comparator 进行排序,具体取决于使用的构造方法。
例:
- public class Practice
- {
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- TreeSet<Integer> ts = new TreeSet<Integer>();
- ts.add(20);
- ts.add(18);
- ts.add(23);
- ts.add(22);
- ts.add(17);
- ts.add(24);
- ts.add(19);
- ts.add(18);
- for(Integer i : ts)
- {
- System.out.print(i+" ");
- }
- }
- }
运行结果:
- 17 18 19 20 22 23 24
17.09 TreeSet保证元素排序的源码解析
- interface Collection {...}
- interface Set extends Collection {...}
- interface NavigableMap {}
- class TreeMap implements NavigableMap
- {
- public V put(K key, V value)
- {
- Entry<K,V> t = root;
- if (t == null)
- {
- compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check
- root = new Entry<>(key, value, null);
- size = 1;
- modCount++;
- return null;
- }
- int cmp;
- Entry<K,V> parent;
- // split comparator and comparable paths
- Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
- if (cpr != null)
- {
- do
- {
- parent = t;
- cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
- if (cmp < 0)
- t = t.left;
- else if (cmp > 0)
- t = t.right;
- else
- return t.setValue(value);
- } while (t != null);
- }
- else
- {
- if (key == null)
- throw new NullPointerException();
- Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
- do
- {
- parent = t;
- cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
- if (cmp < 0)
- t = t.left;
- else if (cmp > 0)
- t = t.right;
- else
- return t.setValue(value);
- } while (t != null);
- }
- Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent);
- if (cmp < 0)
- parent.left = e;
- else
- parent.right = e;
- fixAfterInsertion(e);
- size++;
- modCount++;
- return null;
- }
- }
- class TreeSet implements Set
- {
- private transient NavigableMap<E,Object> m;
- public TreeSet()
- {
- this(new TreeMap<E,Object>());
- }
- public boolean add(E e)
- {
- return m.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
- }
- }
真正的比较是依赖于元素的compareTo()方法,而这个方法是定义在 Comparable里面的。
所以,要想重写该方法,就必须是先实现 Comparable接口。这个接口表示的就是自然排序。
17.10 TreeSet保证元素唯一性和自然排序的原理和图解
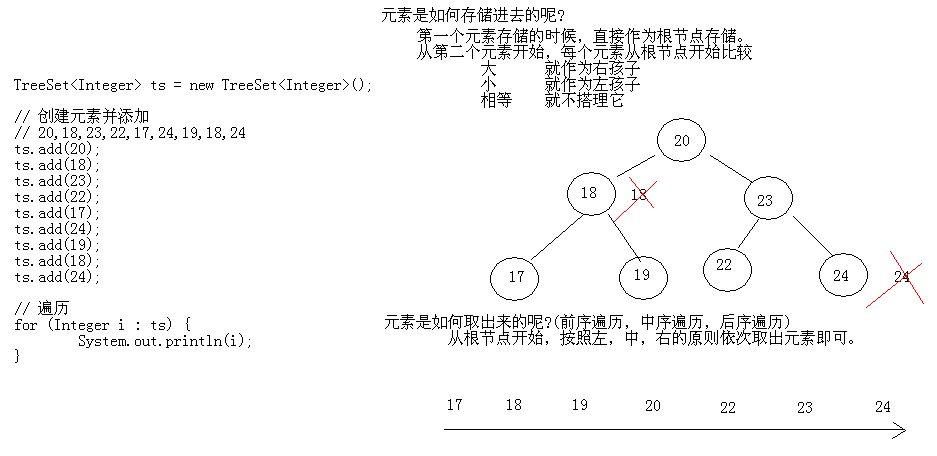
17.11 TreeSet存储自定义对象并遍历练习1
Student类实现自然排序接口Comparable,重写compareTo()方法
- @Override
- public int compareTo(Student s)
- {
- //主要条件,按年龄排
- int num = this.age - s.age;
- //次要条件,年龄相同按姓名排
- int num2 = (num == 0)?this.name.compareTo(s.name):num;
- return num2;
- }
17.12 TreeSet存储自定义对象并遍历练习2
Student类实现自然排序接口Comparable,重写compareTo()方法
- @Override
- public int compareTo(Student s)
- {
- // 主要条件 姓名的长度
- int num = this.name.length() - s.name.length();
- // 姓名的长度相同,比较姓名的内容是否相同
- int num2 = num == 0 ? this.name.compareTo(s.name) : num;
- // 姓名的长度和内容相同,比较年龄是否相同,继续判断年龄
- int num3 = num2 == 0 ? this.age - s.age : num2;
- return num3;
- }
17.13 TreeSet保证元素唯一性和比较器排序的原理及代码实现
- // 比较器排序,让集合具备比较性,匿名内部类实现
- TreeSet<Student> ts = new TreeSet<Student>(new Comparator<Student>()
- {
- @Override
- public int compare(Student s1, Student s2)
- {
- // 姓名长度
- int num = s1.getName().length() - s2.getName().length();
- // 姓名内容
- int num2 = num == 0 ? s1.getName().compareTo(s2.getName()) : num;
- // 年龄
- int num3 = num2 == 0 ? s1.getAge() - s2.getAge() : num2;
- return num3;
- }
- });
17.14 TreeSet对元素排序的总结
唯一性:根据比较的返回的是否是0来决定
排序: 1.自然排序,一个类的元素想要进行自然排序就必须实现自然排序接口Comparable(元素具备比较性)
2.比较器排序,让集合的构造方法接收一个比较器接口的子类对象Comparator(集合具备比较性)
17.15 产生10个1-20之间的随机数要求随机数不能重复案例简洁版
编写一个程序,获取10个1至20的随机数,要求随机数不能重复。
- public class Practice
- {
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- // 创建随机数对象
- Random r = new Random();
- // 创建一个Set集合
- HashSet<Integer> ts = new HashSet<Integer>();
- // 判断集合的长度是不是小于10
- while (ts.size() < 10)
- {
- int num = r.nextInt(20) + 1;
- ts.add(num);
- }
- // 遍历Set集合
- for (Integer i : ts)
- {
- System.out.println(i);
- }
- }
- }
17.16 键盘录入学生信息按照总分排序后输出在控制台案例
Student类
- public class Student
- {
- private String name;
- private int chinese;
- private int math;
- private int english;
- public Student(String name, int chinese, int math, int english)
- {
- super();
- this.name = name;
- this.chinese = chinese;
- this.math = math;
- this.english = english;
- }
- public String getName()
- {
- return name;
- }
- public void setName(String name)
- {
- this.name = name;
- }
- public int getChinese()
- {
- return chinese;
- }
- public void setChinese(int chinese)
- {
- this.chinese = chinese;
- }
- public int getMath()
- {
- return math;
- }
- public void setMath(int math)
- {
- this.math = math;
- }
- public int getEnglish()
- {
- return english;
- }
- public void setEnglish(int english)
- {
- this.english = english;
- }
- public int getSum()
- {
- return this.chinese+this.english+this.math;
- }
- }
测试类
- public class Practice
- {
- public static void main(String[] args)
- {
- TreeSet<Student> ts = new TreeSet<Student>(new Comparator<Student>()
- {
- @Override
- public int compare(Student s1, Student s2)
- {
- //按总分比较
- int num1 = s2.getSum() - s1.getSum();
- //总分相同按语文成绩比较
- int num2 = num1==0?s1.getChinese() - s2.getChinese():num1;
- //语文成绩相同按数学成绩比较
- int num3 = num2==0?s1.getMath() - s2.getMath():num2;
- //数学成绩相同按英语成绩比较
- int num4 = num3==0?s1.getChinese() - s2.getChinese():num3;
- //英语成绩相同按姓名比较
- int num5 = num4==0?s1.getName().compareTo(s2.getName()):num4;
- return num5;
- }
- });
- for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++)
- {
- Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
- System.out.println("请输入第"+i+"位学生的姓名");
- String name = sc.nextLine();
- System.out.println("请输入第"+i+"位学生的语文成绩");
- String chinese = sc.nextLine();
- System.out.println("请输入第"+i+"位学生的数学成绩");
- String math = sc.nextLine();
- System.out.println("请输入第"+i+"位学生的英语成绩");
- String english = sc.nextLine();
- Student s = new Student(name, Integer.parseInt(chinese), Integer.parseInt(math), Integer.parseInt(english));
- ts.add(s);
- }
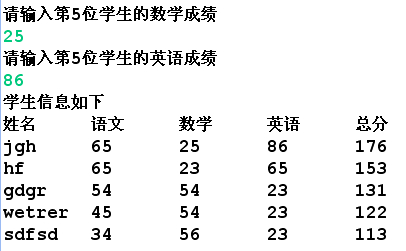
- System.out.println("学生信息如下");
- System.out.println("姓名\t语文\t数学\t英语\t总分");
- for(Student s:ts)
- {
- System.out.println(s.getName()+"\t"+s.getChinese()+"\t"+s.getMath()+"\t"+s.getEnglish()+"\t"+s.getSum());
- }
- }
- }
运行结果:
JavaSE学习总结第17天_集合框架3的更多相关文章
- JavaSE学习总结第15天_集合框架1
15.01 对象数组的概述和使用 public class Student { // 成员变量 private String name; private int age; // 构造方法 publ ...
- JavaSE学习总结第16天_集合框架2
16.01 ArrayList存储字符串并遍历 ArrayList类概述:底层数据结构是数组,查询快,增删慢,线程不安全,效率高 ArrayList类是List 接口的大小可变数组的实现.实现了所 ...
- JavaSE学习总结第18天_集合框架4
18.01 Map集合概述和特点 Map接口概述:将键映射到值的对象,一个映射不能包含重复的键,每个键最多只能映射到一个值 Map接口和Collection接口的不同 1.Map是双列的,Coll ...
- javaSE学习笔记(17)---锁
javaSE学习笔记(17)---锁 Java提供了种类丰富的锁,每种锁因其特性的不同,在适当的场景下能够展现出非常高的效率.本文旨在对锁相关源码(本文中的源码来自JDK 8).使用场景进行举例,为读 ...
- Java基础学习(四)-- 接口、集合框架、Collection、泛型详解
接口 一.接口的基本概念 关键字为:Interface,在JAVA编程语言中是一个抽象类型,是抽象方法的集合.也是使用.java文件编写. 二.接口声明 命名规范:与类名的命名规范相同,通常情况下 ...
- Java之旅_高级教_集合框架
摘自:http://www.runoob.com/java/java-collections.html Java 集合框架 早在Java2之前,java 就提供了特设类.比如:Dictionary,V ...
- Java学习日记基础篇(九) —— 集合框架,泛型,异常
集合框架 有事我们会需要一个能够动态的调整大小的数组,比如说要添加新员工但是数组已经满了,并且数组的大小是在定义的时候定死的,所以我们就需要一个能够动态调整大小的数组或者用链表解决,而java中提供了 ...
- java oop第07章_集合框架
一. 什么是集合: 在Java中提供了一些可以保存同一数据类型的数据集称为集合,就是规定了一些集合的规范(接口.抽象类.实现类)及方法, 方便我们程序在保存数据时进行增.删.改.查操作,编程更加高效. ...
- JavaSE学习总结第27天_反射 & 设计模式 & JDK5、7、8新特性
27.01 反射_类的加载概述和加载时机 类的加载:当程序要使用某个类时,如果该类还未被加载到内存中,则系统会通过加载,连接,初始化三步来实现对这个类进行初始化. 加载:就是指将class文件读 ...
随机推荐
- Radio Checkbox Select 操作
一个小总结 <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta name="description" content= ...
- checkbox 全选反选实现全代码
//跳转到指定action function validateForm(url){ if($("#form").form('validate')){ var x=document. ...
- MOSS 2010 无法同步用户配置文件
The management agent “MOSSAD-Synch AD Connection” failed on run profile “DS_DELTAIMPORT” because of ...
- QT显示如何减轻闪屏(双缓冲和NoErase)
很多同志在些QT 程序后会遇见闪屏的问题, 有时速度非常快,但毕竟影响了显示效果,如何做到减轻屏幕抖动或闪屏呢?我曾试过如下的办法:1.使用双缓冲. 比如我们在一个Widget里面绘多个图的话, 先创 ...
- [置顶] SpecDD(混合的敏捷方法模型)主要过程概述
敏捷已成为当今使用最广泛的开发方法.有趣的是,敏捷方法的流行性并不是因为它取代了其他开发方法,相反它与这些方法进行了更好地融合.现实世界众多敏捷项目的成功,也证明了敏捷将走向杂化的未来. SpecDD ...
- Hash 表详解(哈希表)
散列表(Hash table,也叫哈希表),是根据关键码值(Key value)而直接进行访问的数据结构.也就是说,它通过把关键码值映射到表中一个位置来访问记录,以加快查找的速度.这个映射函数叫做散列 ...
- 基于视觉的Web页面分页算法VIPS的实现源代码下载
基于视觉的Web页面分页算法VIPS的实现源代码下载 - tingya的专栏 - 博客频道 - CSDN.NET 基于视觉的Web页面分页算法VIPS的实现源代码下载 分类: 技术杂烩 2006-04 ...
- iOS加载HTML, CSS代码
NSString *strHTML = @"<div style=\"text-align:center;\"><img src=\"/Upl ...
- fastDFS同步问题讨论
一.文件同步延迟问题 前面也讲过fastDFS同组内storage server数据是同步的, Storage server中由专门的线程根据binlog进行文件同步.为了最大程度地避免相互影响以及出 ...
- GLView基本分析
GLView是cocos2d-x基于OpenGL ES的调用封装UI库. OpenGL本身是跨平台的计算机图形实现API,在每一个平台的详细实现是不一样.所以每次使用之前先要初始化,去设置平台相关的信 ...
