WebRTC中Android Demo中的远程视频流的获取到传输
1.CallActivity#onCreate 执行startCall开始连接或创建房间
2.WebSocketClient#connectToRoom 请求一次服务器
3.回调到CallActivity#onConnectToRoom 开始创建对等连接,同时将视频采集对象,本地和远程的VideoSink,相关参数传入

localProxyVideoSink代理本地视频渲染器
remoteSinks是代理远程视频的渲染器,这里是一个集合
videoCapture是本地视频采集器
4.PeerConnectionClient#createPeerConnectionInternal 创建PeerConnection对象和创建视频轨道

factory是在CallActivity#onCreate中创建的
pcObserver是一个对等连接观察者,用于底层消息的回调
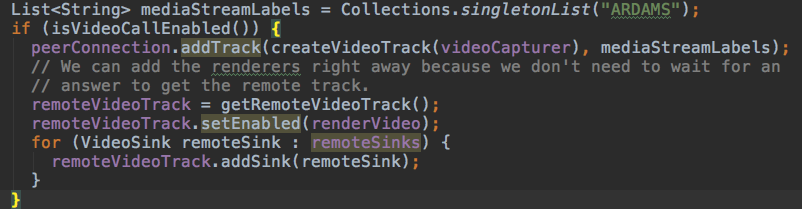
如果开启了视频功能,则将本地采集的数据添加到轨道(通过C++底层完成)
如果是远程的数据,通过(getRemoteVideoTrack调用C++底层方法)获取到远程视频轨道,添加传入进来的remoteSinks

这里继续添加音频轨道。
到这里,可以预览到本地摄像头预览帧。
中间还有一个复杂的过程,就是建立连接的过程。
主要有以下几个步骤吧。
1️⃣ 创建者创建一个连接房间。
i.请求Server(WebSocketRTCClient#connectToRoom)
ii.创建Offer信令(PeerConnection来创建,通过sdpObserver来回调结果)
iii.设置本地SDP,通过sdpObserver来回调结果
iv.发送Offer信令,给服务器(等待别人连接)
2️⃣ 加入者加入该房间。
i.请求Server(有人创建了房间,那就只有加入了),突然还收到一个Offer(创建者给服务器的)呢。
ii.设置远程SDP,通过sdpObserver来回调结果。
iii.创建Answer信令,通过sdpObserver来回调结果。
iv.发送Answer信令,发送给服务器(主要给房间创建者的)
3️⃣ 创建者知道有人加入后。
i.WebSocketRTCClient#onWebSocketMessage(接收到Answer信令和一些ICE数据包)
ii.设置远程SDP,通过sdpObserver来回调结果。
iii.开始添加ICE Candidate。
4️⃣ 然后就是ICE之间的连接,这里的具体逻辑不是特别清楚。以后再补充。
5️⃣ P2P连接建立完毕,可以互相实时视频聊天了哦。
5.那么如何获取到远程的视频流数据呢?或者说怎么将远程的数据渲染出来显示到SurfaceViewRender中?
在demo中,预览本地的视频和远程的视频都是用SurfaceViewRender自定义视图完成的。
public class SurfaceViewRenderer extends SurfaceView
implements SurfaceHolder.Callback, VideoSink, RendererCommon.RendererEvents {
private static final String TAG = "SurfaceViewRenderer"; // Cached resource name.
private final String resourceName;
private final RendererCommon.VideoLayoutMeasure videoLayoutMeasure =
new RendererCommon.VideoLayoutMeasure();
private final SurfaceEglRenderer eglRenderer; // Callback for reporting renderer events. Read-only after initilization so no lock required.
private RendererCommon.RendererEvents rendererEvents; // Accessed only on the main thread.
private int rotatedFrameWidth;
private int rotatedFrameHeight;
private boolean enableFixedSize;
private int surfaceWidth;
private int surfaceHeight; /**
* Standard View constructor. In order to render something, you must first call init().
*/
public SurfaceViewRenderer(Context context) {
super(context);
this.resourceName = getResourceName();
eglRenderer = new SurfaceEglRenderer(resourceName);
getHolder().addCallback(this);
getHolder().addCallback(eglRenderer);
} /**
* Standard View constructor. In order to render something, you must first call init().
*/
public SurfaceViewRenderer(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
this.resourceName = getResourceName();
eglRenderer = new SurfaceEglRenderer(resourceName);
getHolder().addCallback(this);
getHolder().addCallback(eglRenderer);
} /**
* Initialize this class, sharing resources with |sharedContext|. It is allowed to call init() to
* reinitialize the renderer after a previous init()/release() cycle.
*/
public void init(EglBase.Context sharedContext, RendererCommon.RendererEvents rendererEvents) {
init(sharedContext, rendererEvents, EglBase.CONFIG_PLAIN, new GlRectDrawer());
} /**
* Initialize this class, sharing resources with |sharedContext|. The custom |drawer| will be used
* for drawing frames on the EGLSurface. This class is responsible for calling release() on
* |drawer|. It is allowed to call init() to reinitialize the renderer after a previous
* init()/release() cycle.
*/
public void init(final EglBase.Context sharedContext,
RendererCommon.RendererEvents rendererEvents, final int[] configAttributes,
RendererCommon.GlDrawer drawer) {
ThreadUtils.checkIsOnMainThread();
this.rendererEvents = rendererEvents;
rotatedFrameWidth = 0;
rotatedFrameHeight = 0;
eglRenderer.init(sharedContext, this /* rendererEvents */, configAttributes, drawer);
} /**
* Block until any pending frame is returned and all GL resources released, even if an interrupt
* occurs. If an interrupt occurs during release(), the interrupt flag will be set. This function
* should be called before the Activity is destroyed and the EGLContext is still valid. If you
* don't call this function, the GL resources might leak.
*/
public void release() {
eglRenderer.release();
} /**
* Register a callback to be invoked when a new video frame has been received.
*
* @param listener The callback to be invoked. The callback will be invoked on the render thread.
* It should be lightweight and must not call removeFrameListener.
* @param scale The scale of the Bitmap passed to the callback, or 0 if no Bitmap is
* required.
* @param drawer Custom drawer to use for this frame listener.
*/
public void addFrameListener(
EglRenderer.FrameListener listener, float scale, RendererCommon.GlDrawer drawerParam) {
eglRenderer.addFrameListener(listener, scale, drawerParam);
} /**
* Register a callback to be invoked when a new video frame has been received. This version uses
* the drawer of the EglRenderer that was passed in init.
*
* @param listener The callback to be invoked. The callback will be invoked on the render thread.
* It should be lightweight and must not call removeFrameListener.
* @param scale The scale of the Bitmap passed to the callback, or 0 if no Bitmap is
* required.
*/
public void addFrameListener(EglRenderer.FrameListener listener, float scale) {
eglRenderer.addFrameListener(listener, scale);
} public void removeFrameListener(EglRenderer.FrameListener listener) {
eglRenderer.removeFrameListener(listener);
} /**
* Enables fixed size for the surface. This provides better performance but might be buggy on some
* devices. By default this is turned off.
*/
public void setEnableHardwareScaler(boolean enabled) {
ThreadUtils.checkIsOnMainThread();
enableFixedSize = enabled;
updateSurfaceSize();
} /**
* Set if the video stream should be mirrored or not.
*/
public void setMirror(final boolean mirror) {
eglRenderer.setMirror(mirror);
} /**
* Set how the video will fill the allowed layout area.
*/
public void setScalingType(RendererCommon.ScalingType scalingType) {
ThreadUtils.checkIsOnMainThread();
videoLayoutMeasure.setScalingType(scalingType);
requestLayout();
} public void setScalingType(RendererCommon.ScalingType scalingTypeMatchOrientation,
RendererCommon.ScalingType scalingTypeMismatchOrientation) {
ThreadUtils.checkIsOnMainThread();
videoLayoutMeasure.setScalingType(scalingTypeMatchOrientation, scalingTypeMismatchOrientation);
requestLayout();
} /**
* Limit render framerate.
*
* @param fps Limit render framerate to this value, or use Float.POSITIVE_INFINITY to disable fps
* reduction.
*/
public void setFpsReduction(float fps) {
eglRenderer.setFpsReduction(fps);
} public void disableFpsReduction() {
eglRenderer.disableFpsReduction();
} public void pauseVideo() {
eglRenderer.pauseVideo();
} // VideoSink interface.
@Override
public void onFrame(VideoFrame frame) {
eglRenderer.onFrame(frame);
} // View layout interface.
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthSpec, int heightSpec) {
ThreadUtils.checkIsOnMainThread();
Point size =
videoLayoutMeasure.measure(widthSpec, heightSpec, rotatedFrameWidth, rotatedFrameHeight);
setMeasuredDimension(size.x, size.y);
logD("onMeasure(). New size: " + size.x + "x" + size.y);
} @Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
ThreadUtils.checkIsOnMainThread();
eglRenderer.setLayoutAspectRatio((right - left) / (float) (bottom - top));
updateSurfaceSize();
} private void updateSurfaceSize() {
ThreadUtils.checkIsOnMainThread();
if (enableFixedSize && rotatedFrameWidth != 0 && rotatedFrameHeight != 0 && getWidth() != 0
&& getHeight() != 0) {
final float layoutAspectRatio = getWidth() / (float) getHeight();
final float frameAspectRatio = rotatedFrameWidth / (float) rotatedFrameHeight;
final int drawnFrameWidth;
final int drawnFrameHeight;
if (frameAspectRatio > layoutAspectRatio) {
drawnFrameWidth = (int) (rotatedFrameHeight * layoutAspectRatio);
drawnFrameHeight = rotatedFrameHeight;
} else {
drawnFrameWidth = rotatedFrameWidth;
drawnFrameHeight = (int) (rotatedFrameWidth / layoutAspectRatio);
}
// Aspect ratio of the drawn frame and the view is the same.
final int width = Math.min(getWidth(), drawnFrameWidth);
final int height = Math.min(getHeight(), drawnFrameHeight);
logD("updateSurfaceSize. Layout size: " + getWidth() + "x" + getHeight() + ", frame size: "
+ rotatedFrameWidth + "x" + rotatedFrameHeight + ", requested surface size: " + width
+ "x" + height + ", old surface size: " + surfaceWidth + "x" + surfaceHeight);
if (width != surfaceWidth || height != surfaceHeight) {
surfaceWidth = width;
surfaceHeight = height;
getHolder().setFixedSize(width, height);
}
} else {
surfaceWidth = surfaceHeight = 0;
getHolder().setSizeFromLayout();
}
} // SurfaceHolder.Callback interface.
@Override
public void surfaceCreated(final SurfaceHolder holder) {
ThreadUtils.checkIsOnMainThread();
surfaceWidth = surfaceHeight = 0;
updateSurfaceSize();
} @Override
public void surfaceDestroyed(SurfaceHolder holder) {} @Override
public void surfaceChanged(SurfaceHolder holder, int format, int width, int height) {} private String getResourceName() {
try {
return getResources().getResourceEntryName(getId());
} catch (NotFoundException e) {
return "";
}
} /**
* Post a task to clear the SurfaceView to a transparent uniform color.
*/
public void clearImage() {
eglRenderer.clearImage();
} @Override
public void onFirstFrameRendered() {
if (rendererEvents != null) {
rendererEvents.onFirstFrameRendered();
}
} @Override
public void onFrameResolutionChanged(int videoWidth, int videoHeight, int rotation) {
if (rendererEvents != null) {
rendererEvents.onFrameResolutionChanged(videoWidth, videoHeight, rotation);
}
int rotatedWidth = rotation == 0 || rotation == 180 ? videoWidth : videoHeight;
int rotatedHeight = rotation == 0 || rotation == 180 ? videoHeight : videoWidth;
// run immediately if possible for ui thread tests
postOrRun(() -> {
rotatedFrameWidth = rotatedWidth;
rotatedFrameHeight = rotatedHeight;
updateSurfaceSize();
requestLayout();
});
} private void postOrRun(Runnable r) {
if (Thread.currentThread() == Looper.getMainLooper().getThread()) {
r.run();
} else {
post(r);
}
} private void logD(String string) {
Logging.d(TAG, resourceName + ": " + string);
}
}
在CallActivity#onCreate中会调用SurfaceViewRender#init方法来进行初始化。
在CallActivity#onCreate中也会调用SurfaceViewRender#setEnableHardwareScaler方法进行硬件加速。
数据是怎么显示到该视图的呢?
在CallActivity#setSwappedFeeds中
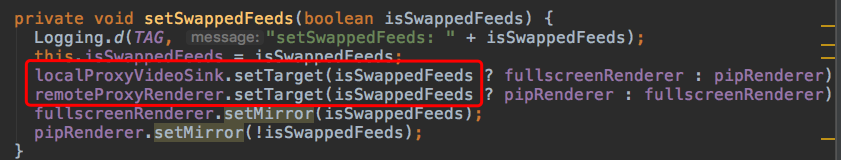
可以知道:
localProxyVideoSink就是本地视频数据流的渲染器代理,它的目标视图就是SurfaceViewRender。
remoteProxyRenderer就是远程视频数据流的渲染器代理,它的目标视图也是SurfaceViewRender。
6.首先来跟踪一下本地视频数据流渲染器的代理==>localProxyVideoSink。
在CallActivity#ProxyVideoSink中,实现了VideoSink接口。(VideoSink接口中只有一个方法onFrame会被native代码调用实现渲染的方法)
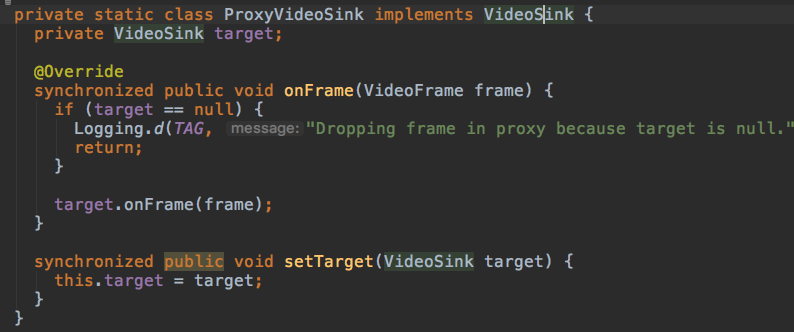
这个静态类部类共两个方法,都加锁了。
一个渲染onFrame,一个设置目标(所以这里知道了SurfaceViewRender视图类为什么会继承VideoSink了)。
然后就是最关键的一步了。CallActivity#onConnectedToRoomInternal。

由上可知,在创建对等连接的时候,就已经将摄像头采集的数据(videoCapturer)关联到本地视频视图的代理类(localProxyVideoSink)中了。
所以在PeerConnectionClient得接收一下这几个非常关键的参数。
PeerConnectionClient#createPeerConnection
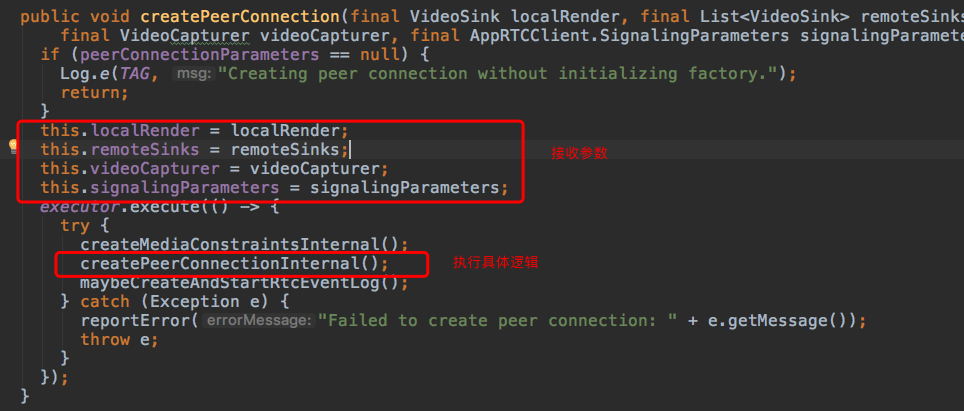
所以在PeerConnectionClient#localRender==>本地视频流数据渲染器代理类。
PeerConnectionClient#remoteSinks==>远程视频流数据渲染器代理类。
PeerConnectionClient#videoCapturer==>本地摄像头采集器(可能不是摄像头,可能是文件或屏幕,我喜欢说成摄像头)
PeerConnectionClient#signalingParameters==>相关参数。
然后呢?localRender去哪里了?
在这里 PeerConnectionClient#createPeerConnectionInternal
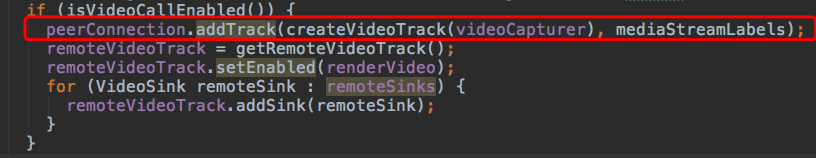
这里没有localRender啊!别急,再看这里 PeerConnectionClient#createVideoTrack
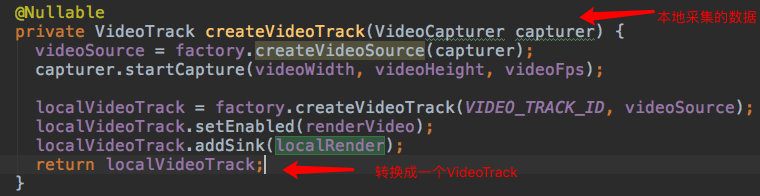
这里也是非常关键的一步,将本地采集的数据->VideoTrack对象。通过底层代码实现。
然后localRender之旅到此结束,下面看看remoteSinks。
7.然后跟踪一下远程视频流数据渲染器代理==>remoteSinks。
首先它是什么呢?它是一个List<VideoSink>集合,然而localRender是一个VideoSink。
为什么本地只有一个VideoSink,而远程的是一个集合呢?
我也不知道。。但是可以猜测一下嘛:本地只能通过一种确定的方式采集数据,而远程的数据流无法确定采集的方式,故只能用一个集合来记录。
看看传入远程视频流代理。
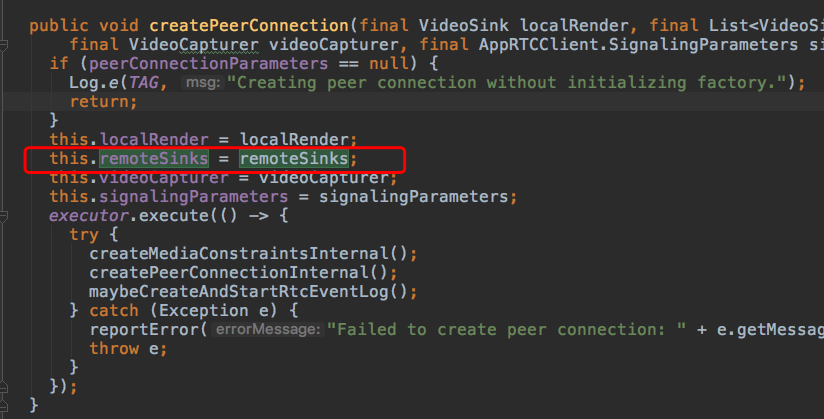
同样地,在PeerConnectionClient#createPeerConnection中,接收一下传入的远程数据流渲染器代理集合(remoteSinks)。
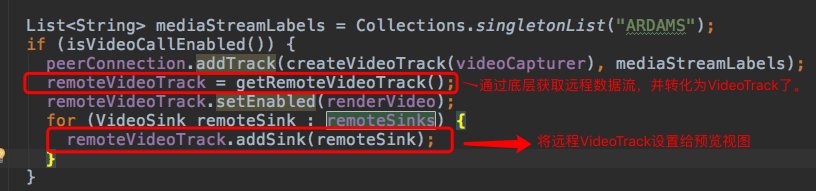
这里有两个点,一个是获取到远程数据流返回的一个VideoTrack。一个是将VideoTrack设置给预览视图,这样就能预览到远程视频数据了。
来详细看一下底层是怎么获取到远程数据流的==>PeerConnectionClient#getRemoteVideoTrack。
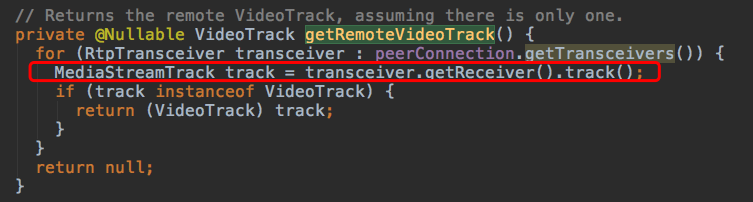
这里通过peerConnection#getTransceivers获取到RtpTransceiver(收发器)对象。(英文叫做收发器,姑且就叫它收发器吧)
通过收发器RtpTransceiver#getReceiver获取到RTPReceiver对象。
通过RTPReceiver#track获取到MediaStreamTrack。它就是我们要的东西。
哦不,将它强制转换成VideoTrack才是我们真正要的东西。
注意点:如果ICE没有正常连接,这里getReceiver估计也是接收不到数据的,所以一定要确保ICE Connected!!!
remoteSinks之旅就到此结束了。
8.剩下还有一个问题:视频流的传输过程。
这个涉及到底层了。简单分析一下。
入口在这里。PeerConnectionClient#createPeerConnectionInternal
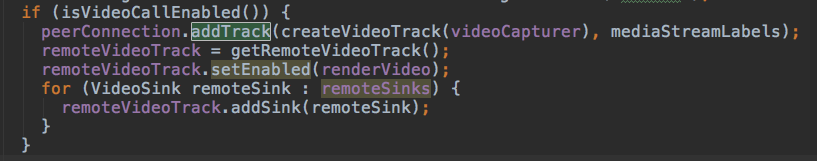
然后深入到PeerConnection#addTrack中看看。
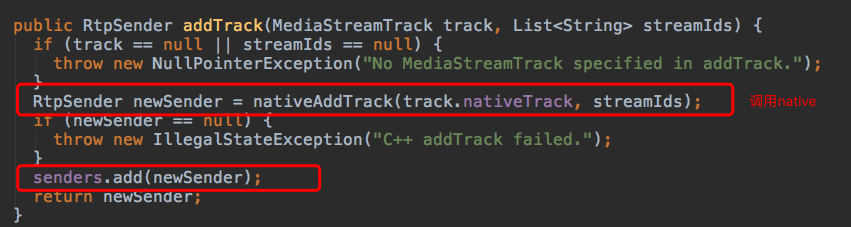
这里开始进行native操作了。PeerConnection#nativeAddTrack。

这里传入一个track和字符串数组,返回一个RtpSender。
那这个RtpSender具体做了什么呢?
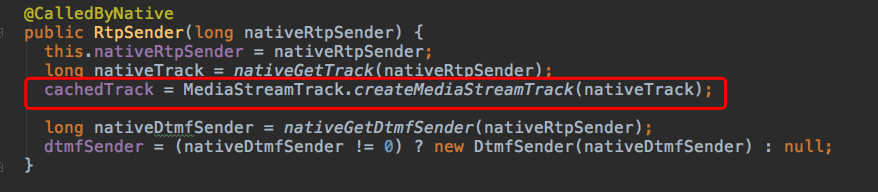
在它的构造函数中,就已经创建了一个cachedTrack,姑且叫做一个缓冲区轨道,所以这里面已经有数据了。
理一下思路:
前面经过了一些SDP,ICE互相传递数据后建立了一个通道(Channel),通道是可以互相发送一些文本信息的。
但是要发送视频流,环境要更加苛刻,还要Track(轨道),这样才能更加顺利的发送视频流。
9.更加底层的C++源码分析视频数据流的传输可参考这篇大神写的文章。
WebRTC中Android Demo中的远程视频流的获取到传输的更多相关文章
- WebRTC中Android Demo中的摄像头从采集到预览流程
APPRTC-Demo调用流程 1.CallActivity#onCreate 执行startCall开始连接或创建房间 2.WebSocketClient#connectToRoom 请求一次服务器 ...
- win10中android studio中的terminal不能输入
1 打开CMD窗口右击 2 3 重启电脑,你试试就知道了.
- Android系统进程间通信(IPC)机制Binder中的Client获得Server远程接口过程源代码分析
文章转载至CSDN社区罗升阳的安卓之旅,原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/luoshengyang/article/details/6633311 在上一篇文章中,我 们分析了And ...
- MVP模式在Android开发中的应用
一.MVP介绍 随着UI创建技术的功能日益增强,UI层也履行着越来越多的职责.为了更好地细分视图(View)与模型(Model)的功能,让View专注于处理数据的可视化以及与用户的交互.同一 ...
- NDK笔记(二)-在Android Studio中使用ndk-build
前面一篇我们接触了CMake,这一篇写写关于ndk-build的使用过程.刚刚用到,想到哪儿写哪儿. 环境背景 Android开发IDE版本:AndroidStudio 2.2以上版本(目前已经升级到 ...
- 在Android Studio中使用shareSDK进行社会化分享(图文教程)
[声明] 欢迎转载,但请保留文章原始出处→_→ 生命壹号:http://www.cnblogs.com/smyhvae/ 文章来源:http://www.cnblogs.com/smyhvae/p/4 ...
- Android系统中的广播(Broadcast)机制简要介绍和学习计划
在Android系统中,广播(Broadcast)是在组件之间传播数据(Intent)的一种机制:这些组件甚至是可以位于不同的进程中,这样它就像Binder机制一样,起到进程间通信的作用:本文通过一个 ...
- 在Android Studio 中正确使用adil ”绝对经典“
今天调用远程服务中遇到了一个问题,哎,调了2个小时,后来终于解决,总结来看还是对新的Android Studio 不够熟悉.那么....就可以睡觉啦!!! 在Android Studio中使用进程通信 ...
- android开发中系统自带语音模块的使用
android开发中系统自带语音模块的使用需求:项目中需要添加语音搜索模块,增加用户体验解决过程:在网上搜到语音搜索例子,参考网上代码,加入到了自己的项目,完成产品要求.这个问题很好解决,网上能找到很 ...
随机推荐
- Shell,Bash,等脚本学习(有区别)
二元比较操作符,比较变量或者比较数字.注意数字与字符串的区别. 整数比较 -eq 等于,如:if [ "$a" -eq "$b" ] -n ...
- 百度地图Label 样式 setStyle
最近一直在整百度地图,发现一个小问题: 创建文本标注对象设置样式的时候,其中的backgroundColor属性居然还支持透明啊,不过改变数值好像对效果没有影响 var numLabel = new ...
- Android(java)学习笔记209:Android线程形态之 HandlerThread
1. HandlerThread Android HandlerThread 完全解析 Handler与HandlerThread区别,HandlerThread应用(对比AsyncTask) 备注 ...
- Android进阶笔记15:选用合适的IPC方式
1. 相信大家都知道Android进程间通信方式很多,比如AIDL.Messenger等等,接下来我就总结一下这些IPC方式优缺点. 2. IPC方式的优缺点和适用场景 3. 附加:使用Intent实 ...
- Intellij IDEA快速补全System.out.print : sout
- Nucleus进程间通信(IPC)方式
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主同意不得转载--"http://blog.csdn.net/suipingsp". https://blog.csdn.net/suiping ...
- EOJ Monthly 2019.2 (based on February Selection) D 进制转换 【数学 进制转换】
任意门:https://acm.ecnu.edu.cn/contest/140/problem/D/ D. 进制转换 单测试点时限: 2.0 秒 内存限制: 256 MB “他觉得一个人奋斗更轻松自在 ...
- 大数据框架-spark
相关详细说明:https://www.csdn.net/article/2015-07-10/2825184 RDD:弹性分布式数据集. Operation:Transformation 和Actio ...
- Maven常用的构建命令
1.mvn -v 查看maven版本 2.mvn compile 编译项目,生成target文件夹,其中包含编译生成的字节码文件和测试报告.打开cmd,cd到项目的根目录,运行该命令如图所示(如果是第 ...
- Oracle中插入千万条测试数据
测试需求,id.姓名.邮箱.手机号不可重复 1.创建序列 create sequence id_sequence; //创建序列id_sequence 2.创建表 create table USERI ...
