Shiro理解与总结
Feature
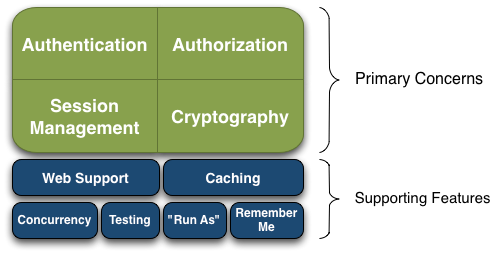
Apache Shiro is a comprehensive application security framework with many features. The following diagram shows where Shiro focuses its energy, and this reference manual will be organized similarly:
Shiro targets what the Shiro development team calls “the four cornerstones of application security” - Authentication, Authorization, Session Management, and Cryptography:
Authentication: Sometimes referred to as ‘login’, this is the act of proving a user is who they say they are.
Authorization: The process of access control, i.e. determining ‘who’ has access to ‘what’.
Session Management: Managing user-specific sessions, even in non-web or EJB applications.
Cryptography: Keeping data secure using cryptographic algorithms while still being easy to use.
There are also additional features to support and reinforce these concerns in different application environments, especially:
- Web Support: Shiro’s web support APIs help easily secure web applications.
- Caching: Caching is a first-tier citizen in Apache Shiro’s API to ensure that security operations remain fast and efficient.
- Concurrency: Apache Shiro supports multi-threaded applications with its concurrency features.
- Testing: Test support exists to help you write unit and integration tests and ensure your code will be secured as expected.
- “Run As”: A feature that allows users to assume the identity of another user (if they are allowed), sometimes useful in administrative scenarios.
- “Remember Me”: Remember users’ identities across sessions so they only need to log in when mandatory.
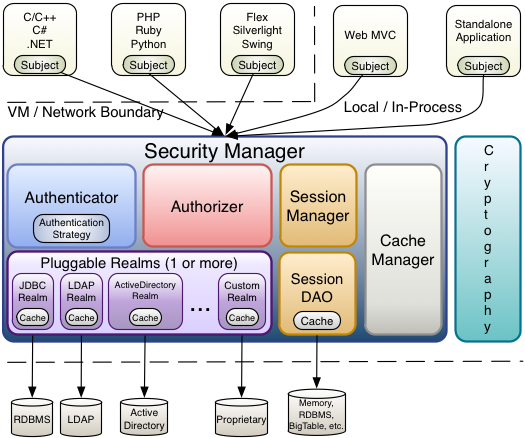
Architecture
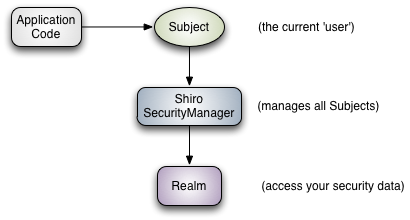
Subject (
org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject)
A security-specific ‘view’ of the entity (user, 3rd-party service, cron job, etc) currently interacting with the software.SecurityManager (org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager)
As mentioned above, theSecurityManageris the heart of Shiro’s architecture. It is mostly an ‘umbrella’ object that coordinates its managed components to ensure they work smoothly together. It also manages Shiro’s view of every application user, so it knows how to perform security operations per user.Authenticator (org.apache.shiro.authc.Authenticator)
TheAuthenticatoris the component that is responsible for executing and reacting to authentication (log-in) attempts by users. When a user tries to log-in, that logic is executed by theAuthenticator. TheAuthenticatorknows how to coordinate with one or moreRealmsthat store relevant user/account information. The data obtained from theseRealmsis used to verify the user’s identity to guarantee the user really is who they say they are.Authentication Strategy (org.apache.shiro.authc.pam.AuthenticationStrategy)
If more than oneRealmis configured, theAuthenticationStrategywill coordinate the Realms to determine the conditions under which an authentication attempt succeeds or fails (for example, if one realm succeeds but others fail, is the attempt successful? Must all realms succeed? Only the first?).
Authorizer (org.apache.shiro.authz.Authorizer)
TheAuthorizeris the component responsible determining users’ access control in the application. It is the mechanism that ultimately says if a user is allowed to do something or not. Like theAuthenticator, theAuthorizeralso knows how to coordinate with multiple back-end data sources to access role and permission information. TheAuthorizeruses this information to determine exactly if a user is allowed to perform a given action.SessionManager (org.apache.shiro.session.mgt.SessionManager)
TheSessionManagerknows how to create and manage userSessionlifecycles to provide a robust Session experience for users in all environments. This is a unique feature in the world of security frameworks - Shiro has the ability to natively manage user Sessions in any environment, even if there is no Web/Servlet or EJB container available. By default, Shiro will use an existing session mechanism if available, (e.g. Servlet Container), but if there isn’t one, such as in a standalone application or non-web environment, it will use its built-in enterprise session management to offer the same programming experience. TheSessionDAOexists to allow any datasource to be used to persist sessions.SessionDAO (org.apache.shiro.session.mgt.eis.SessionDAO)
TheSessionDAOperformsSessionpersistence (CRUD) operations on behalf of theSessionManager. This allows any data store to be plugged in to the Session Management infrastructure.
CacheManager (org.apache.shiro.cache.CacheManager)
TheCacheManagercreates and managesCacheinstance lifecycles used by other Shiro components. Because Shiro can access many back-end data sources for authentication, authorization and session management, caching has always been a first-class architectural feature in the framework to improve performance while using these data sources. Any of the modern open-source and/or enterprise caching products can be plugged in to Shiro to provide a fast and efficient user-experience.Cryptography (org.apache.shiro.crypto.*)
Cryptography is a natural addition to an enterprise security framework. Shiro’scryptopackage contains easy-to-use and understand representations of crytographic Ciphers, Hashes (aka digests) and different codec implementations. All of the classes in this package are carefully designed to be very easy to use and easy to understand. Anyone who has used Java’s native cryptography support knows it can be a challenging animal to tame. Shiro’s crypto APIs simplify the complicated Java mechanisms and make cryptography easy to use for normal mortal human beings.Realms (org.apache.shiro.realm.Realm)
As mentioned above, Realms act as the ‘bridge’ or ‘connector’ between Shiro and your application’s security data. When it comes time to actually interact with security-related data like user accounts to perform authentication (login) and authorization (access control), Shiro looks up many of these things from one or more Realms configured for an application. You can configure as manyRealmsas you need (usually one per data source) and Shiro will coordinate with them as necessary for both authentication and authorization.
Shiro example
java:
package com.hjp.shiro.shiro_tutorial; import org.apache.shiro.SecurityUtils;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.*;
import org.apache.shiro.config.IniSecurityManagerFactory;
import org.apache.shiro.mgt.SecurityManager;
import org.apache.shiro.session.Session;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject;
import org.apache.shiro.util.Factory;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; public class Tutorial { private static final transient Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Tutorial.class); public static void main(String[] args) {
log.info("My First Apache Shiro Application"); Factory<SecurityManager> factory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro.ini");
SecurityManager securityManager = factory.getInstance();
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager); // get the currently executing user:
Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); // Do some stuff with a Session (no need for a web or EJB container!!!)
Session session = currentUser.getSession();
session.setAttribute("someKey", "aValue");
String value = (String) session.getAttribute("someKey");
if (value.equals("aValue")) {
log.info("Retrieved the correct value! [" + value + "]");
} // let's login the current user so we can check against roles and
// permissions:
if (!currentUser.isAuthenticated()) {
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("lonestarr", "vespa");
token.setRememberMe(true);
try {
currentUser.login(token);
} catch (UnknownAccountException uae) {
log.info("There is no user with username of " + token.getPrincipal());
} catch (IncorrectCredentialsException ice) {
log.info("Password for account " + token.getPrincipal() + " was incorrect!");
} catch (LockedAccountException lae) {
log.info("The account for username " + token.getPrincipal() + " is locked. "
+ "Please contact your administrator to unlock it.");
}
// ... catch more exceptions here (maybe custom ones specific to
// your application?
catch (AuthenticationException ae) {
// unexpected condition? error?
}
} // say who they are:
// print their identifying principal (in this case, a username):
log.info("User [" + currentUser.getPrincipal() + "] logged in successfully."); // test a role:
if (currentUser.hasRole("schwartz")) {
log.info("May the Schwartz be with you!");
} else {
log.info("Hello, mere mortal.");
} // test a typed permission (not instance-level)
if (currentUser.isPermitted("lightsaber:weild")) {
log.info("You may use a lightsaber ring. Use it wisely.");
} else {
log.info("Sorry, lightsaber rings are for schwartz masters only.");
} // a (very powerful) Instance Level permission:
if (currentUser.isPermitted("winnebago:drive:eagle5")) {
log.info("You are permitted to 'drive' the winnebago with license plate (id) 'eagle5'. "
+ "Here are the keys - have fun!");
} else {
log.info("Sorry, you aren't allowed to drive the 'eagle5' winnebago!");
} // all done - log out!
currentUser.logout(); System.exit(0); } }
pom:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro.tutorials</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-tutorial</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>First Apache Shiro Application</name>
<packaging>jar</packaging> <properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties> <build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.0.2</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.5</source>
<target>1.5</target>
<encoding>${project.build.sourceEncoding}</encoding>
</configuration>
</plugin> <!-- This plugin is only to test run our little application. It is not
needed in most Shiro-enabled applications: -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.codehaus.mojo</groupId>
<artifactId>exec-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.1</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>java</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
<configuration>
<classpathScope>test</classpathScope>
<mainClass>Tutorial</mainClass>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build> <dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-core</artifactId>
<version>1.1.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Shiro uses SLF4J for logging. We'll use the 'simple' binding in this
example app. See http://www.slf4j.org for more info. -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>1.7.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-simple</artifactId>
<version>1.6.4</version>
</dependency> </dependencies> </project>
output:
0 [main] INFO com.hjp.shiro.shiro_tutorial.Tutorial - My First Apache Shiro Application
26582 [main] INFO org.apache.shiro.session.mgt.AbstractValidatingSessionManager - Enabling session validation scheduler...
44789 [main] INFO com.hjp.shiro.shiro_tutorial.Tutorial - Retrieved the correct value! [aValue]
80397 [main] INFO com.hjp.shiro.shiro_tutorial.Tutorial - User [lonestarr] logged in successfully.
85201 [main] INFO com.hjp.shiro.shiro_tutorial.Tutorial - May the Schwartz be with you!
90551 [main] INFO com.hjp.shiro.shiro_tutorial.Tutorial - You may use a lightsaber ring. Use it wisely.
95185 [main] INFO com.hjp.shiro.shiro_tutorial.Tutorial - You are permitted to 'drive' the winnebago with license plate (id) 'eagle5'. Here are the keys - have fun!
Refer
http://shiro.apache.org/architecture.html
Shiro理解与总结的更多相关文章
- SpringBoot集成Apache Shiro
笔者因为项目转型的原因,对Apache Shiro安全框架做了一点研究工作,故想写点东西以便将来查阅.之所以选择Shiro也是看了很多人的推荐,号称功能丰富强大,而且易于使用.实践下来的确如大多数人所 ...
- shiro的原理理解
1.shiro原理图如下: 框架解释: subject:主体,可以是用户也可以是程序,主体要访问系统,系统需要对主体进行认证.授权. securityManager:安全管理器,主体进行认证和授权都 ...
- shiro登录验证简单理解
这两天接手了下师兄的项目,要给系统加个日志管理模块,其中需要记录登录功能的日志,那么首先要知道系统的登录是在哪里实现验证的. 该系统把所有登录验证还有权限控制的工作都交给了shiro. 这篇文章就先简 ...
- shiro real的理解,密码匹配等
1 .定义实体及关系 即用户-角色之间是多对多关系,角色-权限之间是多对多关系:且用户和权限之间通过角色建立关系:在系统中验证时通过权限验证,角色只是权限集合,即所谓的显示角色:其实权限应该对应到资源 ...
- shiro+jwt+springboot理解
转自 https://www.cnblogs.com/fengli9998/p/6676783.html https://www.jianshu.com/p/0366a1675bb6 https:// ...
- shiro实现session共享
session共享:在多应用系统中,如果使用了负载均衡,用户的请求会被分发到不同的应用中,A应用中的session数据在B应用中是获取不到的,就会带来共享的问题. 假设:用户第一次访问,连接的A服务器 ...
- Shiro安全框架入门篇(登录验证实例详解与源码)
转载自http://blog.csdn.net/u013142781 一.Shiro框架简单介绍 Apache Shiro是Java的一个安全框架,旨在简化身份验证和授权.Shiro在JavaSE和J ...
- Apache Shiro 学习记录5
本来这篇文章是想写从Factory加载ini配置到生成securityManager的过程的....但是貌似涉及的东西有点多...我学的又比较慢...很多类都来不及研究,我又怕等我后面的研究了前面的都 ...
- Apache Shiro 学习记录4
今天看了教程的第三章...是关于授权的......和以前一样.....自己也研究了下....我觉得看那篇教程怎么说呢.....总体上是为数不多的精品教程了吧....但是有些地方确实是讲的太少了.... ...
随机推荐
- C0301 代码块{}的使用,重定向, 从文件中读取行
#!/bin/bash # 从 /etc/fstab 中读行 File=/etc/fstab { read line1 read line2 } < $File # {}代码块, ...
- CSS水平和垂直居中方案
我们在网页布局的时候,经常会碰到需要居中的情况,那下面就来讲一下有哪几种目前比较常用的居中方案,它们的优点和缺点分别又是什么. 一.水平居中 方法①:(父元素)text-align,(子元素)in ...
- 运动规划(Motion Planning)
相关介绍: https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzA5MDE2MjQ0OQ==&mid=2652786406&idx=1&sn=f937dd6a ...
- 嵌入式开发之davinci--- 8148/8168/8127 中的图像采集格式Sensor信号输出YUV、RGB、RAW DATA、JPEG 4种方式区别
简单来说,YUV: luma (Y) + chroma (UV) 格式, 一般情况下sensor支持YUV422格式,即数据格式是按Y-U-Y-V次序输出的RGB: 传统的红绿蓝格式,比如RGB565 ...
- Ideal-image-slider 幻灯片实例演示
链接:http://zaixianshouce.iteye.com/blog/2316300 http://www.shouce.ren/study/api/s/jq--5733e32bf23bb-- ...
- 【VBA】合并多个excel文件
From http://www.zhihu.com/question/20366713 VBA代码如下: Sub 工作薄间工作表合并() Dim FileOpen Dim X As Integer A ...
- Chem 3D中怎么创建立体模型
ChemDraw作为一款很受大家欢迎的化学绘图软件,其在绘制平面化学方面的功能已经非常的强大了,其实它也可以绘制3D图形.Chem 3D就是绘制3D图形的重要组件.而且为了满足不同的用户绘图的需求,可 ...
- CentOS安装Oracle官方JRE
CentOS自带的JRE是OpenJDK,因为一些原因,需要换用Oracle官方出品的JRE. Oracle JRE下载地址http://java.com/zh_CN/(下载时注意选择相应版本) 可以 ...
- Android 热修复 Tinker接入及源代码浅析
本文已在我的公众号hongyangAndroid首发.转载请标明出处: http://blog.csdn.net/lmj623565791/article/details/54882693本文出自张鸿 ...
- 火狐老是弹出下载openh264-win32.zip怎么取消
OpenH264插件是WebRTC需要调用的一个解码器,从33版本开始内置,默认会自动下载安装和更新,出现这种情况的原因是迅雷或其他下载软件监视浏览器进程,导致火狐无法自动下载响应插件到配置文档中.解 ...
