【Android测试】【第三节】ADB——源码浅谈
◆版权声明:本文出自carter_dream的博客,转载必须注明出处。
转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/by-dream/p/4651724.html
前言
由于本人精力平有限,所以这里简单的说说ADB源码。
首先根据前面的理解,我们已经知道了ADB是“连接手机和PC的一个桥梁”,我们经常在PC端开发的时候,会用到eclipse这个工具,这里面有一个工具叫DDMS,如下图:
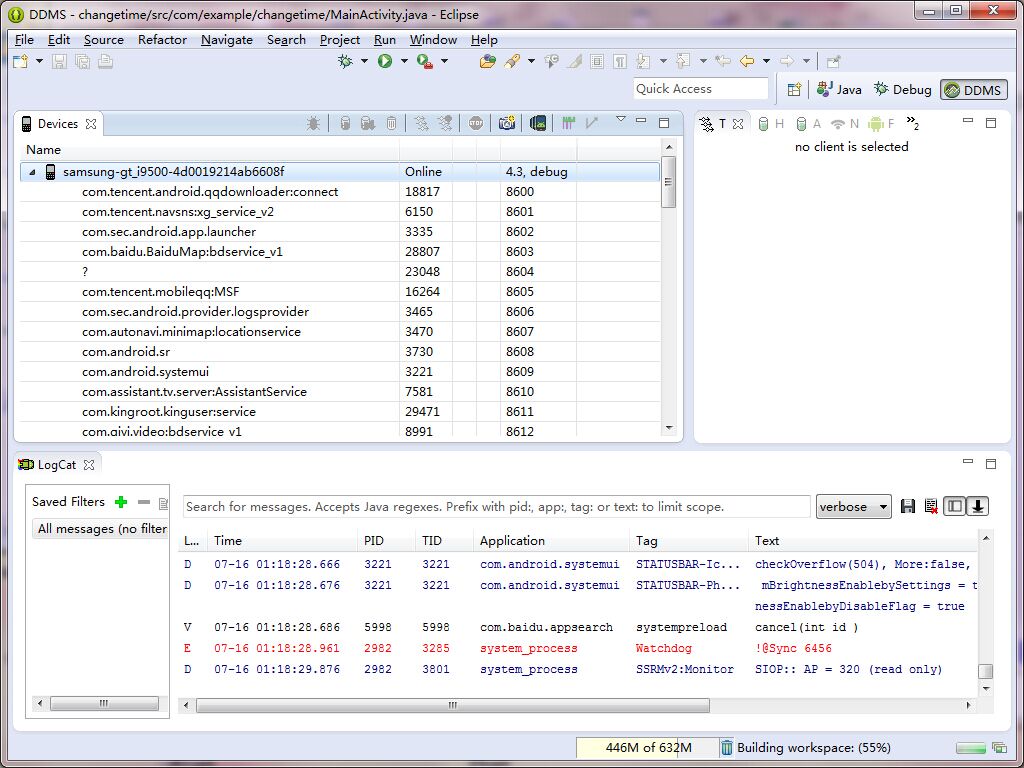
是不是发现通过DDMS在PC端可以看到手机的一些信息,其实呢 它就是通过 “ddmlib.jar” 来建立起ADB的。因此我们今天就通过反编译 “ddmlib.jar” 来分析一下ADB源码。
反编译
首先不得不吐槽一下百度经验的审核人员,我看到里面“反编译jar”的经验没有,于是呢我就写了一个提交了上去,结果提交了很多次,都给我打回了,真不知道这帮审核的人员是怎么想的,这种方便别人参考的内容难道不应该被通过吗?切
好了,说正事吧。
ddmlib.jar 放在 <SDk path>\tools\libs 的文件夹下。
整个反编译的过程如下:
1、下载jd-gui-0.3.3.windows.zip (我的微云链接:http://url.cn/Zz8sOj )
2、解压之后打开,将要编译的jar导入:
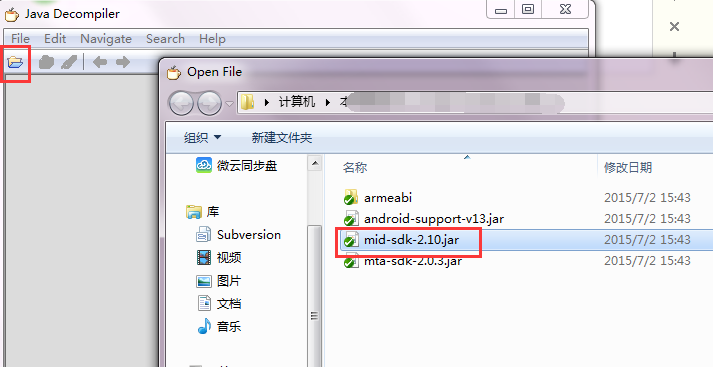
3、展开坐标的树形结构,就是源码啦

上源码
/*
* Copyright (C) 2007 The Android Open Source Project
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ package org.athrun.ddmlib; import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.lang.Thread.State;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
import java.security.InvalidParameterException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern; import org.athrun.ddmlib.Log.LogLevel; /**
* A connection to the host-side android debug bridge (adb)
* <p/>
* This is the central point to communicate with any devices, emulators, or the
* applications running on them.
* <p/>
* <b>{@link #init(boolean)} must be called before anything is done.</b>
*/
public final class AndroidDebugBridge { /*
* Minimum and maximum version of adb supported. This correspond to
* ADB_SERVER_VERSION found in //device/tools/adb/adb.h
*/ private final static int ADB_VERSION_MICRO_MIN = 20;
private final static int ADB_VERSION_MICRO_MAX = -1; private final static Pattern sAdbVersion = Pattern
.compile("^.*(\\d+)\\.(\\d+)\\.(\\d+)$"); //$NON-NLS-1$ private final static String ADB = "adb"; //$NON-NLS-1$
private final static String DDMS = "ddms"; //$NON-NLS-1$
private final static String SERVER_PORT_ENV_VAR = "ANDROID_ADB_SERVER_PORT"; //$NON-NLS-1$ // Where to find the ADB bridge.
final static String ADB_HOST = "127.0.0.1"; //$NON-NLS-1$
final static int ADB_PORT = 5037; private static InetAddress sHostAddr;
private static InetSocketAddress sSocketAddr; private static AndroidDebugBridge sThis;
private static boolean sInitialized = false;
private static boolean sClientSupport; /** Full path to adb. */
private String mAdbOsLocation = null; private boolean mVersionCheck; private boolean mStarted = false; private DeviceMonitor mDeviceMonitor; private final static ArrayList<IDebugBridgeChangeListener> sBridgeListeners = new ArrayList<IDebugBridgeChangeListener>();
private final static ArrayList<IDeviceChangeListener> sDeviceListeners = new ArrayList<IDeviceChangeListener>();
private final static ArrayList<IClientChangeListener> sClientListeners = new ArrayList<IClientChangeListener>(); // lock object for synchronization
private static final Object sLock = sBridgeListeners; /**
* Classes which implement this interface provide a method that deals with
* {@link AndroidDebugBridge} changes.
*/
public interface IDebugBridgeChangeListener {
/**
* Sent when a new {@link AndroidDebugBridge} is connected.
* <p/>
* This is sent from a non UI thread.
*
* @param bridge
* the new {@link AndroidDebugBridge} object.
*/
public void bridgeChanged(AndroidDebugBridge bridge);
} /**
* Classes which implement this interface provide methods that deal with
* {@link IDevice} addition, deletion, and changes.
*/
public interface IDeviceChangeListener {
/**
* Sent when the a device is connected to the {@link AndroidDebugBridge}
* .
* <p/>
* This is sent from a non UI thread.
*
* @param device
* the new device.
*/
public void deviceConnected(IDevice device); /**
* Sent when the a device is connected to the {@link AndroidDebugBridge}
* .
* <p/>
* This is sent from a non UI thread.
*
* @param device
* the new device.
*/
public void deviceDisconnected(IDevice device); /**
* Sent when a device data changed, or when clients are
* started/terminated on the device.
* <p/>
* This is sent from a non UI thread.
*
* @param device
* the device that was updated.
* @param changeMask
* the mask describing what changed. It can contain any of
* the following values: {@link IDevice#CHANGE_BUILD_INFO},
* {@link IDevice#CHANGE_STATE},
* {@link IDevice#CHANGE_CLIENT_LIST}
*/
public void deviceChanged(IDevice device, int changeMask);
} /**
* Classes which implement this interface provide methods that deal with
* {@link Client} changes.
*/
public interface IClientChangeListener {
/**
* Sent when an existing client information changed.
* <p/>
* This is sent from a non UI thread.
*
* @param client
* the updated client.
* @param changeMask
* the bit mask describing the changed properties. It can
* contain any of the following values:
* {@link Client#CHANGE_INFO},
* {@link Client#CHANGE_DEBUGGER_STATUS},
* {@link Client#CHANGE_THREAD_MODE},
* {@link Client#CHANGE_THREAD_DATA},
* {@link Client#CHANGE_HEAP_MODE},
* {@link Client#CHANGE_HEAP_DATA},
* {@link Client#CHANGE_NATIVE_HEAP_DATA}
*/
public void clientChanged(Client client, int changeMask);
} /**
* Initializes the <code>ddm</code> library.
* <p/>
* This must be called once <b>before</b> any call to
* {@link #createBridge(String, boolean)}.
* <p>
* The library can be initialized in 2 ways:
* <ul>
* <li>Mode 1: <var>clientSupport</var> == <code>true</code>.<br>
* The library monitors the devices and the applications running on them. It
* will connect to each application, as a debugger of sort, to be able to
* interact with them through JDWP packets.</li>
* <li>Mode 2: <var>clientSupport</var> == <code>false</code>.<br>
* The library only monitors devices. The applications are left untouched,
* letting other tools built on <code>ddmlib</code> to connect a debugger to
* them.</li>
* </ul>
* <p/>
* <b>Only one tool can run in mode 1 at the same time.</b>
* <p/>
* Note that mode 1 does not prevent debugging of applications running on
* devices. Mode 1 lets debuggers connect to <code>ddmlib</code> which acts
* as a proxy between the debuggers and the applications to debug. See
* {@link Client#getDebuggerListenPort()}.
* <p/>
* The preferences of <code>ddmlib</code> should also be initialized with
* whatever default values were changed from the default values.
* <p/>
* When the application quits, {@link #terminate()} should be called.
*
* @param clientSupport
* Indicates whether the library should enable the monitoring and
* interaction with applications running on the devices.
* @see AndroidDebugBridge#createBridge(String, boolean)
* @see DdmPreferences
*/
public static synchronized void init(boolean clientSupport) {
if (sInitialized) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"AndroidDebugBridge.init() has already been called.");
}
sInitialized = true;
sClientSupport = clientSupport; // Determine port and instantiate socket address.
initAdbSocketAddr(); MonitorThread monitorThread = MonitorThread.createInstance();
monitorThread.start(); HandleHello.register(monitorThread);
HandleAppName.register(monitorThread);
HandleTest.register(monitorThread);
HandleThread.register(monitorThread);
HandleHeap.register(monitorThread);
HandleWait.register(monitorThread);
HandleProfiling.register(monitorThread);
HandleNativeHeap.register(monitorThread);
} /**
* Terminates the ddm library. This must be called upon application
* termination.
*/
public static synchronized void terminate() {
// kill the monitoring services
if (sThis != null && sThis.mDeviceMonitor != null) {
sThis.mDeviceMonitor.stop();
sThis.mDeviceMonitor = null;
} MonitorThread monitorThread = MonitorThread.getInstance();
if (monitorThread != null) {
monitorThread.quit();
} sInitialized = false;
} /**
* Returns whether the ddmlib is setup to support monitoring and interacting
* with {@link Client}s running on the {@link IDevice}s.
*/
static boolean getClientSupport() {
return sClientSupport;
} /**
* Returns the socket address of the ADB server on the host.
*/
public static InetSocketAddress getSocketAddress() {
return sSocketAddr;
} /**
* Creates a {@link AndroidDebugBridge} that is not linked to any particular
* executable.
* <p/>
* This bridge will expect adb to be running. It will not be able to
* start/stop/restart adb.
* <p/>
* If a bridge has already been started, it is directly returned with no
* changes (similar to calling {@link #getBridge()}).
*
* @return a connected bridge.
*/
public static AndroidDebugBridge createBridge() {
synchronized (sLock) {
if (sThis != null) {
return sThis;
} try {
sThis = new AndroidDebugBridge();
sThis.start();
} catch (InvalidParameterException e) {
sThis = null;
} // because the listeners could remove themselves from the list while
// processing
// their event callback, we make a copy of the list and iterate on
// it instead of
// the main list.
// This mostly happens when the application quits.
IDebugBridgeChangeListener[] listenersCopy = sBridgeListeners
.toArray(new IDebugBridgeChangeListener[sBridgeListeners
.size()]); // notify the listeners of the change
for (IDebugBridgeChangeListener listener : listenersCopy) {
// we attempt to catch any exception so that a bad listener
// doesn't kill our
// thread
try {
listener.bridgeChanged(sThis);
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e(DDMS, e);
}
} return sThis;
}
} /**
* Creates a new debug bridge from the location of the command line tool.
* <p/>
* Any existing server will be disconnected, unless the location is the same
* and <code>forceNewBridge</code> is set to false.
*
* @param osLocation
* the location of the command line tool 'adb'
* @param forceNewBridge
* force creation of a new bridge even if one with the same
* location already exists.
* @return a connected bridge.
*/
public static AndroidDebugBridge createBridge(String osLocation,
boolean forceNewBridge) {
synchronized (sLock) {
if (sThis != null) {
if (sThis.mAdbOsLocation != null
&& sThis.mAdbOsLocation.equals(osLocation)
&& forceNewBridge == false) {
return sThis;
} else {
// stop the current server
sThis.stop();
}
} try {
sThis = new AndroidDebugBridge(osLocation);
sThis.start();
} catch (InvalidParameterException e) {
sThis = null;
} // because the listeners could remove themselves from the list while
// processing
// their event callback, we make a copy of the list and iterate on
// it instead of
// the main list.
// This mostly happens when the application quits.
IDebugBridgeChangeListener[] listenersCopy = sBridgeListeners
.toArray(new IDebugBridgeChangeListener[sBridgeListeners
.size()]); // notify the listeners of the change
for (IDebugBridgeChangeListener listener : listenersCopy) {
// we attempt to catch any exception so that a bad listener
// doesn't kill our
// thread
try {
listener.bridgeChanged(sThis);
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e(DDMS, e);
}
} return sThis;
}
} /**
* Returns the current debug bridge. Can be <code>null</code> if none were
* created.
*/
public static AndroidDebugBridge getBridge() {
return sThis;
} /**
* Disconnects the current debug bridge, and destroy the object.
* <p/>
* This also stops the current adb host server.
* <p/>
* A new object will have to be created with
* {@link #createBridge(String, boolean)}.
*/
public static void disconnectBridge() {
synchronized (sLock) {
if (sThis != null) {
sThis.stop();
sThis = null; // because the listeners could remove themselves from the list
// while processing
// their event callback, we make a copy of the list and iterate
// on it instead of
// the main list.
// This mostly happens when the application quits.
IDebugBridgeChangeListener[] listenersCopy = sBridgeListeners
.toArray(new IDebugBridgeChangeListener[sBridgeListeners
.size()]); // notify the listeners.
for (IDebugBridgeChangeListener listener : listenersCopy) {
// we attempt to catch any exception so that a bad listener
// doesn't kill our
// thread
try {
listener.bridgeChanged(sThis);
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e(DDMS, e);
}
}
}
}
} /**
* Adds the listener to the collection of listeners who will be notified
* when a new {@link AndroidDebugBridge} is connected, by sending it one of
* the messages defined in the {@link IDebugBridgeChangeListener} interface.
*
* @param listener
* The listener which should be notified.
*/
public static void addDebugBridgeChangeListener(
IDebugBridgeChangeListener listener) {
synchronized (sLock) {
if (sBridgeListeners.contains(listener) == false) {
sBridgeListeners.add(listener);
if (sThis != null) {
// we attempt to catch any exception so that a bad listener
// doesn't kill our
// thread
try {
listener.bridgeChanged(sThis);
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e(DDMS, e);
}
}
}
}
} /**
* Removes the listener from the collection of listeners who will be
* notified when a new {@link AndroidDebugBridge} is started.
*
* @param listener
* The listener which should no longer be notified.
*/
public static void removeDebugBridgeChangeListener(
IDebugBridgeChangeListener listener) {
synchronized (sLock) {
sBridgeListeners.remove(listener);
}
} /**
* Adds the listener to the collection of listeners who will be notified
* when a {@link IDevice} is connected, disconnected, or when its properties
* or its {@link Client} list changed, by sending it one of the messages
* defined in the {@link IDeviceChangeListener} interface.
*
* @param listener
* The listener which should be notified.
*/
public static void addDeviceChangeListener(IDeviceChangeListener listener) {
synchronized (sLock) {
if (sDeviceListeners.contains(listener) == false) {
sDeviceListeners.add(listener);
}
}
} /**
* Removes the listener from the collection of listeners who will be
* notified when a {@link IDevice} is connected, disconnected, or when its
* properties or its {@link Client} list changed.
*
* @param listener
* The listener which should no longer be notified.
*/
public static void removeDeviceChangeListener(IDeviceChangeListener listener) {
synchronized (sLock) {
sDeviceListeners.remove(listener);
}
} /**
* Adds the listener to the collection of listeners who will be notified
* when a {@link Client} property changed, by sending it one of the messages
* defined in the {@link IClientChangeListener} interface.
*
* @param listener
* The listener which should be notified.
*/
public static void addClientChangeListener(IClientChangeListener listener) {
synchronized (sLock) {
if (sClientListeners.contains(listener) == false) {
sClientListeners.add(listener);
}
}
} /**
* Removes the listener from the collection of listeners who will be
* notified when a {@link Client} property changed.
*
* @param listener
* The listener which should no longer be notified.
*/
public static void removeClientChangeListener(IClientChangeListener listener) {
synchronized (sLock) {
sClientListeners.remove(listener);
}
} /**
* Returns the devices.
*
* @see #hasInitialDeviceList()
*/
public IDevice[] getDevices() {
synchronized (sLock) {
if (mDeviceMonitor != null) {
return mDeviceMonitor.getDevices();
}
} return new IDevice[0];
} /**
* Returns whether the bridge has acquired the initial list from adb after
* being created.
* <p/>
* Calling {@link #getDevices()} right after
* {@link #createBridge(String, boolean)} will generally result in an empty
* list. This is due to the internal asynchronous communication mechanism
* with <code>adb</code> that does not guarantee that the {@link IDevice}
* list has been built before the call to {@link #getDevices()}.
* <p/>
* The recommended way to get the list of {@link IDevice} objects is to
* create a {@link IDeviceChangeListener} object.
*/
public boolean hasInitialDeviceList() {
if (mDeviceMonitor != null) {
return mDeviceMonitor.hasInitialDeviceList();
} return false;
} /**
* Sets the client to accept debugger connection on the custom
* "Selected debug port".
*
* @param selectedClient
* the client. Can be null.
*/
public void setSelectedClient(Client selectedClient) {
MonitorThread monitorThread = MonitorThread.getInstance();
if (monitorThread != null) {
monitorThread.setSelectedClient(selectedClient);
}
} /**
* Returns whether the {@link AndroidDebugBridge} object is still connected
* to the adb daemon.
*/
public boolean isConnected() {
MonitorThread monitorThread = MonitorThread.getInstance();
if (mDeviceMonitor != null && monitorThread != null) {
return mDeviceMonitor.isMonitoring()
&& monitorThread.getState() != State.TERMINATED;
}
return false;
} /**
* Returns the number of times the {@link AndroidDebugBridge} object
* attempted to connect to the adb daemon.
*/
public int getConnectionAttemptCount() {
if (mDeviceMonitor != null) {
return mDeviceMonitor.getConnectionAttemptCount();
}
return -1;
} /**
* Returns the number of times the {@link AndroidDebugBridge} object
* attempted to restart the adb daemon.
*/
public int getRestartAttemptCount() {
if (mDeviceMonitor != null) {
return mDeviceMonitor.getRestartAttemptCount();
}
return -1;
} /**
* Creates a new bridge.
*
* @param osLocation
* the location of the command line tool
* @throws InvalidParameterException
*/
private AndroidDebugBridge(String osLocation)
throws InvalidParameterException {
if (osLocation == null || osLocation.length() == 0) {
throw new InvalidParameterException();
}
mAdbOsLocation = osLocation; checkAdbVersion();
} /**
* Creates a new bridge not linked to any particular adb executable.
*/
private AndroidDebugBridge() {
} /**
* Queries adb for its version number and checks it against
* {@link #MIN_VERSION_NUMBER} and {@link #MAX_VERSION_NUMBER}
*/
private void checkAdbVersion() {
// default is bad check
mVersionCheck = false; if (mAdbOsLocation == null) {
return;
} try {
String[] command = new String[2];
command[0] = mAdbOsLocation;
command[1] = "version"; //$NON-NLS-1$
Log.d(DDMS,
String.format("Checking '%1$s version'", mAdbOsLocation)); //$NON-NLS-1$
Process process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(command); ArrayList<String> errorOutput = new ArrayList<String>();
ArrayList<String> stdOutput = new ArrayList<String>();
int status = grabProcessOutput(process, errorOutput, stdOutput,
true /* waitForReaders */); if (status != 0) {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(
"'adb version' failed!"); //$NON-NLS-1$
for (String error : errorOutput) {
builder.append('\n');
builder.append(error);
}
Log.logAndDisplay(LogLevel.ERROR, "adb", builder.toString());
} // check both stdout and stderr
boolean versionFound = false;
for (String line : stdOutput) {
versionFound = scanVersionLine(line);
if (versionFound) {
break;
}
}
if (!versionFound) {
for (String line : errorOutput) {
versionFound = scanVersionLine(line);
if (versionFound) {
break;
}
}
} if (!versionFound) {
// if we get here, we failed to parse the output.
Log.logAndDisplay(LogLevel.ERROR, ADB,
"Failed to parse the output of 'adb version'"); //$NON-NLS-1$
} } catch (IOException e) {
Log.logAndDisplay(LogLevel.ERROR, ADB,
"Failed to get the adb version: " + e.getMessage()); //$NON-NLS-1$
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
} finally { }
} /**
* Scans a line resulting from 'adb version' for a potential version number.
* <p/>
* If a version number is found, it checks the version number against what
* is expected by this version of ddms.
* <p/>
* Returns true when a version number has been found so that we can stop
* scanning, whether the version number is in the acceptable range or not.
*
* @param line
* The line to scan.
* @return True if a version number was found (whether it is acceptable or
* not).
*/
@SuppressWarnings("all")
// With Eclipse 3.6, replace by @SuppressWarnings("unused")
private boolean scanVersionLine(String line) {
if (line != null) {
Matcher matcher = sAdbVersion.matcher(line);
if (matcher.matches()) {
int majorVersion = Integer.parseInt(matcher.group(1));
int minorVersion = Integer.parseInt(matcher.group(2));
int microVersion = Integer.parseInt(matcher.group(3)); // check only the micro version for now.
if (microVersion < ADB_VERSION_MICRO_MIN) {
String message = String.format(
"Required minimum version of adb: %1$d.%2$d.%3$d." //$NON-NLS-1$
+ "Current version is %1$d.%2$d.%4$d", //$NON-NLS-1$
majorVersion, minorVersion, ADB_VERSION_MICRO_MIN,
microVersion);
Log.logAndDisplay(LogLevel.ERROR, ADB, message);
} else if (ADB_VERSION_MICRO_MAX != -1
&& microVersion > ADB_VERSION_MICRO_MAX) {
String message = String.format(
"Required maximum version of adb: %1$d.%2$d.%3$d." //$NON-NLS-1$
+ "Current version is %1$d.%2$d.%4$d", //$NON-NLS-1$
majorVersion, minorVersion, ADB_VERSION_MICRO_MAX,
microVersion);
Log.logAndDisplay(LogLevel.ERROR, ADB, message);
} else {
mVersionCheck = true;
} return true;
}
}
return false;
} /**
* Starts the debug bridge.
*
* @return true if success.
*/
boolean start() {
if (mAdbOsLocation != null
&& (mVersionCheck == false || startAdb() == false)) {
return false;
} mStarted = true; // now that the bridge is connected, we start the underlying services.
mDeviceMonitor = new DeviceMonitor(this);
mDeviceMonitor.start(); return true;
} /**
* Kills the debug bridge, and the adb host server.
*
* @return true if success
*/
boolean stop() {
// if we haven't started we return false;
if (mStarted == false) {
return false;
} // kill the monitoring services
mDeviceMonitor.stop();
mDeviceMonitor = null; if (stopAdb() == false) {
return false;
} mStarted = false;
return true;
} /**
* Restarts adb, but not the services around it.
*
* @return true if success.
*/
public boolean restart() {
if (mAdbOsLocation == null) {
Log.e(ADB,
"Cannot restart adb when AndroidDebugBridge is created without the location of adb."); //$NON-NLS-1$
return false;
} if (mVersionCheck == false) {
Log.logAndDisplay(LogLevel.ERROR, ADB,
"Attempting to restart adb, but version check failed!"); //$NON-NLS-1$
return false;
}
synchronized (this) {
stopAdb(); boolean restart = startAdb(); if (restart && mDeviceMonitor == null) {
mDeviceMonitor = new DeviceMonitor(this);
mDeviceMonitor.start();
} return restart;
}
} /**
* Notify the listener of a new {@link IDevice}.
* <p/>
* The notification of the listeners is done in a synchronized block. It is
* important to expect the listeners to potentially access various methods
* of {@link IDevice} as well as {@link #getDevices()} which use internal
* locks.
* <p/>
* For this reason, any call to this method from a method of
* {@link DeviceMonitor}, {@link IDevice} which is also inside a
* synchronized block, should first synchronize on the
* {@link AndroidDebugBridge} lock. Access to this lock is done through
* {@link #getLock()}.
*
* @param device
* the new <code>IDevice</code>.
* @see #getLock()
*/
void deviceConnected(IDevice device) {
// because the listeners could remove themselves from the list while
// processing
// their event callback, we make a copy of the list and iterate on it
// instead of
// the main list.
// This mostly happens when the application quits.
IDeviceChangeListener[] listenersCopy = null;
synchronized (sLock) {
listenersCopy = sDeviceListeners
.toArray(new IDeviceChangeListener[sDeviceListeners.size()]);
} // Notify the listeners
for (IDeviceChangeListener listener : listenersCopy) {
// we attempt to catch any exception so that a bad listener doesn't
// kill our
// thread
try {
listener.deviceConnected(device);
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e(DDMS, e);
}
}
} /**
* Notify the listener of a disconnected {@link IDevice}.
* <p/>
* The notification of the listeners is done in a synchronized block. It is
* important to expect the listeners to potentially access various methods
* of {@link IDevice} as well as {@link #getDevices()} which use internal
* locks.
* <p/>
* For this reason, any call to this method from a method of
* {@link DeviceMonitor}, {@link IDevice} which is also inside a
* synchronized block, should first synchronize on the
* {@link AndroidDebugBridge} lock. Access to this lock is done through
* {@link #getLock()}.
*
* @param device
* the disconnected <code>IDevice</code>.
* @see #getLock()
*/
void deviceDisconnected(IDevice device) {
// because the listeners could remove themselves from the list while
// processing
// their event callback, we make a copy of the list and iterate on it
// instead of
// the main list.
// This mostly happens when the application quits.
IDeviceChangeListener[] listenersCopy = null;
synchronized (sLock) {
listenersCopy = sDeviceListeners
.toArray(new IDeviceChangeListener[sDeviceListeners.size()]);
} // Notify the listeners
for (IDeviceChangeListener listener : listenersCopy) {
// we attempt to catch any exception so that a bad listener doesn't
// kill our
// thread
try {
listener.deviceDisconnected(device);
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e(DDMS, e);
}
}
} /**
* Notify the listener of a modified {@link IDevice}.
* <p/>
* The notification of the listeners is done in a synchronized block. It is
* important to expect the listeners to potentially access various methods
* of {@link IDevice} as well as {@link #getDevices()} which use internal
* locks.
* <p/>
* For this reason, any call to this method from a method of
* {@link DeviceMonitor}, {@link IDevice} which is also inside a
* synchronized block, should first synchronize on the
* {@link AndroidDebugBridge} lock. Access to this lock is done through
* {@link #getLock()}.
*
* @param device
* the modified <code>IDevice</code>.
* @see #getLock()
*/
void deviceChanged(IDevice device, int changeMask) {
// because the listeners could remove themselves from the list while
// processing
// their event callback, we make a copy of the list and iterate on it
// instead of
// the main list.
// This mostly happens when the application quits.
IDeviceChangeListener[] listenersCopy = null;
synchronized (sLock) {
listenersCopy = sDeviceListeners
.toArray(new IDeviceChangeListener[sDeviceListeners.size()]);
} // Notify the listeners
for (IDeviceChangeListener listener : listenersCopy) {
// we attempt to catch any exception so that a bad listener doesn't
// kill our
// thread
try {
listener.deviceChanged(device, changeMask);
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e(DDMS, e);
}
}
} /**
* Notify the listener of a modified {@link Client}.
* <p/>
* The notification of the listeners is done in a synchronized block. It is
* important to expect the listeners to potentially access various methods
* of {@link IDevice} as well as {@link #getDevices()} which use internal
* locks.
* <p/>
* For this reason, any call to this method from a method of
* {@link DeviceMonitor}, {@link IDevice} which is also inside a
* synchronized block, should first synchronize on the
* {@link AndroidDebugBridge} lock. Access to this lock is done through
* {@link #getLock()}.
*
* @param device
* the modified <code>Client</code>.
* @param changeMask
* the mask indicating what changed in the <code>Client</code>
* @see #getLock()
*/
void clientChanged(Client client, int changeMask) {
// because the listeners could remove themselves from the list while
// processing
// their event callback, we make a copy of the list and iterate on it
// instead of
// the main list.
// This mostly happens when the application quits.
IClientChangeListener[] listenersCopy = null;
synchronized (sLock) {
listenersCopy = sClientListeners
.toArray(new IClientChangeListener[sClientListeners.size()]); } // Notify the listeners
for (IClientChangeListener listener : listenersCopy) {
// we attempt to catch any exception so that a bad listener doesn't
// kill our
// thread
try {
listener.clientChanged(client, changeMask);
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e(DDMS, e);
}
}
} /**
* Returns the {@link DeviceMonitor} object.
*/
DeviceMonitor getDeviceMonitor() {
return mDeviceMonitor;
} /**
* Starts the adb host side server.
*
* @return true if success
*/
synchronized boolean startAdb() {
if (mAdbOsLocation == null) {
Log.e(ADB,
"Cannot start adb when AndroidDebugBridge is created without the location of adb."); //$NON-NLS-1$
return false;
} Process proc;
int status = -1; try {
String[] command = new String[2];
command[0] = mAdbOsLocation;
command[1] = "start-server"; //$NON-NLS-1$
Log.d(DDMS, String.format(
"Launching '%1$s %2$s' to ensure ADB is running.", //$NON-NLS-1$
mAdbOsLocation, command[1]));
ProcessBuilder processBuilder = new ProcessBuilder(command);
if (DdmPreferences.getUseAdbHost()) {
String adbHostValue = DdmPreferences.getAdbHostValue();
if (adbHostValue != null && adbHostValue.length() > 0) {
// TODO : check that the String is a valid IP address
Map<String, String> env = processBuilder.environment();
env.put("ADBHOST", adbHostValue);
}
}
proc = processBuilder.start(); ArrayList<String> errorOutput = new ArrayList<String>();
ArrayList<String> stdOutput = new ArrayList<String>();
status = grabProcessOutput(proc, errorOutput, stdOutput, false /* waitForReaders */); } catch (IOException ioe) {
Log.d(DDMS, "Unable to run 'adb': " + ioe.getMessage()); //$NON-NLS-1$
// we'll return false;
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
Log.d(DDMS, "Unable to run 'adb': " + ie.getMessage()); //$NON-NLS-1$
// we'll return false;
} if (status != 0) {
Log.w(DDMS,
"'adb start-server' failed -- run manually if necessary"); //$NON-NLS-1$
return false;
} Log.d(DDMS, "'adb start-server' succeeded"); //$NON-NLS-1$ return true;
} /**
* Stops the adb host side server.
*
* @return true if success
*/
private synchronized boolean stopAdb() {
if (mAdbOsLocation == null) {
Log.e(ADB,
"Cannot stop adb when AndroidDebugBridge is created without the location of adb."); //$NON-NLS-1$
return false;
} Process proc;
int status = -1; try {
String[] command = new String[2];
command[0] = mAdbOsLocation;
command[1] = "kill-server"; //$NON-NLS-1$
proc = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(command);
status = proc.waitFor();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
// we'll return false;
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
// we'll return false;
} if (status != 0) {
Log.w(DDMS, "'adb kill-server' failed -- run manually if necessary"); //$NON-NLS-1$
return false;
} Log.d(DDMS, "'adb kill-server' succeeded"); //$NON-NLS-1$
return true;
} /**
* Get the stderr/stdout outputs of a process and return when the process is
* done. Both <b>must</b> be read or the process will block on windows.
*
* @param process
* The process to get the ouput from
* @param errorOutput
* The array to store the stderr output. cannot be null.
* @param stdOutput
* The array to store the stdout output. cannot be null.
* @param displayStdOut
* If true this will display stdout as well
* @param waitforReaders
* if true, this will wait for the reader threads.
* @return the process return code.
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
private int grabProcessOutput(final Process process,
final ArrayList<String> errorOutput,
final ArrayList<String> stdOutput, boolean waitforReaders)
throws InterruptedException {
assert errorOutput != null;
assert stdOutput != null;
// read the lines as they come. if null is returned, it's
// because the process finished
Thread t1 = new Thread("") { //$NON-NLS-1$
@Override
public void run() {
// create a buffer to read the stderr output
InputStreamReader is = new InputStreamReader(
process.getErrorStream());
BufferedReader errReader = new BufferedReader(is); try {
while (true) {
String line = errReader.readLine();
if (line != null) {
Log.e(ADB, line);
errorOutput.add(line);
} else {
break;
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// do nothing.
}
}
}; Thread t2 = new Thread("") { //$NON-NLS-1$
@Override
public void run() {
InputStreamReader is = new InputStreamReader(
process.getInputStream());
BufferedReader outReader = new BufferedReader(is); try {
while (true) {
String line = outReader.readLine();
if (line != null) {
Log.d(ADB, line);
stdOutput.add(line);
} else {
break;
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// do nothing.
}
}
}; t1.start();
t2.start(); // it looks like on windows process#waitFor() can return
// before the thread have filled the arrays, so we wait for both threads
// and the
// process itself.
if (waitforReaders) {
try {
t1.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
try {
t2.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
} // get the return code from the process
return process.waitFor();
} /**
* Returns the singleton lock used by this class to protect any access to
* the listener.
* <p/>
* This includes adding/removing listeners, but also notifying listeners of
* new bridges, devices, and clients.
*/
static Object getLock() {
return sLock;
} /**
* Instantiates sSocketAddr with the address of the host's adb process.
*/
private static void initAdbSocketAddr() {
try {
int adb_port = determineAndValidateAdbPort();
sHostAddr = InetAddress.getByName(ADB_HOST);
sSocketAddr = new InetSocketAddress(sHostAddr, adb_port);
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
// localhost should always be known.
}
} /**
* Determines port where ADB is expected by looking at an env variable.
* <p/>
* The value for the environment variable ANDROID_ADB_SERVER_PORT is
* validated, IllegalArgumentException is thrown on illegal values.
* <p/>
*
* @return The port number where the host's adb should be expected or
* started.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
* if ANDROID_ADB_SERVER_PORT has a non-numeric value.
*/
private static int determineAndValidateAdbPort() {
String adb_env_var;
int result = ADB_PORT;
try {
adb_env_var = System.getenv(SERVER_PORT_ENV_VAR); if (adb_env_var != null) {
adb_env_var = adb_env_var.trim();
} if (adb_env_var != null && adb_env_var.length() > 0) {
// C tools (adb, emulator) accept hex and octal port numbers, so
// need to accept
// them too.
result = Integer.decode(adb_env_var); if (result <= 0) {
String errMsg = "env var " + SERVER_PORT_ENV_VAR //$NON-NLS-1$
+ ": must be >=0, got " //$NON-NLS-1$
+ System.getenv(SERVER_PORT_ENV_VAR);
throw new IllegalArgumentException(errMsg);
}
}
} catch (NumberFormatException nfEx) {
String errMsg = "env var " + SERVER_PORT_ENV_VAR //$NON-NLS-1$
+ ": illegal value '" //$NON-NLS-1$
+ System.getenv(SERVER_PORT_ENV_VAR) + "'"; //$NON-NLS-1$
throw new IllegalArgumentException(errMsg);
} catch (SecurityException secEx) {
// A security manager has been installed that doesn't allow access
// to env vars.
// So an environment variable might have been set, but we can't
// tell.
// Let's log a warning and continue with ADB's default port.
// The issue is that adb would be started (by the forked process
// having access
// to the env vars) on the desired port, but within this process, we
// can't figure out
// what that port is. However, a security manager not granting
// access to env vars
// but allowing to fork is a rare and interesting configuration, so
// the right
// thing seems to be to continue using the default port, as forking
// is likely to
// fail later on in the scenario of the security manager.
Log.w(DDMS,
"No access to env variables allowed by current security manager. " //$NON-NLS-1$
+ "If you've set ANDROID_ADB_SERVER_PORT: it's being ignored."); //$NON-NLS-1$
}
return result;
} }
AndroidDebugBridge
实现
既然ddmlib包含了ADB,因为我们就引入它,来进行一些ADB操作。
1、建立一个普通的Java工程;
2、将ddmlib.jar,包含进来(这里需要主要,还需要引入guava-15.0.jar,否则会提示少 com/geogle/common/*** 的错误,guava和ddmlib存放在同一个目录下)
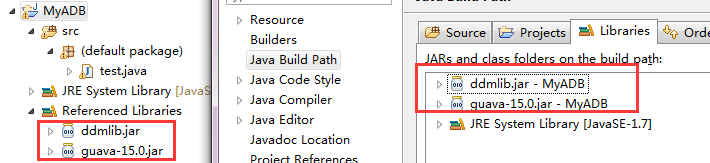
3、调用AndroidDebugBridge类中的方法,完成要实现的方法(例如下面)
import com.android.ddmlib.AndroidDebugBridge;
import com.android.ddmlib.IDevice; public class test
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println(" begin ");
AndroidDebugBridge.init(false);
//AndroidDebugBridge adb = AndroidDebugBridge.createBridge("E:\\adt-bundle-windows-x86_64-20140702\\sdk\\platform-tools\\adb.exe", true);
AndroidDebugBridge adb = AndroidDebugBridge.createBridge(); WaitDevices(adb); for (IDevice device : adb.getDevices())
{
System.out.println("Device Name: " + device.getName());
System.out.println("Device isOnline: " + device.isOnline() );
System.out.println("Device SerialNumber: : " + device.getSerialNumber());
}
System.out.println(" end ");
} public static void WaitDevices(AndroidDebugBridge adb)
{
int count = 0;
while (adb.hasInitialDeviceList() == false)
{
try
{
Thread.sleep(500);
System.err.println("wait for devices");
count++;
} catch (InterruptedException e)
{
}
if (count > 50)
{
System.err.println("time out\n");
break;
}
}
}
}
运行上面的代码输出结果为:
begin
wait for devices
Device Name: samsung-gt_i9500-4d0019214ab6608f
Device isOnline: true
Device SerialNumber: : 4d0019214ab6608f
end
注意区分,上面代码里的createBridge() 的方法,无参得到代表使用系统当前的ADB,如果指定了参数,且第二个参数为ture,则启动指定的ADB,这些通过源代码都可以看到。另外createBridge() 之前必须要调用 init 的方法。接下来拿到Idevice 对象就可以实现各种各样的功能了,这里只是说一下怎么用这个lib,具体你想通过这个东西来拿到什么信息,还需自己动手去写写。
【Android测试】【第三节】ADB——源码浅谈的更多相关文章
- 【Android测试】【第七节】Monkey——源码浅谈
◆版权声明:本文出自胖喵~的博客,转载必须注明出处. 转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/by-dream/p/4713466.html 前言 根据上一篇我们学会了Monke ...
- 源码浅谈(一):java中的 toString()方法
前言: toString()方法 相信大家都用到过,一般用于以字符串的形式返回对象的相关数据. 最近项目中需要对一个ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> ...
- 源码浅谈(二):java中的 Integer.parseInt(String str)方法
这个方法是将字符串转换为整型 一.parseInt方法 ,可以看到默认又调用了parseInt(s,10) , 第二个参数为基数,默认10 ,当然也可以自己设置 public static int ...
- 结合源码浅谈Spring容器与其子容器Spring MVC 冲突问题
容器是整个Spring 框架的核心思想,用来管理Bean的整个生命周期. 一个项目中引入Spring和SpringMVC这两个框架,Spring是父容器,SpringMVC是其子容器,子容器可以看见父 ...
- glibc memcpy() 源码浅谈
其实我本来只是想搞懂为什么memcpy()函数的参数类型是void *的: 我以为会在memcpy()源码中能找到答案,其实并没有,void *只是在传递参数的时候起了作用,可以让memcpy()接受 ...
- Android Small插件化框架源码分析
Android Small插件化框架源码分析 目录 概述 Small如何使用 插件加载流程 待改进的地方 一.概述 Small是一个写得非常简洁的插件化框架,工程源码位置:https://github ...
- ADB 源码分析(一) ——ADB模块简述【转】
ADB源码分析(一)——ADB模块简述 1.Adb 源码路径(system/core/adb). 2.要想很快的了解一个模块的基本情况,最直接的就是查看该模块的Android.mk文件,下面就来看看a ...
- 基于Android开发的天气预报app(源码下载)
原文:基于Android开发的天气预报app(源码下载) 基于AndroidStudio环境开发的天气app -系统总体介绍:本天气app使用AndroidStudio这个IDE工具在Windows1 ...
- Android Studio导入Android 4.4.4r1的源码
本文博客地址:http://blog.csdn.net/qq1084283172/article/details/70339471 一.环境配置 1.ubuntu 14.04.5 x64bit 2.j ...
随机推荐
- Regionals 2012 :: HangZhou
题目传送门排行榜 一个人做了12年北大出的题,自己还是太弱了,图论的知识忘光光,最小生成树裸题写不来,Dijkstra TLE不知道用SPFA. 简单几何(点到线段的距离) + 三分 B Steali ...
- BZOJ3329 : Xorequ
第一问: 打表可得规律:当且仅当x&(x<<1)=0时才会是解,于是数位DP f[i][j][k]表示二进制中前i位,上一位是j,前i位是否等于n的方案数 第二问: 打表可得规律: ...
- MySQL安装问题:Unable to update security settings解决方案
主要问题还是之前装过,卸载的时候卸载不干净导致的. 如下: 安装到最后出现: Unable to update security settings. Access denied for user 'r ...
- PHP 常用到的一些小程序
1.计算两个时间的相差几天 $startdate=strtotime(“2009-12-09”); $enddate=strtotime(“2009-12-05”); 上面的php时间日期函数strt ...
- easyui datagrid 增删改查示例
查询JSP页面 <!doctype html> <%@include file="/internet/common.jsp"%> <!-- 新样式右侧 ...
- Servlet 编程 请求的转发
在上篇的基础上,修改servlet *转发只能在同一应用内转发. 将forward 地址改为:youku.com 不能访问 重定向是可以访问外部应用的
- [转]Multiple outputs from T4 made easy
本文转自:http://damieng.com/blog/2009/01/22/multiple-outputs-from-t4-made-easy One of the things I wante ...
- Error 2147943712 during task creation
In a Windows 2008 server, when you confirm the creation of a new task, you may obtain the following ...
- Spring-JDBC通用Dao
JdbcBaseDao JdbcBaseDao接口,内容如下: package com.sun4j.core.jdbc.dao; import java.io.Serializable; import ...
- Windows系统中Git的安装配置
一.Git安装 1.下载 Git官网:https://git-scm.com/download/ 选择windows版本下载即可. 百度软件中心:http://rj.baidu.com/ 如官网下载不 ...
