Vue SSR初探
因为之前用nuxt开发过应用程序,但是nuxt早就达到了开箱即用的目的,所以一直对vue ssr的具体实现存在好奇。
构建步骤
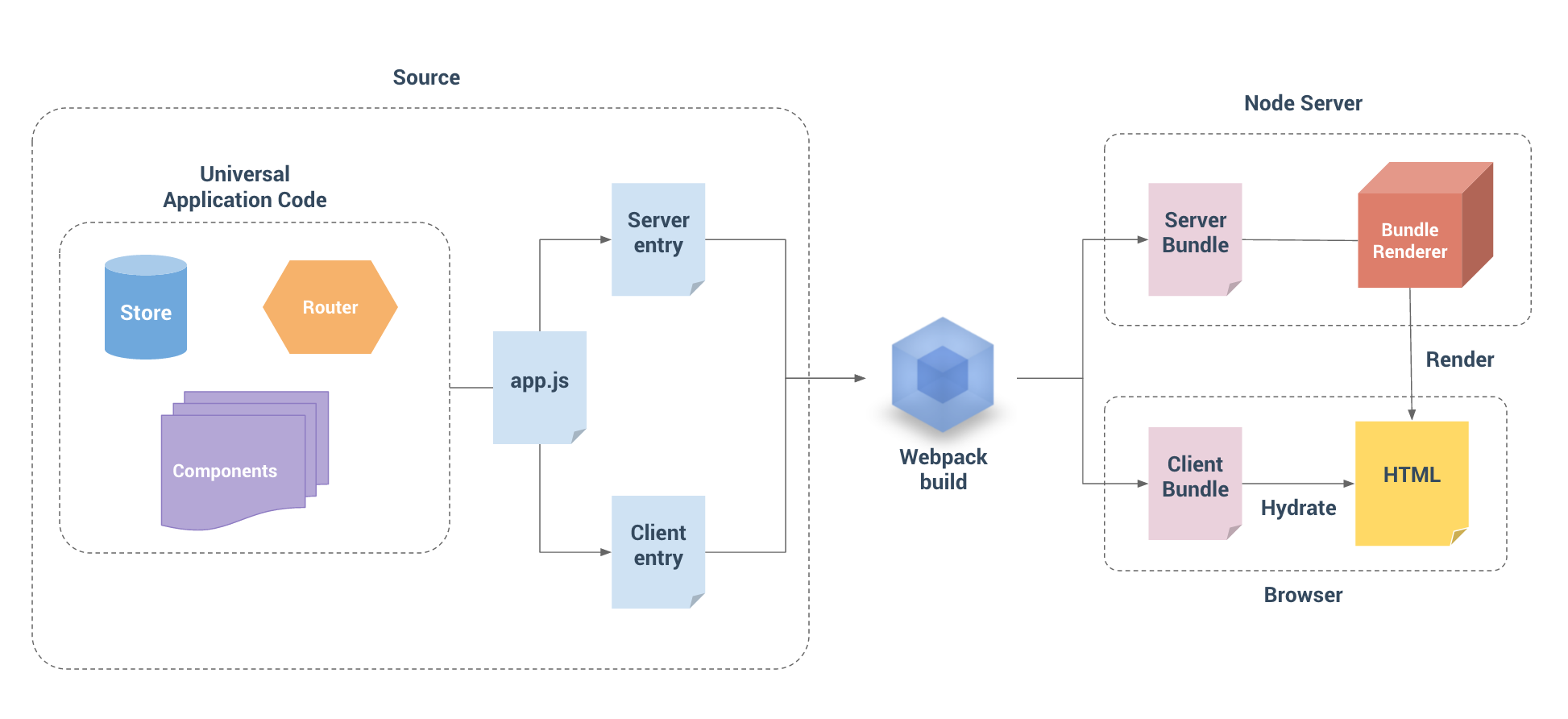
我们通过上图可以看到,vue ssr 也是离不开 webpack 的打包。
利用 webpack的打包将 vue 应用程序生成 Server Bundle 和 Client Bundle。 有了Client manifest (Client Bundle的产物)和 Server Bundle,Bundle Renderer 现在具有了服务器和客户端的构建信息,因此它可以自动推断和注入资源预加载 / 数据预取指令(preload / prefetch directive),以及 css 链接 / script 标签到所渲染的 HTML。
项目结构

build 文件构建配置
public 模板文件
src 项目文件
通过上面可以看出整体和平时的vue项目区别不是很大,主要集中在 build 中 存在了 webpack.server.config.js 文件 以及 src 文件下的 entry-client.js 和 entry-server.js, 在这里特殊说下 src 下的 app.js 和 template.html 与我们平时写的vue项目中的也有所区别。
template.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><title>Hello</title></head>
<body>
<!--vue-ssr-outlet-->
</body>
</html>当在渲染 Vue 应用程序时,renderer 只会生成 HTML 标记, 我们需要用一个额外的 HTML 页面包裹容器,来包裹生成的 HTML 标记,一般直接在创建 renderer 时提供一个页面模板。
- 注意
<!--vue-ssr-outlet-->注释 这里将是应用程序 HTML 标记注入的地方。
app.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import { createRouter } from '@/router'
import { createStore } from '@/store'
import { sync } from 'vuex-router-sync'
// 导出一个工厂函数,用于创建新的
// 应用程序、router 和 store 实例
export function createApp () {
// 创建 router 实例
const router = createRouter()
// 创建 store 实例
const store = createStore()
// 同步路由状态(route state)到 store
sync(store, router)
const app = new Vue({
// 根实例简单的渲染应用程序组件。
router,
store,
render: h => h(App)
})
return { app, router, store }
}在服务器端渲染(SSR),本质上是在渲染应用程序的"快照",所以如果应用程序依赖于一些异步数据,那么在开始渲染过程之前,需要先预取和解析好这些数据。
而且对于客户端渲染,在挂载 (mount) 到客户端应用程序之前,客户端需要获取到与服务器端应用程序完全相同的数据。
为了解决以上问题,获取的数据需要位于视图组件之外,即放置在专门的数据预取存储容器(data store)或"状态容器(state container))"中。首先,在服务器端,我们可以在渲染之前预取数据,并将数据填充到 store 中。此外,我们将在 HTML 中序列化(serialize)和内联预置(inline)状态。这样,在挂载(mount)到客户端应用程序之前,可以直接从 store 获取到内联预置(inline)状态。
当编写纯客户端 (client-only) 代码时,我们习惯于每次在新的上下文中对代码进行取值。但是,Node.js 服务器是一个长期运行的进程。当我们的代码进入该进程时,它将进行一次取值并留存在内存中。这意味着如果创建一个单例对象,它将在每个传入的请求之间共享。
我们为每个请求创建一个新的根 Vue 实例。这与每个用户在自己的浏览器中使用新应用程序的实例类似。如果我们在多个请求之间使用一个共享的实例,很容易导致交叉请求状态污染 (cross-request state pollution)。
因此,我们不应该直接创建一个应用程序实例,而是应该暴露一个可以重复执行的工厂函数,为每个请求创建新的应用程序实例。
entry-client.js
import { createApp } from '@/app'
const { app, router, store } = createApp()
if (window.__INITIAL_STATE__) {
store.replaceState(window.__INITIAL_STATE__)
}
router.onReady(() => {
// 添加路由钩子函数,用于处理 asyncData.
// 在初始路由 resolve 后执行,
// 以便我们不会二次预取(double-fetch)已有的数据。
// 使用 `router.beforeResolve()`,以便确保所有异步组件都 resolve。
router.beforeResolve((to, from, next) => {
const matched = router.getMatchedComponents(to)
const prevMatched = router.getMatchedComponents(from)
// 我们只关心非预渲染的组件
// 所以我们对比它们,找出两个匹配列表的差异组件
let diffed = false
const activated = matched.filter((c, i) => {
return diffed || (diffed = (prevMatched[i] !== c))
})
if (!activated.length) {
return next()
}
// 这里如果有加载指示器 (loading indicator),就触发
Promise.all(activated.map(c => {
if (c.asyncData) {
return c.asyncData({ store, route: to })
}
})).then(() => {
// 停止加载指示器(loading indicator)
next()
}).catch(next)
})
app.$mount('#app')
})当服务端渲染完毕后,Vue 在浏览器端接管由服务端发送的静态 HTML,使其变为由 Vue 管理的动态 DOM (即:客户端激活)。
entry-server.js
import { createApp } from '@/app'
const isDev = process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production'
// This exported function will be called by `bundleRenderer`.
// This is where we perform data-prefetching to determine the
// state of our application before actually rendering it.
// Since data fetching is async, this function is expected to
// return a Promise that resolves to the app instance.
export default context => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const s = isDev && Date.now()
const { app, router, store } = createApp()
const { url } = context
const { fullPath } = router.resolve(url).route
if (fullPath !== url) {
return reject({ url: fullPath })
}
// set router's location
router.push(url)
console.log(router)
// wait until router has resolved possible async hooks
router.onReady(() => {
const matchedComponents = router.getMatchedComponents()
console.log(matchedComponents)
// no matched routes
if (!matchedComponents.length) {
return reject({ code: 404 })
}
// Call fetchData hooks on components matched by the route.
// A preFetch hook dispatches a store action and returns a Promise,
// which is resolved when the action is complete and store state has been
// updated.
Promise.all(matchedComponents.map(({ asyncData }) => asyncData && asyncData({
store,
route: router.currentRoute
}))).then(() => {
isDev && console.log(`data pre-fetch: ${Date.now() - s}ms`)
// After all preFetch hooks are resolved, our store is now
// filled with the state needed to render the app.
// Expose the state on the render context, and let the request handler
// inline the state in the HTML response. This allows the client-side
// store to pick-up the server-side state without having to duplicate
// the initial data fetching on the client.
context.state = store.state
resolve(app)
}).catch(reject)
}, reject)
})
}
可以通过路由获得与 router.getMatchedComponents() 相匹配的组件,如果组件暴露出 asyncData,就调用这个方法。然后我们需要将解析完成的状态,附加到渲染上下文(render context)中。
当使用 template 时,context.state 将作为 window.__INITIAL_STATE__ 状态,自动嵌入到最终的 HTML 中。而在客户端,在挂载到应用程序之前,store 就应该获取到状态。
server.js
const fs = require('fs')
const path = require('path')
const LRU = require('lru-cache')
const express = require('express')
const compression = require('compression')
const microcache = require('route-cache')
const resolve = file => path.resolve(__dirname, file)
const { createBundleRenderer } = require('vue-server-renderer')
const isProd = process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production'
const useMicroCache = process.env.MICRO_CACHE !== 'false'
const serverInfo =
`express/${require('express/package.json').version} ` +
`vue-server-renderer/${require('vue-server-renderer/package.json').version}`
const app = express()
function createRenderer (bundle, options) {
// https://github.com/vuejs/vue/blob/dev/packages/vue-server-renderer/README.md#why-use-bundlerenderer
return createBundleRenderer(bundle, Object.assign(options, {
// for component caching
cache: LRU({
max: 1000,
maxAge: 1000 * 60 * 15
}),
// this is only needed when vue-server-renderer is npm-linked
basedir: resolve('./dist'),
// recommended for performance
runInNewContext: false
}))
}
let renderer
let readyPromise
const templatePath = resolve('./public/index.template.html')
if (isProd) {
// In production: create server renderer using template and built server bundle.
// The server bundle is generated by vue-ssr-webpack-plugin.
const template = fs.readFileSync(templatePath, 'utf-8')
const bundle = require('./dist/vue-ssr-server-bundle.json')
// The client manifests are optional, but it allows the renderer
// to automatically infer preload/prefetch links and directly add <script>
// tags for any async chunks used during render, avoiding waterfall requests.
const clientManifest = require('./dist/vue-ssr-client-manifest.json')
renderer = createRenderer(bundle, {
template,
clientManifest
})
} else {
// In development: setup the dev server with watch and hot-reload,
// and create a new renderer on bundle / index template update.
readyPromise = require('./build/setup-dev-server')(
app,
templatePath,
(bundle, options) => {
renderer = createRenderer(bundle, options)
}
)
}
const serve = (path, cache) => express.static(resolve(path), {
maxAge: cache && isProd ? 1000 * 60 * 60 * 24 * 30 : 0
})
app.use(compression({ threshold: 0 }))
app.use('/dist', serve('./dist', true))
app.use('/public', serve('./public', true))
app.use('/manifest.json', serve('./manifest.json', true))
app.use('/service-worker.js', serve('./dist/service-worker.js'))
// since this app has no user-specific content, every page is micro-cacheable.
// if your app involves user-specific content, you need to implement custom
// logic to determine whether a request is cacheable based on its url and
// headers.
// 1-second microcache.
// https://www.nginx.com/blog/benefits-of-microcaching-nginx/
app.use(microcache.cacheSeconds(1, req => useMicroCache && req.originalUrl))
function render (req, res) {
const s = Date.now()
res.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/html")
res.setHeader("Server", serverInfo)
const handleError = err => {
if (err.url) {
res.redirect(err.url)
} else if (err.code === 404) {
res.status(404).send('404 | Page Not Found')
} else {
// Render Error Page or Redirect
res.status(500).send('500 | Internal Server Error')
console.error(`error during render : ${req.url}`)
console.error(err.stack)
}
}
const context = {
title: 'Vue HN 2.0', // default title
url: req.url
}
renderer.renderToString(context, (err, html) => {
if (err) {
return handleError(err)
}
res.send(html)
if (!isProd) {
console.log(`whole request: ${Date.now() - s}ms`)
}
})
}
app.get('*', isProd ? render : (req, res) => {
readyPromise.then(() => render(req, res))
})
const port = process.env.PORT || 8888
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`server started at localhost:${port}`)
})通过 vue-server-renderer 将我们打包出来的 server bundle 渲染成 html 返回响应。
服务器代码使用了一个 * 处理程序,它接受任意 URL。这允许我们将访问的 URL 传递到我们的 Vue 应用程序中,然后对客户端和服务器复用相同的路由配置。
构建代码
webpack.base.config.js
const path = require('path')
const webpack = require('webpack')
const ExtractTextPlugin = require('extract-text-webpack-plugin')
const FriendlyErrorsPlugin = require('friendly-errors-webpack-plugin')
const { VueLoaderPlugin } = require('vue-loader')
const isProd = process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production'
module.exports = {
devtool: isProd
? false
: '#cheap-module-source-map',
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, '../dist'),
publicPath: '/dist/',
filename: '[name].[chunkhash].js'
},
mode: isProd ? 'production' : 'development',
resolve: {
alias: {
'public': path.resolve(__dirname, '../public'),
vue$: 'vue/dist/vue.esm.js',
'@': path.resolve('src')
},
extensions: ['.js', '.vue', '.json']
},
module: {
noParse: /es6-promise\.js$/, // avoid webpack shimming process
rules: [
{
test: /\.vue$/,
loader: 'vue-loader',
options: {
compilerOptions: {
preserveWhitespace: false
}
}
},
{
test: /\.js$/,
loader: 'babel-loader',
exclude: /node_modules/
},
{
test: /\.(png|jpg|gif|svg)$/,
loader: 'url-loader',
options: {
limit: 10000,
name: '[name].[ext]?[hash]'
}
},
{
test: /\.styl(us)?$/,
use: isProd
? ExtractTextPlugin.extract({
use: [
{
loader: 'css-loader',
options: { minimize: true }
},
'stylus-loader'
],
fallback: 'vue-style-loader'
})
: ['vue-style-loader', 'css-loader', 'stylus-loader']
},
]
},
performance: {
hints: false
},
plugins: isProd
? [
new VueLoaderPlugin(),
// new webpack.optimize.UglifyJsPlugin({
// compress: { warnings: false }
// }),
new webpack.optimize.ModuleConcatenationPlugin(),
new ExtractTextPlugin({
filename: 'common.[chunkhash].css'
})
]
: [
new VueLoaderPlugin(),
new FriendlyErrorsPlugin()
]
}基础构建过程
webpack.client.config.js
const webpack = require('webpack')
const merge = require('webpack-merge')
const baseConfig = require('./webpack.base.config')
const VueSSRClientPlugin = require('vue-server-renderer/client-plugin')
module.exports = merge(baseConfig, {
entry: {
app: './src/entry-client.js'
},
plugins: [
new webpack.DefinePlugin({
'process.env.NODE_ENV': JSON.stringify(process.env.NODE_ENV || 'development'),
'process.env.VUE_ENV': '"client"'
}),
// 重要信息:这将 webpack 运行时分离到一个引导 chunk 中,
// 以便可以在之后正确注入异步 chunk。
// 这也为你的 应用程序/vendor 代码提供了更好的缓存。
// new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin({
// name: "manifest",
// minChunks: Infinity
// }),
// 此插件在输出目录中
// 生成 `vue-ssr-client-manifest.json`。
new VueSSRClientPlugin()
],
optimization: {
// Automatically split vendor and commons
splitChunks: {
chunks: 'all',
name: 'vendors'
},
// Keep the runtime chunk seperated to enable long term caching
runtimeChunk: true
}
})配置 client bundle 的构建过程
webpack.server.config.js
const merge = require('webpack-merge')
const nodeExternals = require('webpack-node-externals')
const baseConfig = require('./webpack.base.config')
const VueSSRServerPlugin = require('vue-server-renderer/server-plugin')
module.exports = merge(baseConfig, {
// 将 entry 指向应用程序的 server entry 文件
entry: './src/entry-server.js',
// 这允许 webpack 以 Node 适用方式(Node-appropriate fashion)处理动态导入(dynamic import),
// 并且还会在编译 Vue 组件时,
// 告知 `vue-loader` 输送面向服务器代码(server-oriented code)。
target: 'node',
// 对 bundle renderer 提供 source map 支持
devtool: 'source-map',
// 此处告知 server bundle 使用 Node 风格导出模块(Node-style exports)
output: {
libraryTarget: 'commonjs2'
},
// https://webpack.js.org/configuration/externals/#function
// https://github.com/liady/webpack-node-externals
// 外置化应用程序依赖模块。可以使服务器构建速度更快,
// 并生成较小的 bundle 文件。
externals: nodeExternals({
// 不要外置化 webpack 需要处理的依赖模块。
// 你可以在这里添加更多的文件类型。例如,未处理 *.vue 原始文件,
// 你还应该将修改 `global`(例如 polyfill)的依赖模块列入白名单
whitelist: /\.css$/
}),
// 这是将服务器的整个输出
// 构建为单个 JSON 文件的插件。
// 默认文件名为 `vue-ssr-server-bundle.json`
plugins: [
new VueSSRServerPlugin()
]
})配置 server bundle 的构建过程
setup-dev-server.js
const fs = require('fs')
const path = require('path')
const MFS = require('memory-fs')
const webpack = require('webpack')
const chokidar = require('chokidar')
const clientConfig = require('./webpack.client.config')
const serverConfig = require('./webpack.server.config')
const readFile = (fs, file) => {
try {
return fs.readFileSync(path.join(clientConfig.output.path, file), 'utf-8')
} catch (e) { }
}
module.exports = function setupDevServer (app, templatePath, cb) {
let bundle
let template
let clientManifest
let ready
const readyPromise = new Promise(r => { ready = r })
const update = () => {
if (bundle && clientManifest) {
ready()
cb(bundle, {
template,
clientManifest
})
}
}
// read template from disk and watch
template = fs.readFileSync(templatePath, 'utf-8')
chokidar.watch(templatePath).on('change', () => {
template = fs.readFileSync(templatePath, 'utf-8')
console.log('index.html template updated.')
update()
})
// modify client config to work with hot middleware
clientConfig.entry.app = ['webpack-hot-middleware/client', clientConfig.entry.app]
clientConfig.output.filename = '[name].js'
clientConfig.plugins.push(
new webpack.HotModuleReplacementPlugin(),
new webpack.NoEmitOnErrorsPlugin()
)
// dev middleware
const clientCompiler = webpack(clientConfig)
const devMiddleware = require('webpack-dev-middleware')(clientCompiler, {
publicPath: clientConfig.output.publicPath,
noInfo: true
})
app.use(devMiddleware)
clientCompiler.plugin('done', stats => {
stats = stats.toJson()
stats.errors.forEach(err => console.error(err))
stats.warnings.forEach(err => console.warn(err))
if (stats.errors.length) return
clientManifest = JSON.parse(readFile(
devMiddleware.fileSystem,
'vue-ssr-client-manifest.json'
))
update()
})
// hot middleware
app.use(require('webpack-hot-middleware')(clientCompiler, { heartbeat: 5000 }))
// watch and update server renderer
const serverCompiler = webpack(serverConfig)
const mfs = new MFS()
serverCompiler.outputFileSystem = mfs
serverCompiler.watch({}, (err, stats) => {
if (err) throw err
stats = stats.toJson()
if (stats.errors.length) return
// read bundle generated by vue-ssr-webpack-plugin
bundle = JSON.parse(readFile(mfs, 'vue-ssr-server-bundle.json'))
update()
})
return readyPromise
}用于 dev 状态下 热更新
到此,基本上上vue ssr的基本结构以了解完毕。但是还是有很多可以做的事情,比如类似于 nuxt 的根据文件目录动态生成 route 等等
后续让我们继续探究...
Vue SSR初探的更多相关文章
- 转载一篇好理解的vue ssr文章
转载:原文链接https://www.86886.wang/detail/5b8e6081f03d630ba8725892,谢谢作者的分享 前言 大多数Vue项目要支持SSR应该是为了SEO考虑,毕竟 ...
- Vue SSR不可不知的问题
Vue SSR不可不知的问题 本文主要介绍Vue SSR(vue服务端渲染)的应用场景,开发中容易遇到的一些问题,提升ssr性能的方法,以及ssr的安全性问题. ssr的应用场景 1.SEO需求 SE ...
- Vue SSR 配合Java的Javascript引擎j2v8实现服务端渲染2创建Vue2+webpack4项目
前提 安装好nodejs并配置好环境变量,最好是 node10,https://nodejs.org/en/download/ 参考我之前的文章 debian安装nodejs Yarn &&a ...
- Vue SSR常见问题、异常处理以及优化方案
本文主要介绍Vue SSR(vue服务端渲染)的应用场景,开发中容易遇到的一些问题,提升ssr性能的方法,以及ssr的安全性问题. SSR的应用场景 1.SEO需求 SEO(Search Engine ...
- Vue(SPA) WebPack模块化打包、SEO优化(Vue SSR服务端同构直出)、全浏览器兼容完整解决方案
白驹过隙,时光荏苒 大概去年这个时候写了angular 结合webpack的一套前端方案,今年此时祭出vue2结合webpack的一套前端方案. 明年的这个时候我又是在做什么... 读在最前面: 1. ...
- Vue SSR的渲染性能
一.前言 前端技术年年有新宠,Vue.js 2.0以其轻量级.渐进式.简洁的语法在MVVM框架中脱颖而出,一经推出便很受业界青睐. 为了提高首屏渲染速度 缓存+直出 是必不可少的.在Vue 1× 时代 ...
- 理解vue ssr原理,自己搭建简单的ssr框架
前言 大多数Vue项目要支持SSR应该是为了SEO考虑,毕竟对于WEB应用来说,搜索引擎是一个很大的流量入口.Vue SSR现在已经比较成熟了,但是如果是把一个SPA应用改造成SSR应用,成本还是有些 ...
- vue ssr
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/v1c69bJ5PxGcqt-ZU4FVXw https://juejin.im/entry/590ca74b2f301e006c10465f h ...
- vue SSR 部署详解
先用vue cli初始化一个项目吧. 输入命令行开始创建项目: vue create my-vue-ssr 记得不要选PWA,不知为何加了这个玩意儿就报错. 后续选router模式记得选 histor ...
随机推荐
- VS2005下第一个ATL
作者:kagula 日期: 2008-9-2 环境: [1]VisualStudio2005简体中文版(必需已经安装C语言开发环境支持) [2]WinXP+SP3 读者要求: 初步使用过Visual ...
- Rust 2017 调查报告:学习曲线是最大痛点(最大的问题是这门语言太偏底层了,现在做底层的少了。还有C这个绕不过去的存在)
Rust 官方在社区上做了一次调查,以了解用户如何看待 Rust 的发展.调查共收到 5368 份回复,其中有 大约 2/3 的是 Rust 用户,剩下的 1/3 是非 Rust 用户,调查结果如下. ...
- 怎样从一名程序员过度到项目经理(整理自csdn论坛) 选择自 whoopee 的 Blog
1.从程序员到PM,是一条脱变的路,事实上程序员走的路最终不应该是项目经理.首先有一点需要明白的就是,一定规模的项目中,项目经理不需要太懂技术,他可以是一知半解.项目经理的任务不是在技术方面,技术相关 ...
- android自定义View绘制天气温度曲线
原文:android自定义View绘制天气温度曲线 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载. https://blog.csdn.net/u012942410/article/detail ...
- 发现意外之美 - SwiftyJSON 源码学习 | 咖啡时间
SwiftyJSON 是一个很优秀 Swift 语言第三方库.我们在之前的文章中对它有过介绍.相信大家对它也有了一些了解.提升开发功力最好的方式就是学习优秀的源代码了,记得大神 TJ Holowayc ...
- UWP开发学习笔记2
RelativePanel控件: 用法 描述 RelativePanel.Above 设置当前element为目标element的上方 RelativePanel.AlignBottomWith 设置 ...
- ps 专题
ps p 22763 -L -o pcpu,pid,tid,time,tname,cmd,pmem,rss --sort rss 按rss排序 ps p 26653 -L -o pcpu,tid ...
- Linux下如何查看高CPU占用率线程 专题
Java 系统性能分析 命令 1. cpu分析 top , pidstat(sysstat) pid -p PID -t 1 10 vmstat 1 CPU上下文切换.运行队列.利用率 ps Hh - ...
- win10 应用商店/相机/计算器误删后的修复方法
“以管理员身份运行”Windows Powershell. 然后在打开的“管理员:Windows Powershell”窗口中输入以下重装应用商店的命令: //商店恢复 Get-AppXPackage ...
- 【Python】:用python做下百度2014笔试题
国庆节最后一天,明天就要上班了,闲来无事做做百度2014笔试题,好久没用过C++了,索性就用python简单的写一下,体验下题目难度.题目是从[大卫David]那里copy过来的. 1.给定任意一个正 ...
