OsgEearh 中的 FeatureEditor的实现原理
先来看看FeatureEditor的用法:
const osgEarth::SpatialReference* mapSRS = mapNode->getMapSRS();
osgEarth::Symbology::Style geomStyle;
geomStyle.getOrCreate<osgEarth::LineSymbol>()->stroke()->color() = osgEarth::Symbology::Color::Cyan;
geomStyle.getOrCreate<osgEarth::LineSymbol>()->stroke()->width() = 5.0f;
geomStyle.getOrCreate<osgEarth::LineSymbol>()->tessellationSize() = 75000;
geomStyle.getOrCreate<osgEarth::AltitudeSymbol>()->clamping() = osgEarth::AltitudeSymbol::CLAMP_TO_TERRAIN;
geomStyle.getOrCreate<osgEarth::AltitudeSymbol>()->technique() = osgEarth::AltitudeSymbol::TECHNIQUE_DRAPE;
osg::ref_ptr<osgEarth::Symbology::Polygon> polygon = new osgEarth::Symbology::Polygon();
polygon->push_back(osg::Vec3d(0, 40, 0));
polygon->push_back(osg::Vec3d(-60, 40, 0));
polygon->push_back(osg::Vec3d(-60, 60, 0));
polygon->push_back(osg::Vec3d(0, 60, 0));
osg::ref_ptr<osgEarth::Features::Feature> feature = new osgEarth::Features::Feature(polygon, mapSRS);
osg::ref_ptr<osgEarth::Annotation::FeatureNode> featureNode = new osgEarth::Annotation::FeatureNode(feature, geomStyle);
geometryGroup->addChild(featureNode);
osg::ref_ptr<osgEarth::Annotation::FeatureEditor> editor = new osgEarth::Annotation::FeatureEditor(featureNode);
mapNode->addChild(editor);
用FeatureNode作为参数来构造出一个FeatureEditor,然后将该FeatureEditor添加到MapNode中,即可实现通过鼠标拖动对FeatureNode的编辑功能。那么FeatureEditor是如何做到的呢?
先看看FeatureEditor的继承图
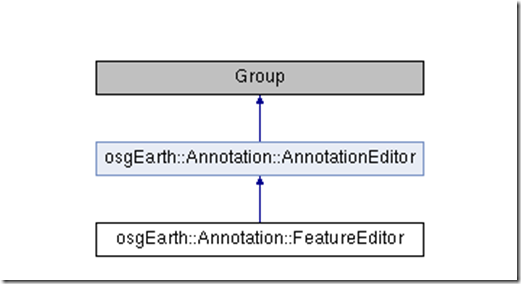
FeatureEditor继承自AnnotationEditor,AnnotationEditor继承自Group,看看AnnotationEditor的代码
class OSGEARTHANNO_EXPORT AnnotationEditor : public osg::Group
{
protected:
AnnotationEditor(); virtual ~AnnotationEditor() { }
};
AnnotationEditor::AnnotationEditor() :
osg::Group()
{
// editor geometry should always be visible.
osg::StateSet* stateSet = this->getOrCreateStateSet();
stateSet->setMode(GL_DEPTH_TEST, 0);
stateSet->setRenderBinDetails(99, "RenderBin");
}
AnnotationEditor这个类并没有做太多的事情,仅仅是在构造函数中设置了一下渲染状态而已。
接着看看FeatureEditor这个类
class OSGEARTHANNO_EXPORT FeatureEditor : public AnnotationEditor
{
public:
/**
* Constructs a new FeatureEditor
* @param featureNode
* The FeatureNode to edit
*/
FeatureEditor( FeatureNode* featureNode ); /**
*Gets the color of the draggers when they are selected
*/
const osg::Vec4f& getPickColor() const; /**
*Sets the color of the draggers when they are selected
*/
void setPickColor( const osg::Vec4f& pickColor ); /**
*Gets the color of the draggers
*/
const osg::Vec4f& getColor() const; /**
*Sets the color of the draggers
*/
void setColor( const osg::Vec4f& color ); /**
*Gets the dragger size
*/
float getSize() const; /**
*Sets the dragger size
*/
void setSize( float size ); protected:
void init(); osg::Vec4f _pickColor;
osg::Vec4f _color;
float _size; osg::ref_ptr< FeatureNode > _featureNode;
};
这个类的代码也比较简单,只包含四个成员变量,两个color,一个size,以及该Editor所要编辑的FeatureNode。
FeatureEditor::FeatureEditor( FeatureNode* featureNode):
_featureNode( featureNode ),
_color(osg::Vec4(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f)),
_pickColor(osg::Vec4(1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f)),
_size( 5.0f )
{
init();
}
构造函数初始化了四个成员变量,然后调用init()函数。
void
FeatureEditor::init()
{
removeChildren( 0, getNumChildren() ); Feature* feature = _featureNode->getFeatures().front().get();
//Create a dragger for each point
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < feature->getGeometry()->size(); i++)
{
SphereDragger* dragger = new SphereDragger( _featureNode->getMapNode() );
dragger->setColor( _color );
dragger->setPickColor( _pickColor );
dragger->setSize( _size );
dragger->setPosition(GeoPoint(feature->getSRS(), (*feature->getGeometry())[i].x(), (*feature->getGeometry())[i].y()));
dragger->addPositionChangedCallback(new MoveFeatureDraggerCallback( _featureNode.get(), i) ); addChild(dragger);
}
}
正如官方所给的注释:这个函数为geometry中的每个point都创建了一个dragger,dragger又是个什么东东?这个我们现在还不知道,接下来我们的内容就是研究dragger,在此处,我们主要需要注意这四句代码,此时不懂不要紧,看完后面,就会串起来了。
void
FeatureEditor::init()
{
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < feature->getGeometry()->size(); i++)
{
//构造函数
SphereDragger* dragger = new SphereDragger( _featureNode->getMapNode() );
//根据point的位置来设置dragger的位置
dragger->setPosition(GeoPoint(feature->getSRS(), (*feature->getGeometry())[i].x(), (*feature->getGeometry())[i].y()));
//为dragger添加回调
dragger->addPositionChangedCallback(new MoveFeatureDraggerCallback( _featureNode.get(), i) );
//将dragger添加到场景中
addChild(dragger);
}
}
下面来看看dragger
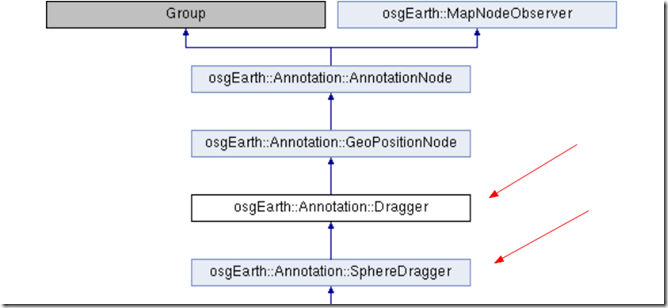
dragger继承自GeoPositionNode,对于GeoPositionNode,我们不需要知道太多,GeoPositionNode继承自Group,它的特殊之处在于它具有地理信息(毕竟人家叫 Geo Positon嘛),它提供了一个setPosition接口,我们可以通过这个接口来设置GeoPositionNode的位置。
/**
* Dragger is a handle you can use to control things in the scene.
* You drag it around with the mouse and it fires PositionChangedCallback's
* that you can listen to to repond to.
*/
class OSGEARTHANNO_EXPORT Dragger : public GeoPositionNode
{
public:
/**
* Callback that is fired when the position changes
*/
struct PositionChangedCallback : public osg::Referenced
{
public:
virtual void onPositionChanged(const Dragger* sender, const osgEarth::GeoPoint& position) {};
virtual ~PositionChangedCallback() { }
}; typedef std::list< osg::ref_ptr<PositionChangedCallback> > PositionChangedCallbackList; enum DragMode
{
DRAGMODE_HORIZONTAL,
DRAGMODE_VERTICAL
}; Dragger( MapNode* mapNode, int modKeyMask=0, const DragMode& defaultMode=DRAGMODE_HORIZONTAL ); /** dtor */
virtual ~Dragger(); /** Sets the map position of the dragger, optionally firing a PositionChanged event. */
void setPosition(const osgEarth::GeoPoint& position, bool fireEvents); /** Drag mode */
void setDefaultDragMode(const DragMode& mode) { _defaultMode = mode; }
DragMode& getDefaultDragMode() { return _defaultMode; } /** Add a callback that runs whenever the user moves the dragger */
void addPositionChangedCallback( PositionChangedCallback* callback ); /** Remove a callback. */
void removePositionChangedCallback( PositionChangedCallback* callback ); public: // GeoPositionNode virtual void setPosition(const GeoPoint& point); public: // osg::Node virtual void traverse(osg::NodeVisitor& nv); protected:
virtual bool handle(const osgGA::GUIEventAdapter& ea, osgGA::GUIActionAdapter& aa);
void firePositionChanged(); bool _dragging;
bool _hovered;
PositionChangedCallbackList _callbacks; osg::ref_ptr< osgManipulator::LineProjector > _projector;
osgManipulator::PointerInfo _pointer;
osg::Vec3d _startProjectedPoint;
bool _elevationDragging;
int _modKeyMask;
DragMode _defaultMode;
double _verticalMinimum;
};
dragger的代码有一丢丢长,为求直观,上面的代码中我删除了其中一部分代码。
/**
* Dragger is a handle you can use to control things in the scene.
* You drag it around with the mouse and it fires PositionChangedCallback's
* that you can listen to to repond to.
*/
官方给的注释是:可以利用dragger来control scene中的对象,当你用鼠标拖动dragger时,会触发PositionChangedCallback回调。
还记得之前FeatureEditor中init函数中的这句代码么?
//为dragger添加回调
dragger->addPositionChangedCallback(new MoveFeatureDraggerCallback( _featureNode.get(), i) );
我们先不管MoveFeatureDraggerCallback具体是什么,只需要知道它继承自PositionChangedCallback(PostionChangedCallback的代码在上面的代码里),PositionChangedCallback这个函数包含一个虚函数:
virtual void onPositionChanged(const Dragger* sender, const osgEarth::GeoPoint& position) {};
显然MoveFeatureChangedCallback对这个函数进行了重写,重写的内容具体是什么,我们先不管,先将注意力放在addPositionChangedCallback这个函数上。
void Dragger::addPositionChangedCallback( PositionChangedCallback* callback )
{
_callbacks.push_back( callback );
}
这个函数的功能也很直观,将PositionChangedCallback添加进一个列表中,这个列表何时被用到?
void Dragger::firePositionChanged()
{
for( PositionChangedCallbackList::iterator i = _callbacks.begin(); i != _callbacks.end(); i++ )
{
i->get()->onPositionChanged(this, getPosition());
}
}
firePositonChanged函数遍历列表中的PositionChangedCallback对象,调用其onPositionChanged函数。firePositionChanged函数何时被调用?
void Dragger::setPosition(const GeoPoint& position, bool fireEvents)
{
GeoPositionNode::setPosition( position );
if ( fireEvents )
firePositionChanged();
}
再看看handle函数。handle函数是用来处理gui事件的,在handle函数中,firePositionChanged()和setPosition()多次出现过。
bool Dragger::handle(const osgGA::GUIEventAdapter& ea, osgGA::GUIActionAdapter& aa)
{
if (ea.getHandled()) return false; osgViewer::View* view = dynamic_cast<osgViewer::View*>(&aa);
if (!view) return false;
if (!getMapNode()) return false; if (ea.getEventType() == osgGA::GUIEventAdapter::PUSH)
{
IntersectionPicker picker( view, this );
IntersectionPicker::Hits hits; if ( picker.pick( ea.getX(), ea.getY(), hits ) )
{
const GeoPoint& position = getPosition(); _dragging = true; //Check for and handle vertical dragging if necessary
bool pressedAlt = _modKeyMask && (ea.getModKeyMask() & _modKeyMask) > 0;
_elevationDragging = (_defaultMode == Dragger::DRAGMODE_VERTICAL && !pressedAlt) || (_defaultMode == Dragger::DRAGMODE_HORIZONTAL && pressedAlt); if (_elevationDragging)
{
_pointer.reset(); // set movement range
// TODO: values 0.0 and 300000.0 are rather experimental
GeoPoint posStart(position.getSRS(), position.x(), position.y(), 0.0, ALTMODE_ABSOLUTE);
osg::Vec3d posStartXYZ;
posStart.toWorld(posStartXYZ); GeoPoint posEnd(position.getSRS(), position.x(), position.y(), 300000.0, ALTMODE_ABSOLUTE);
osg::Vec3d posEndXYZ;
posEnd.toWorld(posEndXYZ); _projector->setLine(posStartXYZ, posEndXYZ); // set camera
osgUtil::LineSegmentIntersector::Intersections intersections;
osg::Node::NodeMask intersectionMask = 0xffffffff;
osgViewer::View* view = dynamic_cast<osgViewer::View*>(&aa);
if ( !view )
return true; if (view->computeIntersections(ea.getX(),ea.getY(),intersections, intersectionMask))
{
for (osgUtil::LineSegmentIntersector::Intersections::iterator hitr = intersections.begin(); hitr != intersections.end(); ++hitr)
{
_pointer.addIntersection(hitr->nodePath, hitr->getLocalIntersectPoint());
} bool draggerFound = false;
for (osgManipulator::PointerInfo::IntersectionList::iterator piit = _pointer._hitList.begin(); piit != _pointer._hitList.end(); ++piit)
{
for (osg::NodePath::iterator itr = piit->first.begin(); itr != piit->first.end(); ++itr)
{
Dragger* dragger = dynamic_cast<Dragger*>(*itr);
if (dragger==this)
{
draggerFound = true;
osg::Camera *rootCamera = view->getCamera();
osg::NodePath nodePath = _pointer._hitList.front().first;
osg::NodePath::reverse_iterator ritr;
for (ritr = nodePath.rbegin(); ritr != nodePath.rend(); ++ritr)
{
osg::Camera* camera = dynamic_cast<osg::Camera*>(*ritr);
if (camera && (camera->getReferenceFrame()!=osg::Transform::RELATIVE_RF || camera->getParents().empty()))
{
rootCamera = camera;
break;
}
}
_pointer.setCamera(rootCamera);
_pointer.setMousePosition(ea.getX(), ea.getY()); break;
}
} if (draggerFound)
break;
}
}
} aa.requestRedraw();
return true;
}
}
else if (ea.getEventType() == osgGA::GUIEventAdapter::RELEASE)
{
_elevationDragging = false; if ( _dragging )
{
_dragging = false;
firePositionChanged();
} aa.requestRedraw();
}
else if (ea.getEventType() == osgGA::GUIEventAdapter::DRAG)
{
if (_elevationDragging)
{
_pointer._hitIter = _pointer._hitList.begin();
_pointer.setMousePosition(ea.getX(), ea.getY()); if (_projector->project(_pointer, _startProjectedPoint))
{
const GeoPoint& position = getPosition(); //Get the absolute mapPoint that they've drug it to.
GeoPoint projectedPos;
projectedPos.fromWorld(position.getSRS(), _startProjectedPoint); // make sure point is not dragged down below
// TODO: think of a better solution / HeightAboveTerrain performance issues?
if (projectedPos.z() >= _verticalMinimum)
{
//If the current position is relative, we need to convert the absolute world point to relative.
//If the point is absolute then just emit the absolute point.
if (position.altitudeMode() == ALTMODE_RELATIVE)
{
projectedPos.transformZ(ALTMODE_RELATIVE, getMapNode()->getTerrain());
} setPosition( projectedPos );
aa.requestRedraw();
}
} return true;
} if (_dragging)
{
osg::Vec3d world;
if ( getMapNode() && getMapNode()->getTerrain()->getWorldCoordsUnderMouse(view, ea.getX(), ea.getY(), world) )
{
const GeoPoint& position = getPosition(); //Get the absolute mapPoint that they've drug it to.
GeoPoint mapPoint;
mapPoint.fromWorld( getMapNode()->getMapSRS(), world ); //If the current position is relative, we need to convert the absolute world point to relative.
//If the point is absolute then just emit the absolute point.
if (position.altitudeMode() == ALTMODE_RELATIVE)
{
mapPoint.alt() = position.alt();
mapPoint.altitudeMode() = ALTMODE_RELATIVE;
} setPosition( mapPoint );
aa.requestRedraw();
return true;
}
}
}
else if (ea.getEventType() == osgGA::GUIEventAdapter::MOVE)
{
IntersectionPicker picker( view, this );
IntersectionPicker::Hits hits; if ( picker.pick( ea.getX(), ea.getY(), hits ) )
{
setHover( true );
}
else
{
setHover( false );
}
aa.requestRedraw();
}
return false;
}
dragger有两种模式,水平模式和垂直模式,这两种模式的差异在handle()中得到了体现。
enum DragMode
{
DRAGMODE_HORIZONTAL,
DRAGMODE_VERTICAL
};
handle函数的内容我大体说明一下:当鼠标push时,判断是否点击到了dragger上,如果击中的话,判断当前拖动模式是水平模式还是垂直模式,如果是垂直模式的话,就创建一个projector对象,根据dragger当前的位置得到一条直线,将projector的投影对象设为该直线。之后drag时,将鼠标所处位置的世界坐标投影到该直线上。(顺带一提,这部分代码可以参考一下osg中的dragger类的handle函数,两者还是挺相似的,都用到了投影的方法)

若为水平模式,那就不需要投影了,在drag时,直接根据鼠标的位置,得到地面坐标就ok了。
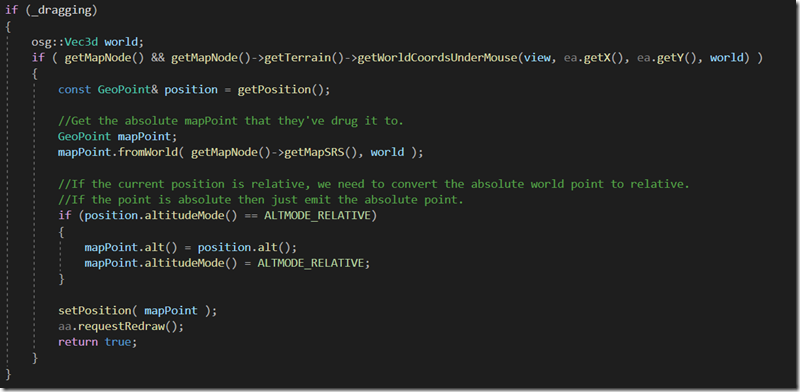
故handle函数的主要作用就是当drag dragger时,利用setPosition函数实时地更新dragger的位置,并触发回调。
最后再回头看看MoveFeatureChangedCallback()这个类。
class MoveFeatureDraggerCallback : public Dragger::PositionChangedCallback
{
public:
MoveFeatureDraggerCallback(FeatureNode* featureNode, int point):
_featureNode( featureNode ),
_point(point)
{} virtual void onPositionChanged(const Dragger* sender, const osgEarth::GeoPoint& position)
{
Feature* feature = _featureNode->getFeatures().front().get();
(*feature->getGeometry())[_point] = osg::Vec3d(position.x(), position.y(), 0);
_featureNode->init();
} osg::ref_ptr< FeatureNode > _featureNode; int _point; };
重点关注onPositionChanged这个重写的虚函数,它有两个参数,sender代表调用这个函数的dragger,position表示dragger的位置,函数内容很简单,就是根据dragger的位置来更改geometry中point的位置,最后再重绘geometry。
剖析到此结束,我们总结一下:假设一个geometry有十个point,当我们根据这个geometry创建一个FeatureEditor是,FeatureEditor会创建十个Dragger,每个Dragger的初始位置都是Point所处的位置,当Draggr被移动时,会触发回调,从而改变这个Dragger所绑定的point的位置,以上!
建议再重头看一下上面的剖析过程。
OsgEearh 中的 FeatureEditor的实现原理的更多相关文章
- 学习重点:1、金典的设计模式在实际中应用2、JVM原理3、jui源代码
学习重点:1.金典的设计模式在实际中应用 2.JVM原理 3.jui源代码
- Spring中EmptyResultDataAccessException异常产生的原理及处理方法
Spring中EmptyResultDataAccessException异常产生的原理及处理方法 Spring中使用JdbcTemplate的queryForObject方法,当查不到数据时会抛出如 ...
- 基于接口回调详解JUC中Callable和FutureTask实现原理
Callable接口和FutureTask实现类,是JUC(Java Util Concurrent)包中很重要的两个技术实现,它们使获取多线程运行结果成为可能.它们底层的实现,就是基于接口回调技术. ...
- Spring框架中IoC(控制反转)的原理(转)
原文链接:Spring框架中IoC(控制反转)的原理 一.IoC的基础知识以及原理: 1.IoC理论的背景:在采用面向对象方法设计的软件系统中,底层实现都是由N个对象组成的,所有的对象通过彼此的合作, ...
- [置顶] Hadoop2.2.0中HDFS的高可用性实现原理
在Hadoop2.0.0之前,NameNode(NN)在HDFS集群中存在单点故障(single point of failure),每一个集群中存在一个NameNode,如果NN所在的机器出现了故障 ...
- Oracle中的SQL分页查询原理和方法详解
Oracle中的SQL分页查询原理和方法详解 分析得不错! http://blog.csdn.net/anxpp/article/details/51534006
- Java网络编程和NIO详解7:浅谈 Linux 中NIO Selector 的实现原理
Java网络编程和NIO详解7:浅谈 Linux 中NIO Selector 的实现原理 转自:https://www.jianshu.com/p/2b71ea919d49 本系列文章首发于我的个人博 ...
- Java中的HashMap的工作原理是什么?
问答题23 /120 Java中的HashMap的工作原理是什么? 参考答案 Java中的HashMap是以键值对(key-value)的形式存储元素的.HashMap需要一个hash函数,它使用ha ...
- Spring.Net是怎么在MVC中实现注入的(原理)
本文将介绍Spring.Net(不仅仅是Spring.Net,其实所有的IoC容器要向控制器中进行注入,原理都是差不多的)在MVC控制器中依赖注入的实现原理,本文并没有关于在MVC使用Spring怎么 ...
随机推荐
- ATOM插件及快捷键
xml-formatter :https://atom.io/packages/xml-formatter xml格式化工具 SHIFT-CTRL-X:快速格式化 SHIFT-CTRL-M:移除换行符 ...
- JUnit 5和Selenium基础(二)
使用Selenium内置的PageFactory实现页面对象模式 在这一部分中,将通过Selenium的内置PageFactory支持类来介绍Page Object模式的实现.PageFactory提 ...
- 从操作系统层面理解Linux下的网络IO模型
I/O( INPUT OUTPUT),包括文件I/O.网络I/O. 计算机世界里的速度鄙视: 内存读数据:纳秒级别. 千兆网卡读数据:微妙级别.1微秒=1000纳秒,网卡比内存慢了千倍. 磁盘读数据: ...
- AWS、阿里云、Azure、Google Cloud、华为云、腾讯云 各种云服务器价格收费对比(上)
他来了,他来了~ 他带着六家公有云厂商的资源价格走来了~ 不久前,我们上线了一款小工具——[多云成本计算器]1.0版,公众号菜单栏可以直接体验.详细介绍可以戳这里<3秒即得最低价,速石上线「多云 ...
- python列表(数组)
列表(list) 就是 数组 - 列表是Python中的一个对象 - 对象(object)就是内存中专门用来存储数据的一块区域 - 之前我们学习的对象,像数值,它只能保存一个单一的数据 - 列表中可 ...
- APICloud联合腾讯云推出“云主机解决方案“,各种福利等你拿
为了帮助开发者一站式打通云.开发.运维全流程服务,更全面提供基于自身业务情况的云服务器.数据库.存储等基础设施服务,APICloud联合腾讯云重磅推出“云主机解决方案“.开发者可通过控制台简单清晰的购 ...
- hdu4417 主席树求区间小于等于K
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4417 Problem Description Mario is world-famous plum ...
- Git基础知识 —— 获取Git仓库
前言 官方提供了两种获取Git仓库的方法,第一种是在本地现有项目目录下导入所有文件到Git中,第二种就是从Git仓库中clone项目到本地 这里就不说Git的安装了哈,有需要的小伙伴可以查看该博文:h ...
- java项目Jenkins部署
假设背景: Nginx跳板机服务器:192.168.10.1 Tomcat应用服务器:192.168.10.3 端口:10083 应用名称:appXXX 1.配置跳板机的转发路径 如:192.168. ...
- C语言进阶——编译预处理指令
编译预处理指令 • #开头的是编译预处理指令 • 它们不是C语⾔的成分,但是C语⾔程序离不开它们 • #define⽤来定义⼀个宏 #define • #define <名字> <值 ...
