1. 使用 fluent-bit 采集文件
1. 使用 fluent-bit 采集文件

简介
Fluent Bit是一款快速、灵活的日志处理器,旨在收集、解析、过滤日志,并将日志发送到远程数据库,以便执行数据分析。
数据分析通常发生在数据存储和数据库索引之后,但对于实时和复杂的分析需求,在日志处理器中处理仍在运行的数据会带来很多好处,这种方法被称为边缘流处理(Stream Processing on the Edge)。
流式处理引擎架构
fluent-bit之所以这么说,其实是因为其架构设计了一个流式的处理引擎:
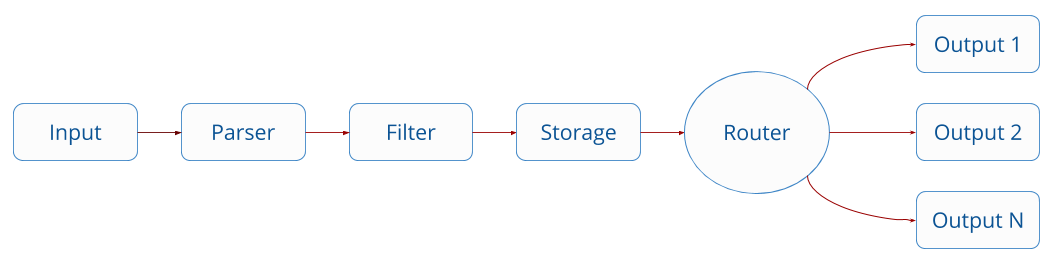
默认实现组件
fluent-bit实现了不少默认的组件:
INPUT
collectd, cpu-metrics, disk-io-metrics, docker-events, docker-metrics, dummy, exec, fluentbit-metrics, forward, head, health, http, kernel-logs, memory-metrics, mqtt, network-io-metrics, nginx, node-exporter-metrics, process, random, serial-interface, standard-input, statsd, syslog, systemd, tail, tcp, thermal, windows-event-log, windows-event-log-winevtlog, windows-exporter-metrics,OUTPUT
new-relic, forward, prometheus-remote-write, treasure-data, opensearch, skywalking, prometheus-exporter, azure, azure_blob, postgresql, bigquery, loki, elasticsearch, counter, null, cloudwatch, standard-output, syslog, websocket, flowcounter, logdna, firehose, influxdb, tcp-and-tls, kinesis, stackdriver, kafka-rest-proxy, opentelemetry, stackdriver_special_fields, slack, gelf, s3, datadog, splunk, file, http, kafka, natsFILTERS
grep, aws-metadata, nightfall, lua, parser, type-converter, nest, record-modifier, standard-output, throttle, multiline-stacktrace, expect, tensorflow, geoip2-filter, modify, checklist, kubernetes, rewrite-tagPARSERS
ltsv, configuring-parser, regular-expression, decoders, json, logfmt
该系列文章将介绍如何使用
Fluent Bit,进行数据采集、处理、分发的过程。
本节将以采集文本文件入手,并结合监控方法来逐步为您展开介绍;
编译部署
前置条件
fluent-bit 采用c语言编写,可以通过容器或者二进制进行部署安装;其占用较少的CPU和内存资源,目前能够兼容绝大部分基于x86、x86_64、arm32v7和arm64v8的系统平台;
为了能够进行在本地进行测试编译,你需要如下依赖环境:
- GCC or Clang
- CMake
- Flex & Bison: 仅当你需要流处理和记录访问器特性(这两种功能默认也是开启的)
编译
# clone 代码
git clone https://github.com/fluent/fluent-bit.git
# 切换到当前最新的一个发布分支
git checkout -b v1.9.1 v.9.1
# 编译
cd build
cmake ..
make
# 安装
# sudo make install 先不着急安装,我们来测试一下
测试
1. 先来创建一个测试路径:
mkdir ~/iSoft/fluent-bit -p
mkdir ~/isoft/fluent-bit/bin
mkdir ~/isoft/fluent-bit/conf
mkdir ~/isoft/fluent-bit/db
mkdir ~/isoft/fluent-bit/data
mkdir ~/isoft/fluent-bit/tmp
# 先将我们编译路径build下bin子路径内的东西全部复制过去
cp build/bin/* ~/iSoft/fluent-bit/bin/
2. 在conf目录下,创建三个配置文件:
fluent-bit.conf
[SERVICE]
# Flush
# =====
# set an interval of seconds before to flush records to a destination
flush 1
# Daemon
# ======
# instruct Fluent Bit to run in foreground or background mode.
daemon Off
# Log_Level
# =========
# Set the verbosity level of the service, values can be:
#
# - error
# - warning
# - info
# - debug
# - trace
#
# by default 'info' is set, that means it includes 'error' and 'warning'.
log_level info
# Parsers File
# ============
# specify an optional 'Parsers' configuration file
parsers_file parsers.conf
# Plugins File
# ============
# specify an optional 'Plugins' configuration file to load external plugins.
# plugins_file plugins.conf
# HTTP Server
# ===========
# Enable/Disable the built-in HTTP Server for metrics
http_server On
http_listen 0.0.0.0
http_port 2020
# Storage
# =======
# Fluent Bit can use memory and filesystem buffering based mechanisms
#
# - https://docs.fluentbit.io/manual/administration/buffering-and-storage
#
# storage metrics
# ---------------
# publish storage pipeline metrics in '/api/v1/storage'. The metrics are
# exported only if the 'http_server' option is enabled.
#
#storage.metrics on
# storage.path
# ------------
# absolute file system path to store filesystem data buffers (chunks).
#
# storage.path /tmp/storage
# storage.sync
# ------------
# configure the synchronization mode used to store the data into the
# filesystem. It can take the values normal or full.
#
# storage.sync normal
# storage.checksum
# ----------------
# enable the data integrity check when writing and reading data from the
# filesystem. The storage layer uses the CRC32 algorithm.
#
# storage.checksum off
# storage.backlog.mem_limit
# -------------------------
# if storage.path is set, Fluent Bit will look for data chunks that were
# not delivered and are still in the storage layer, these are called
# backlog data. This option configure a hint of maximum value of memory
# to use when processing these records.
#
# storage.backlog.mem_limit 5M
[INPUT]
Name tail
Path /home/etl/iSoft/fluent-bit/data/*.txt
DB /home/etl/iSoft/fluent-bit/db/tail.db
[OUTPUT]
Name stdout
Match *
parser.conf
[PARSER]
Name json
Format json
Time_Key time
Time_Format %d/%b/%Y:%H:%M:%S %z%
plugins.conf
这个文件其实暂时还用不上,是为我们自定义扩展插件的配置文件
[PLUGINS]
# Path /path/to/out_gstdout.so
3. 启动fluent-bit
先进入到我们自己创建的tmp目录, 创建一些测试数据
cd ~/iSoft/fluent-bit/tmp
cat <<EOF > test-data.txt
{"log":"Done","stream":"stdout","time":"2018-02-19T23:25:29.1845622Z"}
{"log":"Done","stream":"stdout","time":"2018-02-19T23:25:29.1845622Z"}
{"log":"Done","stream":"stdout","time":"2018-02-19T23:25:29.1845622Z"}
{"log":"Done","stream":"stdout","time":"2018-02-19T23:25:29.1845622Z"}
{"log":"Done","stream":"stdout","time":"2018-02-19T23:25:29.1845622Z"}
{"log":"Done","stream":"stdout","time":"2018-02-19T23:25:29.1845622Z"}
{"log":"Done","stream":"stdout","time":"2018-02-19T23:25:29.1845622Z"}
{"log":"Done","stream":"stdout","time":"2018-02-19T23:25:29.1845622Z"}
{"log":"Done","stream":"stdout","time":"2018-02-19T23:25:29.1845622Z"}
{"log":"Done","stream":"stdout","time":"2018-02-19T23:25:29.1845622Z"}
EOF
根据上面fluent-bit.conf配置文件当中的INPUT/OUTPUT可以看出,我们利用了tail组件来监听data目录中的txt文件,并将结果输出到标准输出上来;
所以,启动程序
./fluent-bit -c ../conf/fluent-bit.conf
Fluent Bit v1.9.1
* Git commit: 619277847c6343dea9e4215deacd36cf61caf0a3
* Copyright (C) 2015-2021 The Fluent Bit Authors
* Fluent Bit is a CNCF sub-project under the umbrella of Fluentd
* https://fluentbit.io
[2022/03/20 15:23:43] [ info] [engine] started (pid=15543)
[2022/03/20 15:23:43] [ info] [storage] version=1.1.6, initializing...
[2022/03/20 15:23:43] [ info] [storage] in-memory
[2022/03/20 15:23:43] [ info] [storage] normal synchronization mode, checksum disabled, max_chunks_up=128
[2022/03/20 15:23:43] [ info] [cmetrics] version=0.3.0
[2022/03/20 15:23:43] [ info] [output:stdout:stdout.0] worker #0 started
[2022/03/20 15:23:43] [ info] [http_server] listen iface=0.0.0.0 tcp_port=2020
[2022/03/20 15:23:43] [ info] [sp] stream processor started
ok, fluent-bit已经阻塞开始监听了
4. 开始测试
重新开启一个终端创口,进入到创建好的tmp目录,将测试数据手动批量的输出到data目录下:
cd ~/iSoft/fluent-bit/tmp
cat test-data.txt >> ../data/test.txt
cat test-data.txt >> ../data/test.txt
cat test-data.txt >> ../data/test.txt
cat test-data.txt >> ../data/test.txt
cat test-data.txt >> ../data/test.txt
cat test-data.txt >> ../data/test.txt
cat test-data.txt >> ../data/test.txt
这时可以看到fluent-bit阻塞的窗口已经在一直输出了
Fluent Bit v1.9.1
* Git commit: 619277847c6343dea9e4215deacd36cf61caf0a3
* Copyright (C) 2015-2021 The Fluent Bit Authors
* Fluent Bit is a CNCF sub-project under the umbrella of Fluentd
* https://fluentbit.io
[2022/03/20 15:23:43] [ info] [engine] started (pid=15543)
[2022/03/20 15:23:43] [ info] [storage] version=1.1.6, initializing...
[2022/03/20 15:23:43] [ info] [storage] in-memory
[2022/03/20 15:23:43] [ info] [storage] normal synchronization mode, checksum disabled, max_chunks_up=128
[2022/03/20 15:23:43] [ info] [cmetrics] version=0.3.0
[2022/03/20 15:23:43] [ info] [output:stdout:stdout.0] worker #0 started
[2022/03/20 15:23:43] [ info] [http_server] listen iface=0.0.0.0 tcp_port=2020
[2022/03/20 15:23:43] [ info] [sp] stream processor started
[2022/03/20 15:23:43] [ info] [input:tail:tail.0] inotify_fs_add(): inode=11409520 watch_fd=1 name=/home/etl/iSoft/fluent-bit/data/test.txt
[0] tail.0: [1647761052.113552720, {"log"=>"{"log":"Done","stream":"stdout","time":"2018-02-19T23:25:29.1845622Z"}"}]
[0] tail.0: [1647763863.114999757, {"log"=>"{"log":"Done","stream":"stdout","time":"2018-02-19T23:25:29.1845622Z"}"}]
[1] tail.0: [1647763863.403883305, {"log"=>"{"log":"Done","stream":"stdout","time":"2018-02-19T23:25:29.1845622Z"}"}]
[0] tail.0: [1647763893.545292283, {"log"=>"{"log":"Done","stream":"stdout","time":"2018-02-19T23:25:29.1845622Z"}"}]
[0] tail.0: [1647763954.515264556, {"log"=>"{"log":"Done","stream":"stdout","time":"2018-02-19T23:25:29.1845622Z"}"}]
[1] tail.0: [1647763954.515268143, {"log"=>"{"log":"Done","stream":"stdout","time":"2018-02-19T23:25:29.1845622Z"}"}]
[2] tail.0: [1647763954.515268725, {"log"=>"{"log":"Done","stream":"stdout","time":"2018-02-19T23:25:29.1845622Z"}"}]
[3] tail.0: [1647763954.515269171, {"log"=>"{"log":"Done","stream":"stdout","time":"2018-02-19T23:25:29.1845622Z"}"}]
[4] tail.0: [1647763954.515269621, {"log"=>"{"log":"Done","stream":"stdout","time":"2018-02-19T23:25:29.1845622Z"}"}]
[5] tail.0: [1647763954.515270065, {"log"=>"{"log":"Done","stream":"stdout","time":"2018-02-19T23:25:29.1845622Z"}"}]
[6] tail.0: [1647763954.515270512, {"log"=>"{"log":"Done","stream":"stdout","time":"2018-02-19T23:25:29.1845622Z"}"}]
[7] tail.0: [1647763954.515270965, {"log"=>"{"log":"Done","stream":"stdout","time":"2018-02-19T23:25:29.1845622Z"}"}]
[8] tail.0: [1647763954.515271452, {"log"=>"{"log":"Done","stream":"stdout","time":"2018-02-19T23:25:29.1845622Z"}"}]
[9] tail.0: [1647763954.515276040, {"log"=>"{"log":"Done","stream":"stdout","time":"2018-02-19T23:25:29.1845622Z"}"}]
小结
通过上面的配置文件fluent-bit.conf看到,我们为INPUT tail组件,还配置了一个DB参数,那是因为tail组件采用了嵌入式的sqlite3的数据库来记录监听文件的偏移量,我们可以去查看一下:
cd ~/iSoft/fluent-bit/db
sqlite3 tail.db
sqlite> .schema
CREATE TABLE in_tail_files ( id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY, name TEXT NOT NULL, offset INTEGER, inode INTEGER, created INTEGER, rotated INTEGER DEFAULT 0);
sqlite>
sqlite> select * from in_tail_files ;
1|/home/etl/iSoft/fluent-bit/data/test.txt|77520|11409520|1647761023|0
sqlite>
通过字段名称可以看出来,分别是文件全路径名称、读取到的文件偏移量(字节数)、文件inode、文件创建时间、文件滚动标记
监控
根据fluent-bit官网的介绍,我们在上面的配置文档中,将fluent-bit进程的http_server设置为On,并且暴露在2020端口上,那么我们可以使用如下两个接口来查看其输出情况:
curl -s http://127.0.0.1:2020/api/v1/uptime | jq
{
"uptime_sec": 391,
"uptime_hr": "Fluent Bit has been running: 0 day, 0 hour, 6 minutes and 31 seconds"
}
curl -s http://127.0.0.1:2020/api/v1/metrics | jq
{
"input": {
"tail.0": {
"records": 1,
"bytes": 88,
"files_opened": 1,
"files_closed": 0,
"files_rotated": 0
}
},
"filter": {},
"output": {
"stdout.0": {
"proc_records": 1,
"proc_bytes": 88,
"errors": 0,
"retries": 0,
"retries_failed": 0,
"dropped_records": 0,
"retried_records": 0
}
}
}
拉取promethues grafana镜像
fluent-bit为promethues提供了监控接口,那么我们来尝试一下:
在本地拉取promethues和grafana的镜像(这里就简单的将这两位泡在容器里)
docker pull prom/prometheus
docker pull grafana/grafana
配置promethues
mkdir ~/isoft/prometheus
vim ~/isoft/prometheus/fluent-bit-prom.yaml
这里为prometheus增加了一个job,因为是运行在docker里面,所以选择了另外一个宿主机IP, 以能否访问运行在宿主机上的fluent-bit
# my global config
global:
scrape_interval: 15s # Set the scrape interval to every 15 seconds. Default is every 1 minute.
evaluation_interval: 15s # Evaluate rules every 15 seconds. The default is every 1 minute.
# scrape_timeout is set to the global default (10s).
# Alertmanager configuration
alerting:
alertmanagers:
- static_configs:
- targets:
# - alertmanager:9093
# Load rules once and periodically evaluate them according to the global 'evaluation_interval'.
rule_files:
# - "first_rules.yml"
# - "second_rules.yml"
# A scrape configuration containing exactly one endpoint to scrape:
# Here it's Prometheus itself.
scrape_configs:
# The job name is added as a label `job=<job_name>` to any timeseries scraped from this config.
- job_name: "prometheus"
# metrics_path defaults to '/metrics'
# scheme defaults to 'http'.
static_configs:
- targets: ["localhost:9090"]
- job_name: "fluent-bit"
metrics_path: '/api/v1/metrics/prometheus' # metrics_path defaults to '/metrics'
# scheme defaults to 'http'.
static_configs:
# 宿主机IP
- targets: ["192.168.241.1:2020"]
启动
docker run -d -p 9090:9090 --name prom -v /home/etl/iSoft/prometheus/fluent-bit-prom.yaml:/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml prom/prometheus
通过浏览器访问 http://localhost:9090/
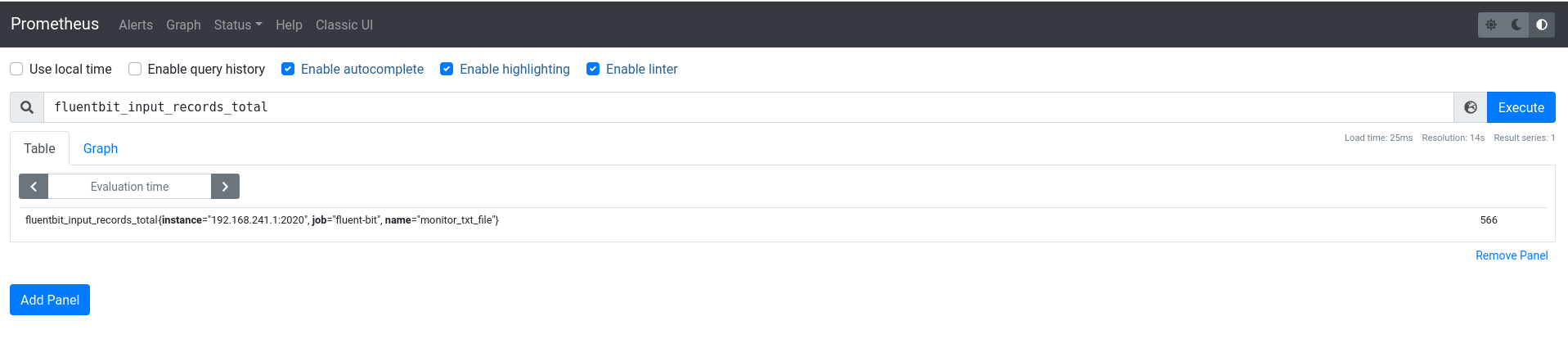
配置grafana
mkdir ~/isoft/grafana/storage -p
chmod 777 ~/isoft/grafana/storage
启动
docker run -d -p 3000:3000 --name grafana -v /home/etl/iSoft/grafana/storage:/var/lib/grafana grafana/grafana
添加promethues数据源
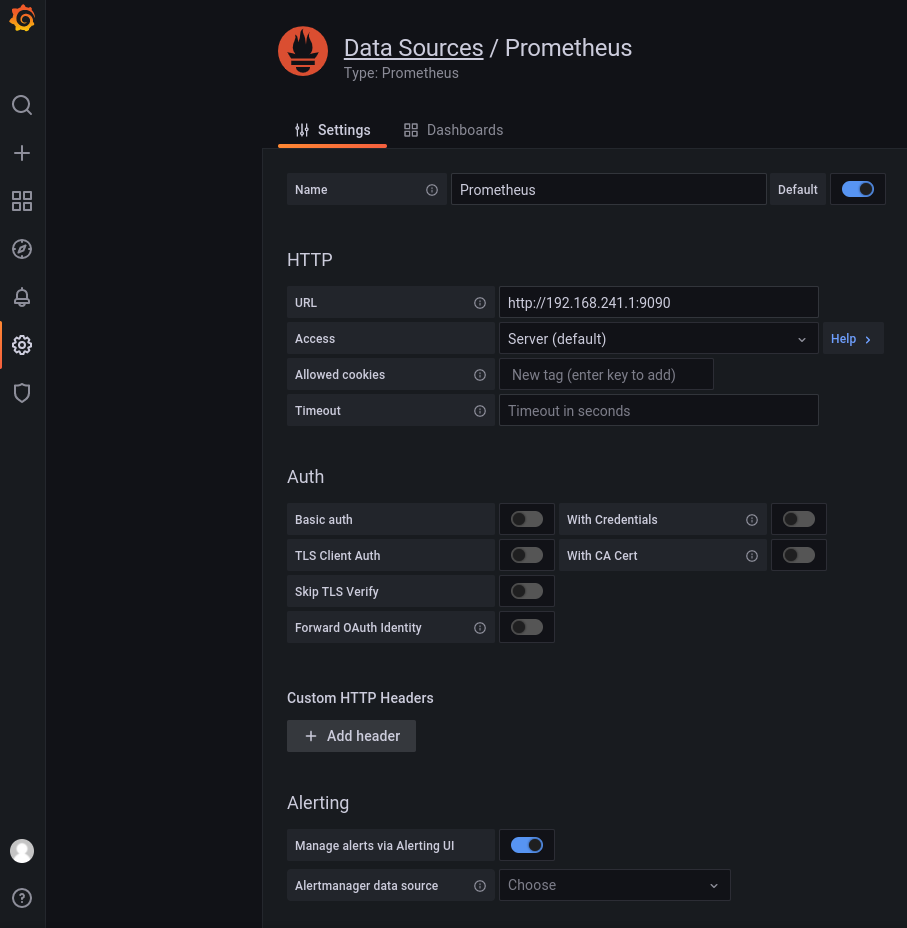
导入fluent-bit提供的默认dashboard
fluent-bit-dashboard.json
查看监控界面
输入项
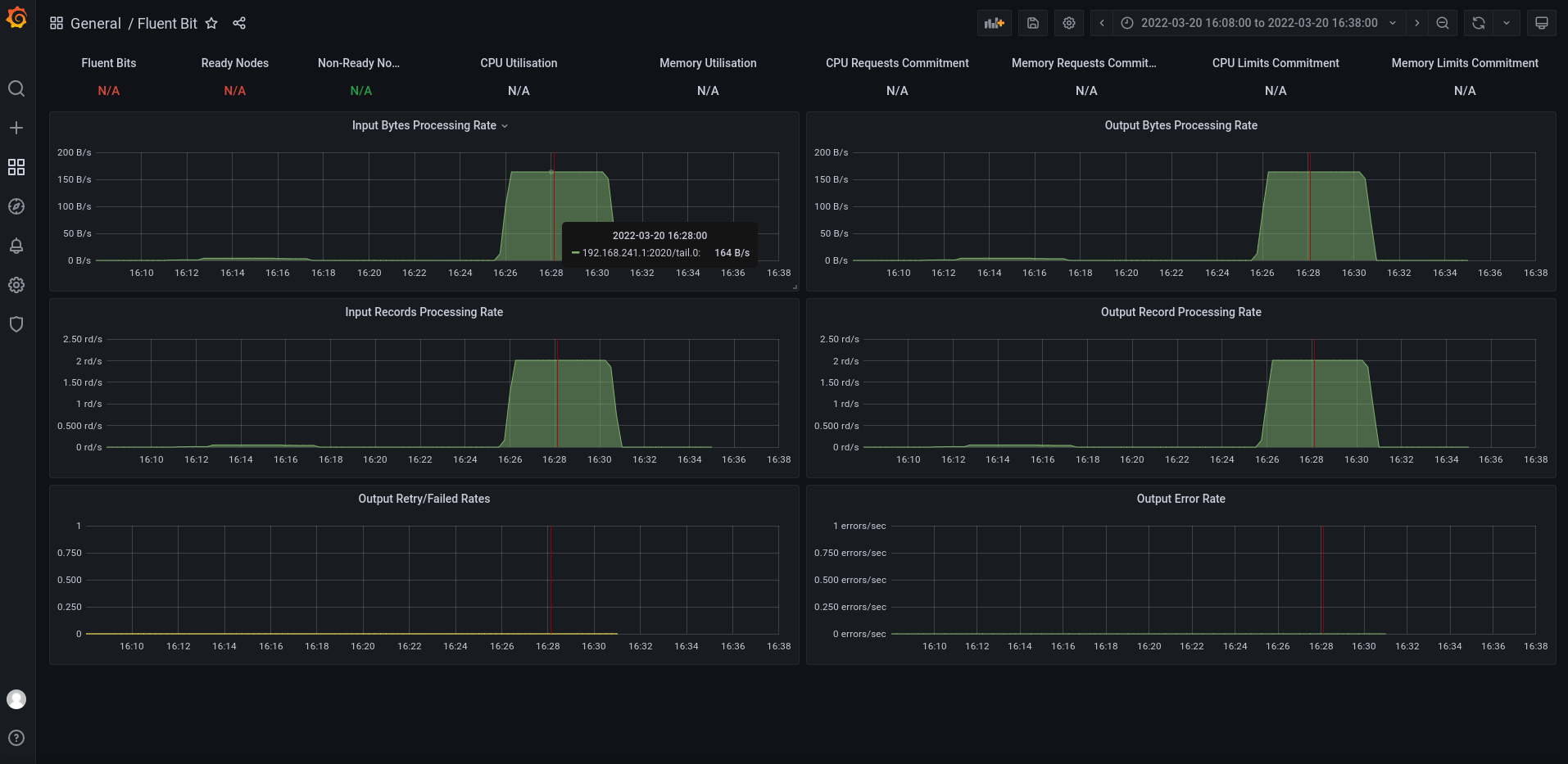
输出项
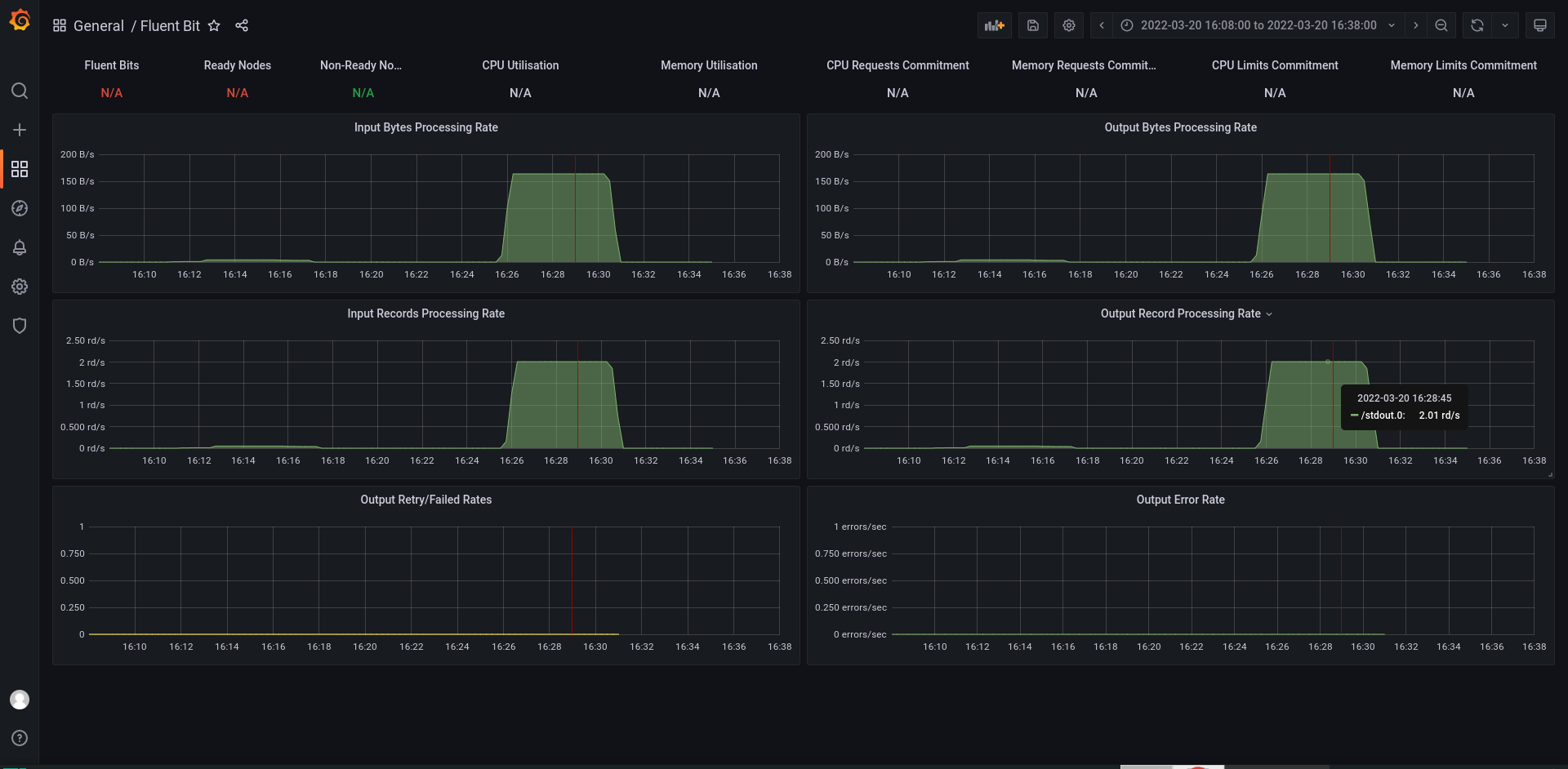
发现资源都叫 tail.0,所以根据文档,将配置文件INPUT/OUTPUT处增加两个别名,以区分可能监控到的多个配置
[INPUT]
Name tail
Path /home/etl/iSoft/fluent-bit/data/*.txt
DB /home/etl/iSoft/fluent-bit/db/tail.db
Alias monitor_txt_file
[OUTPUT]
Name stdout
Match *
Alias output_txt_file
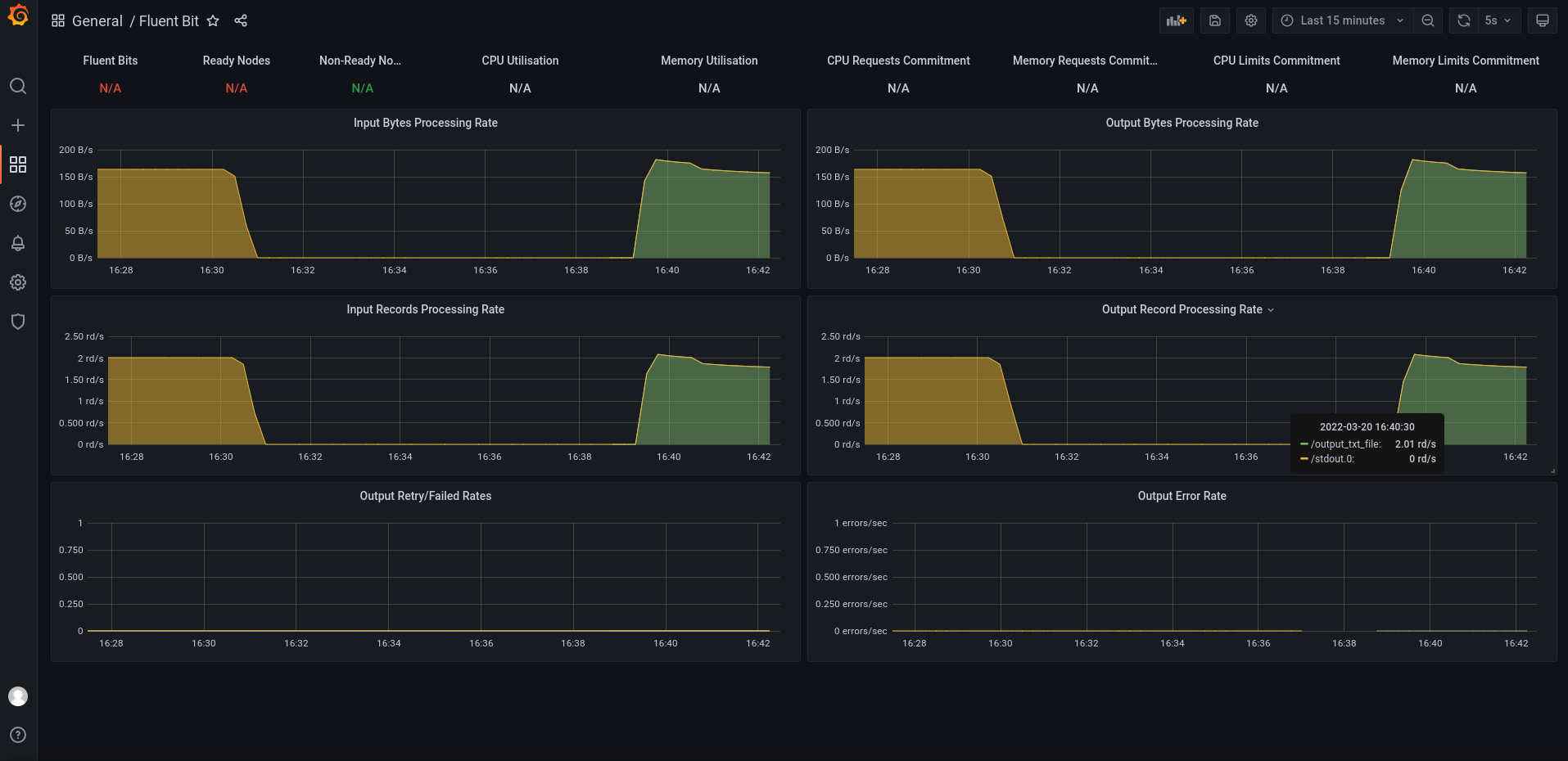
再次查看监控界面
输入项
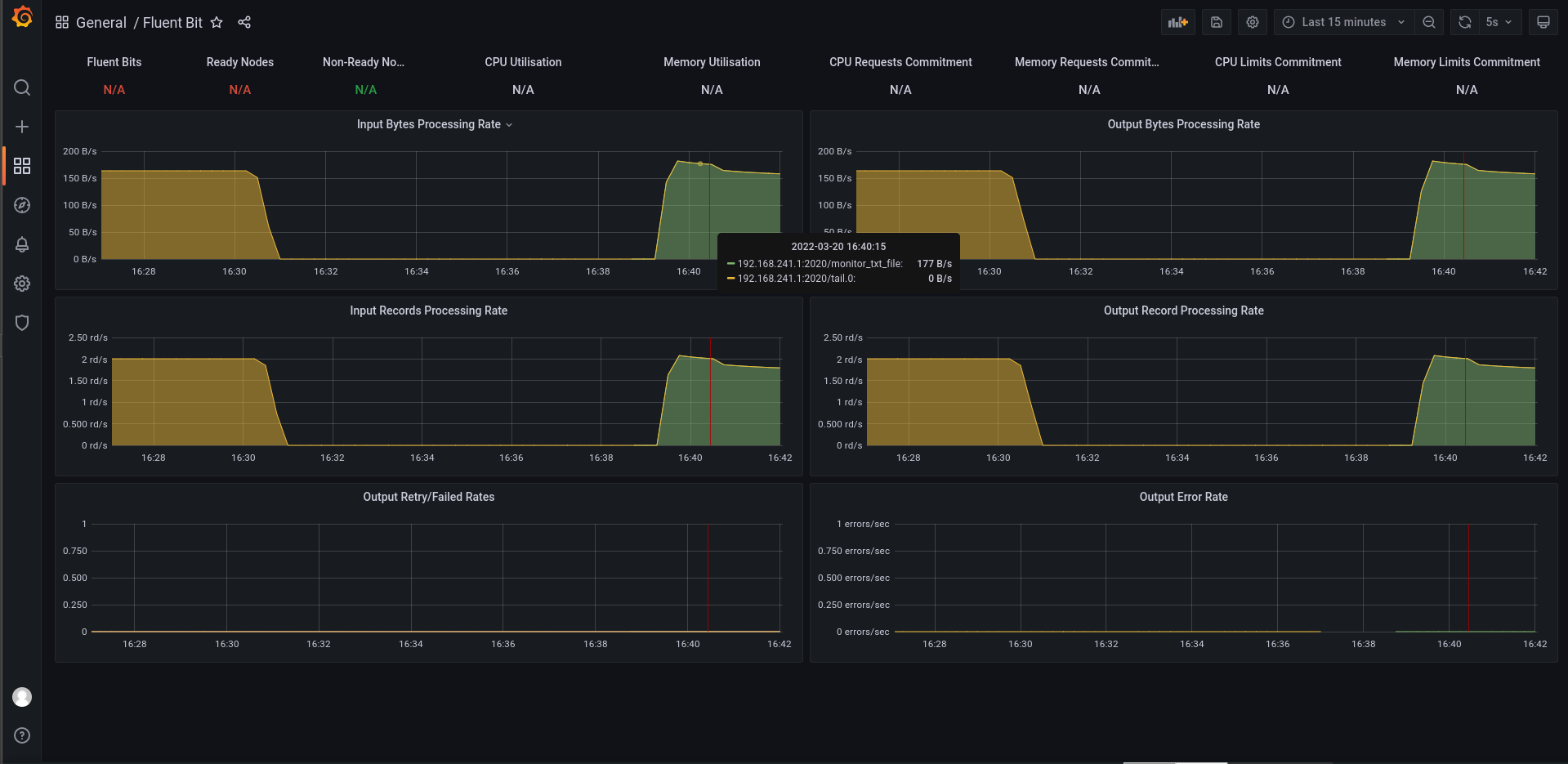
输出项
总结
至此,先完成初步测试,感兴趣的同学可以持续关注,后续会逐个介绍异构数据处理和发送(尽量多介绍相关组件和场景的使用)、如何使用pipline streaming的窗口SQL统计、为fluent-bit开发扩展组件等功能;
至于windows环境编译较为复杂(需要微软编译环境,我已测试过),感兴趣的同学,可以直接从github下载对应的win版本来进行测试;(我测试是OK的)
1. 使用 fluent-bit 采集文件的更多相关文章
- 大数据学习——采集文件到HDFS
采集需求:比如业务系统使用log4j生成的日志,日志内容不断增加,需要把追加到日志文件中的数据实时采集到hdfs 根据需求,首先定义以下3大要素 l 采集源,即source——监控文件内容更新 : ...
- 04_ Flume采集文件到HDFS案例
采集需求:比如业务系统使用log4j生成的日志,日志内容不断增加,需要把追加到日志文件中的数据实时采集到hdfs 根据需求,首先定义以下3大要素 采集源,即source——监控文件内容更新 : ex ...
- Flume采集目录及文件到HDFS案例
采集目录到HDFS 使用flume采集目录需要启动hdfs集群 vi spool-hdfs.conf # Name the components on this agent a1.sources = ...
- 第1节 flume:8、flume采集某个文件内容到hdfs上
2. 采集文件内容到HDFS 需求分析: 采集需求:比如业务系统使用log4j生成的日志,日志内容不断增加,需要把追加到日志文件中的数据实时采集到hdfs. 同一个日志文件的内容不断增 ...
- fluent批量处理——模型参数的设置
对于常见的工程应用来说,计算的工况很多,尤其优化工作,少则几百,多则上千,面对如此之多的case文件要写,假如按照一个一个的读写的话,相信你一定会为这么机械的工作烦躁,甚至影响今后好几天的心情,那么有 ...
- flume日志采集
1. Log4j Appender 1.1. 使用说明 1.1.2. Client端Log4j配置文件 (黄色文字为需要配置的内容) log4j.rootLogger=INFO,A1,R # C ...
- 日志采集框架Flume以及Flume的安装部署(一个分布式、可靠、和高可用的海量日志采集、聚合和传输的系统)
Flume支持众多的source和sink类型,详细手册可参考官方文档,更多source和sink组件 http://flume.apache.org/FlumeUserGuide.html Flum ...
- gambit软件license文件
最近自己的gambit软件license文件已经到期,后面采用fluent的license文件后,可以使用,但不能导入文件.不过通过努力,终于找到了可以实现导入文件的代码,并且可以实现无限期的使用fl ...
- PHP cURL实现模拟登录与采集使用方法详解教程
来源:http://www.zjmainstay.cn/php-curl 本文将通过案例,整合浏览器工具与PHP程序,教你如何让数据 唾手可得 . 对于做过数据采集的人来说,cURL一定不会陌生.虽然 ...
- 【转】iOS 自动化性能采集
前言 对于iOS总体生态是比较封闭的,相比Android没有像adb这种可以查看内存.cpu的命令.在日常做性能测试,需要借助xcode中instruments查看内存.cpu等数据. 但是借助i ...
随机推荐
- SpringBoot自定义注解+异步+观察者模式实现业务日志保存
一.前言 我们在企业级的开发中,必不可少的是对日志的记录,实现有很多种方式,常见的就是基于AOP+注解进行保存,但是考虑到程序的流畅和效率,我们可以使用异步进行保存,小编最近在spring和sprin ...
- Rock18框架之整体框架介绍
1. 总体框架图 2.框架能解决哪些问题? 问题1: 自动化设备包含龙门架.机械手.伺服.步进等电机.IO控制.定位及纠偏.界面展示等部分.其中硬件(伺服.IO等)是需要更换的,硬件的更换不影响整套系 ...
- springboot启动问题集合
1.Cannot resolve org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-autoconfigure:2.3.4.RELEASE 首先出现的就是这个问题,由于我之前使 ...
- JetBrains新产品Aqua——自动化测试开发工具(抢鲜体验)
转载请注明出处️ 作者:测试蔡坨坨 原文链接:caituotuo.top/9a093c88.html 你好,我是测试蔡坨坨. 随着行业内卷越来越严重,自动化测试已成为测试工程师的必备技能,谈及自动化测 ...
- Nginx重写功能(rewrite与location)
一.常用的Nginx 正则表达式 二.访问路由location 2.1location的分类 location 大致可以分为三类: 精准匹配:location = / {} 一般匹配:location ...
- c语言内存四区、数据存储范围和内存存储方向
(1)代码区通常是共享只读(代码无法修改)的,即可以被其他的程序调用,例如运行两个qq,除了数据不一样,代码都是一样的, 每次运行qq,都会将代码和数据加载到内存中,除了数据,每次加载的代码都是一样的 ...
- 【CVE-2022-0543】Redis Lua沙盒绕过命令执行复现
免责声明: 本文章仅供学习和研究使用,严禁使用该文章内容对互联网其他应用进行非法操作,若将其用于非法目的,所造成的后果由您自行承担,产生的一切风险与本文作者无关,如继续阅读该文章即表明您默认遵守该内容 ...
- 云原生之旅 - 13)基于 Github Action 的自动化流水线
前言 GItHub Actions是一个持续集成和持续交付的平台,能够让你自动化你的编译.测试和部署流程.GitHub 提供 Linux.Windows 和 macOS 虚拟机来运行您的工作流程,或者 ...
- OSI传输层TCP与UDP协议、应用层简介、socket模块介绍及代码优化、半连接池的概念
目录 传输层之TCP与UDP协议 应用层 socket模块 socket基本使用 代码优化 半连接池的概念 传输层之TCP与UDP协议 TCP与UDP都是用来规定通信方式的 通信的时候可以随心所欲的聊 ...
- 基于Spring-AOP的自定义分片工具
作者:陈昌浩 1 背景 随着数据量的增长,发现系统在与其他系统交互时,批量接口会出现超时现象,发现原批量接口在实现时,没有做分片处理,当数据过大时或超过其他系统阈值时,就会出现错误.由于与其他系统交互 ...
