sql优化(oracle)
系统优化中很重要的方面是SQL语句的优化,对于海量数据,优质的SQL能够有效的提高系统的可用性。
总结的有点罗嗦,列个简单的目录啦~
目录
第一部分知识准备 第二部分 常用sql用法和注意事项 第三部分 sql优化总结
1. sql执行过程 1. exists 和 in 1. 优化一般原则
2. sql 共享 2. union 和 union all 2. 具体注意事项
3. 绑定变量 3. with as
知识准备
1. sql执行过程
1)执行过程
当一个oracle实例接收到一条sql后,执行过程如下:
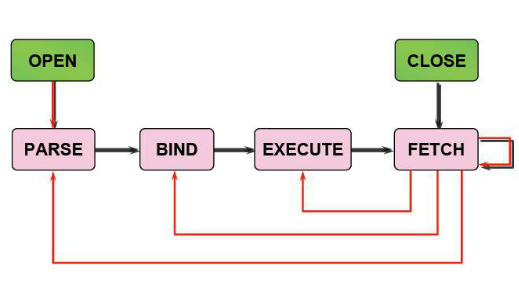
1) create a cursor 创建游标
2) parse the statement 分析语句
3) describe results of a query 描述查询的结果集
4)define output of a query 定义查询的输出数据
5)bind any variables 绑定变量
6)parallelize the statement 并行执行语句
7)run the statement 运行语句
8)fetch rows of a query 取查询结果
9)close the cursor 关闭游标
2.SQL 共享
1. 为不重复解析相同的SQL语句,oracle 将执行过的SQL语句存放在内存的共享池(shared buffer pool)中,可以被所有数据库用户共享
2. 当执行一个SQL语句时,如果它和之前执行过的语句完全相同(注意同义词和表是不同对象),oracle就能获得已经被解析的语句;
3.bind variables绑定变量
1)解决重编译问题
eg1:
insert into tab1(col1,col2) values (val1,val2); --普通方式 insert into tab1(col1,col2) values (:v1,:v2);--绑定变量,只需编译一次
eg2:使用PreparedStatement
PreparedStatement ps = con.prepareStatement("insert into tab1 (col1, col2) values (?,?)");
2)共享游标
好处:减少解析;提高内存使用率;动态内存调整
假如输入如下两个sql:
select * from tab1 where id = :c;
select * from tab1 where id = :d;
这两句sql会被转化为:
select * from tab1 where id = :b;
4.访问数据表方式
1)全表扫描——顺序访问表中每条记录
oracle采用一个读入多个数据块的方式优化全表扫描
2)通过rowid访问表——rowid包含了表中记录的物理位置信息, 基于rowid访问方式可以提高访问表的效率
oracle通过索引实现了数据和存放数据位置rowid之间的联系,通常索引提供了快速访问rowid的方法
5. select sql执行顺序
1)select子句
(8)SELECT (9)DISTINCT (11)<Top Num> <select list>
(1)FROM <left_table>
(3)<join_type> JOIN <right_table>
(2)ON <join_condition>
(4)WHERE <where_condition>
(5)GROUP BY <group_by_list>
(6)WITH <CUBE | RollUP>
(7)HAVING <having_condition>
(10)ORDER BY <order_by_list>
2)执行顺序说明
1)FROM [left table]——from前的表做笛卡尔集 ——虚拟表VT1 2) ON <join condition>——筛选——VT2 3) [join type] JOIN [right table]——连接——VT3 详细见 oracle连接 4) WHERE ——where筛选——VT4 5)GROUP BY ——按照GROUP BY子句中的列对VT4中行分组——VT5 6)CUBE|ROLLUP——分组,eg:ROLLUP(A, B),首先会对(A、B)进行GROUP BY,然后对(A)进行GROUP BY,最后对全表GROUP BY CUBE(A,B), 首先对(A、B)GROUP BY, 然后(A)、(B) GROUP BY, 最后全表GROUP BY; ——VT6 7) HAVING——HAVING筛选——VT7 8)SELECT——VT8 9) DISTINCT——移除重复的行——VT9 10)ORDER BY——按照order by子句中的列将VT9中列表排序,生成游标——VC10 11) TOP ——从VC10的开始处选择一定数量或者比例的行——VT11,返回结果
3)注意事项
1. 只有ORDER BY 子句中可以使用select列表中列的别名
如果要在其他地方使用需要使用如下方式:
SELECT * FROM (SELECT NAME, SALARY AS s FROM EMP ) vt WHERE vt.s<5000;
2. 使用了ORDER BY子句的查询不能用作表表达式(视图、内联表值函数、子查询、派生表和共用表达式),如下的语句都会产生错误
create table tab1 as select * from student order by score; select * from (select * from student order by score);
6.索引使用
正确使用索引可以有效提高系统性能,详细见 oracle索引总结
常用sql用法和及注意事项
1.exits和in用法
1)说明:
1. exists对外表做循环,每次循环对内表查询;in将内表和外表做hash连接
2. 使用exists oracle会先检查主查询; 使用in,首先执行子查询,并将结果存储在临时表中
2)使用:
表class和student表
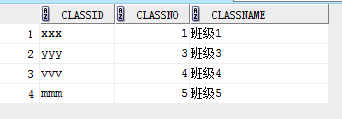
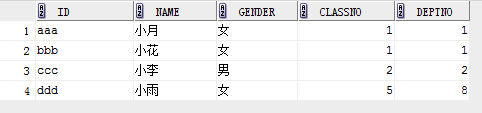
下面查询student中classno在class中的数据
1. 使用exists和not exists
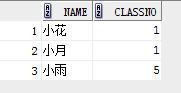
select name, classno from student where exists (select * from class where student.classno= class.classno);
结果:
select name, classno from student where not exists (select * from class where student.classno= class.classno);
结果:
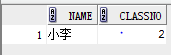
select name, classno from student where classno in (select classno from class);
2. 使用in 和not in
select name, classno from student where classno not in (select classno from class);

结果:

3)比较
1. 如果两个表大小相当,in和exists差别不大
2. 如果两个表大小相差较大则子查询表大的用exists,子查询表小的用in
3.尽量不要使用not in
2.union和union all
1)说明:
1. 使用场景:需要将两个select语句结果整体显示时,可以使用union和union all
2. union对两个结果集取并集不包含重复结果同时进行默认规则的排序;而union all对两个结果集去并集,包括重复行,不进行排序
3. union需要进行重复值扫描,效率低,如果没有要删除重复行,应该使用union all
4. insersect和minus分别交集和差集,都不包括重复行,并且进行默认规则的排序
2)使用注意事项
1.可以将多个结果集合并
2. 必须保证select集合的结果有相同个数的列,并且每个列的类型是一样的(列名不一定要相同,会默认将第一个结果的列名作为结果集的列名)
3)例子:
表student
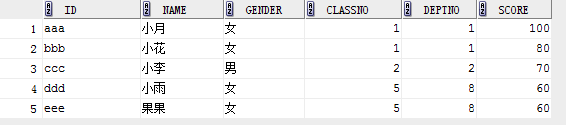
eg1:
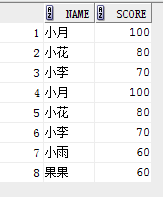
select name, score from student where score> 60
union all
select name, score from student where score <200;
结果:(有重复,没有排序)
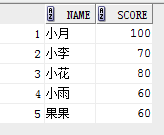
select name, score from student where score> 60
union
select name, score from student where score <200;
结果:(没有重复,并且排序了)
3.with as
1)说明:
1. with table as 可以建立临时表,一次分析,多次使用
2. 对于复杂查询,使用with table as可以抽取公共查询部分,多次查询时可以提高效率
3. 增强了易读性
2)语法:
with tabName as (select ...)
3)例子:
表student

eg1:
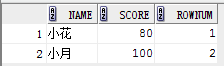
select rownum, name, score from (select rownum, name,score from student where score >70 order by score);
可以更换成:
with table_s as (select rownum, name,score from student where score >70 order by score)
select name, score from table_s;
结果:
4)多个with table as 一起使用时用逗号隔开,并且只能使用一个with如下例子
eg1:
with vt1 as (select * from student where score >=60),
vt2 as (select * from class),
vt3 as (select * from teacher)
select vt1.name, vt1.score, vt2.classname, vt3.teachername from vt1,vt2,vt3 where vt1.classno= vt2.classno and vt1.teacherid=vt3.teacherid;
eg2:
with vt as (select t.*
from travelrecord t where t.starttime>=to_date('2014-02-01','yyyy-mm-dd') and t.endtime<=to_date('2014-04-30','yyyy-mm-dd')+1 and to_char(starttime,'hh24')>='' and to_char(endtime,'hh24')<='' and t.vehiclenum=''),
vt1 as (select sum(vt4.traveltime) as stoptime from ((select * from vt where vt.state='')vt4)),
vt2 as (select sum(vt.traveltime)as "ONLINETIME1",sum(vt.distance)as "DISTANCE1"from vt)
select vt1.stoptime,vt2.distance1, vt2.onlinetime1 from vt2, vt1;
4. order by
1)说明:
1. order by 决定oracle如何将查询结果排序
2. 不指定asc或者desc时默认asc
2)使用:
1. 单列升序(可以去掉asc)
select * from student order by score asc;
2. 多列升序
select * from student order by score, deptno;
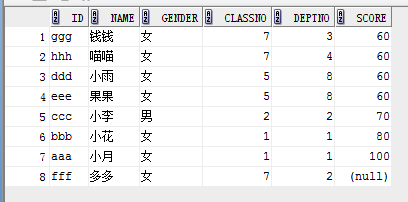
3. 多列降序
select * from student order by score desc, deptno desc;
4. 混合
select * from student order by score asc, deptno desc;
3)对NULL的处理
1. oracle在order by 时认为null是最大值,asc时排在最后,desc时排在最前
eg:
select * from student order by score asc;
结果: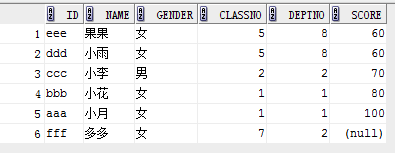
2. 使用nulls first (不管asc或者desc,null记录排在最前)或者nulls last 可以控制null的位置,eg:
select * from student order by score asc nulls first;
结果如下:
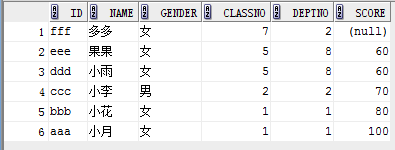
4)将某行数据置顶(decode)
eg1:
select * from student order by decode(score,100,1,2);
结果:
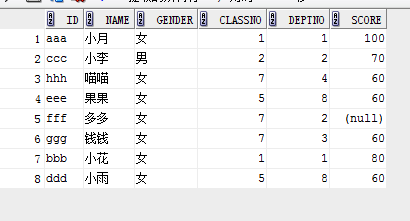
eg2: (某一行置顶,其他的升序)
select * from student order by decode(score,100,1,2), score;
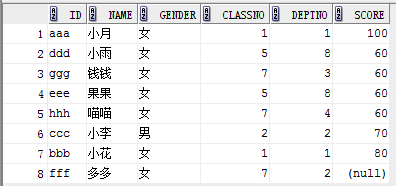
5)注意事项
1. 任何在order by 语句的非索引项都将降低查询速度
2. 避免在order by 子句中使用表达式
5. group by
1)说明:
1.用于对where执行结果进行分组
2)简单例子:
eg1:

select sum(score), deptno from student group by deptno;
结果:
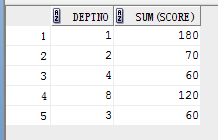
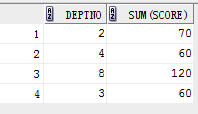
eg2:
select deptno,sum(score) from student where deptno>1 group by deptno;
结果:
6.where和having
1)说明:
1. where和having都是用来筛选数据,但是执行的顺序不同 where --group by--having(即分组计算前计算where语句,分组计算后计算having'语句),详情查看章节一sql执行顺序
2. having一般用来对分组后的数据进行筛选
3. where中不能使用聚组函数如sum,count,max等
2)例子:
eg1: 对 5 中group by 的数据筛选
select deptno,sum(score) from student where deptno>1 group by deptno having sum(score)>100;
结果:

7. case when 和decode
1)说明:
1. decode更简洁
2. decode只能做等值的条件区分,case when可以使用区间的做判断
2)语法:
decode(条件,值1,返回值1,值2,返回值2,...值n,返回值n,缺省值) --等价于: IF 条件=值1 THEN
RETURN(翻译值1)
ELSIF 条件=值2 THEN
RETURN(翻译值2)
......
ELSIF 条件=值n THEN
RETURN(翻译值n)
ELSE
RETURN(缺省值)
END IF
CASE expr WHEN comparison_expr1 THEN return_expr1
[WHEN comparison_expr2 THEN return_expr2
WHEN comparison_exprn THEN return_exprn
ELSE else_expr]
END
CASE
WHEN comparison_expr1 THEN return_expr1
[WHEN comparison_expr2 THEN return_expr2
WHEN comparison_exprn THEN return_exprn
ELSE else_expr]
END
3)例子:
eg1:
方式一:
select name, score,gender,
case gender when '' then '女'
when '' then '男'
else '未说明'
end gender_t
from student;
方式二:
select name, score,gender,
case when gender='' then '女'
when gender='' then '男'
else '未说明'
end gender_t
from student;
方式三:
select name,gender,decode(gender,'','女','','男','未说明')gender_t from student;
结果:
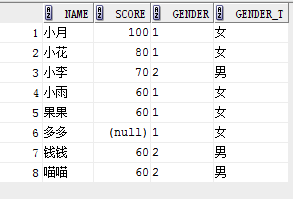
eg2:
select name,score,
case when score >80 then'优秀'
when score>=60 and score <=80 then '良好'
when score<60 then '不及格'
end evalution
from student;
结果:
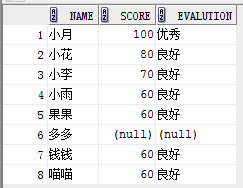
设置默认值,将null置为没成绩:
select name,score,
case when score >80 then'优秀'
when score>=60 and score <=80 then '良好'
when score<60 then '不及格'
else '没成绩'
end evalution
from student;
结果:

4)注意:
1.case有两种形式,其中case 表达式 when then方式效率高于case when 表达式效率
2.使用decode函数可以避免重复扫描相同记录或者重复连接相同的表,因而某些情况可以减少处理时间
SQL 优化总结
1. SQL优化一般性原则
1)目标:减少服务器资源消耗(主要是磁盘IO)
2)设计:
1. 尽量依赖oracle优化器
2. 合适的索引(数据重复量大的列不要简历二叉树索引,可以使用位图索引; 对应数据操作频繁的表,索引需要定期重建,减少失效的索引和碎片)
3)编码:
1.利用索引
2. 合理利用临时表
3. 避免写过于复杂的sql;
4. 尽量减小事务的粒度
2. 具体注意事项
1)查询时尽量使用确定的列名
2)尽量少使用嵌套的子查询,这种查询很消耗cpu资源
3)多表查询的时候,选择最有效率的表名顺序
oracle解析器对表的处理顺序从右到左,所以记录少的表放在右边(最右边的表为基础表,drivering table最先被处理), 如果3个以上的表连接查询,则要选择交叉表作为基础表
4)or比较多时分为多个查询,使用union all(尽量用union all代替union)联结(适应于索引列)
详细见上一章节union和union all
5) 尽量多用commit提交事务,可以及时释放资源、解锁、释放日志
6)访问频繁的表可以放置在内存中
7)避免复杂的多表关联
8)避免distinct,union(并集),minus(差集),intersect(交集),order by等耗费资源的操作,因为会执行耗费资源的排序功能
9)使用exists替代distinct
eg:
select c.distinct c.classname, c.classid, classno from student s, class c where s.classno= c.classno; --替换为 select classname, classid, classno from class c where exists (select * from student s where s.classno = c.classno);
10)删除全表时利用truncate代替delete
delete删除时,没有commit前可以回滚;truncate后不能回滚,执行时间较短
11)使用表的别名,可以减少解析时间
12)exists和in的选择问题,不同时候区分对待
具体见上一章节exists和in
13)合理使用索引,详细见:oracle索引总结
sql优化(oracle)的更多相关文章
- SQL优化——ORACLE
SQL优化——ORACLE 索引是由Oracle维护的可选结构,为数据提供快速的访问.准确地判断在什么地方需要使用索引是困难的,使用索引有利于调节检索速度. 当建立一个索引时,必须指定用于跟踪的表名以 ...
- SQL优化(Oracle)
(转)SQL优化原则 一.问题的提出 在应用系统开发初期.因为开发数据库数据比較少.对于查询SQL语句,复杂视图的的编写等体会不出SQL语句各种写法的性能优劣,可是假设将应用系统提交实际应用后,随着数 ...
- SQL优化 | Oracle 绑定变量
之前整理过一篇有关绑定变量的文章,不太详细,重新补充一下. Oracle 绑定变量 http://www.cndba.cn/Dave/article/1275 一.绑定变量 bind variable ...
- ORACLE常用SQL优化hint语句
在SQL语句优化过程中,我们经常会用到hint,现总结一下在SQL优化过程中常见Oracle HINT的用法: 1. /*+ALL_ROWS*/ 表明对语句块选择基于开销的优化方法,并获得最佳吞吐量, ...
- 基于Oracle的SQL优化(社区万众期待 数据库优化扛鼎巨著)
基于Oracle的SQL优化(社区万众期待数据库优化扛鼎巨著) 崔华 编 ISBN 978-7-121-21758-6 2014年1月出版 定价:128.00元 856页 16开 编辑推荐 本土O ...
- Oracle SQL 优化原则(实用篇)
由于SQL优化优化起来比较复杂,并且还受环境限制,在开发过程中,写SQL必须遵循以下几点原则: 1.Oracle 采用自下而上的顺序解析WHERE子句,根据这个原理,表之间的连接必须写在其他Where ...
- Oracle 建立索引及SQL优化
数据库索引: 索引有单列索引,复合索引之说,如果某表的某个字段有主键约束和唯一性约束,则Oracle 则会自动在相应的约束列上建议唯一索引.数据库索引主要进行提高访问速度. 建设原则: 1.索引应该经 ...
- oracle sql优化
整理一下网上所看到sql优化方法 1.使用大写字母书写sql,因为oracle解释器会先将sql语句转换成大写后再解释 2 减少访问数据库的次数,多数情况下一条sql可以达到目的的,就不要使用多 ...
- Oracle SQL优化一(常见方法)
1.表访问方式优化: a)普通表优先“Index Lookup 索引扫描”,避免全表扫描 大多数场景下,通过“Index Lookup 索引扫描”要比“Full Table Scan (FTS) 全表 ...
- SQL性能优化(Oracle)
首先要搞明白什么叫执行计划? 执行计划是数据库根据SQL语句和相关表的统计信息作出的一个查询方案,这个方案是由查询优化器自动分析产生的,比如一条SQL语句如果用来从一个 10万条记录的表中查1条记录, ...
随机推荐
- Linux 开机自检的设置(tune2fs和fsck)
tune2fs和fsck的用法 tune2fs--调整ext2/ext3文件系统特性的工具. -l <device> 查看文件系统信息 -c <count> 设置强制自检的 ...
- Git 版本控制工具使用介绍------Windows系统下使用
Git 是用于 Linux内核开发的版本控制工具.与常用的版本控制工具 CVS, Subversion 等不同,它采用了分布式版本库的方式,不必服务器端软件支持(wingeddevil注:这得分是用什 ...
- ERROR 1372 (HY000): Password hash should be a 41-digit hexadecimal number;
rpm 安装了 mysql 5.6 的版本 遇到的问题 1. 提示与5.1版本的有冲突. 解决方式, 是 rpm --force -ivh rpm包.rpm 进行强制安装 2. 启动 mysql 后, ...
- Bootstrap Modal 框 alert confirm loading
/** * Created by Administrator on 2016/5/4. */ /** * 模态窗口 */ window.Modal = { tpls:{ alert:'<div ...
- java 类处理工具
public class ClassUtils { private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ClassUtils.cl ...
- H5移动端的注意细节
1. max-width用在pc端页面,max-device-width用在移动设备上 2. device-pixel-ratio 设备像素比 3.设备自己单位-物理单位dp/dip css像素 px ...
- (转)一步一步学习PHP(3)——函数
相信每个人在学习PHP之前至少都有着一定的C语言,或者是C++/Java/C#等其他语言的基础,所以在这里也不从头开始说起,只是来谈谈PHP方法的独特之处. 1. 方法概述 首先,写一个最简单的函数, ...
- DataTable去重复方法
//去掉重复行 DataTable table=new DataTable(); DataView dv = table.DefaultView; table = dv.ToTable(true, n ...
- asp.net中Page.ClientScript.RegisterStartupScript用法小结(转)
//ASP.NET后台页面跳转 Page.ClientScript.RegisterStartupScript(Page.GetType(), "", "<scri ...
- 05_Smart-image通过SoftReference提高性能
文章导读: 文件介绍了常见的图片下载开源插件smart-image, 由于移动设备硬件受限,因此Android的相关app都要考虑到性能的关系, 所以很多的第三方插件都使用到了缓存cache技术,本人 ...
