spring mvc DispatcherServlet详解之二---request通过Controller获取ModelAndView过程
整个spring mvc的架构如下图所示:
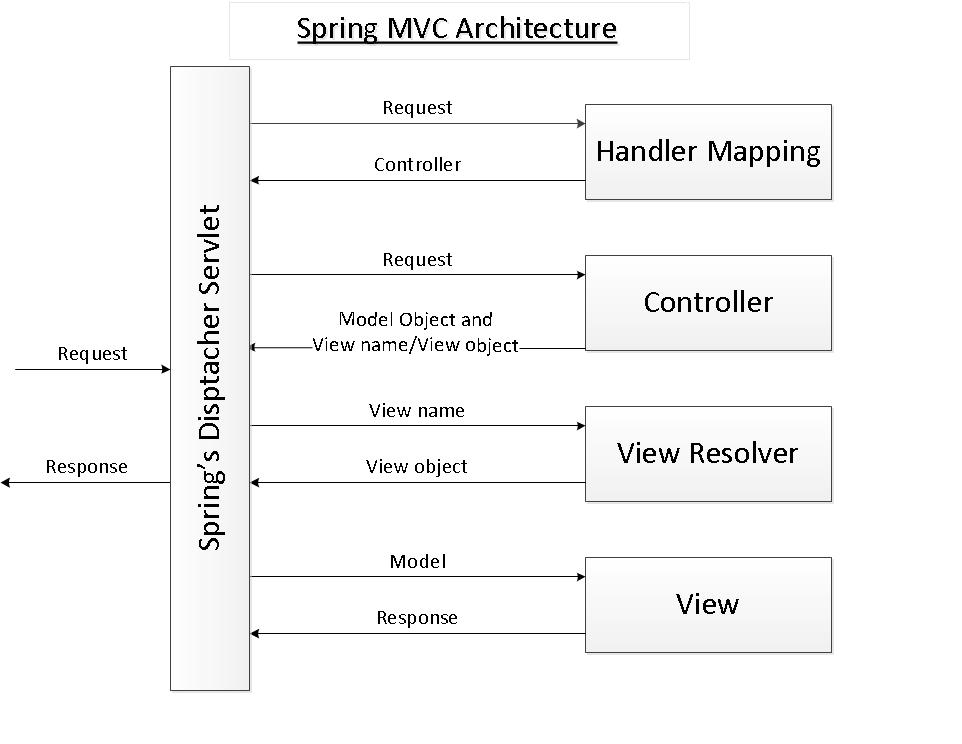
上篇文件讲解了DispatcherServlet通过request获取控制器Controller的过程,现在来讲解DispatcherServletDispatcherServlet的第二步:通过request从Controller获取ModelAndView。
DispatcherServlet调用Controller的过程:
DispatcherServlet.java
doService()--->doDispatch()--->handlerAdapter的handle()方法
try {// Actually invoke the handler.
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
}
最常用的实现了HandlerAdapter接口是SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter类,该类将
两个不兼容的类:DispatcherServlet 和Controller 类连接到一起。
Adapter to use the plain {@link Controller} workflow interface with
the generic {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet}.
Supports handlers that implement the {@link LastModified} interface.
<p>This is an SPI class, not used directly by application code.
类之间的转换代码如下所示,调用了Controller类的handleRequest()方法来处理请求:
@Override
public ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception { return ((Controller) handler).handleRequest(request, response);
}
重量级人物控制器Controller开始闪亮登场,Controller是一个基本的接口,它接受request和response,从这点上来说,它有点像servlet,但不同之处在于它在mvc模式流程中起作用,它和struts中的Action作用类似。继承该接口的控制器或者类应该保证是线程安全的,可复用的,能够在一个应用生命周期中处理大量的request。为了使Controller的配置更便捷,通常使用javaBeans来继承Controller。
/**
* Base Controller interface, representing a component that receives
* {@code HttpServletRequest} and {@code HttpServletResponse}
* instances just like a {@code HttpServlet} but is able to
* participate in an MVC workflow. Controllers are comparable to the
* notion of a Struts {@code Action}.
*
* <p>Any implementation of the Controller interface should be a
* <i>reusable, thread-safe</i> class, capable of handling multiple
* HTTP requests throughout the lifecycle of an application. To be able to
* configure a Controller easily, Controller implementations are encouraged
* to be (and usually are) JavaBeans.
* </p>
*
* <p><b><a name="workflow">Workflow</a></b></p>
*
* <p>
* After a <cde>DispatcherServlet</code> has received a request and has
* done its work to resolve locales, themes and suchlike, it then tries
* to resolve a Controller, using a
* {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping HandlerMapping}.
* When a Controller has been found to handle the request, the
* {@link #handleRequest(HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse) handleRequest}
* method of the located Controller will be invoked; the located Controller
* is then responsible for handling the actual request and - if applicable -
* returning an appropriate
* {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView ModelAndView}.
* So actually, this method is the main entrypoint for the
* {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet DispatcherServlet}
* which delegates requests to controllers.</p>
*
* <p>So basically any <i>direct</i> implementation of the Controller interface
* just handles HttpServletRequests and should return a ModelAndView, to be further
* interpreted by the DispatcherServlet. Any additional functionality such as
* optional validation, form handling, etc should be obtained through extending
* one of the abstract controller classes mentioned above.</p>
*
* <p><b>Notes on design and testing</b></p>
*
* <p>The Controller interface is explicitly designed to operate on HttpServletRequest
* and HttpServletResponse objects, just like an HttpServlet. It does not aim to
* decouple itself from the Servlet API, in contrast to, for example, WebWork, JSF or Tapestry.
* Instead, the full power of the Servlet API is available, allowing Controllers to be
* general-purpose: a Controller is able to not only handle web user interface
* requests but also to process remoting protocols or to generate reports on demand.</p>
*
* <p>Controllers can easily be tested by passing in mock objects for the
* HttpServletRequest and HttpServletResponse objects as parameters to the
* {@link #handleRequest(HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse) handleRequest}
* method. As a convenience, Spring ships with a set of Servlet API mocks
* that are suitable for testing any kind of web components, but are particularly
* suitable for testing Spring web controllers. In contrast to a Struts Action,
* there is no need to mock the ActionServlet or any other infrastructure;
* HttpServletRequest and HttpServletResponse are sufficient.</p>
*
* <p>If Controllers need to be aware of specific environment references, they can
* choose to implement specific awareness interfaces, just like any other bean in a
* Spring (web) application context can do, for example:</p>
* <ul>
* <li>{@code org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware}</li>
* <li>{@code org.springframework.context.ResourceLoaderAware}</li>
* <li>{@code org.springframework.web.context.ServletContextAware}</li>
* </ul>
*
* <p>Such environment references can easily be passed in testing environments,
* through the corresponding setters defined in the respective awareness interfaces.
* In general, it is recommended to keep the dependencies as minimal as possible:
* for example, if all you need is resource loading, implement ResourceLoaderAware only.
* Alternatively, derive from the WebApplicationObjectSupport base class, which gives
* you all those references through convenient accessors - but requires an
* ApplicationContext reference on initialization.
*
* <p>Controllers can optionally implement the {@link LastModified} interface.
*/
Controller的handleRequest()方法处理请求,并返回ModelAndView给DispatcherServlet去渲染render。
Controller接口的抽象实现类为:AbstractController,它通过互斥锁(mutex)来保证线程安全。
/**
* Set if controller execution should be synchronized on the session,
* to serialize parallel invocations from the same client.
* <p>More specifically, the execution of the {@code handleRequestInternal}
* method will get synchronized if this flag is "true". The best available
* session mutex will be used for the synchronization; ideally, this will
* be a mutex exposed by HttpSessionMutexListener.
* <p>The session mutex is guaranteed to be the same object during
* the entire lifetime of the session, available under the key defined
* by the {@code SESSION_MUTEX_ATTRIBUTE} constant. It serves as a
* safe reference to synchronize on for locking on the current session.
* <p>In many cases, the HttpSession reference itself is a safe mutex
* as well, since it will always be the same object reference for the
* same active logical session. However, this is not guaranteed across
* different servlet containers; the only 100% safe way is a session mutex.
* @see AbstractController#handleRequestInternal
* @see org.springframework.web.util.HttpSessionMutexListener
* @see org.springframework.web.util.WebUtils#getSessionMutex(javax.servlet.http.HttpSession)
*/
线程安全实现:
public ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws Exception { // Delegate to WebContentGenerator for checking and preparing.
checkAndPrepare(request, response, this instanceof LastModified); // Execute handleRequestInternal in synchronized block if required.
if (this.synchronizeOnSession) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if (session != null) {
Object mutex = WebUtils.getSessionMutex(session);
synchronized (mutex) {
return handleRequestInternal(request, response);
}
}
} return handleRequestInternal(request, response);
}
handleRequestInternal()为抽象方法,留待具体实现类来实现。它的直接子类有:
简单Controller实现
在web.xml中有时候定义节点<welcome-list>index.html</welcome-list>等,这种简单的请,Controller是如何实现的呢?我们来看看UrlFilenameViewController,它是Controller的一个间接实现,实现了AbstractUrlViewController。它把url的虚拟路径转换成一个view的名字,然后返回这个view。
protected ModelAndView handleRequestInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);
String viewName = getViewNameForRequest(request);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Returning view name '" + viewName + "' for lookup path [" + lookupPath + "]");
}
return new ModelAndView(viewName, RequestContextUtils.getInputFlashMap(request));
}
复杂Controller实现
一个可以处理多种请求类型的Controller实现:MultiActionController。它类似于struts中的DispatcherAction,但更灵活,而且支持代理。
/**
* {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.Controller Controller}
* implementation that allows multiple request types to be handled by the same
* class. Subclasses of this class can handle several different types of
* request with methods of the form
*
* <pre class="code">public (ModelAndView | Map | String | void) actionName(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, [,HttpSession] [,AnyObject]);</pre>
*
* A Map return value indicates a model that is supposed to be passed to a default view
* (determined through a {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.RequestToViewNameTranslator}).
* A String return value indicates the name of a view to be rendered without a specific model.
*
* <p>May take a third parameter (of type {@link HttpSession}) in which an
* existing session will be required, or a third parameter of an arbitrary
* class that gets treated as the command (that is, an instance of the class
* gets created, and request parameters get bound to it)
*
* <p>These methods can throw any kind of exception, but should only let
* propagate those that they consider fatal, or which their class or superclass
* is prepared to catch by implementing an exception handler.
*
* <p>When returning just a {@link Map} instance view name translation will be
* used to generate the view name. The configured
* {@link org.springframework.web.servlet.RequestToViewNameTranslator} will be
* used to determine the view name.
*
* <p>When returning {@code void} a return value of {@code null} is
* assumed meaning that the handler method is responsible for writing the
* response directly to the supplied {@link HttpServletResponse}.
*
* <p>This model allows for rapid coding, but loses the advantage of
* compile-time checking. It is similar to a Struts {@code DispatchAction},
* but more sophisticated. Also supports delegation to another object.
*
* <p>An implementation of the {@link MethodNameResolver} interface defined in
* this package should return a method name for a given request, based on any
* aspect of the request, such as its URL or an "action" parameter. The actual
* strategy can be configured via the "methodNameResolver" bean property, for
* each {@code MultiActionController}.
*
* <p>The default {@code MethodNameResolver} is
* {@link InternalPathMethodNameResolver}; further included strategies are
* {@link PropertiesMethodNameResolver} and {@link ParameterMethodNameResolver}.
*
* <p>Subclasses can implement custom exception handler methods with names such
* as:
*
* <pre class="code">public ModelAndView anyMeaningfulName(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, ExceptionClass exception);</pre>
*
* The third parameter can be any subclass or {@link Exception} or
* {@link RuntimeException}.
*
* <p>There can also be an optional {@code xxxLastModified} method for
* handlers, of signature:
*
* <pre class="code">public long anyMeaningfulNameLastModified(HttpServletRequest request)</pre>
*
* If such a method is present, it will be invoked. Default return from
* {@code getLastModified} is -1, meaning that the content must always be
* regenerated.
*
* <p><b>Note that all handler methods need to be public and that
* method overloading is <i>not</i> allowed.</b>
*
* <p>See also the description of the workflow performed by
* {@link AbstractController the superclass} (in that section of the class
* level Javadoc entitled 'workflow').
*
* <p><b>Note:</b> For maximum data binding flexibility, consider direct usage of a
* {@link ServletRequestDataBinder} in your controller method, instead of relying
* on a declared command argument. This allows for full control over the entire
* binder setup and usage, including the invocation of {@link Validator Validators}
* and the subsequent evaluation of binding/validation errors.*/
根据方法名决定处理的handler
protected ModelAndView handleRequestInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws Exception {
try {
String methodName = this.methodNameResolver.getHandlerMethodName(request);
return invokeNamedMethod(methodName, request, response);
}
catch (NoSuchRequestHandlingMethodException ex) {
return handleNoSuchRequestHandlingMethod(ex, request, response);
}
}
触发执行方法:
protected final ModelAndView invokeNamedMethod(
String methodName, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { Method method = this.handlerMethodMap.get(methodName);
if (method == null) {
throw new NoSuchRequestHandlingMethodException(methodName, getClass());
} try {
Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
List<Object> params = new ArrayList<Object>(4);
params.add(request);
params.add(response); if (paramTypes.length >= 3 && paramTypes[2].equals(HttpSession.class)) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if (session == null) {
throw new HttpSessionRequiredException(
"Pre-existing session required for handler method '" + methodName + "'");
}
params.add(session);
} // If last parameter isn't of HttpSession type, it's a command.
if (paramTypes.length >= 3 &&
!paramTypes[paramTypes.length - 1].equals(HttpSession.class)) {
Object command = newCommandObject(paramTypes[paramTypes.length - 1]);
params.add(command);
bind(request, command);
} Object returnValue = method.invoke(this.delegate, params.toArray(new Object[params.size()]));
return massageReturnValueIfNecessary(returnValue);
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
// The handler method threw an exception.
return handleException(request, response, ex.getTargetException());
}
catch (Exception ex) {
// The binding process threw an exception.
return handleException(request, response, ex);
}
处理返回结果,要么返回null要么返回ModelAndView实例。当返回一个Map类型时,ModelAndView实例包装的Map类型。
/**
* Processes the return value of a handler method to ensure that it either returns
* {@code null} or an instance of {@link ModelAndView}. When returning a {@link Map},
* the {@link Map} instance is wrapped in a new {@link ModelAndView} instance.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private ModelAndView massageReturnValueIfNecessary(Object returnValue) {
if (returnValue instanceof ModelAndView) {
return (ModelAndView) returnValue;
}
else if (returnValue instanceof Map) {
return new ModelAndView().addAllObjects((Map<String, ?>) returnValue);
}
else if (returnValue instanceof String) {
return new ModelAndView((String) returnValue);
}
else {
// Either returned null or was 'void' return.
// We'll assume that the handle method already wrote the response.
return null;
}
}
小结:
DispatcherServlet接受一个请求,然后解析完locales, themes等后,通过HadlerMapping解析控制器Controller去处理请求。
找到Controller后,出发当前controller的handleRequest()方法,此controller负责真正处理请求,然后一个ModelAndView实例。
DispatcherServlet 代理此Controller,接收返回结果,然后进行渲染。
spring mvc DispatcherServlet详解之二---request通过Controller获取ModelAndView过程的更多相关文章
- spring mvc DispatcherServlet详解之三---request通过ModelAndView中获取View实例的过程
整个spring mvc的架构如下图所示: 上篇文件讲解了DispatcherServlet第二步:通过request从Controller获取ModelAndView.现在来讲解第三步:reques ...
- spring mvc DispatcherServlet详解之一--request通过HandlerMaping获取控制器Controller过程
整个spring mvc的架构如下图所示: 现在来讲解DispatcherServletDispatcherServlet的第一步:获取控制器. HandlerMapping HandlerMappi ...
- spring mvc DispatcherServlet详解之前传---FrameworkServlet
做项目时碰到Controller不能使用aop进行拦截,从网上搜索得知:使用spring mvc 启动了两个context:applicationContext 和WebapplicationCont ...
- (转载)spring mvc DispatcherServlet详解之一---处理请求深入解析
要深入理解spring mvc的工作流程,就需要先了解spring mvc的架构: 从上图可以看到 前端控制器DispatcherServlet在其中起着主导作用,理解了DispatcherServl ...
- spring mvc DispatcherServlet详解之四---视图渲染过程
整个spring mvc的架构如下图所示: 现在来讲解DispatcherServletDispatcherServlet的最后一步:视图渲染.视图渲染的过程是在获取到ModelAndView后的过程 ...
- spring mvc DispatcherServlet详解之interceptor和filter的区别
首先我们看一下spring mvc Interceptor的功能及实现: http://wenku.baidu.com/link?url=Mw3GaUhCRMhUFjU8iIDhObQpDcbmmRy ...
- spring mvc DispatcherServlet详解之一---处理请求深入解析
要深入理解spring mvc的工作流程,就需要先了解spring mvc的架构: 从上图可以看到 前端控制器DispatcherServlet在其中起着主导作用,理解了DispatcherServl ...
- spring mvc DispatcherServlet详解之前传---前端控制器架构
前端控制器是整个MVC框架中最为核心的一块,它主要用来拦截符合要求的外部请求,并把请求分发到不同的控制器去处理,根据控制器处理后的结果,生成相应的响应发送到客户端.前端控制器既可以使用Filter实现 ...
- spring mvc DispatcherServlet详解前传---HttpServletBean类
从上章里我们已经看到: DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean impl ...
随机推荐
- python库tkinter、pygame中几点需要注意的问题
恍然之间已经16年快四月份了,已经好久都没有写过东西了.. 最近在用python做一些小的游戏,在网上找了一些Python库,Python中游戏编程最常用的还是pygame了,其次是Tkinter p ...
- APCS
arm汇编程序中,R0,R1,R2,R3,R12都是作为中间寄存器,而R4-R11是不能随便使用的,暂时我还不知它们的用途.所以,中间寄存器,在程序运行的开始处与结束的时候值是可以不一样的,也就是说中 ...
- 金山网络2014春季Android实习生招聘-成都站-笔试第二题
一个文件名为input.txt的文件当中,每一行都有一个单词,要求统计单词出现的频率,并且按照从小到大出现次数打印,次数相同的按照首字母顺序排序. package jinshanwangluo.exa ...
- Umbraco TextBoxFor 如何加样式和属性
前些天一直在找免费的CMS开源代码,搜索了很多,大都是介绍CMS开源系统的的文章或者是安装的主要流程.再深的也有但是都是很多年前的文章.我一个英语半吊子加MVC零基础只能像缓慢爬行的蜗牛一步步走了.为 ...
- prototype.js 源码解读(01)
prototype.js是一个设计的非常优雅且很有实用价值的js基础类库,其源码非常值得研究.研究它的源码不仅能提升个人水平,而且对你打下坚实的js基础也很有帮助.因本人技术水平有限,该解读仅供参考. ...
- 如何在DJANGO里,向有外键(一对多和多对多)的DB里插入数据?
需要插入的数据表结构如下: class UserInfo(models.Model): user_id =models.AutoField(primary_key=True) user_name=mo ...
- Qt学习笔记网络(URL和下载的功能都有)
http://www.cnblogs.com/li-peng/p/3656613.html
- Android日志框架darks-logs使用教程
一.配置文件 在使用darks-logs之前,我们需要为它创建一个名叫logd.properties的配置文件.如果你是需要在JAVA或WEB上使用该组件,那么你可以像配置log4j一样将它放在cla ...
- 演示:纯CSS实现自适应布局表格
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title> ...
- nginx+tomcat配置https
nginx代理https后,应用redirect https变成http,很多页面报404.情况类似http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_56d8ea900101hlhv.ht ...
