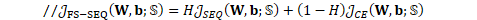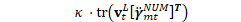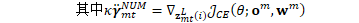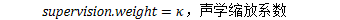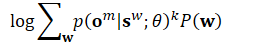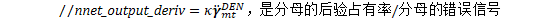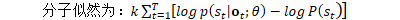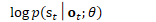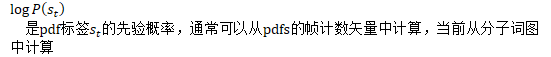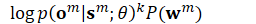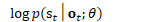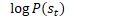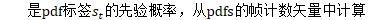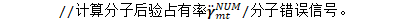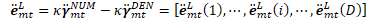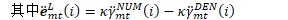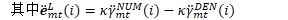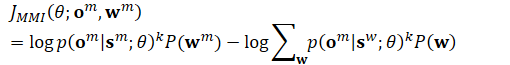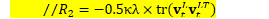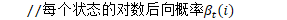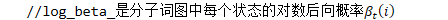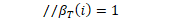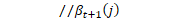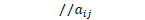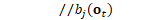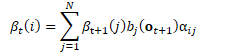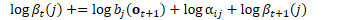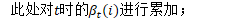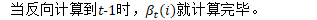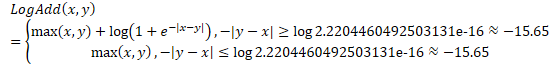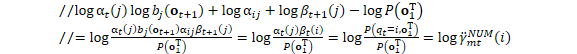kaldi chain模型的序列鉴别性训练代码分析
chainbin/nnet3-chain-train.cc
|
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { ... Nnet nnet; ReadKaldiObject(nnet_rxfilename, &nnet); bool ok; { fst::StdVectorFst den_fst; ReadFstKaldi(den_fst_rxfilename, &den_fst);
//NnetChainTrainer读取训练参数opts、分母词图den_fst、神经网络nnet NnetChainTrainer trainer(opts, den_fst, &nnet); //SequentialNnetChainExampleReader以语句为单位读取样本 SequentialNnetChainExampleReader example_reader(examples_rspecifier); for (; !example_reader.Done(); example_reader.Next()) //以句为单位进行训练 trainer.Train(example_reader.Value()); ok = trainer.PrintTotalStats(); }n ... WriteKaldiObject(nnet, nnet_wxfilename, binary_write); ... } |
nnet3/nnet-chain-training.cc
|
void NnetChainTrainer::Train(const NnetChainExample &chain_eg) { bool need_model_derivative = true; const NnetTrainerOptions &nnet_config = opts_.nnet_config; bool use_xent_regularization = (opts_.chain_config.xent_regularize != 0.0); ComputationRequest request; //This function takes a NnetChainExample and produces a ComputationRequest. GetChainComputationRequest(*nnet_, chain_eg, need_model_derivative, nnet_config.store_component_stats, use_xent_regularization, need_model_derivative, &request); //进行编译,返回到结果的常量指针。 //返回的常量指针由CachingOptimizingCompiler //如果编译失败,用std::shared_ptr<const NnetComputation>接收返回值 std::shared_ptr<const NnetComputation> computation = compiler_.Compile(request);
if (nnet_config.backstitch_training_scale > 0.0 && num_minibatches_processed_ % nnet_config.backstitch_training_interval == srand_seed_ % nnet_config.backstitch_training_interval) { // backstitch training is incompatible with momentum > 0 KALDI_ASSERT(nnet_config.momentum == 0.0); FreezeNaturalGradient(true, delta_nnet_); bool is_backstitch_step1 = true; srand(srand_seed_ + num_minibatches_processed_); ResetGenerators(nnet_); TrainInternalBackstitch(chain_eg, *computation, is_backstitch_step1); FreezeNaturalGradient(false, delta_nnet_); // un-freeze natural gradient is_backstitch_step1 = false; srand(srand_seed_ + num_minibatches_processed_); ResetGenerators(nnet_); TrainInternalBackstitch(chain_eg, *computation, is_backstitch_step1); } else { // conventional training TrainInternal(chain_eg, *computation); } num_minibatches_processed_++; } |
|
void NnetChainTrainer::TrainInternal(const NnetChainExample &eg, const NnetComputation &computation) { //NnetComputer类负责执行"computation"对象描述的计算。 //以以下顺序调用: 构造函数 AcceptInput()【或AcceptInputs()】 Run() GetOutput() AcceptOutputDeriv()【若可用】 Run()【如果需要反向计算】 GetInputDeriv()【若可用】: NnetComputer computer(nnet_config.compute_config, computation, nnet_, delta_nnet_); computer.AcceptInputs(*nnet_, eg.inputs); //前向传播,计算 computer.Run(); //该函数调用了GetOutput() this->ProcessOutputs(false, eg, &computer); //反向传播,计算权重更新量delta_nnet_ computer.Run(); //根据L2正则化项,修改权重更新量delta_nnet_ ApplyL2Regularization(*nnet_, GetNumNvalues(eg.inputs, false) * nnet_config.l2_regularize_factor, delta_nnet_); //根据权重更新量delta_nnet_,更新神经网络,上限为nnet_config.max_param_change bool success = UpdateNnetWithMaxChange(*delta_nnet_, nnet_config.max_param_change, 1.0, 1.0 - nnet_config.momentum, nnet_, &num_max_change_per_component_applied_, &num_max_change_global_applied_);
|
|
void NnetChainTrainer::ProcessOutputs(bool is_backstitch_step2, const NnetChainExample &eg, NnetComputer *computer) { // normally the eg will have just one output named 'output', but // we don't assume this. // In backstitch training, the output-name with the "_backstitch" suffix is // the one computed after the first, backward step of backstitch. const std::string suffix = (is_backstitch_step2 ? "_backstitch" : ""); std::vector<NnetChainSupervision>::const_iterator iter = eg.outputs.begin(), end = eg.outputs.end(); for (; iter != end; ++iter) { //检查每个样本的标签是否与网络相匹配 const NnetChainSupervision &sup = *iter; int32 node_index = nnet_->GetNodeIndex(sup.name); if (node_index < 0 || !nnet_->IsOutputNode(node_index)) KALDI_ERR << "Network has no output named " << sup.name; const CuMatrixBase<BaseFloat> &nnet_output = computer->GetOutput(sup.name); CuMatrix<BaseFloat> nnet_output_deriv(nnet_output.NumRows(), nnet_output.NumCols(), kUndefined); //是否进行交叉熵正则化 bool use_xent = (opts_.chain_config.xent_regularize != 0.0); //从名为"output-xent"的component-node获取交叉熵的目标函数值 std::string xent_name = sup.name + "-xent"; // typically "output-xent". CuMatrix<BaseFloat> xent_deriv; //tot_objf,目标函数值,未包含L2正则化项,未包含交叉熵正则化项 //tot_l2_term,L2正则化项 //tot_weight,L2正则化项权重 BaseFloat tot_objf, tot_l2_term, tot_weight; //根据预测和标签计算目标函数值及其梯度,计算交叉熵正则化项及其权重 //帧平滑-序列鉴别性准则
ComputeChainObjfAndDeriv(opts_.chain_config, den_graph_, sup.supervision, nnet_output, &tot_objf, &tot_l2_term, &tot_weight, &nnet_output_deriv, (use_xent ? &xent_deriv : NULL)); //更新梯度统计量 if (use_xent) { // 从神经网络中获取交叉熵output-node的输出 const CuMatrixBase<BaseFloat> &xent_output = computer->GetOutput( xent_name); /*
/* BaseFloat xent_objf = TraceMatMat(xent_output, xent_deriv, kTrans); objf_info_[xent_name + suffix].UpdateStats(xent_name + suffix, opts_.nnet_config.print_interval, num_minibatches_processed_, tot_weight, xent_objf); } //乘以梯度权重 if (opts_.apply_deriv_weights && sup.deriv_weights.Dim() != 0) { CuVector<BaseFloat> cu_deriv_weights(sup.deriv_weights); nnet_output_deriv.MulRowsVec(cu_deriv_weights); if (use_xent) //xent_deriv=diag(cu_deriv_weights)*xent_deriv //用cu_deriv_weights[i]对xent_deriv的第i行进行缩放 xent_deriv.MulRowsVec(cu_deriv_weights); } //计算器接收梯度 computer->AcceptInput(sup.name, &nnet_output_deriv);
objf_info_[sup.name + suffix].UpdateStats(sup.name + suffix, opts_.nnet_config.print_interval, num_minibatches_processed_, tot_weight, tot_objf, tot_l2_term); if (use_xent) { //以交叉熵正则化因子进行缩放 xent_deriv.Scale(opts_.chain_config.xent_regularize); //接收交叉熵正则化的梯度 computer->AcceptInput(xent_name, &xent_deriv); } } } |
chain/chain-training.cc
|
//该函数只计算交叉熵正则化项所需的数据,但并不在梯度中应用交叉熵正则化项! const DenominatorGraph &den_graph, const Supervision &supervision, const CuMatrixBase<BaseFloat> &nnet_output, BaseFloat *objf, BaseFloat *l2_term, BaseFloat *weight, CuMatrixBase<BaseFloat> *nnet_output_deriv, CuMatrix<BaseFloat> *xent_output_deriv) { if (!supervision.e2e_fsts.empty()) { ComputeChainObjfAndDerivE2e(opts, den_graph, supervision, nnet_output, objf, l2_term, weight, nnet_output_deriv, xent_output_deriv); return; } BaseFloat num_logprob_weighted, den_logprob_weighted; bool ok = true; if (nnet_output_deriv != NULL) nnet_output_deriv->SetZero(); { // Doing the denominator first helps to reduce the maximum // memory use, as we can set 'xent_deriv' to nonempty after // we've freed the memory in this object. DenominatorComputation denominator(opts, den_graph, supervision.num_sequences, nnet_output); /*
denominator.Forward()的结果为分母词图的后验概率
*/ den_logprob_weighted = supervision.weight * denominator.Forward(); if (nnet_output_deriv)
//其中负号来自于对分母取log ok = denominator.Backward(-supervision.weight, nnet_output_deriv); } if (xent_output_deriv != NULL) { // the reason for kStrideEqualNumCols is so that we can share the memory // block with the memory that was used for exp_nnet_output_transposed_ from // chain-denominator.cc, which has just been freed; it also uses the // kStrideEqualNumCols arg (its shape is the transpose of this matrix's // shape). xent_output_deriv->Resize(nnet_output.NumRows(), nnet_output.NumCols(), kSetZero, kStrideEqualNumCols); } { /*supervision是一句话完整标注对应的分子词图,其中包含每个音素序列的时间范围信息
其中
相当于nnet_output
*/ //NumeratorComputation类负责'supervision'(分子)FST的前向后向计算 NumeratorComputation numerator(supervision, nnet_output); // note: supervision.weight is included as a factor in the derivative from // the numerator object, as well as the returned logprob. */ 分子词图的后验概率
这与Kaldi nnet1
不同,Kaldi nnet3直接对分子词图进行计算 由于词图包含了 状态分布(NN)、状态、音素、字的全部信息。 因此,对词图的前向后向计算后,得到的是后验概率 */ num_logprob_weighted = numerator.Forward(); //此处,无法是否进行交叉熵正则化, //序列鉴别性训练的梯度nnet_output_deriv都不变。 //此时,还并没有在梯度中应用交叉熵正则化项! if (xent_output_deriv) {
numerator.Backward(xent_output_deriv); if (nnet_output_deriv)
nnet_output_deriv->AddMat(1.0, *xent_output_deriv); } else if (nnet_output_deriv) {
numerator.Backward(nnet_output_deriv); } } /*
*/ *objf = num_logprob_weighted - den_logprob_weighted;
*weight = supervision.weight * supervision.num_sequences * supervision.frames_per_sequence; //若梯度为无穷大/不可用 if (!((*objf) - (*objf) == 0) || !ok) { // inf or NaN detected, or denominator computation returned false. if (nnet_output_deriv) //将梯度设为零 nnet_output_deriv->SetZero(); if (xent_output_deriv) //将交叉熵梯度设为零 xent_output_deriv->SetZero(); BaseFloat default_objf = -10; KALDI_WARN << "Objective function is " << (*objf) << " and denominator computation (if done) returned " << std::boolalpha << ok << ", setting objective function to " << default_objf << " per frame."; //将权重设置为加权默认权重 *objf = default_objf * *weight; } // This code helps us see how big the derivatives are, on average, // for different frames of the sequences. As expected, they are // smaller towards the edges of the sequences (due to the penalization // of 'incorrect' pdf-ids. if (GetVerboseLevel() >= 1 && nnet_output_deriv != NULL && RandInt(0, 10) == 0) { int32 tot_frames = nnet_output_deriv->NumRows(), frames_per_sequence = supervision.frames_per_sequence, num_sequences = supervision.num_sequences; CuVector<BaseFloat> row_products(tot_frames); row_products.AddDiagMat2(1.0, *nnet_output_deriv, kNoTrans, 0.0); Vector<BaseFloat> row_products_cpu(row_products); Vector<BaseFloat> row_products_per_frame(frames_per_sequence); for (int32 i = 0; i < tot_frames; i++) row_products_per_frame(i / num_sequences) += row_products_cpu(i); KALDI_LOG << "Derivs per frame are " << row_products_per_frame; } if (opts.l2_regularize == 0.0) { *l2_term = 0.0; } else { // compute the l2 penalty term and its derivative BaseFloat scale = supervision.weight * opts.l2_regularize; //计算L2正则化项
*l2_term = -0.5 * scale * TraceMatMat(nnet_output, nnet_output, kTrans); if (nnet_output_deriv) // nnet_output_deriv->AddMat(-1.0 * scale, nnet_output); } } |
chain/chain-numerator.cc
|
//进行前向计算,返回 ComputeLookupIndexes(); nnet_logprobs_.Resize(nnet_output_indexes_.Dim(), kUndefined); nnet_output_.Lookup(nnet_output_indexes_, nnet_logprobs_.Data()); const fst::StdVectorFst &fst = supervision_.fst; KALDI_ASSERT(fst.Start() == 0); int32 num_states = fst.NumStates(); log_alpha_.Resize(num_states, kUndefined); log_alpha_.Set(-std::numeric_limits<double>::infinity()); tot_log_prob_ = -std::numeric_limits<double>::infinity(); log_alpha_(0) = 0.0; // note, state zero is the start state, we checked above const BaseFloat *nnet_logprob_data = nnet_logprobs_.Data(); std::vector<int32>::const_iterator fst_output_indexes_iter = fst_output_indexes_.begin(); double *log_alpha_data = log_alpha_.Data(); for (int32 state = 0; state < num_states; state++) { double this_log_alpha = log_alpha_data[state]; for (fst::ArcIterator<fst::StdVectorFst> aiter(fst, state); !aiter.Done(); aiter.Next(), ++fst_output_indexes_iter) { const fst::StdArc &arc = aiter.Value(); int32 nextstate = arc.nextstate; BaseFloat transition_logprob = -arc.weight.Value(); int32 index = *fst_output_indexes_iter; BaseFloat pseudo_loglike = nnet_logprob_data[index]; double &next_log_alpha = log_alpha_data[nextstate]; next_log_alpha = LogAdd(next_log_alpha, pseudo_loglike + transition_logprob + this_log_alpha); } if (fst.Final(state) != fst::TropicalWeight::Zero()) { BaseFloat final_logprob = -fst.Final(state).Value(); tot_log_prob_ = LogAdd(tot_log_prob_, this_log_alpha + final_logprob); } } KALDI_ASSERT(fst_output_indexes_iter == fst_output_indexes_.end()); return tot_log_prob_ * supervision_.weight; } |
|
//进行后向计算,计算神经网络输出的导数 // 对数似然 * supervision_.weight * deriv_weight //加到nnet_output_deriv上 CuMatrixBase<BaseFloat> *nnet_output_deriv) { //分子词图 const fst::StdVectorFst &fst = supervision_.fst; //分子词图的状态数 int32 num_states = fst.NumStates();
log_beta_.Resize(num_states, kUndefined); //神经网络对数似然导数向量 nnet_logprob_derivs_.Resize(nnet_logprobs_.Dim()); // we'll be counting backwards and moving the 'fst_output_indexes_iter' // pointer back. //'fst_output_indexes'包含监督FST中每个弧的条目,如果按顺序访问每个状态的每个弧,则获得它们时也是顺序的。 fst_output_indexes_的内容是nnet_output_indexes_和nnet_logprobs_的索引。 const int32 *fst_output_indexes_iter = &(fst_output_indexes_[0]) + fst_output_indexes_.size(); //在CPU上的nnet输出中查找获得的log-probs。此向量与nnet_output_indexes_具有相同的大小。在反向计算中,将被重新用于存储导数。 const BaseFloat *nnet_logprob_data = nnet_logprobs_.Data(); //tot_log_prob_是前向后向计算中得到的总伪对数似然 double tot_log_prob = tot_log_prob_;
double *log_beta_data = log_beta_.Data();
const double *log_alpha_data = log_alpha_.Data(); //nnet_logprob_derivs_是关于神经网络对数似然的导数。可以理解为占有概率 BaseFloat *nnet_logprob_deriv_data = nnet_logprob_derivs_.Data(); //遍历分子词图中的每个状态 for (int32 state = num_states - 1; state >= 0; state--) { //与该状态相连的弧数量 int32 this_num_arcs = fst.NumArcs(state); // on the backward pass we access the fst_output_indexes_ vector in a zigzag // pattern. //fst_output_indexes_iter是前向计算中统计的所有弧的数量 fst_output_indexes_iter -= this_num_arcs; const int32 *this_fst_output_indexes_iter = fst_output_indexes_iter;
double this_log_beta = -fst.Final(state).Value(); double this_log_alpha = log_alpha_data[state]; //遍历与状态相连的所有弧 for (fst::ArcIterator<fst::StdVectorFst> aiter(fst, state); !aiter.Done(); aiter.Next(), this_fst_output_indexes_iter++) { const fst::StdArc &arc = aiter.Value();
double next_log_beta = log_beta_data[arc.nextstate];
BaseFloat transition_logprob = -arc.weight.Value(); //t int32 index = *this_fst_output_indexes_iter;
BaseFloat pseudo_loglike = nnet_logprob_data[index]; /*累加:
*/ this_log_beta = LogAdd(this_log_beta, pseudo_loglike + transition_logprob + next_log_beta); //分子的后验占用率
BaseFloat occupation_logprob = this_log_alpha + pseudo_loglike + transition_logprob + next_log_beta - tot_log_prob, occupation_prob = exp(occupation_logprob);
nnet_logprob_deriv_data[index] += occupation_prob; } // check for -inf. KALDI_PARANOID_ASSERT(this_log_beta - this_log_beta == 0); log_beta_data[state] = this_log_beta; } KALDI_ASSERT(fst_output_indexes_iter == &(fst_output_indexes_[0])); int32 start_state = 0; // the fact that the start state is numbered 0 is // implied by other properties of the FST // (epsilon-free-ness and topological sorting, and // connectedness).
double tot_log_prob_backward = log_beta_(start_state);
if (!ApproxEqual(tot_log_prob_backward, tot_log_prob_)) KALDI_WARN << "Disagreement in forward/backward log-probs: " << tot_log_prob_backward << " vs. " << tot_log_prob_; // copy this data to GPU. CuVector<BaseFloat> nnet_logprob_deriv_cuda; nnet_logprob_deriv_cuda.Swap(&nnet_logprob_derivs_); /*nnet_output_indexes是一个(行,列)索引的列表,我们需要在nnet_output_中查找前向后向计算。 (行,列)=(PDFS数,特征数) matrix-common.h:69 nnet_output_deriv(nnet_output_indexes_[i].first, nnet_output_indexes_[i].second) += supervision_.weight * nnet_logprob_deriv_cuda.Data()[i]; */ nnet_output_deriv->AddElements(supervision_.weight, nnet_output_indexes_, nnet_logprob_deriv_cuda.Data()); } |
kaldi chain模型的序列鉴别性训练代码分析的更多相关文章
- Kaldi中的Chain模型
Chain模型的训练流程 链式模型的训练过程是MMI的无网格的版本,从音素级解码图生成HMM,对其使用前向后向算法,获得分母状态后验,通过类似的方式计算分子状态后验,但限于对应于转录的序列. 对于神经 ...
- 从Word Embedding到Bert模型—自然语言处理中的预训练技术发展史(转载)
转载 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/49271699 首发于深度学习前沿笔记 写文章 从Word Embedding到Bert模型—自然语言处理中的预训练技术发展史 张 ...
- [转]语音识别中区分性训练(Discriminative Training)和最大似然估计(ML)的区别
转:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_66f725ba0101bw8i.html 关于语音识别的声学模型训练方法已经是比较成熟的方法,一般企业或者研究机构会采用HTK工具包 ...
- zz从Word Embedding到Bert模型—自然语言处理中的预训练技术发展史
从Word Embedding到Bert模型—自然语言处理中的预训练技术发展史 Bert最近很火,应该是最近最火爆的AI进展,网上的评价很高,那么Bert值得这么高的评价吗?我个人判断是值得.那为什么 ...
- HanLP《自然语言处理入门》笔记--5.感知机模型与序列标注
笔记转载于GitHub项目:https://github.com/NLP-LOVE/Introduction-NLP 5. 感知机分类与序列标注 第4章我们利用隐马尔可夫模型实现了第一个基于序列标注的 ...
- TensorFlow从1到2(七)线性回归模型预测汽车油耗以及训练过程优化
线性回归模型 "回归"这个词,既是Regression算法的名称,也代表了不同的计算结果.当然结果也是由算法决定的. 不同于前面讲过的多个分类算法或者逻辑回归,线性回归模型的结果是 ...
- 如何在Django模型中管理并发性 orm select_for_update
如何在Django模型中管理并发性 为单用户服务的桌面系统的日子已经过去了 - 网络应用程序现在正在为数百万用户提供服务,许多用户出现了广泛的新问题 - 并发问题. 在本文中,我将介绍在Django模 ...
- TensorFlow 训练好模型参数的保存和恢复代码
TensorFlow 训练好模型参数的保存和恢复代码,之前就在想模型不应该每次要个结果都要重新训练一遍吧,应该训练一次就可以一直使用吧. TensorFlow 提供了 Saver 类,可以进行保存和恢 ...
- pytorch入门2.2构建回归模型初体验(开始训练)
pytorch入门2.x构建回归模型系列: pytorch入门2.0构建回归模型初体验(数据生成) pytorch入门2.1构建回归模型初体验(模型构建) pytorch入门2.2构建回归模型初体验( ...
随机推荐
- python☞自动发送邮件
一.SMTP 协议 SMTP(Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)是简单邮件传输协议,它是一组用于由源地址到目的地址传送邮件的规则,由它来控制信件的中转方式 二.smtplib ...
- Redis和MongoDB的区别(面试受用)
项目中用的是MongoDB,但是为什么用其实当时选型的时候也没有太多考虑,只是认为数据量比较大,所以采用MongoDB. 最近又想起为什么用MongoDB,就查阅一下,汇总汇总: 之前也用过redis ...
- A Diversity-Promoting Objective Function for Neural Conversation Models论文阅读
本文来自李纪为博士的论文 A Diversity-Promoting Objective Function for Neural Conversation Models 1,概述 对于seq2seq模 ...
- IDEA导入项目jar包红线、依赖问题....
一般遇到这种情况用以下两种方式解决....... 1.reimport包 2.清缓存重启 针对1方法: a.确实不缺包: 可以先注释掉pom文件中的jar包, 此时idea会提示import, 那就i ...
- IP包头结构详解
版本号(Version):长度4比特.标识目前采用的IP协议的版本号.一般的值为0100(IPv4),0110(IPv6) IP包头长度(Header Length):长度4比特.这个字段的作用是为了 ...
- React 精要面试题讲解(五) 高阶组件真解
说明与目录 在学习本章内容之前,最好是具备react中'插槽(children)'及'组合与继承' 这两点的知识积累. 详情请参照React 精要面试题讲解(四) 组合与继承不得不说的秘密. 哦不好意 ...
- VS2019 实用操作
本文列出了在编写程序过程中的几个非常实用的操作方式,通过这些操作方式,可以在一定程度上减少重复操作.提高编码效率.改善编程体验. 列模式操作 列操作是一项很常用且实用的功能,可以一次性修改不同的行. ...
- 团队开发项目--NABCD模型
N(need)需求: 鉴于在学校中的大部分爱学习的学生平时都去拍空教室的占有情况,我们发现有的时候太多,导致同学们们拍照会浪费很长的时间,而且空教室的显示不是一下子全出来,有的时候还会出现无法显示的情 ...
- MVC中使用Hangfire按秒执行任务
更新Hangfire版本到1.7.0,才支持使用按秒循环任务执行 RecurringJob.AddOrUpdate("test",()=>writeLog("每20 ...
- springcloud 设置feign超时时间
转载网址:http://www.pianshen.com/article/187038775/