[C++ Primer Plus] 第7章、函数(一)程序清单——递归,指针和const,指针数组和数组指针,函数和二维数组
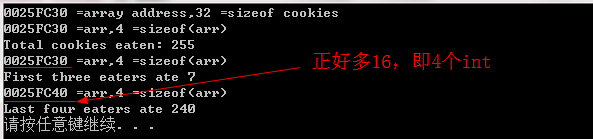
程序清单7.6
#include<iostream>
using namespace std; const int Size = ;
int sum_arr(int arr[], int n);//函数声明
void main()
{
int cookies[Size] = { ,,,,,,, };
cout << cookies << " =array address," << sizeof cookies << " =sizeof cookies" << endl;
int sum = sum_arr(cookies, Size);
cout << "Total cookies eaten: " << sum << endl;
sum = sum_arr(cookies, );
cout << "First three eaters ate " << sum << endl;
sum = sum_arr(cookies+,);
cout << "Last four eaters ate " << sum << endl; system("pause");
} int sum_arr(int arr[], int n)//输出地址,大小,计算和
{
int total = ;
cout << arr << " =arr," << sizeof(arr) << " =sizeof(arr)" << endl;
for (int i = ; i <n; i++)
total += arr[i];
return total;
}
指针和const
const的位置不同,指针可以进行的操作也不同


month数组被const修饰了,所以如果要使用sum函数的话,需要修改第四行代码
int sum(const int arr[],int n)
函数和二维数组
先修知识:指针数组和数组指针

#include <iostream>
using namespace std; int main()
{
int c[] = { ,,, };
int *a[]; //指针数组
int(*b)[]; //数组指针
b = &c;
for (int i = ; i<; i++)//将数组c中元素赋给数组a
{
a[i] = &c[i];
}
cout << *a[] << endl; //输出2就对
cout << (*b)[] << endl; //输出3就对
return ;
}
OK,进入正题,函数与二维数组

#include<iostream>
using namespace std; //数组表示法
int sum(int arr[][], int n)
{
int total = ;
for (int r = ; r < n; r++)
{
for (int c = ; c < ; c++)
{
cout << arr[r][c] << "\t";
total += arr[r][c];
}
cout << endl;
}
return total;
} //指针表示法
int sum2(int (*arr)[],int n)//数组指针:指向数组的指针
{
int total = ;
for (int r = ; r < n; r++)
{
for (int c = ; c < ; c++)
{
cout << *(*(arr+r)+c)<< "\t";//arr是一个指向数组(4个int整数)的指针,*(arr+r)=arr[r]表示指向第(r+1)个数组
total += *(*(arr + r) + c);
}
cout << endl;
}
return total;
} void main()
{
int data[][] = { {,,,},{,,,},{,,,} };
int s = sum(data, );
cout << s << endl;
getchar();
}

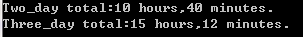
程序清单7.11
#include<iostream>
using namespace std; const int Rate = ;
struct time {
int hour;
int mins;
}; time sum(time a, time b) {
time total;
total.hour = a.hour + b.hour + (a.mins + b.mins) / Rate;
total.mins = (a.mins + b.mins) % ;
return total;
}
void show(time t) {
cout << t.hour << " hours," << t.mins << " minutes." << endl;
} void main()
{
time d1 = { , };
time d2 = { , };
time trip = sum(d1, d2);
cout << "Two_day total:";
show(trip); time d3 = { , };
cout << "Three_day total:";
show(sum(trip, d3)); getchar();
}
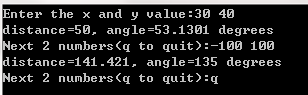
程序清单7.12+7.13
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std; struct polar{
double distance;
double angle;
};
struct rect {
double x;
double y;
}; void rect_to_polar(const rect *pxy, polar *pda) {//由于形参是指针而不是结构,所以只能用箭头操作符而不能用点操作符
pda->distance = sqrt( pxy->x*pxy->x + pxy->y*pxy->y );
pda->angle = atan2(pxy->y, pxy->x);
}
void show(const polar *pda) {
const double Rate = 57.29577951;
cout << "distance=" << pda->distance;
cout << ",angle=" << pda->angle*Rate<<" degrees"<<endl;
} void main()
{
rect r;
polar p;
cout << "Enter the x and y value:";
while (cin>>r.x>>r.y)
{
rect_to_polar(&r, &p);
show(&p);
cout << "Next 2 numbers(q to quit):";
}
cout << "Done." << endl;
getchar();
}
程序清单7.14(string对象数组)
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std; const int Size = ;
void display(const string s[],int n) {
for (int i = ; i < n; i++)
cout << i+ <<": "<<s[i]<<endl;
} void main()
{
string list[Size];
cout << "Enter your " << Size << " favorite XX" << endl;
for (int i = ; i < Size; i++)
{
cout << i + << ": ";
getline(cin, list[i]);//读取string对象
}
cout << "Your list:" << endl;
display(list, Size);
system("pause");
}

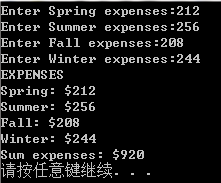
程序清单7.15(array对象)
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<array>
using namespace std; const array<string, > Sname = { "Spring","Summer","Fall","Winter" }; void fill(array<double, > *p) {
for (int i = ; i < ; i++)
{
cout << "Enter " << Sname[i] << " expenses:";
cin >> (*p)[i];//p是地址,*p是array对象,(*p)[i]是array对象里的第(i+1)个double数据
}
}
void show(array<double, > q) {
double sum = 0.0;
cout << "EXPENSES" << endl;
for (int i = ; i < ; i++)
{
cout << Sname[i] << ": $" << q[i] << endl;
sum += q[i];
}
cout << "Sum expenses: $" << sum << endl;
} void main()
{
array<double, > expense;
fill(&expense);
show(expense);
system("pause");
}
程序清单7.16,7.17(递归)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std; void down(int n) {
cout << "Counting down " << n <<",\tn at "<<&n<< endl;
if (n > )
down(n - );
cout << n << ": Kaboom!" << "\t\tn at " << &n << endl;
} void main()
{
down();
system("pause");
}

#include<iostream>
using namespace std; const int Len = ;
const int Div = ;
void subdivide(char ar[],int low,int high,int level) {
if (level == )
return;
int mid = (high + low) / ;
ar[mid] = '|';
subdivide(ar, low, mid, level - );
subdivide(ar, mid, high,level - );
} void main()
{
char ruler[Len];
int i;
for (i = ; i < Len - ; i++)//去掉一个头,两个尾
ruler[i] = ' ';
ruler[Len - ] = '\0';//末尾设置为结束符
int max = Len - ;//倒数第二位(去掉结束符后的末尾)
int min = ;
ruler[min] = ruler[max] = '|';
cout << ruler << endl;
for (i = ; i <=Div; i++)
{
subdivide(ruler, min, max, i);
cout << ruler << endl;
}
system("pause");
}

函数指针
double (*pf)(int);//pf是一个指向函数(函数返回double)的指针
double *pd(int);//pd()是一个返回double *的函数
函数声明
void aa(int n, double(*pf)(int));
指出,pf是一个函数指针,它指向的函数接受一个int参数,并返回一个double值。
aa(50,函数名) 即可进行调用。
程序清单7.18
#include<iostream>
using namespace std; void estimate(int line,double (*pf)(int)) {
cout << line << " lines will take ";
cout << (*pf)(line) << " hour(s)." << endl;
}
double bet(int lns) {
return 0.05*lns;
}
double pam(int lns) {
return 0.03*lns + 0.0004*lns*lns;;
} void main()
{
int code;
cout << "How many lines? ";
cin >> code;
cout << "Here is Bet's estimate:" << endl;
estimate(code, bet);
cout << "Here is Pam's estimate:" << endl;
estimate(code, pam);
system("pause");
}
函数指针数组
const double * f1(const double ar[], int n);
const double * f2(const double [], int);
const double * f3(const double *, int);//这三行代码的含义完全相同
const double *(*pa[])(const double *, int) = { f1,f2,f3 };//声明,并初始化 *pd[] //an array of 3 pointers
(*pd)[] //a pointer to an array of 3 elements
程序清单7.19
#include<iostream>
using namespace std; const double * f1(const double *ar, int n) { //f1()是一个返回double类型指针的函数
return ar;//返回的是地址,要得到值得话,必须加上*符号
}
const double * f2(const double ar[], int n) {
return ar + ;
}
const double * f3(const double ar[], int n) {
return ar + ;
} void main()
{
double av[] = { 1112.3,1542.6,2227.9 };
const double *(*p1)(const double *, int) = f1;//p1是函数指针,指向f1函数的地址,*p1(即f1函数)传入double地址和int长度,返回double地址
auto p2 = f2;
cout << "Using pointers to functions:" << endl << "Address Value" << endl;
cout << (*p1)(av, ) << ": " << *(*p1)(av, ) << endl;//*p1表示函数,前者调用函数,返回double值得地址,后者为取出地址所代表的的double值
cout << p2(av, ) << ": " << *p2(av, ) << endl;//p2表示函数 const double *(*pa[])(const double *, int) = { f1,f2,f3 };//声明一个函数指针数组
auto pb = pa;//pa表示函数指针数组的地址
cout << "Using an array of pointers to functions:" << endl << "Address Value" << endl;
for (int i = ; i < ; i++)
cout << pa[i](av, ) << ": " << *pa[i](av, ) << endl;
cout << "Using a pointer to a pointer to a functions:" << endl << "Address Value" << endl;
for (int i = ; i < ; i++)
cout << pb[i](av, ) << ": " << *pb[i](av, ) << endl; cout << "Using pointers to an array of pointers :" << endl << "Address Value" << endl;
auto pc = &pa;
cout << (*pc)[](av, ) << ": " << *(*pc)[](av, ) << endl;
const double *(*(*pd)[])(const double *, int) = &pa;//参见23行,pd表示pa的地址,所以在23行定义的基础上再多一个*号
const double * pdb = (*pd)[](av, );//(*pd)=pa,pdb表示av[1]的地址
cout << pdb << ": " << *pdb << endl;
cout << (*(*pd)[])(av, ) << ": " << *(*(*pd)[])(av, ) << endl;//(*pd)=pa,(*(*pd)[2])=(*pa[2])表示函数指针数组的第三个指针元素 system("pause");
}


[C++ Primer Plus] 第7章、函数(一)程序清单——递归,指针和const,指针数组和数组指针,函数和二维数组的更多相关文章
- C语言学习笔记 (005) - 二维数组作为函数参数传递剖析
前言 很多文章不外乎告诉你下面这几种标准的形式,你如果按照它们来用,准没错: //对于一个2行13列int元素的二维数组 //函数f的形参形式 f(int daytab[2][13]) {...} / ...
- C语言指针系列 - 一级指针.一维数组,二级指针,二维数组,指针数组,数组指针,函数指针,指针函数
1. 数组名 C语言中的数组名是一个特殊的存在, 从本质上来讲, 数组名是一个地址, 我们可以打印一个指针的值,和打印一个数组的值来观察出这个本质: int nArray[10] ={ 0 }; in ...
- C语言二维数组作为函数参数
设有整型二维数组a[3][4]如下:0 1 2 34 5 6 78 9 10 11 它的定义为: int a[3][4]={{0,1,2,3},{4,5,6,7} ...
- PHP如何判断一个数组是一维数组或者是二维数组?用什么函数?
如题:如何判断一个数组是一维数组或者是二维数组?用什么函数? 判断数量即可 <?php if (count($array) == count($array, 1)) { echo '是一维数组' ...
- ytu 1050:写一个函数,使给定的一个二维数组(3×3)转置,即行列互换(水题)
1050: 写一个函数,使给定的一个二维数组(3×3)转置,即行列互换 Time Limit: 1 Sec Memory Limit: 128 MBSubmit: 154 Solved: 112[ ...
- C语言中如何将二维数组作为函数的参数传递
今天写程序的时候要用到二维数组作参数传给一个函数,我发现将二维数组作参数进行传递还不是想象得那么简单里,但是最后我也解决了遇到的问题,所以这篇文章主要介绍如何处理二维数组当作参数传递的情况,希望大家不 ...
- PHP二维数组提取函数----把不需要的数据剔除
首先说明一些这个函数的应用场景,比如说你得到的数据是个二维数组,里面的很多成员其实是不必要的,比如说api调用后不必要给别人返回一些用不到的垃圾数据吧,如下是代码. <?php /* * del ...
- 二维数组去除重复值和array_unique函数
今天遇到了一个问题,就是从数据库中去除的数组为一个二维数组,现在就是想将二位数组进行去重,但是在php中,对于一个一维数组,我们可以直接使用php的系统函数array_unique,但是这个函数不能对 ...
- ***php解析JSON二维数组字符串(json_decode函数第二个参数True和False的区别)
客户端的请求体中的数据:[{"msg_id": 1, "msg_status": "HAS_READ" }, { "msg_id& ...
随机推荐
- 扫描系统进程和获取某进程的PID
扫描系统的所有进程 #include <stdio.h> #include <windows.h> #include <tlhelp32.h> int scan() ...
- 7款让人惊叹的HTML5粒子动画特效(转载)
1.HTML5 Canvas粒子模拟效果 这是一款利用HTML5 Canvas模拟出来的30000个粒子动画,当你用鼠标在canvas画布上移动时,鼠标周围的一些粒子就会跟着你移动,并形成一定的图案, ...
- metasploit 常用命令备忘
metasploit 常用命令备忘 MSFconsole Commands-------------------------------------24show exploits 查看所有exp ...
- IDEA多个服务打断点 各服务乱窜的问题
Setting --> Build, Execution, Deployment --> Debugger 选中即可
- Android 学习书籍下载
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1Y6LHLJlYDfbNjoMAVjfjMw 密码:ywbk 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/ ...
- 再次重温《Right here waiting》
记得高中时候听到这首曲子(当时还让同桌帮我抄了这首曲子,后来这个本子也不知道扔到哪里去了), 前天偶尔在虾米遇到这首曲子,过去的青涩岁月历历在目,自己手动打打歌词,一方面是为了重温这首曲子,另一方面, ...
- ASP.NET Core ResponseCaching:基于 VaryByHeader 定制缓存 Key
ASP.NET Core ResponseCaching 提供了缓存http响应内容的能力,通过它可以在本地内存中直接缓存http响应内容,这是速度最快的服务端缓存,省却了网络传输与生成响应内容的开销 ...
- RMQPOJ3264
Balanced Lineup POJ-3264 DP分析 设A[i]是要求区间最值的数列,F[i, j]表示从第i个数起连续2^j个数中的最大值.(DP的状态) 初状态是F[i,0]=A[i] 状态 ...
- php 延迟静态绑定: static关键字
abstract class DomainObject { public static function create() { return new self(); } } class User ex ...
- Spark Streaming实战演练
一.spark streaming简介 Streaming是一种数据传输技术,它把客户机收到的数据变成一个稳定连续的流,源源不断的输出,使用户听到的声音和图像十分稳定,而用户在整个文件传输完成开始前就 ...
