I2C驱动详解
I2C讲解:
在JZ2440开发板上,I2C是由两条数据线构成的SCL,SDA;SCL作为时钟总线,SDA作为数据总线;两条线上可挂载I2C设备,如:AT24C08
两条线连接ARM9 I2C控制器,通过控制来控制I2C设备的识别设备地址、读、写操作;如图所示
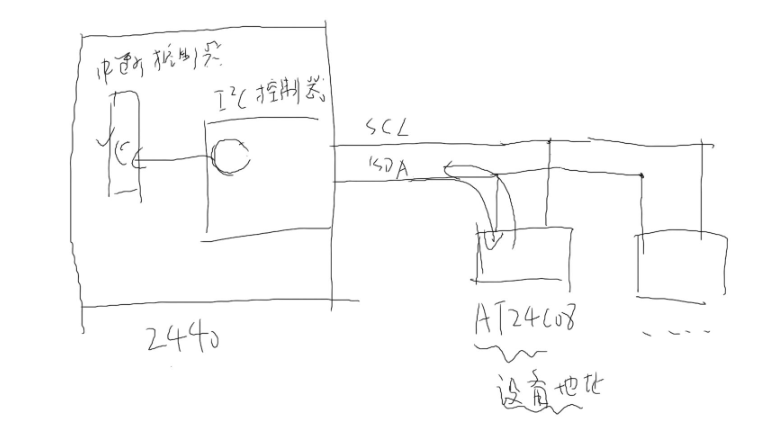
从中所知:I2C线上可以挂载很多个I2C设备;挂载简单,只需要一根数据线和一根时钟线就可以挂载上去,通过地址来去别每个设备的区别;
I2C操作:
对I2C操作主要思想为:1、找到设备 2、进行读写操作 主要原理为:
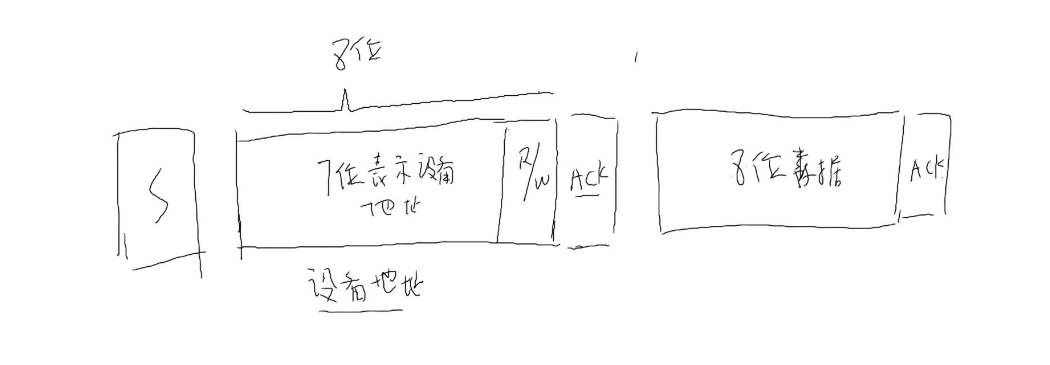
1、发送开始信号S 然后紧接着发生设备8位地址如:0x50,然后等待设备发出一个应答ACK信号
2、当控制器接收到ACK信号后,表面找到这条I2C总线上确实有这个设备,然后发出数据,是进行读还是进行写,由第8位来决定
原理如下图:
JZ2440对I2c驱动框架
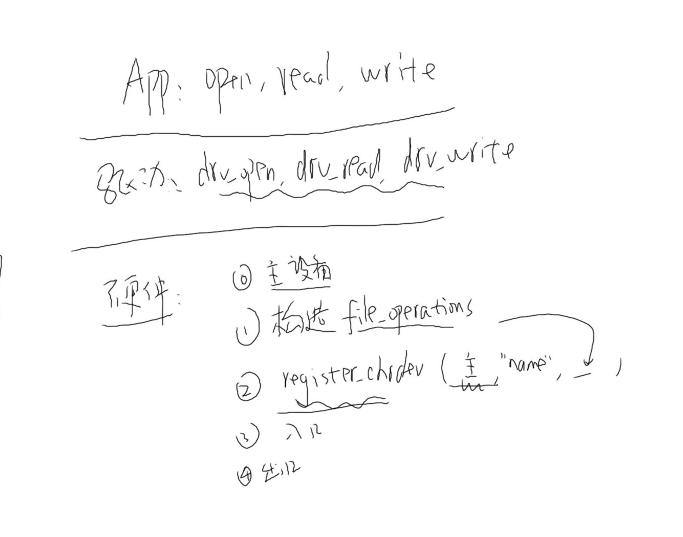
正常的设备驱动程序,大体框架为:
1、通过应用程序open、read、write、ioctl函数去对硬件操作
2、在内核里,接收到应用程序发送过来的open、read、write、ioctl命令,出发中断,进而会跳到一个字符描述符的数组(open时返回值)当中,查找驱动程序ID(驱动程序进行注册);通过该ID找到相对应的drv_open、drv_read、drv_wrte等操作;
3、drv_open、drv_read、drv_wrte等操作跟字符设备的硬件驱动程序紧密相关,会最终会跳到字符设备驱动程序file_operation结构体进行硬件的操作过程。
4、在此之前,需要编写I2C驱动程序,驱动程序要有主入口、出口、file_openration结构体、进行注册等操作;
具体字符设备驱动程序框架为:
而I2C设备驱动采用的是总线—设备-驱动模型
总线-设备-驱动模型:
总线-设备-驱动模型:其原理为在一条总线上分为两部分,一部分作为设备链表对象的,另一部分作为driver链表;设备链表对象就是
注册一个设备client对象挂载到这条链表上,但注册的设备名需要与右边driver链表注册的驱动名相比配才有意义,才能对进入driver链表
上与设备名相匹配的驱动程序里面的probe函数进行i2c驱动操作;举个例子:将驱动程序比作学生,驱动程序的名字比作学生的宿舍号码
管理员相当于总线,总线知道两个信息:1、学生 2、宿舍号 ;当有一个学生进行入住,学生想住A10-208,好,经过管理员同意好,就
住进A10-208(注册一个i2c_driver)了,当管理员想找到那个学生,则需要通过A10-208这个名字去查找到学生所在住处,通过管理员
管理的学生信息本(注册一个设备)找到名字,进而去到宿舍找到这个学生,让他扫地、打扫卫生什么的;主要原理图如下:
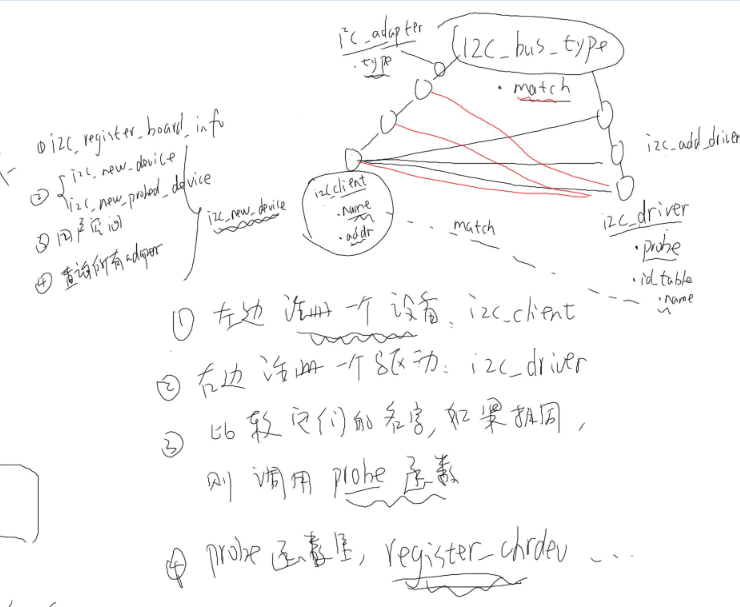
i2c-总线-驱动模型

应用程序是如何调用的呢?如图所示
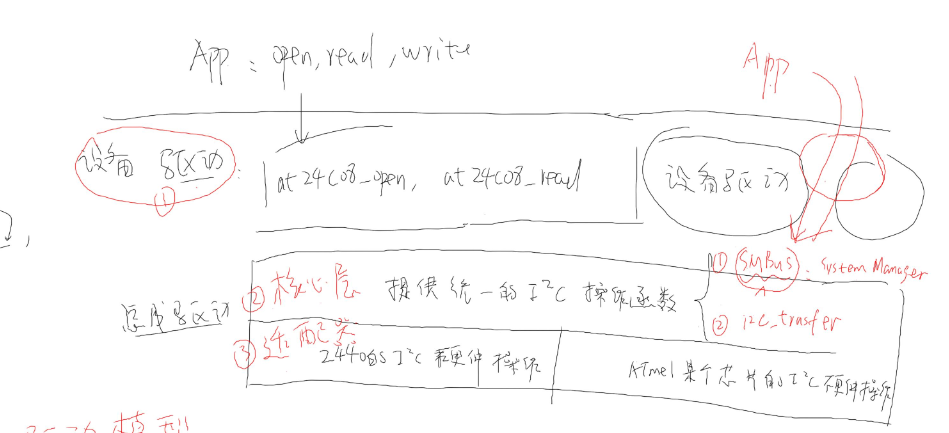
i2c进行open、read、write、ioctl等操作会进入内核太,找到相关设备驱动函数,然后就进入了总线控制层,I2c总线层两部分组成,核心层
里面已经定义了对i2c提供的操作函数,不需要用户自己定义,适配器就是具体的对2440的i2c硬件操作或者定义其它的芯片的硬件操作;
总结:总得来说,我们需要进行的操作为
1、注册一个设备,里面要有设备名,以及该设备id,并挂载到这条设备链表上
2、注册一个驱动,该设备驱动需要有设备名,probe函数、id_table设备地址,然后挂载到驱动链表上
3、比较两条链表上的设备名字是否相同,如果有相同的话,就去到相关的驱动设备上的probe函数,进行
操作
4、probe函数里面就是我们正常的驱动程序的编程程序了,主入口、出口、file_operation结构体的构造等等操作;最终应用程序会进入这里操作硬件对象
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
如图代码所示:新建一个设备有多种方法,该方法为第二种i2c_new_probed_device
at24cxx_dev:注册一个新设备
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/i2c.h>
#include <linux/err.h>
#include <linux/regmap.h>
#include <linux/slab.h> static struct i2c_client *at24cxx_client; static const unsigned short addr_list[] = { 0x60, 0x50, I2C_CLIENT_END }; static int at24cxx_dev_init(void)
{
struct i2c_adapter *i2c_adap;
struct i2c_board_info at24cxx_info; memset(&at24cxx_info, , sizeof(struct i2c_board_info));
strlcpy(at24cxx_info.type, "at24c08", I2C_NAME_SIZE); i2c_adap = i2c_get_adapter();
at24cxx_client = i2c_new_probed_device(i2c_adap, &at24cxx_info, addr_list, NULL);
i2c_put_adapter(i2c_adap); if (at24cxx_client)
return ;
else
return -ENODEV;
} static void at24cxx_dev_exit(void)
{
i2c_unregister_device(at24cxx_client);
} module_init(at24cxx_dev_init);
module_exit(at24cxx_dev_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
at24cxx_drv:注册一个新驱动 注:probe函数并没有进行i2c的·操作,只是打印一些信息而已
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/i2c.h>
#include <linux/err.h>
#include <linux/regmap.h>
#include <linux/slab.h> static int __devinit at24cxx_probe(struct i2c_client *client,
const struct i2c_device_id *id)
{
printk("%s %s %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return ;
} static int __devexit at24cxx_remove(struct i2c_client *client)
{
printk("%s %s %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return ;
} static const struct i2c_device_id at24cxx_id_table[] = {
{ "at24c08", },
{}
}; /* 1. 分配/设置i2c_driver */
static struct i2c_driver at24cxx_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "100ask",
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
},
.probe = at24cxx_probe,
.remove = __devexit_p(at24cxx_remove),
.id_table = at24cxx_id_table,
}; static int at24cxx_drv_init(void)
{
/* 2. 注册i2c_driver */
i2c_add_driver(&at24cxx_driver); return ;
} static void at24cxx_drv_exit(void)
{
i2c_del_driver(&at24cxx_driver);
} module_init(at24cxx_drv_init);
module_exit(at24cxx_drv_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
Makefile:
KERN_DIR = /work/system/linux-3.4. all:
make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules clean:
make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules clean
rm -rf modules.order obj-m += at24cxx_dev.o
obj-m += at24cxx_drv.o
#obj-m += i2c_bus_s3c2440.o
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
对I2c驱动的操作
前面已经讲过对于I2c的操作可以调用总线上现成的函数来操作i2c_smbus_write_byte_data
at24cxx_dev:
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/i2c.h>
#include <linux/err.h>
#include <linux/regmap.h>
#include <linux/slab.h> static struct i2c_board_info at24cxx_info = {
I2C_BOARD_INFO("at24c08", 0x50),
}; static struct i2c_client *at24cxx_client; static int at24cxx_dev_init(void)
{
struct i2c_adapter *i2c_adap; i2c_adap = i2c_get_adapter();
at24cxx_client = i2c_new_device(i2c_adap, &at24cxx_info);
i2c_put_adapter(i2c_adap); return ;
} static void at24cxx_dev_exit(void)
{
i2c_unregister_device(at24cxx_client);
} module_init(at24cxx_dev_init);
module_exit(at24cxx_dev_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
at24cxx_drv:注册驱动程序,进行I2c操作
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/i2c.h>
#include <linux/err.h>
#include <linux/regmap.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h> static int major;
static struct class *class;
static struct i2c_client *at24cxx_client; /* 传入: buf[0] : addr
* 输出: buf[0] : data
*/
static ssize_t at24cxx_read(struct file * file, char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *off)
{
unsigned char addr, data; copy_from_user(&addr, buf, );
data = i2c_smbus_read_byte_data(at24cxx_client, addr);
copy_to_user(buf, &data, );
return ;
} /* buf[0] : addr
* buf[1] : data
*/
static ssize_t at24cxx_write(struct file *file, const char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *off)
{
unsigned char ker_buf[];
unsigned char addr, data; copy_from_user(ker_buf, buf, );
addr = ker_buf[];
data = ker_buf[]; printk("addr = 0x%02x, data = 0x%02x\n", addr, data); if (!i2c_smbus_write_byte_data(at24cxx_client, addr, data))
return ;
else
return -EIO;
} static struct file_operations at24cxx_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = at24cxx_read,
.write = at24cxx_write,
}; static int __devinit at24cxx_probe(struct i2c_client *client,
const struct i2c_device_id *id)
{
at24cxx_client = client; //printk("%s %s %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
major = register_chrdev(, "at24cxx", &at24cxx_fops);
class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "at24cxx");
device_create(class, NULL, MKDEV(major, ), NULL, "at24cxx"); /* /dev/at24cxx */ return ;
} static int __devexit at24cxx_remove(struct i2c_client *client)
{
//printk("%s %s %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
device_destroy(class, MKDEV(major, ));
class_destroy(class);
unregister_chrdev(major, "at24cxx"); return ;
} static const struct i2c_device_id at24cxx_id_table[] = {
{ "at24c08", },
{}
}; /* 1. 分配/设置i2c_driver */
static struct i2c_driver at24cxx_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "100ask",
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
},
.probe = at24cxx_probe,
.remove = __devexit_p(at24cxx_remove),
.id_table = at24cxx_id_table,
}; static int at24cxx_drv_init(void)
{
/* 2. 注册i2c_driver */
i2c_add_driver(&at24cxx_driver); return ;
} static void at24cxx_drv_exit(void)
{
i2c_del_driver(&at24cxx_driver);
} module_init(at24cxx_drv_init);
module_exit(at24cxx_drv_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
应用测试程序i2c_test:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h> /* i2c_test r addr
* i2c_test w addr val
*/ void print_usage(char *file)
{
printf("%s r addr\n", file);
printf("%s w addr val\n", file);
} int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd;
unsigned char buf[]; if ((argc != ) && (argc != ))
{
print_usage(argv[]);
return -;
} fd = open("/dev/at24cxx", O_RDWR);
if (fd < )
{
printf("can't open /dev/at24cxx\n");
return -;
} if (strcmp(argv[], "r") == )
{
buf[] = strtoul(argv[], NULL, );
read(fd, buf, );
printf("data: %c, %d, 0x%2x\n", buf[], buf[], buf[]);
}
else if ((strcmp(argv[], "w") == ) && (argc == ))
{
buf[] = strtoul(argv[], NULL, );
buf[] = strtoul(argv[], NULL, );
if (write(fd, buf, ) != )
printf("write err, addr = 0x%02x, data = 0x%02x\n", buf[], buf[]);
}
else
{
print_usage(argv[]);
return -;
} return ;
}
Makefile:
KERN_DIR = /work/system/linux-3.4. all:
make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules clean:
make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules clean
rm -rf modules.order obj-m += at24cxx_dev.o
obj-m += at24cxx_drv.o
#obj-m += i2c_bus_s3c2440.o
I2C驱动详解的更多相关文章
- linux usb 驱动详解
linux usb 驱动详解 USB 设备驱动代码通过urb和所有的 USB 设备通讯.urb用 struct urb 结构描述(include/linux/usb.h ). urb 以一种异步的方式 ...
- 25.Linux-Nor Flash驱动(详解)
1.nor硬件介绍: 从原理图中我们能看到NOR FLASH有地址线,有数据线,它和我们的SDRAM接口相似,能直接读取数据,但是不能像SDRAM直接写入数据,需要有命令才行 1.1其中我们2440的 ...
- 16.Linux-LCD驱动(详解)
在上一节LCD层次分析中,得出写个LCD驱动入口函数,需要以下4步: 1) 分配一个fb_info结构体: framebuffer_alloc(); 2) 设置fb_info 3) 设置硬件相关的操作 ...
- 使用VS2010编译MongoDB C++驱动详解
最近为了解决IM消息记录的高速度写入.多文档类型支持的需求,决定使用MongoDB来解决. 考虑到MongoDB对VS版本要求较高,与我现有的VS版本不兼容,在leveldb.ssdb.redis.h ...
- 16.Linux-LCD驱动(详解)【转】
转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/lifexy/p/7604011.html 在上一节LCD层次分析中,得出写个LCD驱动入口函数,需要以下4步: 1) 分配一个fb_info结构 ...
- i2c总线,核心,驱动详解
Linux I2C驱动分析(一)----I2C架构和总线驱动 一.I2C总线原理 I2C是一种常用的串行总线,由串行数据线SDA 和串线时钟线SCL组成.I2C是一种多主机控制总线,它和USB总线不同 ...
- 18.Llinux-触摸屏驱动(详解)
本节的触摸屏驱动也是使用之前的输入子系统 1.先来回忆之前第12节分析的输入子系统 其中输入子系统层次如下图所示, 其中事件处理层的函数都是通过input_register_handler()函数注册 ...
- 18.Llinux-触摸屏驱动(详解)【转】
转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/lifexy/p/7628889.html 本节的触摸屏驱动也是使用之前的输入子系统 1.先来回忆之前第12节分析的输入子系统 其中输入子系统层次 ...
- si4745 FM-AM-SW 音量控制芯片 驱动详解
在论坛上看到有人发这个dsp 芯片,仔细看了下,发现功能正合我意,网上能找到的资料(源码)不多 软件环境:linux4.1.36 arm-linux-gcc 4.3.2 实现功能:自动搜台,上一台, ...
随机推荐
- django10 使用自定义标签配置说明
1).在app目录下建目录templatetags[不可改名]目录,然后在该目录下建一个空的__init__.py 2).mytags.py 在templatetags下建一个mytags.py,添加 ...
- apache的proxy代理总访问后端web的第一个虚拟主机
先查看cat /usr/local/apache2/modules 时候有mod_proxy.so mod_proxy_http.so mod_proxy_connect 如果没有,使用apache ...
- 级联关系(内容大部分来自JavaEE轻量型解决方案其余的是我的想法)
1. 级联关系 在Hibernate程序中持久化的对象之间会通过关联关系互相引用.对象进行保存.更新和删除等操作时,有时需要被关联的对象也执行相应的操作,如:假设需要关联关系的主动方对象执行操作时,被 ...
- ES6里关于类的拓展(一)
大多数面向对象的编程语言都支持类和类继承的特性,而JS却不支持这些特性,只能通过其他方法定义并关联多个相似的对象,这种状态一直延续到了ES5.由于类似的库层出不穷,最终还是在ECMAScript 6中 ...
- 使用Zxing 一维码
最近看到满大街的二维码扫码有惊喜,对二维码也有过一些了解,想看看到底是什么原理,在网上找了一些资料,自己弄了一个实例,采用的是MVC,贴出来分享一下 一维码生成 Controller public A ...
- 简单的图片处理servlet
好久没写博客了.近期做了一个比較有趣的商城项目,里面的业务还真的非常复杂,好在做了特殊的处理之后商城也能正常的使用了. 可是没中不足的就是图片目录和项目掺杂在一块,实在有些难以维护.之后找了点资料就搞 ...
- A read-only user or a user in a read-only database is not permitted to disable
A read-only user or a user in a read-only database is not permitted to disable 出现如题的问题通常是由于db.lck的所属 ...
- Windows为什么双击打开‘我的电脑’, 没有了‘前进’‘ 后退’‘向上’等按钮?
如图所示 点击查看 工具栏 标准按钮即可 左侧的数值虚线可以拖动到任意,还可以添加按钮如搜索,删除,复制,剪切等
- spring 国际化-i18n
i18n(其 来源是英文单词 internationalization的首末字符i和n,18为中间的字符数)是“国际化”的简称.在资讯领域,国际化(i18n)指让产品(出版 物,软件,硬件等)无需做大 ...
- jQuery的$.fn使用
jquery中文网为您提供jQuery的$.fn使用等资源,欢迎您收藏本站,我们将为您提供最新的jQuery的$.fn使用资源 $.fn是指jquery的命名空间,加上fn上的方法及属性,会对jque ...
