Redis源码阅读-Dict哈希字典
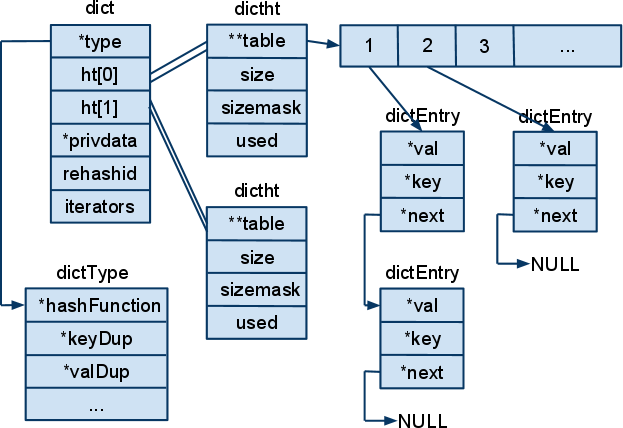
Dict和Java中的HashMap很相似,都是数组开链法解决冲突。
但是Redis为了高性能, 有很多比较微妙的方法,例如 数组的大小总是2的倍数,初始大小是4。
rehash并不是一次就执行完,而是分多次执行。每次执行一部分。其中rehashidx表示现在hash到哪一个桶啦,-1表示现在并没有rehash.
dict包含两个dicttable, 编号为0,1, dictht0是直接存储哈希表的地方, dictht1在rehash中用到,当rehashidx不为-1时, 查找key,同时在dictht1和dictht0中查找。
 、
、
数据结构
typedef struct dictEntry {
void *key;
union {
void *val;
uint64_t u64;
int64_t s64;
double d;
} v;
struct dictEntry *next;
} dictEntry;
typedef struct dictType {
unsigned int (*hashFunction)(const void *key);
void *(*keyDup)(void *privdata, const void *key);
void *(*valDup)(void *privdata, const void *obj);
int (*keyCompare)(void *privdata, const void *key1, const void *key2);
void (*keyDestructor)(void *privdata, void *key);
void (*valDestructor)(void *privdata, void *obj);
} dictType;
/* This is our hash table structure. Every dictionary has two of this as we
* implement incremental rehashing, for the old to the new table. */
typedef struct dictht {
dictEntry **table;
unsigned long size;
unsigned long sizemask;
unsigned long used;
} dictht;
typedef struct dict {
dictType *type;
void *privdata;
dictht ht[];
long rehashidx; /* rehashing not in progress if rehashidx == -1 */
int iterators; /* number of iterators currently running */
} dict;
/* If safe is set to 1 this is a safe iterator, that means, you can call
* dictAdd, dictFind, and other functions against the dictionary even while
* iterating. Otherwise it is a non safe iterator, and only dictNext()
* should be called while iterating. */
typedef struct dictIterator {
dict *d;
long index;
int table, safe;
dictEntry *entry, *nextEntry;
/* unsafe iterator fingerprint for misuse detection. */
long long fingerprint;
} dictIterator;
typedef void (dictScanFunction)(void *privdata, const dictEntry *de);
查找key
dictEntry *dictFind(dict *d, const void *key)
{
dictEntry *he;
unsigned int h, idx, table; if (d->ht[].size == ) return NULL; /* We don't have a table at all */
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d);
h = dictHashKey(d, key);
for (table = ; table <= ; table++) {
idx = h & d->ht[table].sizemask;
he = d->ht[table].table[idx];
while(he) {
if (dictCompareKeys(d, key, he->key))
return he;
he = he->next;
}
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) return NULL;
}
return NULL;
}
redis的rehash是增量rehash,每次rehash一部分
rehash过程:
1. 从 dictht0的table 0到----N-1查找不为NULL的位置(非空桶)
2. 对该位置的链表进行处理, hash到dictht 1的table 1中。
rehash的函数,设置了n参数,表示要处理的非空桶的个数,但是在函数内部设置了最多访问10*n个空桶。
int dictRehash(dict *d, int n) {
int empty_visits = n*; /* Max number of empty buckets to visit. */
if (!dictIsRehashing(d)) return ;
while(n-- && d->ht[].used != ) {
dictEntry *de, *nextde;
/* Note that rehashidx can't overflow as we are sure there are more
* elements because ht[0].used != 0 */
assert(d->ht[].size > (unsigned long)d->rehashidx);
while(d->ht[].table[d->rehashidx] == NULL) {
d->rehashidx++;
if (--empty_visits == ) return ;
}
de = d->ht[].table[d->rehashidx];
/* Move all the keys in this bucket from the old to the new hash HT */
while(de) {
unsigned int h;
nextde = de->next;
/* Get the index in the new hash table */
h = dictHashKey(d, de->key) & d->ht[].sizemask;
de->next = d->ht[].table[h];
d->ht[].table[h] = de;
d->ht[].used--;
d->ht[].used++;
de = nextde;
}
d->ht[].table[d->rehashidx] = NULL;
d->rehashidx++;
}
/* Check if we already rehashed the whole table... */
if (d->ht[].used == ) {
zfree(d->ht[].table);
d->ht[] = d->ht[];
_dictReset(&d->ht[]);
d->rehashidx = -;
return ;
}
/* More to rehash... */
return ;
}
和adlist一样,dict也有迭代器
迭代方法如下:
dictEntry *dictNext(dictIterator *iter)
{
//对表的桶进行遍历,直到找到一个非空桶,返回
while () {
if (iter->entry == NULL) {
dictht *ht = &iter->d->ht[iter->table];
if (iter->index == - && iter->table == ) {
if (iter->safe)
iter->d->iterators++;
else
iter->fingerprint = dictFingerprint(iter->d);//对dict进行指纹
}
iter->index++;
//如果迭代到表的最后一个桶,就判断要不要迭代第二个表
if (iter->index >= (long) ht->size) {
if (dictIsRehashing(iter->d) && iter->table == ) {
iter->table++;
iter->index = ;
ht = &iter->d->ht[];
} else {
break;
}
}
iter->entry = ht->table[iter->index];
} else {
iter->entry = iter->nextEntry;
}
if (iter->entry) {
/* We need to save the 'next' here, the iterator user
* may delete the entry we are returning. */
iter->nextEntry = iter->entry->next;
return iter->entry;
}
}
return NULL;
}
Dict的API如下:
/* API */
/* 字典创建, type参数制定各类对字典的自定义函数,会初始化dictht, dict */
dict *dictCreate(dictType *type, void *privDataPtr);
int dictExpand(dict *d, unsigned long size);
/* 添加键值对,内部调用addRaw和setvalue ,如果已经存在,返回NULL*/
int dictAdd(dict *d, void *key, void *val);
/* 添加键 ,如果已经存在,返回NULL*/
dictEntry *dictAddRaw(dict *d, void *key);
/* 添加一个key,如果存在,直接设置value,设置key的value */
int dictReplace(dict *d, void *key, void *val);
/* 添加一个key,如果存在,直接返回 */
dictEntry *dictReplaceRaw(dict *d, void *key);
/* 删除一个节点,需要free那个节点 */
int dictDelete(dict *d, const void *key);
/* 删除一个节点,不需要free那个节点 */
int dictDeleteNoFree(dict *d, const void *key);
/* 删除dict*/
void dictRelease(dict *d);
/* 查找key*/
dictEntry * dictFind(dict *d, const void *key);
/* 查找key的value*/
void *dictFetchValue(dict *d, const void *key);
/* 将dict的size设置和元素数量一样,但是符合2的倍数*/
int dictResize(dict *d);
dictIterator *dictGetIterator(dict *d);
dictIterator *dictGetSafeIterator(dict *d);
dictEntry *dictNext(dictIterator *iter);
void dictReleaseIterator(dictIterator *iter);
dictEntry *dictGetRandomKey(dict *d);
unsigned int dictGetSomeKeys(dict *d, dictEntry **des, unsigned int count);
void dictPrintStats(dict *d);
unsigned int dictGenHashFunction(const void *key, int len);
unsigned int dictGenCaseHashFunction(const unsigned char *buf, int len);
void dictEmpty(dict *d, void(callback)(void*));
void dictEnableResize(void);
void dictDisableResize(void);
int dictRehash(dict *d, int n);
/* rehash,设置一个最长时间*/
int dictRehashMilliseconds(dict *d, int ms);
void dictSetHashFunctionSeed(unsigned int initval);
unsigned int dictGetHashFunctionSeed(void);
unsigned long dictScan(dict *d, unsigned long v, dictScanFunction *fn, void *privdata);
上面的API很多函数内部都会判断当前是不是还在rehash状态,如果是,就rehash一步。
在rehash前,会判断是不是有迭代器存在,如果有迭代器存在,就不rehash
static void _dictRehashStep(dict *d) {
if (d->iterators == 0) dictRehash(d,1);
}
Redis源码阅读-Dict哈希字典的更多相关文章
- Redis源码阅读(五)集群-故障迁移(上)
Redis源码阅读(五)集群-故障迁移(上) 故障迁移是集群非常重要的功能:直白的说就是在集群中部分节点失效时,能将失效节点负责的键值对迁移到其他节点上,从而保证整个集群系统在部分节点失效后没有丢失数 ...
- Redis源码阅读(四)集群-请求分配
Redis源码阅读(四)集群-请求分配 集群搭建好之后,用户发送的命令请求可以被分配到不同的节点去处理.那Redis对命令请求分配的依据是什么?如果节点数量有变动,命令又是如何重新分配的,重分配的过程 ...
- Redis源码阅读(三)集群-连接初始化
Redis源码阅读(三)集群-连接建立 对于并发请求很高的生产环境,单个Redis满足不了性能要求,通常都会配置Redis集群来提高服务性能.3.0之后的Redis支持了集群模式. Redis官方提供 ...
- Redis源码阅读(二)高可用设计——复制
Redis源码阅读(二)高可用设计-复制 复制的概念:Redis的复制简单理解就是一个Redis服务器从另一台Redis服务器复制所有的Redis数据库数据,能保持两台Redis服务器的数据库数据一致 ...
- Redis源码阅读(六)集群-故障迁移(下)
Redis源码阅读(六)集群-故障迁移(下) 最近私人的事情比较多,没有抽出时间来整理博客.书接上文,上一篇里总结了Redis故障迁移的几个关键点,以及Redis中故障检测的实现.本篇主要介绍集群检测 ...
- Redis源码阅读(一)事件机制
Redis源码阅读(一)事件机制 Redis作为一款NoSQL非关系内存数据库,具有很高的读写性能,且原生支持的数据类型丰富,被广泛的作为缓存.分布式数据库.消息队列等应用.此外Redis还有许多高可 ...
- Redis源码阅读-Adlist双向链表
Redis源码阅读-链表部分- 链表数据结构在Adlist.h Adlist.c Redis的链表是双向链表,内部定义了一个迭代器. 双向链表的函数主要是链表创建.删除.节点插入.头插入.尾插入. ...
- [Redis源码阅读]dict字典的实现
dict的用途 dict是一种用于保存键值对的抽象数据结构,在redis中使用非常广泛,比如数据库.哈希结构的底层. 当执行下面这个命令: > set msg "hello" ...
- [Redis源码阅读]sds字符串实现
初衷 从开始工作就开始使用Redis,也有一段时间了,但都只是停留在使用阶段,没有往更深的角度探索,每次想读源码都止步在阅读书籍上,因为看完书很快又忘了,这次逼自己先读代码.因为个人觉得写作需要阅读文 ...
随机推荐
- 洛谷——P1170 兔八哥与猎人
P1170 兔八哥与猎人 题目描述 兔八哥躲藏在树林旁边的果园里.果园有M × N棵树,组成一个M行N列的矩阵,水平或垂直相邻的两棵树的距离为1.兔八哥在一棵果树下. 猎人背着猎枪走进了果园,他爬上一 ...
- zzc种田
题目背景 可能以后 zzc就去种田了. 题目描述 田地是一个巨大的矩形,然而zzc 每次只能种一个正方形,而每种一个正方形时zzc所花的体力值是正方形的周长,种过的田不可以再种,zzc很懒还要节约体力 ...
- luogu P3819 松江1843路
题目描述 涞坊路是一条长L米的道路,道路上的坐标范围从0到L,路上有N座房子,第i座房子建在坐标为x[i]的地方,其中住了r[i]人. 松江1843路公交车要在这条路上建一个公交站,市政府希望让最多的 ...
- Python数据结构:序列(列表[]、元组())与映射(字典{})语法总结
一.概述:Python中两种基本的数据结构是序列和映射,序列包含:可变的列表和不可变的元组:而当序列不够用时就出现了映射:字典.列表中的元素是可以变化的,元组里面的元素一旦初始化后就不可更改.列表和元 ...
- 墨卡托投影、高斯-克吕格投影、UTM投影及我国分带方法
转自原文 墨卡托投影.高斯-克吕格投影.UTM投影及我国分带方法 一.墨卡托投影.高斯-克吕格投影.UTM投影 1. 墨卡托(Mercator)投影 墨卡托(Mercator)投影,是一种" ...
- Enum枚举类使用集合
1.使用扩展方法使用枚举值对于的Description属性值 public static class EnumExtenstion { public static string GetDescript ...
- VUE -- 不推荐使用jQuery
- python之生成excel
#_*_coding:utf-8_*_ import MySQLdb import xlwt from datetime import datetime def get_data(sql): # 创建 ...
- mysql update 的时候使用left join和where语句
在使用update语句的时候我们有时候需要利用left join 关联表,以下是正确操作: 效果,让指定的order表id为1,2,3数据的finish_at字段更新为freports表的create ...
- wget jdk
wget --no-check-certificate --no-cookies --header "Cookie: oraclelicense=accept-securebackup-co ...
