Java基础--NIO
NIO库在JDK1.4中引入,它以标准Java代码提供了高速的,面向块的IO,弥补了之前同步IO的不足。
缓冲区Buffer
Buffers是一个对象,包含了一些要写入或读出的数据。在面向流的IO模型中,数据是直接写入或读出到Stream对象中的,在NIO中,所有数据都是用缓冲区处理的,在读取数据时,数据直接读到缓冲区中,写入数据时直接写到缓冲区,在任何时候访问NIO中的数据都要通过缓冲区。缓冲区是基于数组实现的,同时提供了对数据的结构化访问并且维护了读写位置。一个ByteBuffer提供了一组功能用于操作byte数组,每种Java类型都对应了一种缓冲区:CharBuffer字符缓冲区,Shortbuffer短整型缓冲区,IntBuffer整型缓冲区,LongBuffer长整型缓冲区,FloatBuffer浮点型缓冲区,DoubleBuffer双精度浮点缓冲区。每一个Buffer类都是Buffer接口的子实例,每一个Buffer类都有完全一样的操作,只是操作的数据类型不一样,ByteBuffer在一般缓冲区操作外提供了一些特有的操作。
缓冲区是包在一个对象内的基本数据元素数组,其有四个重要属性
容量( Capacity):缓冲区能够容纳的数据元素的最大数量,容量在缓冲区创建时被设定,并且永远不能被改变。
上界(Limit):缓冲区的第一个不能被读或写的元素。或者说,缓冲区中现存元素的计数。
位置(Position):下一个要被读或写的元素的索引。位置会自动由相应的 get( )和 put( )函数更新。
标记(Mark):一个备忘位置。调用 mark( )来设定 mark = postion。调用 reset( )设定 position = mark。标记在设定前是未定义的(undefined)。
四个属性之间的关系如下: 0 <= mark <= position <= limit <= capacity
初始时,mark未被设定,position为0,capacity为10,limit为10,第一个元素存放至position为0的位置,capacity不变,其他三个属性会变化。position在调用 put()时,会自动指出了下一个数据元素应该被插入的位置,或者当 get()被调用时指出下一个元素应从何处取出。当put完数据后需要读取时,需要调用flip函数,其将limit设置为position,然后将position设置为0, 之后开始读取。
buffer常见方法如下:
- flip(): 写模式转换成读模式
- rewind():将 position 重置为 0 ,一般用于重复读。
- clear() :清空 buffer ,准备再次被写入 (position 变成 0 , limit 变成 capacity) 。
- compact(): 将未读取的数据拷贝到 buffer 的头部位。
- mark(): reset():mark 可以标记一个位置, reset 可以重置到该位置。
通道Channel
Channel是一个通道,如水管一样,网络数据通过Channel读取和写入,通道是双向的,流是单向的,一个流必须是InputStream或者OutputStream的子类,通道可以用于读写同时进行,所以它是全双工的。Channel可以分为两大类,用于网络读写的SelectableChannel和用于文件操作的FileChannel,ServerSocketChannel和SocketChannel都是SelectableChannel的子类。
Channel接口类只定义了两个方法(isOpen和close),分别表示通道是否打开和关闭通道,具体细节需要子类实现。
IO操作可分为File IO和Stream IO,对应通道也有它们是文件( file)通道和套接字( socket)通道 。通道可以有多种方式创建。Socket 通道有可以直接创建新 socket 通道的工厂方法。但File通道不能直接创建,只能通过在一个打开的RandomAccessFile、FileInputStream或FileOutputStream的对象上调用getChannel( )方法来获取。
通道将数据传输给 ByteBuffer 对象或者从 ByteBuffer 对象获取数据进行传输,通道可以是单向或者双向的。一个 channel 类可能实现定义read( )方法的 ReadableByteChannel 接口,而另一个 channel 类也许实现 WritableByteChannel 接口以提供 write( )方法。实现这两种接口其中之一的类都是单向的,一个类同时实现这两个接口,那么它是双向的,如ByteChannel 接口。从 FileInputStream 对象的getChannel( )方法获取的 FileChannel 对象是只读的,不过从接口声明的角度来看却是双向的,因为FileChannel 实现 ByteChannel 接口。在这样一个通道上调用 write( )方法将抛出未经检查的NonWritableChannelException 异常,因为 FileInputStream 对象总是以 read-only 的权限打开文件。
通道会连接一个特定 I/O 服务且通道实例( channel instance)的性能受它所连接的 I/O 服务的特征限制。如一个连接到只读文件的 Channel 实例不能进行写操作,即使该实例所属的类可能有 write( )方法。
通道可以以阻塞( blocking)或非阻塞( nonblocking)模式运行,非阻塞模式的通道永远不会让调用的线程休眠。请求的操作要么立即完成,要么返回一个结果表明未进行任何操作。只有面向流的( stream-oriented)的通道,如 sockets 和 pipes 才能使用非阻塞模式。通道不能被重复使用,一个打开的通道即代表与一个特定 I/O 服务的特定连接并封装该连接的状态。当通道关闭时,连接会丢失,通道将不再连接任何东西。
1. FileChannel写文件,读文件
public class FileChannelTest {
static void write() throws IOException {
File file = new File("test");
FileOutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
FileChannel channel = outputStream.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(128);
String string = "123 456 abcd EFG !@#$% 测试";
buffer.put(string.getBytes());
buffer.flip();
channel.write(buffer);
channel.close();
outputStream.close();
}
static void read() throws IOException {
File file = new File("test.txt");
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
FileChannel channel = inputStream.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(128);
channel.read(buffer);
buffer.flip();
String string = new String(buffer.array());
System.out.print(string);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
write();
read();
}
}
---
2.使用Channel接收和发送数据
public class ChannelServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
ServerSocket serverSocket = serverSocketChannel.socket();
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverSocket.bind(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080));
int count = 0;
SocketChannel socketChannel = null;
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(512);
while (count < 20) {
if (socketChannel == null) {
socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
} else {
count++;
byteBuffer.clear();
socketChannel.read(byteBuffer);
byteBuffer.flip();
String message = getString(byteBuffer);
System.out.println(count + " server received: " + message);
byteBuffer.clear();
byteBuffer.put(message.getBytes());
byteBuffer.flip();
socketChannel.write(byteBuffer);
System.out.println(count + " server send: " + message);
}
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500);
}
serverSocketChannel.close();
}
public static String getString(ByteBuffer buffer) {
Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
CharBuffer charBuffer = charset.decode(buffer);
return charBuffer.toString();
}
}
---
public class ChannelClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080));
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(512);
int count = 0;
while (count < 20) {
count++;
String message = "message " + count;
byteBuffer.clear();
byteBuffer.put(message.getBytes());
byteBuffer.flip();
socketChannel.write(byteBuffer);
System.out.println(count + " client send: " + message);
byteBuffer.clear();
int readBytes = socketChannel.read(byteBuffer);
if (readBytes > 0) {
byteBuffer.flip();
System.out.println(count + " client receive: " + getString(byteBuffer));
}
}
socketChannel.close();
}
public static String getString(ByteBuffer buffer) {
Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
CharBuffer charBuffer = charset.decode(buffer.asReadOnlyBuffer());
return charBuffer.toString();
}
}
---
多路复用Selector
Selector是NIO的基础,Selector提供了选择已经就绪的任务的能力,它会不断的轮询注册在其上的Channel,如果某个Channel上发生读或者写事件,这个Channel就出于就绪状态,会被Selector轮询出来,然后通过SelectingKey可以获取就绪的Channel集合,进行后续的IO操作。一个Selector可以同时轮询多个Channel,由于JDK使用了epoll代替传统的select实现,所以它并没有最大连接句柄的限制。
选择器管理一个被注册的通道集合的信息和它们的就绪状态,通道和选择器一起被注册,并且选择器可更新通道的就绪状态,也可将被唤醒的线程挂起,直到有通道就绪。
SelectableChannel 可被注册到 Selector 对象上,同时可以指定对那个选择器而言,哪种操作是感兴趣的。一个通道可以被注册到多个选择器上,但对每个选择器而言,只能被注册一次,通道在被注册到一个选择器上之前,必须先设置为非阻塞模式,通过调用通道的configureBlocking(false)方法即可。这意味着不能将FileChannel与Selector一起使用,因为FileChannel不能切换到非阻塞模式,而套接字通道都可以。
选择键封装了特定的通道与特定的选择器的注册关系,选择键对象被SelectableChannel.register( ) 方法返回并提供一个表示这种注册关系的标记。选择键包含了两个比特集(以整数的形式进行编码),指示了该注册关系所关心的通道操作及通道已经准备好的操作。
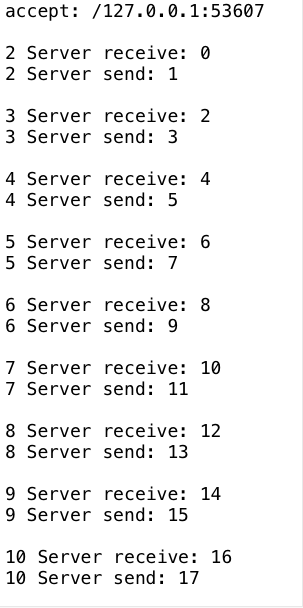
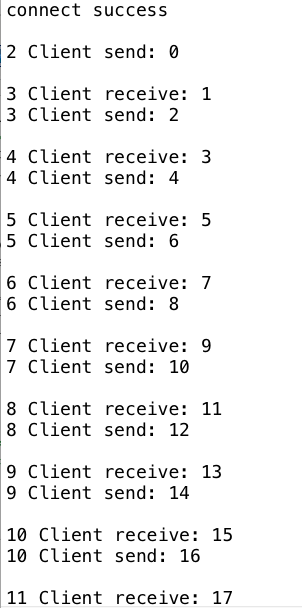
3. 使用Selector发送和接收数据
package com.luangeng.jdk.nio; import com.luangeng.utils.Q; import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; public class NioServer { private static final Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8"); public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException { int count = 0; int msgValue = 0; //打开ServerSocketChannel,用于监听客户端的连接,是所有客户端连接的父管道
ServerSocketChannel serverChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); //绑定监听端口,设置连接为非阻塞模式
serverChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080));
serverChannel.configureBlocking(false); //创建Reactor线程,创建多路复用器并启动线程
Selector selector = Selector.open(); //将SercerSocketChannel注册到Reactor线程的多路复用器Selector上监听ACCEPT事件
serverChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); while (true) {
//多路复用器在线程run方法中无限循环体内轮询准备就绪的Key
int num = selector.select();
if (num == 0) {
continue;
} Iterator it = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
count++;
SelectionKey key = (SelectionKey) it.next(); if (key.isAcceptable()) {
//多路复用器监听到有新的客户端接入,处理新的接入请求,完成TCP三次握手,建立物理链路
SocketChannel channel = serverChannel.accept(); //设置客户端链路为非阻塞状态
channel.configureBlocking(false);
channel.socket().setReuseAddress(true); //将新接入的客户端连接注册到Reactor线程的多路复用器上,监听读操作,读取客户端发送的网络信息
channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
Q.p("accept: " + channel.getRemoteAddress());
}
if (key.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
//异步读取客户端请求消息到缓冲区
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
channel.read(buffer);
buffer.flip();
String msg = charset.decode(buffer).toString();
Q.p(count + " Server receive: " + msg);
msgValue = Integer.valueOf(msg.trim()) + 1;
buffer.clear();
}
if (key.isValid() && key.isWritable()) {
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
channel.write(charset.encode("" + msgValue));
Q.p(count + " Server send: " + msgValue);
} Q.p();
it.remove();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
}
//if (msgValue==100){
// break;
//}
} //关闭
//selector.close();
//serverChannel.close();
} }
---
package com.luangeng.jdk.nio; import com.luangeng.utils.Q; import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; public class NioClient { private static final int BUFFER_SIZE = 1024; private static final Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8"); public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException { int count = 0;
int msgValue = 0; //打开SocketChannel,绑定客户端本地地址(可选,默认系统会随机分配一个可用的本地地址)
SocketChannel clientChannel = SocketChannel.open(); //设置SocketChannel为非阻塞模式,同时设置客户端连接的TCP参数
clientChannel.configureBlocking(false); Socket socket = clientChannel.socket();
socket.setReuseAddress(true);
socket.setReceiveBufferSize(BUFFER_SIZE);
socket.setSendBufferSize(BUFFER_SIZE); //创建Reactor线程,创建多路复用器并启动线程
Selector selector = Selector.open(); //异步连接服务端
boolean connected = clientChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080)); //向Reactor线程的多路复用器注册OP_CONNECT状态位,监听服务器端的TCP ACK应答
clientChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT); while (true) {
//多路复用器在线程run方法的无限循环体内轮询准备就绪的Key
int num = selector.select();
if (num == 0) {
continue;
} Iterator it = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
count++;
SelectionKey key = (SelectionKey) it.next(); //接收connect事件进行处理
if (key.isConnectable()) {
//判断连接成功,如果成功,注册读事件到多路复用器
if (clientChannel.finishConnect()) {
Q.p("connect success");
//clientChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
key.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
}
} if (key.isReadable()) {
//异步读取客户端请求消息到缓冲区
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
clientChannel.read(buffer);
buffer.flip();
String msg = charset.decode(buffer).toString();
Q.p(count + " Client receive: " + msg);
msgValue = Integer.valueOf(msg.trim()) + 1;
buffer.clear();
}
if (key.isValid() && key.isWritable()) {
//调用SocketChannel的异步write接口,将消息异步发送给客户端
clientChannel.write(charset.encode("" + msgValue));
Q.p(count + " Client send: " + msgValue);
} Q.p();
it.remove();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
}
if (msgValue == 20) {
clientChannel.finishConnect();
Q.p("finish");
//break;
}
} //关闭连接
//selector.close();
//clientChannel.close();
} }
---
输出:
end
Java基础--NIO的更多相关文章
- Java基础——NIO(一)通道与缓冲区
一.概述 1.什么是NIO NIO即New IO,这个库是在JDK1.4中才引入的.NIO和IO有相同的作用和目的,但实现方式不同,NIO主要用到的是块,所以NIO的效率要比IO高很多. 在Java ...
- Java基础——NIO(二)非阻塞式网络通信与NIO2新增类库
一.NIO非阻塞式网络通信 1.阻塞与非阻塞的概念 传统的 IO 流都是阻塞式的.也就是说,当一个线程调用 read() 或 write() 时,该线程被阻塞,直到有一些数据被读取或写入,该线程在 ...
- java基础-网络编程(Socket)技术选型入门之NIO技术
java基础-网络编程(Socket)技术选型入门之NIO技术 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 一.传统的网络编程 1>.编写socket通信的MyServer ...
- JAVA基础(10)——IO、NIO
转载:http://blog.csdn.net/weitry/article/details/52964948 JAVA基础系列规划: JAVA基础(1)——基本概念 JAVA基础(2)——数据类型 ...
- Java基础之NIO
NIO简介: Java NIO(New IO)是从Java 1.4版本开始引入的一个新的IO API,可以替代标准的Java IO API.NIO与原来的IO有同样的作用和目的,但是使用的方式完全不同 ...
- [Java面经]干货整理, Java面试题(覆盖Java基础,Java高级,JavaEE,数据库,设计模式等)
如若转载请注明出处: http://www.cnblogs.com/wang-meng/p/5898837.html 谢谢.上一篇发了一个找工作的面经, 找工作不宜, 希望这一篇的内容能够帮助到大 ...
- 万能的林萧说:一篇文章教会你,如何做到招聘要求中的“要有扎实的Java基础”。
来历 本文来自于一次和群里猿友的交流,具体的情况且听LZ慢慢道来. 一日,LZ在群里发话,"招人啦." 然某群友曰,"群主,俺想去." LZ回之,"你 ...
- java基础-java核心知识库
本人从事java开发6年左右,主要从事互联网相关的开发,目前还是奋战在一线的码农,痛并快乐着.受互联网产品热潮的影响,关注高性能低成本架构,互联网开发框架,以下是我认为作为一个资深java程序员应该掌 ...
- Java基础之读文件——使用通道读取混合数据2(ReadPrimesMixedData2)
控制台程序,本例读取Java基础之写文件部分(PrimesToFile2)写入的Primes.txt. 方法二:设置一个任意容量的.大小合适的字节缓冲区并且使用来自文件的字节进行填充.然后整理出缓冲区 ...
随机推荐
- Java进阶4表达式中的陷阱
Java进阶4表达式中的陷阱 20131103 表达式是Java中最基本的组成单元,各种表达式是Java程序员最司空见惯的内容,Java中的表达式并不是十分的复杂,但是也有一些陷阱.例如当程序中使用算 ...
- 转载:【Oracle 集群】RAC知识图文详细教程(七)--Oracle 11G RAC集群安装
文章导航 集群概念介绍(一) ORACLE集群概念和原理(二) RAC 工作原理和相关组件(三) 缓存融合技术(四) RAC 特殊问题和实战经验(五) ORACLE 11 G版本2 RAC在LINUX ...
- C# 设计模式巩固 - 工厂方法模式
前言 实在编不出来了~ 介绍 - 工厂方法模式 官方定义:(下面摘自百度百科)工厂方法模式(FACTORY METHOD)是一种常用的对象创建型设计模式,此模式的核心精神是封装类中不变的部分,提取其中 ...
- UML_00_资源帖
一.官方文档 https://www.uml-diagrams.org/ https://www.omg.org/spec/UML/ 二.精选资料 UML教程-w3cschool UML建模图实战笔记 ...
- Spring Framework Artifacts
GroupId ArtifactId Description org.springframework spring-aop Proxy-based AOP support org.springfram ...
- Python3的基础语法(四)
1,编码 默认情况下,Python 3 源码文件以 UTF-8 编码,所有字符串都是 unicode 字符串. 当然你也可以为源码文件指定不同的编码: # -*- coding: cp-1252 -* ...
- pig 自定义udf中读取hdfs 文件
最近几天,在研究怎么样把日志中的IP地址转化成具体省份城市. 希望写一个pig udf IP数据库采用的纯真IP数据库文件qqwry.dat,可以从http://www.cz88.net/下载. 这里 ...
- React-Native进阶_2.加载指示动画 ActivityIndicator
在安卓原始 App中使用的加载框 ProgressBar 在React -Native 中也是有相对应的视图,叫做ActivityIndicator,对应ios 中React-Native 提供的是 ...
- Okhttp之连接池ConnectionPool简单分析(一)
开篇声明:由于本篇博文用到的一些观点或者结论在之前的博文中都已经分析过,所以本篇博文直接拿来用,建议读此博文的Monkey们按照下面的顺序读一下博主以下博文,以便于对此篇博文的理解: <Okht ...
- C#将html代码转换成文本代码
/// <summary> /// 去除HTML标记 /// </summary> /// <param name="strHtml">包括HT ...
