吴恩达《深度学习》-课后测验-第一门课 (Neural Networks and Deep Learning)-Week 3 - Shallow Neural Networks(第三周测验 - 浅层神 经网络)
Week 3 Quiz - Shallow Neural Networks(第三周测验 - 浅层神经网络)
\1. Which of the following are true? (Check all that apply.) Notice that I only list correct options(以下哪一项是正确的?只列出了正确的答案)
【 】 is a matrix in which each column is one training example.(是一个矩阵,其中每个列都 是一个训练样本。)
【 】\(_4^{[2]}\) is the activation output by the 4th neuron of the 2nd layer(4 [2]是第二层第四层神经 元的激活的输出。)
【 】\(^{[2](12)}\) denotes the activation vector of the 2nd layer for the 12th training example.(表\(^{[2](12)}\)示第二层和第十二层的激活向量。)
【 】\(^{[2]}\) denotes the activation vector of the 2nd layer.(\(^{[2]}\) 表示第二层的激活向量。)
答案
全对
\2. The tanh activation usually works better than sigmoid activation function for hidden units because the mean of its output is closer to zero, and so it centers the data better for the next layer. True/False?(tanh 激活函数通常比隐藏层单元的 sigmoid 激活函数效果更好,因为其 输出的平均值更接近于零,因此它将数据集中在下一层是更好的选择,请问正确吗?)
【 】True(正确) 【 】 False(错误)
答案
True
Note: You can check this post and(this paper)(请注意,你可以看一下这篇文章 和这篇文档.)
As seen in lecture the output of the tanh is between -1 and 1, it thus centers the data which makes the learning simpler for the next layer.(tanh 的输出在-1 和 1 之间,因此它将数据集中在一起,使得下 一层的学习变得更加简单。)
\3. Which of these is a correct vectorized implementation of forward propagation for layer , where ≤ ≤ ? Notice that I only list correct options(其中哪一个是第 l 层向前传播的正确 向量化实现,其中 ≤ ≤ )(以下哪一项是正确的?只列出了正确的答案)
【 】$^{[]} = {[]}{[−1]} + ^{[]} $
【 】\(^{[]} = ^{[]} (^{[]} )\)
答案
全对
\4. You are building a binary classifier for recognizing cucumbers (y=1) vs. watermelons (y=0). Which one of these activation functions would you recommend using for the output layer?(您 正在构建一个识别黄瓜(y = 1)与西瓜(y = 0)的二元分类器。 你会推荐哪一种激活函数 用于输出层?)
【 】 ReLU 【 】 Leaky ReLU 11 【 】 sigmoid 【 】 tanh
答案
sigmoid
Note: The output value from a sigmoid function can be easily understood as a probability.(注意:来自 sigmoid 函数的输出值可以很容易地理解为概率。)
Sigmoid outputs a value between 0 and 1 which makes it a very good choice for binary classification.You can classify as 0 if the output is less than 0.5 and classify as 1 if the output is more than 0.5. It can be done with tanh as well but it is less convenient as the output is between -1 and 1. Sigmoid 输出的值介于 0 和 1 之间,这使其成为二元分类的一个非常好的选择。 如果输出小于 0.5,则可以将其归类为 0,如果输出大于 0.5,则归类为 1。 它也可以用 tanh 来完成,但是它不太方便,因为输出在-1 和 1 之间。)
\5. Consider the following code:(看一下下面的代码:)
A = np.random.randn(4,3)
B = np.sum(A, axis = 1, keepdims = True)
What will be B.shape?(请问 B.shape 的值是多少?)
答案
B.shape = (4, 1)
we use (keepdims = True) to make sure that A.shape is (4,1) and not (4, ). It makes our code more rigorous.(我们使用(keepdims = True)来确保 A.shape 是(4,1)而不是(4,),它使 我们的代码更加严格。)
\6. Suppose you have built a neural network. You decide to initialize the weights and biases to be zero. Which of the following statements are True? (Check all that apply)(假设你已经建立 了一个神经网络。 您决定将权重和偏差初始化为零。 以下哪项陈述是正确的?)
【 】Each neuron in the first hidden layer will perform the same computation. So even after multiple iterations of gradient descent each neuron in the layer will be computing the same thing as other neurons.(第一个隐藏层中的每个神经元节点将执行相同的计算。 所以即使经过 多次梯度下降迭代后,层中的每个神经元节点都会计算出与其他神经元节点相同的东西。)
【 】Each neuron in the first hidden layer will perform the same computation in the first iteration. But after one iteration of gradient descent they will learn to compute different things because we have “broken symmetry”.( 第一个隐藏层中的每个神经元将在第一次迭代中执行相 同的计算。 但经过一次梯度下降迭代后,他们将学会计算不同的东西,因为我们已经“破坏了 对称性”。)
【 】Each neuron in the first hidden layer will compute the same thing, but neurons in different layers will compute different things, thus we have accomplished “symmetry breaking” as described in lecture.(第一个隐藏层中的每一个神经元都会计算出相同的东西,但是不同层的神 经元会计算不同的东西,因此我们已经完成了“对称破坏”。)
【 】The first hidden layer’s neurons will perform different computations from each other even in the first iteration; their parameters will thus keep evolving in their own way.(即使在第一次迭 代中,第一个隐藏层的神经元也会执行不同的计算, 他们的参数将以自己的方式不断发展。)
答案
【★】Each neuron in the first hidden layer will perform the same computation. So even after multiple iterations of gradient descent each neuron in the layer will be computing the same thing as other neurons.(第一个隐藏层中的每个神经元节点将执行相同的计算。 所以即使经过 多次梯度下降迭代后,层中的每个神经元节点都会计算出与其他神经元节点相同的东西。)
\7. Logistic regression’s weights w should be initialized randomly rather than to all zeros, because if you initialize to all zeros, then logistic regression will fail to learn a useful decision boundary because it will fail to “break symmetry”, True/False?(Logistic 回归的权重 w 应该随 机初始化,而不是全零,因为如果初始化为全零,那么逻辑回归将无法学习到有用的决策边 界,因为它将无法“破坏对称性”,是正确的吗?)
【 】True(正确) 【 】 False(错误)
答案
False
Note: Logistic Regression doesn’t have a hidden layer. If you initialize the weights to zeros, the first example x fed in the logistic regression will output zero but the derivatives of the Logistic Regression depend on the input x (because there’s no hidden layer) which is not zero. So at the second iteration, the weights values follow x’s distribution and are different from each other if x is not a constant vector.(Logistic 回归没有隐藏层。 如果将权重初始化为零,则 Logistic 回归中的第一个样本 x 将输 出零,但 Logistic 回归的导数取决于不是零的输入 x(因为没有隐藏层)。 因此,在第二次迭代 中,如果 x 不是常量向量,则权值遵循 x 的分布并且彼此不同。)
\8. You have built a network using the tanh activation for all the hidden units. You initialize the weights to relative large values, using np.random.randn(..,..)1000. What will happen?(您已经 为所有隐藏单元使用 tanh 激活建立了一个网络。 使用 np.random.randn(..,..) 1000 将 权重初始化为相对较大的值。 会发生什么?)
【 】 It doesn’t matter. So long as you initialize the weights randomly gradient descent is not affected by whether the weights are large or small.(这没关系。只要随机初始化权重,梯度下降 不受权重大小的影响。)
【 】 This will cause the inputs of the tanh to also be very large, thus causing gradients to also become large. You therefore have to set \(\alpha\) to be very small to prevent divergence; this will slow down learning.(这将导致 tanh 的输入也非常大,因此导致梯度也变大。因此,您必须将 α 设 置得非常小以防止发散; 这会减慢学习速度。)
【 】 This will cause the inputs of the tanh to also be very large, causing the units to be “highly activated” and thus speed up learning compared to if the weights had to start from small values.(这会导致 tanh 的输入也非常大,导致单位被“高度激活”,从而加快了学习速度,而权重必须从小数值开始。)
【 】 This will cause the inputs of the tanh to also be very large, thus causing gradients to be close to zero. The optimization algorithm will thus become slow.(这将导致 tanh 的输入也很 大,因此导致梯度接近于零, 优化算法将因此变得缓慢。)
答案
【★】 This will cause the inputs of the tanh to also be very large, thus causing gradients to be close to zero. The optimization algorithm will thus become slow.(这将导致 tanh 的输入也很大,因此导致梯度接近于零, 优化算法将因此变得缓慢。)
Note:tanh becomes flat for large values, this leads its gradient to be close to zero. This slows down the optimization algorithm.(注:tanh 对于较大的值变得平坦,这导致其梯度接近于零。 这减慢了 优化算法。)
\9. Consider the following 1 hidden layer neural network:(看一下下面的单隐层神经网络)
【 】\(^{[1]}\) will have shape (4, 1)(\(^{[1]}\)的维度是(4, 1))
【 】\(^{[1]}\) will have shape (4, 2)(\(^{[1]}\)的维度是 (4, 2))
【 】\(^{[2]}\) will have shape (1, 4)(\(^{[2]}\) 的维度是 (1, 4))
【 】\(^{[2]}\) will have shape (1, 1)(\(^{[2]}\)的维度是 (1, 1))
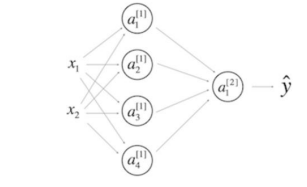
答案
全对
Note: Check here for general formulas to do this.(注:来看一下公式) 
\10. In the same network as the previous question, what are the dimensions of \(^{[]}\) and \(^{[]}\) ?(在 和上一个相同的网络中,\(^{[]}\) 和 \(^{[]}\)的维度是多少?)
答案
【★】维度都是 (4,m))

Week 3 Code Assignments:
✧Course 1 - 神经网络和深度学习 - 第三周测验 - 浅层神经网络
✦assignment3:Planar data classification with one hidden layer)
吴恩达《深度学习》-课后测验-第一门课 (Neural Networks and Deep Learning)-Week 3 - Shallow Neural Networks(第三周测验 - 浅层神 经网络)的更多相关文章
- 吴恩达深度学习课后习题第5课第1周第3小节: Jazz Improvisation with LSTM
目录 Improvise a Jazz Solo with an LSTM Network Packages 1 - Problem Statement 1.1 - Dataset What are ...
- 【Deeplearning.ai 】吴恩达深度学习笔记及课后作业目录
吴恩达深度学习课程的课堂笔记以及课后作业 代码下载:https://github.com/douzujun/Deep-Learning-Coursera 吴恩达推荐笔记:https://mp.weix ...
- 吴恩达深度学习第2课第2周编程作业 的坑(Optimization Methods)
我python2.7, 做吴恩达深度学习第2课第2周编程作业 Optimization Methods 时有2个坑: 第一坑 需将辅助文件 opt_utils.py 的 nitialize_param ...
- 吴恩达深度学习第1课第4周-任意层人工神经网络(Artificial Neural Network,即ANN)(向量化)手写推导过程(我觉得已经很详细了)
学习了吴恩达老师深度学习工程师第一门课,受益匪浅,尤其是吴老师所用的符号系统,准确且易区分. 遵循吴老师的符号系统,我对任意层神经网络模型进行了详细的推导,形成笔记. 有人说推导任意层MLP很容易,我 ...
- 吴恩达深度学习第4课第3周编程作业 + PIL + Python3 + Anaconda环境 + Ubuntu + 导入PIL报错的解决
问题描述: 做吴恩达深度学习第4课第3周编程作业时导入PIL包报错. 我的环境: 已经安装了Tensorflow GPU 版本 Python3 Anaconda 解决办法: 安装pillow模块,而不 ...
- 吴恩达深度学习 反向传播(Back Propagation)公式推导技巧
由于之前看的深度学习的知识都比较零散,补一下吴老师的课程希望能对这块有一个比较完整的认识.课程分为5个部分(粗体部分为已经看过的): 神经网络和深度学习 改善深层神经网络:超参数调试.正则化以及优化 ...
- 深度学习 吴恩达深度学习课程2第三周 tensorflow实践 参数初始化的影响
博主 撸的 该节 代码 地址 :https://github.com/LemonTree1994/machine-learning/blob/master/%E5%90%B4%E6%81%A9%E8 ...
- 吴恩达深度学习笔记(十二)—— Batch Normalization
主要内容: 一.Normalizing activations in a network 二.Fitting Batch Norm in a neural network 三.Why does ...
- 吴恩达深度学习笔记(deeplearning.ai)之卷积神经网络(二)
经典网络 LeNet-5 AlexNet VGG Ng介绍了上述三个在计算机视觉中的经典网络.网络深度逐渐增加,训练的参数数量也骤增.AlexNet大约6000万参数,VGG大约上亿参数. 从中我们可 ...
随机推荐
- 思维导图概览SpringCloud
@ 目录 1.什么是微服务 1.1.架构演进 1.2.微服务架构 1.3.微服务解决方案 2.SpringCloud概览 2.1.什么是SpringCloud 2.1.SpringCloud主要组件 ...
- K8S 创建管理员账号
一.生成管理员证书 cat > admin-csr.json <<EOF { "CN": "admin", "hosts" ...
- python3 - selenium常用的参数
# 选用开发者模式,创建一个浏览器对象,可避免被检测到是selenium模拟浏览器 chrome_options = webdriver.ChromeOptions() chrome_options ...
- Centos7第一安装后无法联网
- DataGrid添加进度条列
DataGridColumn类型的继承树 DataGridColumn的派生类: 一般情况下DataGridBoundColumn和DataGridComboBoxColumn足以满足多数列的样式,如 ...
- 初识ABP vNext(5):ABP扩展实体
Tips:本篇已加入系列文章阅读目录,可点击查看更多相关文章. 目录 前言 开始 扩展实体 路由整理 最后 前言 上一篇实现了前端vue部分的用户登录和菜单权限控制,但是有一些问题需要解决,比如用户头 ...
- Debian 镜像使用帮助
链接: Debian 镜像使用帮助 buster: # 默认注释了源码镜像以提高 apt update 速度,如有需要可自行取消注释 deb https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua ...
- Windows如何快速远程到另一台Windows并管理多个远程服务器
Windows如何远程到另一台 Windows管理多个远程服务器 Windows第三方远程管理工具 准备远程机器 开启远程机器的远程桌面功能 首先在此电脑(我的电脑)图标上点击鼠标右键,选择" ...
- 算法-图(2)Bellman-Ford算法求最短路径
template <class T,class E> void Bellman-Ford(Graph<T,E>&G, int v, E dist[], int path ...
- Go语言从入门到高薪之路(一)-- 初识与安装
为什么要学习Go语言? Go语言又称Golang,它是21世纪的编程语言,学好了就能拿高薪,拿了高薪就能实力装逼,有了实力就能泡妹子...(我就问你吊不吊,想不想学?) Go语言有什么特点和优势? G ...
