Simulink仿真入门到精通(八) M语言对Simulink模型的自动化操作及配置
8.1 M语言控制模型的仿真
M语言与Simulink结合的方式:
- 在Simulink模型或模块中使用回调函数
- 在M语言中调用与模型相关的命令,控制模型的建立,设置模块的属性,增删信号线,以及运行模型仿真等
为了调用和操作Simulink模型,M语言中最常用的函数有sim、set_param、get_param。
8.1.1 sim控制模型仿真及参数配置
(1)simOut=sim('model','ParameterName1',value1,'ParameterName2',value2,...);
对名为model的模型进行仿真,仿真时将其参数通过[参数名,参数值]的方式进行配置。
simOut是一个Simulink.SimulationOutput对象,包含了仿真的输出:仿真采样时间、状态值和信号值。
- sim_out=sim('mymodel','SimulationMode','Normal','stoptime','30');
(2)simOut=sim('model',ParameterStruct);
仿真时通过结构体变量配置参数。
- param_struct=struct('SimulationMode','Normal','stoptime','30');
- sim_out=sim('mymodel',param_struct);
(3)simOut=sim('model',ConfigSet);
仿真时通过配置集合来配置参数。
- getActiveConfigSet() %获取模型的配置集合变量
- attachConfigSet() %绑定参数配置集合到模型
- setActiveConfigSet() %激活模型的某个参数配置
对ConfigSet对象进行参数获取/设定也使用set_param()/get_param()。
(4)sim('model');
当不需要该表模型的参数配置,也不关心模型仿真的输出时,可以直接sim。
使用上述命令运行仿真时,并不修改模型的配置,而是通过sim函数暂时设置某个参数应用于此次仿真,仿真后模型的配置参数仍然保持之前的设定不受影响。
当希望观察模型参数配置不同对仿真结果有何影响时,直接使用多个sim语句带上不同的参数配置作为M脚本运行即可。
示例:
Data Export选Array。
- param_struct1.SaveState = 'on';
- param_struct1.StateSaveName = 'xout1';
- param_struct1.SaveOutput = 'on';
- param_struct1.OutputSaveName = 'yout1';
- param_struct1.SolverType = 'Fixed-step';
- param_struct1.Solver = 'FixedStepDiscrete';
- param_struct1.FixedStep = '0.01';
- sim_out1 = sim('mymodel',param_struct1);
- param_struct2 = param_struct1;
- param_struct2.FixedStep = '2';
- param_struct2.OutputSaveName ='yout2';
- sim_out2 = sim('mymodel',param_struct2);
- t1 = get(sim_out1, 'tout');
- t2 = get(sim_out2, 'tout');
- y1 = get(sim_out1, 'yout1');
- y2 = get(sim_out2, 'yout2');
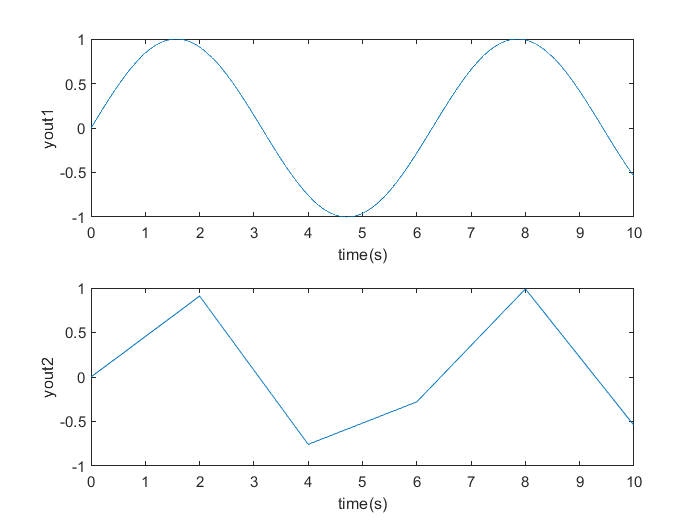
- figure;
- title('Sim a model with different config parameters');
- subplot(211);
- plot(t1,y1);
- xlabel('time(s)');
- ylabel('yout1');
- subplot(212);
- plot(t2,y2);
- xlabel('time(s)');
- ylabel('yout2');
8.1.2 set_param控制模型仿真过程
- set_param(object,param1,value1,param2,value2,...);
- object:模型或模块对象,既可以使用路径表示,也可以使用句柄表示;
- paramX:模型或模块的参数名;
- valueX:对应于paramX的参数值。
获取参数则使用get_param(object,param),每次只能获取一个参数的值。
有一个参数名为SimulationCommand,可由set_param设置不同的值来控制模型仿真的过程。
| 值 | 功能说明 |
| start | 启动模型仿真 |
| pause | 暂停模型仿真 |
| step | 单步执行仿真 |
| continue | 继续模型放着 |
| stop | 停止模型仿真 |
例:在仿真过程中某些时刻改变某些参数的值。
- set_param('mymodel','SolverType','Fixed-step','Solver','FixedStepDiscrete','FixedStep','0.1');
- set_param('mymodel', 'SimulationCommand', 'start');
- set_param('mymodel', 'SimulationCommand', 'pause');
- set_param('mymodel', 'SimulationCommand', 'step');
- pause(0.2);
- t = get_param('mymodel', 'SimulationTime') % get current simulation time
- while t~=0
- t = get_param('mymodel', 'SimulationTime'); % get current simulation time
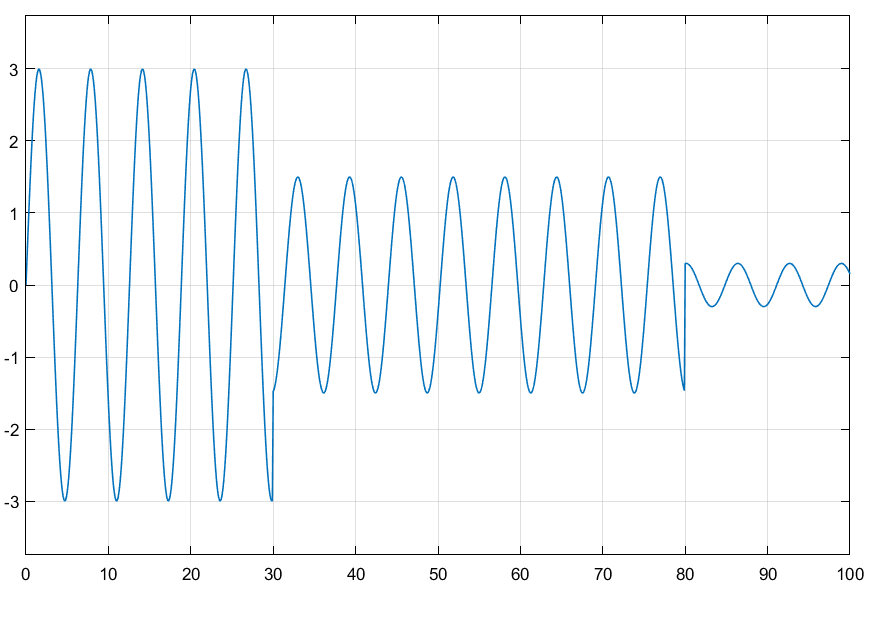
- if t < 30
- set_param('mymodel/Gain', 'Gain','3');
- elseif t < 80
- set_param('mymodel/Gain', 'Gain','1.5');
- else
- set_param('mymodel/Gain', 'Gain','-0.3');
- end
- set_param('mymodel', 'SimulationCommand', 'step');
- pause(0.2);
- end
- set_param('mymodel', 'SimulationCommand', 'stop');
8.2 M语言修改模块属性
- set_param('m_control_05','SimulationCommand','start');
- scope_h = find_system('m_control_05', 'findall','on','blockType','Scope');
- num_scope = length(scope_h);
- for ii = 1: num_scope
- set(scope_h(ii), 'Open', 'on');
- end
8.3 M语言自动建立模型
几个重要的函数:
- 模型相关:new_system创建新模型,load_system将模型加载到内存(不可见),open_system打开模型使可视化;
- 模块相关:add_block向模型中追加模块,delete_block删除模块,replace_block替换模块;
- 信号线相关:add_line在模块输入/输出口之间连线,delete_line将既存的信号线删除。
8.3.1 模型的建立及打开
new_system可以有返回值,返回模型的句柄。
- >> h=new_system('new')
- h =
- 1.8480e+03
save_system可以与new_system连用而直接将模型保存在硬盘上。
load_system将模型隐式打开。
close_system关闭模型,参数为模型名,不写参数时关闭选中的模型(gcs)。
bdclose all可以无条件关闭所有隐式或显示打开的模型,即使模型存在改动也不提示保存,谨慎使用。
8.3.2 模块的添加、删除及替换
add_block('src','dest')
src指所添加的模块的路径,dest表示这个源模块添加到的目标路径。
- add_block('simulink/Sources/Constant','mymodel/Constant')
add_block('src','dest','param1','value1',...)
可以在添加模块的同时对其参数进行设定。
注意:在添加模块时应避免命名的重复,否则会导致错误;在添加模块之前,要先显示或隐式的将模型打开。
replace_block('sys','old_blk','new_blk')
sys为模型名,old_blk为需要被替换的模块类型名,new_blk为用来替换其他模块的模块名。
当模型中被替换的模块类型存在多个模块时,会弹出对话框供用户选择。
替换后模块名没有改变。
- replace_block('mymodel','Scope','simulink/Sinks/Out1')
delete_block('blk')将此类模块全部删掉。
8.3.3 信号线的添加及删除
h=add_line('sys','oport','iport')
在模型sys中追加从输出口oport到输入口iport的信号线,并返回其句柄h。
输入输出端口都需要在模块名后追加斜杠和端口序号。
- add_block('simulink/Sources/In1','mymodel/In1');
- add_block('simulink/Sinks/Out1','mymodel/Out1');
- add_line('mymodel','In1/1','Out1/1','autorouting','on');

autorouting可以使连线仅保持水平和竖直两个方向。
8.3.4 M语言自动创建模型
自动创建switch模型。
- function varargout = section_model(varargin)
- % SECTION_MODEL MATLAB code for section_model.fig
- % SECTION_MODEL, by itself, creates a new SECTION_MODEL or raises the existing
- % singleton*.
- %
- % H = SECTION_MODEL returns the handle to a new SECTION_MODEL or the handle to
- % the existing singleton*.
- %
- % SECTION_MODEL('CALLBACK',hObject,eventData,handles,...) calls the local
- % function named CALLBACK in SECTION_MODEL.M with the given input arguments.
- %
- % SECTION_MODEL('Property','Value',...) creates a new SECTION_MODEL or raises the
- % existing singleton*. Starting from the left, property value pairs are
- % applied to the GUI before section_model_OpeningFcn gets called. An
- % unrecognized property name or invalid value makes property application
- % stop. All inputs are passed to section_model_OpeningFcn via varargin.
- %
- % *See GUI Options on GUIDE's Tools menu. Choose "GUI allows only one
- % instance to run (singleton)".
- %
- % See also: GUIDE, GUIDATA, GUIHANDLES
- % Edit the above text to modify the response to help section_model
- % Last Modified by GUIDE v2.5 02-Jan-2015 09:24:44
- % Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
- gui_Singleton = 1;
- gui_State = struct('gui_Name', mfilename, ...
- 'gui_Singleton', gui_Singleton, ...
- 'gui_OpeningFcn', @section_model_OpeningFcn, ...
- 'gui_OutputFcn', @section_model_OutputFcn, ...
- 'gui_LayoutFcn', [] , ...
- 'gui_Callback', []);
- if nargin && ischar(varargin{1})
- gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{1});
- end
- if nargout
- [varargout{1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
- else
- gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
- end
- % End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
- % --- Executes just before section_model is made visible.
- function section_model_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
- % This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.
- % hObject handle to figure
- % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
- % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
- % varargin command line arguments to section_model (see VARARGIN)
- % Choose default command line output for section_model
- handles.output = hObject;
- % Update handles structure
- guidata(hObject, handles);
- % UIWAIT makes section_model wait for user response (see UIRESUME)
- % uiwait(handles.figure1);
- % --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
- function varargout = section_model_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
- % varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT);
- % hObject handle to figure
- % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
- % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
- % Get default command line output from handles structure
- varargout{1} = handles.output;
- function edit1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
- % hObject handle to edit1 (see GCBO)
- % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
- % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
- % Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit1 as text
- % str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit1 as a double
- % --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
- function edit1_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
- % hObject handle to edit1 (see GCBO)
- % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
- % handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
- % Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
- % See ISPC and COMPUTER.
- if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
- set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
- end
- function edit2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
- % hObject handle to edit2 (see GCBO)
- % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
- % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
- % Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit2 as text
- % str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit2 as a double
- % --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
- function edit2_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
- % hObject handle to edit2 (see GCBO)
- % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
- % handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
- % Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
- % See ISPC and COMPUTER.
- if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
- set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
- end
- function edit3_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
- % hObject handle to edit3 (see GCBO)
- % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
- % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
- % Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit3 as text
- % str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit3 as a double
- % --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
- function edit3_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
- % hObject handle to edit3 (see GCBO)
- % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
- % handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
- % Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
- % See ISPC and COMPUTER.
- if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
- set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
- end
- % --------------------------------------------------------------------
- function Untitled_1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
- % hObject handle to Untitled_1 (see GCBO)
- % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
- % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
- % --------------------------------------------------------------------
- function Untitled_2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
- % hObject handle to Untitled_2 (see GCBO)
- % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
- % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
- bdclose all;
- threshold = get(handles.edit1,'string');
- up_out = get(handles.edit2, 'string');
- down_out = get(handles.edit3, 'string');
- rel = get(handles.popupmenu1,'Value');
- mdl_name = 'switch_section';
- mdl_handle = new_system(mdl_name);
- open_system(mdl_handle);
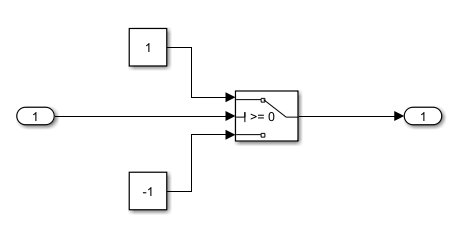
- add_block('simulink/Signal Routing/Switch',[mdl_name,'/Switch']);
- add_block('simulink/Commonly Used Blocks/In1',[mdl_name,'/In1'],'Position',[35 213 65 227]);
- add_block('simulink/Commonly Used Blocks/Out1',[mdl_name, '/Out1'],'Position',[345 213 375 227]);
- add_block('simulink/Commonly Used Blocks/Constant',[mdl_name, '/Constant'],'Position',[125 150 155 180]);
- add_block('simulink/Commonly Used Blocks/Constant',[mdl_name, '/Constant1'],'Position',[125 265 155 295]);
- if rel == 2
- criterial = 'u2 > Threshold';
- elseif rel == 1
- criterial = 'u2 >= Threshold';
- else
- criterial = 'u2 ~= 0';
- end
- set_param([mdl_name,'/Switch'], 'Criteria', criterial, 'Threshold', threshold);
- set_param([mdl_name, '/Constant'],'Value', up_out);
- set_param([mdl_name, '/Constant1'],'Value', down_out);
- autorouting = get(handles.checkbox1, 'value');
- if isequal(autorouting, 0)
- add_line(mdl_name,'In1/1','Switch/2');
- add_line(mdl_name,'Switch/1','Out1/1');
- add_line(mdl_name,'Constant/1','Switch/1');
- add_line(mdl_name,'Constant1/1','Switch/3');
- else
- add_line(mdl_name,'In1/1','Switch/2','autorouting','on');
- add_line(mdl_name,'Switch/1','Out1/1','autorouting','on');
- add_line(mdl_name,'Constant/1','Switch/1','autorouting','on');
- add_line(mdl_name,'Constant1/1','Switch/3','autorouting','on');
- end
- % --------------------------------------------------------------------
- function Untitled_5_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
- % hObject handle to Untitled_5 (see GCBO)
- % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
- % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
- web('http://www.ilovematlab.cn/article-29-1.html');
- % --------------------------------------------------------------------
- function Untitled_4_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
- % hObject handle to Untitled_4 (see GCBO)
- % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
- % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
- bdclose all;
- close(gcf);
- % --------------------------------------------------------------------
- function Untitled_7_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
- % hObject handle to Untitled_7 (see GCBO)
- % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
- % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
- % --------------------------------------------------------------------
- function Untitled_8_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
- % hObject handle to Untitled_8 (see GCBO)
- % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
- % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
- web('http://weibo.com/u/2300570331');
- % --- Executes on selection change in popupmenu1.
- function popupmenu1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
- % hObject handle to popupmenu1 (see GCBO)
- % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
- % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
- % Hints: contents = cellstr(get(hObject,'String')) returns popupmenu1 contents as cell array
- % contents{get(hObject,'Value')} returns selected item from popupmenu1
- if 3 == get(hObject,'Value')
- set(handles.edit1, 'Enable', 'off', 'string','0');
- else
- set(handles.edit1, 'Enable', 'on');
- end
- % --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
- function popupmenu1_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
- % hObject handle to popupmenu1 (see GCBO)
- % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
- % handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
- % Hint: popupmenu controls usually have a white background on Windows.
- % See ISPC and COMPUTER.
- if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
- set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
- end
- % --- Executes on button press in checkbox1.
- function checkbox1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
- % hObject handle to checkbox1 (see GCBO)
- % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
- % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
- % Hint: get(hObject,'Value') returns toggle state of checkbox1

Simulink仿真入门到精通(八) M语言对Simulink模型的自动化操作及配置的更多相关文章
- Simulink仿真入门到精通(十四) Simulink自定义环境
14.1 Simulink环境自定义功能 sl_sustomization.m函数是Simulink提供给用户使用MATLAB语言自定义Simulink标准人机界面的函数机制.若sl_sustomiz ...
- Simulink仿真入门到精通(十六) Simulink基于模型设计的工业应用概述
16.1 Simulink用途概述 在基于模型设计广泛应用于汽车电子嵌入式开发的今天,MBD(Model Besed Design)技术也逐步推广到各种嵌入式控制方面.与传统的嵌入式开发相比,BMD以 ...
- Simulink仿真入门到精通(十五) Simulink在流程工业中的仿真应用
15.1 工业乙醇生产与计算机仿真 乙醇作为可再生清洁能源不仅可以代替四乙基铅作为汽油的防爆剂,还可以制造汽油醇.这一巨大的潜在需求促使人们去寻找提高乙醇工业生产率的途径,使人们着手于发酵工程的研究. ...
- Simulink仿真入门到精通(十九) 总结回顾&自我练习
从2019年12月27到2020年2月12日,学习了Simulink仿真及代码生成技术入门到精通,历时17天. 学习的比较粗糙,有一些地方还没理解透彻,全书梳理总结: Simulink的基础模块已基本 ...
- Simulink仿真入门到精通(十七) Simulink代码生成技术详解
17.1 基于模型的设计 基于模型设计是一种流程,较之传统软件开发流程而言,使开发者能够更快捷.更高效地进行开发.适用范围包括汽车电子信号处理.控制系统.通信行业和半导体行业. V字模型开发流程整体描 ...
- Simulink仿真入门到精通(五) Simulink模型的仿真
5.1 模型的配置仿真 由各种模块所构建的可视化逻辑连接,只是模型的外在表现,模型仿真的核心驱动器是被称作解算器(Solver)的组件,相当于Simulink仿真过程的心脏,驱动着模型仿真,它在每一个 ...
- Simulink仿真入门到精通(二) Simulink模块
2.1 Simulink模块的组成要素 用户构建系统模型时无需直接面对成千上万行的代码,而是通过模块化图形界面以模块化的方式构建,能够使理解变得容易,让大脑减负.通过层次化模块分布将系统功能模块化,而 ...
- Simulink仿真入门到精通(十一) 模块的封装
当用户编写了自定义的S函数或者使用Simulink标准库中的模块搭建子系统后,可以通过封装为其设计显示外观,追加参数对话框. 封装是构建一个以对话框为接口的交互界面的过程,它将复杂的模块逻辑关系隐藏起 ...
- Simulink仿真入门到精通(四) Simulink子系统
4.1 Simulink子系统详解 4.1.1 子系统概述 Simulink根据仿真特性将模块的属性分为两种:虚拟模块和非虚拟模块. 非虚拟模块在仿真过程中起到实际的作用,对其进行编辑或者增加删除操作 ...
随机推荐
- Linux把内存挂载成硬盘提高读写速度
tmpfs是一种虚拟内存文件系统正如这个定义它最大的特点就是它的存储空间在VM里面,这里提一下VM(virtual memory),VM是由linux内核里面的vm子系统管理,现在大多数操作系统都采用 ...
- python语法基础-函数-基础-长期维护
############### 函数的定义调用,返回值和返回值接收 ############## def mylen(): s = "myname" i = 0 for ...
- ORs-5-OR Subgenomes Variation among Birds, Sea Turtle and Alligator
OR Subgenomes Variation among Birds, Sea Turtle and Alligator 由 该图数据计算每种鸟的relative percentage,得到下图: ...
- 7)加了基础控制器Controller.php
文件目录展示: 改动代码展示: Controller.php <?php /** * Created by PhpStorm. * User: Interact * Date: 2017/8/2 ...
- MOOC(7)- case依赖、读取json配置文件进行多个接口请求-模拟接口响应数据(18)
这里是把传入的请求数据作为响应值返回 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # @Time : 2020/2/15 9:47 # @File : do_mock_18.py # @Autho ...
- the Uneducated are|anymore|that| so as to |die from|die of|
定冠词加上某些形容词可以泛指一类人,谓语动词一般用复数形式,the uneducated泛指未受过教育的人, the Uneducated are more to be pitied than bla ...
- Android开发之《实现类似Toast可以自动消失的提示栏Tip》
import java.util.Timer; import java.util.TimerTask; import android.app.Activity; import android.cont ...
- Pycharm 2019 破解激活方法
转载:https://blog.csdn.net/guofang110/article/details/87793264 使用破解补丁方法虽然麻烦,但是可用激活到2099年,基本上是永久激活了,毕竟在 ...
- 将js进行到底:node学习9
node.js数据库篇--Mongoose ODM 介绍mongoose 几乎所有的语言都有原生数据库连接驱动,这个我们上一回已经了解了,比如java的jdbc,mysql-connector,但是实 ...
- LG承认手机业务遭到中国厂商碾压!这是输得心服口服的节奏?
近日,关于LG手机业退出中国市场的消息传的沸沸洋洋.不少相关媒体也对此事向LG北京办事处求证,得到的结果确实是手机业务退出中国市场.并且据韩媒报道,LG还将会逐渐取消高端手机业务,也就是说未来V系列和 ...
