Java的clone方法效率问题
在Java中,经常会需要新建一个对象,很多情况下,需要这个新建的对象和现有的某个对象保持属性一致。
那么,就有两种方式来实现这个对象的构造:
①通过新建一个对象,为这个对象的属性根据原有对象的属性来进行赋值
②调用clone方法,来实现实例对象的克隆
对于Java的clone方法,需要注意的就是它实际上是一种“浅克隆”(Shallow Clone),对于int、double这种基本数据类型,直接拷贝值;对于String这样的类对象,则是直接拷贝引用。因此对于通过clone得到的对象来说,它很大程度上还是和原有被克隆对象之间有着很大的联系(例如修改clone对象的String属性,则原有对象的String属性也会变化)。
于是,为了得到两个完全“独立”的具有相同属性的实例对象,就涉及到“深克隆”(Deep Clone)。至于如何来编写实现“深克隆”,可参考这篇博客(来自大学同学朱大佬分享): https://blog.csdn.net/zhangjg_blog/article/details/18369201
当然,至此要说明的重点并不是如何实现“深克隆”和“浅克隆”,而是要比较一下上面提到的①②两种方法,哪种效率更高一些。
首先,对于“浅克隆”来进行测试:
注:这里的SimpleTest类只包含一个name属性(String型),而Test类则包括name以及line0~line9这11个属性(均为String型)。这里让这些属性值在构造器中完成初始化。
测试代码:
说明: 这里分别对四种情况进行测试:
1). 简单的“浅克隆”,通过用SimpleTest的“浅克隆”来进行测试
2). 简单的“构造”,通过用SimpleTest的构造器来实例对象,其name值,直接通被克隆对象的name值来获取
3). 复杂的“浅克隆”,通过Test的“浅克隆”来进行测试
4). 复杂的“构造”,通过正常构造Test,来获得Test实例,需要注意的就是,此时Test的构造器内涉及到一系列的new操作(代表复杂构造操作)
测试结果:

结果说明:
①对于轻量型的类对象,通过new操作来构造,效率会更高(对比987ms和7ms)。
②对于重量型的类对象,通过clone操作来进行构造,效率会更高(对比1016ms和4503ms)。
原因分析:
①对于轻量型的类对象,通过new操作即可很快地进行构造,而clone方法依旧涉及到new操作,但其会进行更多的方法调用,执行流程会消耗一些时间
②对于重量型的类对象,new操作则需要构造相当多的对象,从而会消耗很多时间;但clone方法(这里是“浅克隆”)只需要拷贝引用给新的对象即可,因此消耗的时间会更少
但是,这只是对于“浅克隆”来说,clone的构造效率会更高,但对于“深克隆”来说,情况却并不乐观。
首先,按照前面提到的那篇博客,来进一步构造深克隆:
class Person implements Cloneable {
public int age;
public String name;
public Body body;
public Person(int age, String name, Body body) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
this.body = body;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Person newPerson = (Person)super.clone();
newPerson.body = (Body)body.clone();
return newPerson;
}
}
class Body implements Cloneable {
public Head head;
public Body(Head head) {
this.head = head;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Body newBody = (Body)super.clone();
newBody.head = (Head)head.clone();
return newBody;
}
}
class Head implements Cloneable {
public Face face;
public Head(Face face) {
this.face = face;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Head newHead = (Head)super.clone();
newHead.face = (Face)face.clone();
return newHead;
}
}
class Face implements Cloneable {
public Mouth mouth;
public Face(Mouth mouth) {
this.mouth = mouth;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Face newFace = (Face)super.clone();
newFace.mouth = (Mouth)mouth.clone();
return newFace;
}
}
class Mouth implements Cloneable {
public Tooth tooth;
public Mouth(Tooth tooth) {
this.tooth = tooth;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Mouth newMouth = (Mouth)super.clone();
newMouth.tooth = (Tooth)tooth.clone();
return newMouth;
}
}
class Tooth implements Cloneable {
public final int number;
public Tooth(int number) {
this.number = number;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
Deep Clone
测试代码:
// 测试Deep Clone/New 的测试代码
Person person1 = new Person(20, "Test", new Body(new Head(new Face(new Mouth(new Tooth(32)))))); Person person2 = null;
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i = 0; i < 100000000; i++)
person2 = (Person)person1.clone();
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Deep Clone : " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms"); System.out.println();
System.out.println("person1 == person2: " + (person1 == person2));
System.out.println(); System.out.println("person1.age == person2.age: " + (person1.age == person2.age));
System.out.println("person1.name == person2.age: " + (person1.name == person2.name));
System.out.println(); System.out.println("person1.body == person2.body: " + (person1.body == person2.body));
System.out.println("person1.body.head == person2.body.head: " + (person1.body.head == person2.body.head));
System.out.println("person1.body.head.face == person2.body.head.face: " + (person1.body.head.face == person2.body.head.face));
System.out.println("person1.body.head.face.mouth == person2.body.head.face.mouth: "
+ (person1.body.head.face.mouth == person2.body.head.face.mouth));
System.out.println("person1.body.head.face.mouth.tooth == person2.body.head.face.mouth.tooth: "
+ (person1.body.head.face.mouth.tooth == person2.body.head.face.mouth.tooth));
System.out.println("person1.body.head.face.mouth.tooth.number == person2.body.head.face.mouth.tooth.number: "
+ (person1.body.head.face.mouth.tooth.number == person2.body.head.face.mouth.tooth.number));
System.out.println(); Person person3 = null;
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i = 0; i < 100000000; i++) {
Tooth tooth = new Tooth(person1.body.head.face.mouth.tooth.number);
Mouth mouth = new Mouth(tooth);
Face face = new Face(mouth);
Head head = new Head(face);
Body body = new Body(head);
person3 = new Person(20, "Test", body);
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Deep New : " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms"); System.out.println();
System.out.println("person1 == person3: " + (person1 == person3));
System.out.println(); System.out.println("person1.age == person3.age: " + (person1.age == person3.age));
System.out.println("person1.name == person3.age: " + (person1.name == person3.name));
System.out.println(); System.out.println("person1.body == person3.body: " + (person1.body == person3.body));
System.out.println("person1.body.head == person3.body.head: " + (person1.body.head == person3.body.head));
System.out.println("person1.body.head.face == person3.body.head.face: " + (person1.body.head.face == person3.body.head.face));
System.out.println("person1.body.head.face.mouth == person3.body.head.face.mouth: "
+ (person1.body.head.face.mouth == person3.body.head.face.mouth));
System.out.println("person1.body.head.face.mouth.tooth == person3.body.head.face.mouth.tooth: "
+ (person1.body.head.face.mouth.tooth == person3.body.head.face.mouth.tooth));
System.out.println("person1.body.head.face.mouth.tooth.number == person3.body.head.face.mouth.tooth.number: "
+ (person1.body.head.face.mouth.tooth.number == person3.body.head.face.mouth.tooth.number));
System.out.println();
完整测试代码
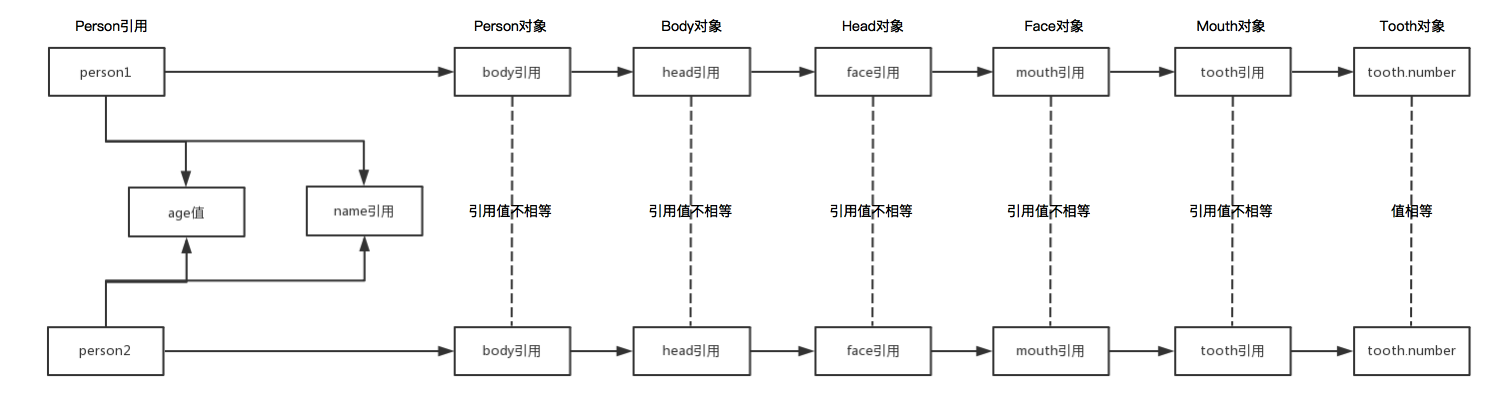
按照这个结构,深克隆得到的对象和原有对象的关系如图:
测试结果:
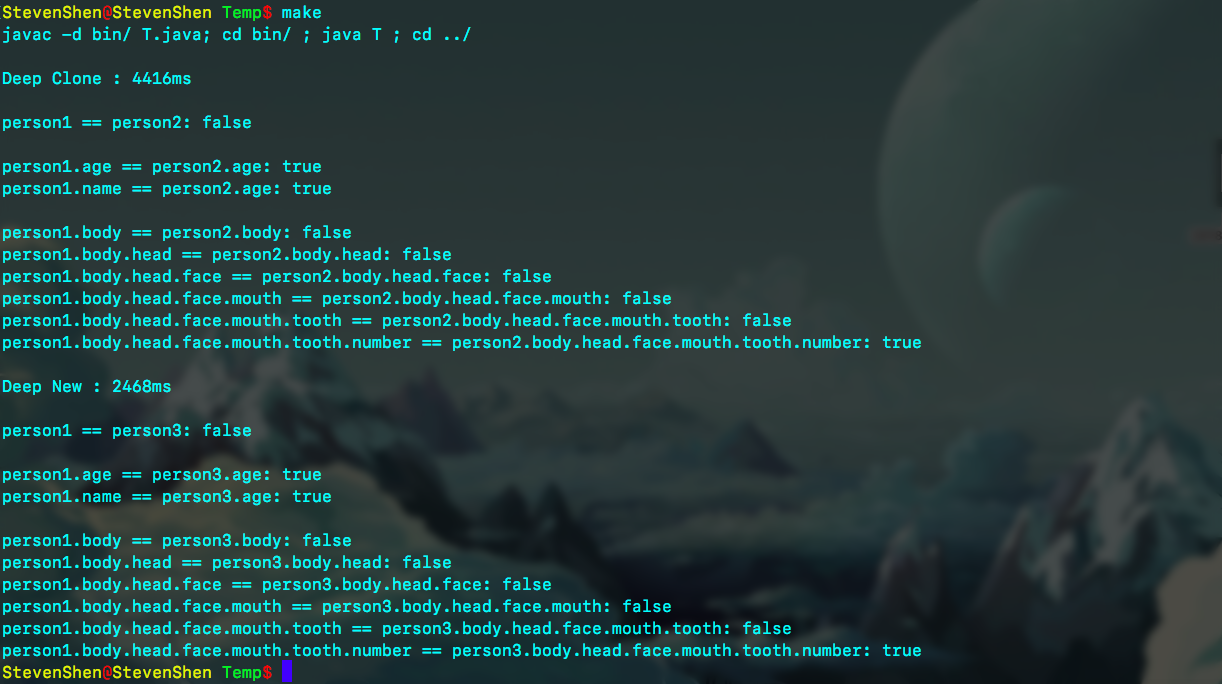
注: 这里的person3是通过new来构造的对象,其内部包含的每个引用对象(不包括其name),均是通过new来进行构造的。
结论: 可以发现,“深克隆”并没有提高克隆的效率!相反,这种方法此时比通过new构造对象的方法效率还低。
原因分析: 就和上面的测试一样: 此处的“深克隆”依旧会通过new的方法来不断构造对象,因而本质上并没有提高效率(不似“浅克隆”一般直接复制引用即可),反而由于操作流程的层层调用,使得其执行速度不如new构造对象的方法快。
至此,基本可以确定,clone方法只有在进行复杂的“浅克隆”时效率才会明显高于new构造方式,但由于此时的克隆本质上依旧是“浅克隆”,因此需要注意引用的指向问题,避免错误更改关联的信息值。
但是,对于测试一来说,这个比较是不全面的。因为浅克隆本质上,只是把类中的引用复制到新的对象属性中,而该测试中,new构造的对象的内部引用则是完全“独立”的。
因此,为了测试clone方法的“浅克隆”方式是否真正会提高效率,还要进行测试:
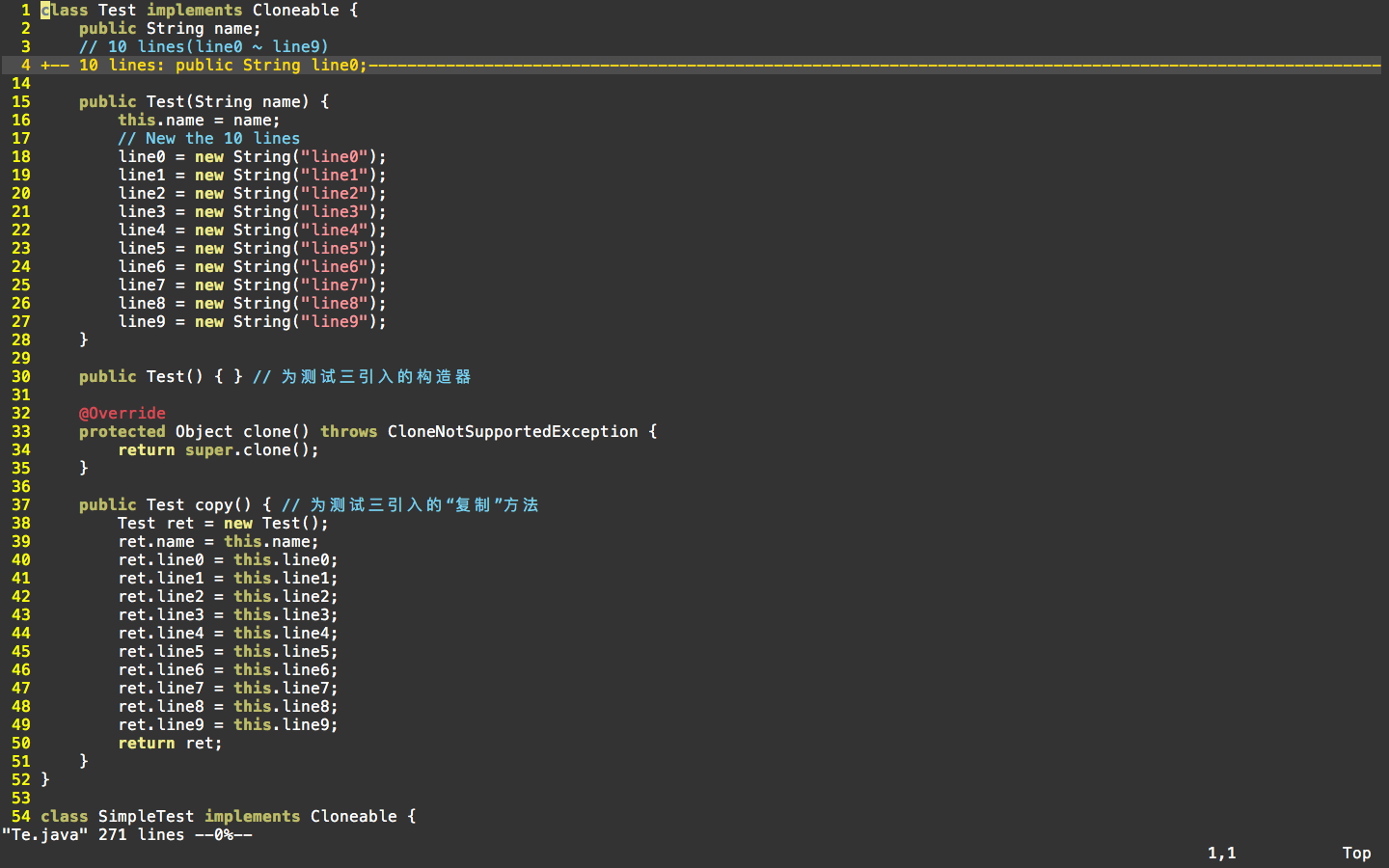
这里,更改了Test类的代码,为Test新增了一种构造器,便于构造对象;为Test新增了copy方法,该方法只是构建一个新的Test对象,并将自身的所有属性引用拷贝到这个新的对象属性中。
代码如图:
测试代码:
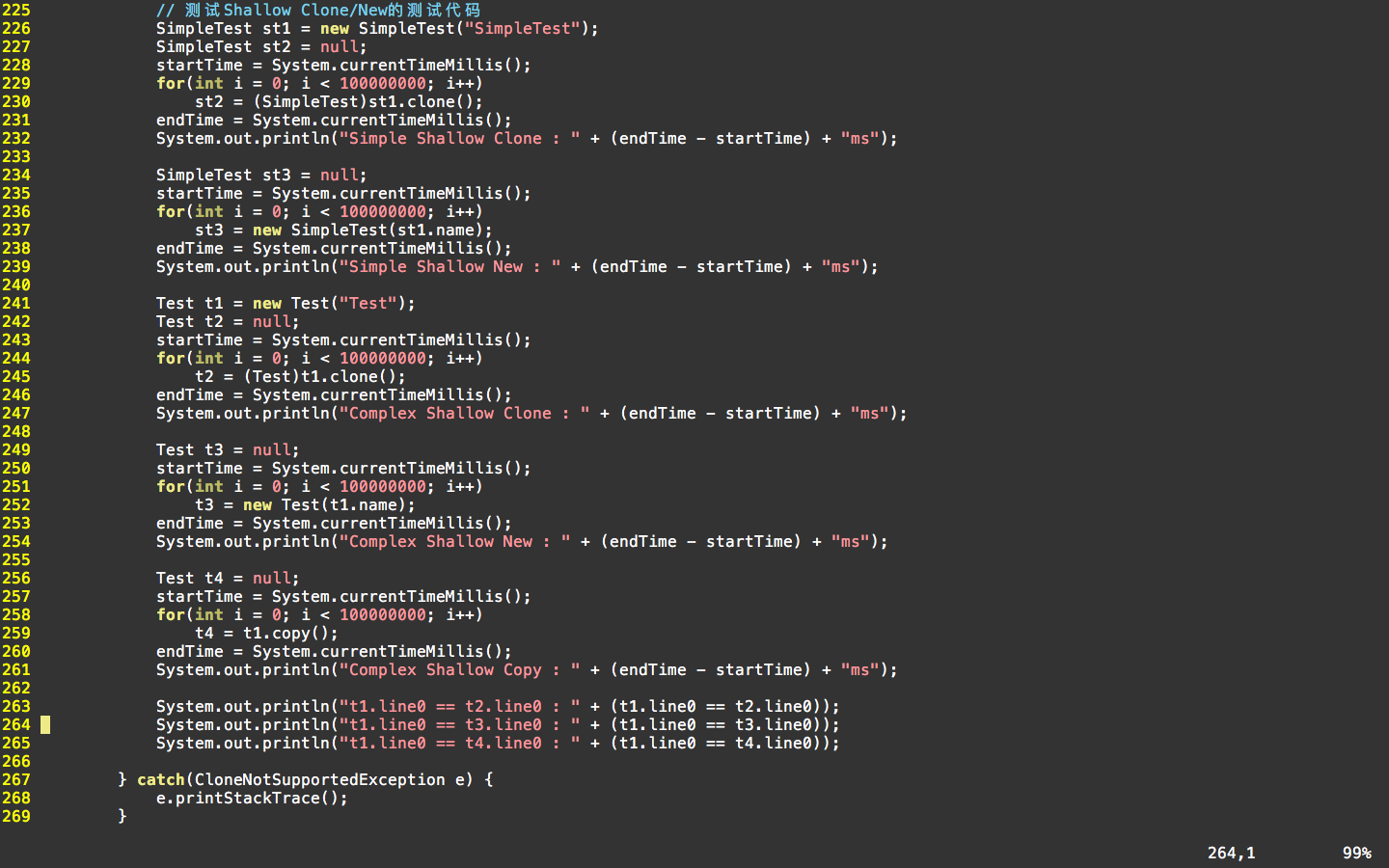
说明: 在原有测试代码的基础上,新增了测试对象t4,该对象的属性值通过调用copy方法来获得。当然,这里的copy实现的就是“浅克隆”的过程,即仅仅复制引用。
最后会打印三行信息:反映对于类内属性是否为真正的克隆。如果返回值为true,则表明line0引用指向的是相同空间,为“浅克隆”;如果返回值为false,则表明为真克隆,即对象真正隔离。
测试结果:

结论: 对于复杂的“浅克隆”,通过Copy的方式可实现类似Clone的实现(可以看到,Copy方法和Clone方法都是将引用直接拷贝),但是效率并没有Clone高(多次测试都是如此),这才是真正体现了Clone方法效率高的测试。
需要注意的是,clone尽管默认是“浅克隆”,但是依旧有很多应用情况。clone方法,可以将原有对象的private属性的信息也克隆下来,需要对此注意。
通过查阅stackoverflow,可以看到更多关于这方面的内容,其中也包括clone方法的应用场合(例如GUI面板等)。
最后,附上这篇博客的所有代码:
class Test implements Cloneable {
public String name;
// 10 lines(line0 ~ line9)
public String line0;
public String line1;
public String line2;
public String line3;
public String line4;
public String line5;
public String line6;
public String line7;
public String line8;
public String line9;
public Test(String name) {
this.name = name;
// New the 10 lines
line0 = new String("line0");
line1 = new String("line1");
line2 = new String("line2");
line3 = new String("line3");
line4 = new String("line4");
line5 = new String("line5");
line6 = new String("line6");
line7 = new String("line7");
line8 = new String("line8");
line9 = new String("line9");
}
public Test() { } // 为测试三引入的构造器
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
public Test copy() { // 为测试三引入的“复制”方法
Test ret = new Test();
ret.name = this.name;
ret.line0 = this.line0;
ret.line1 = this.line1;
ret.line2 = this.line2;
ret.line3 = this.line3;
ret.line4 = this.line4;
ret.line5 = this.line5;
ret.line6 = this.line6;
ret.line7 = this.line7;
ret.line8 = this.line8;
ret.line9 = this.line9;
return ret;
}
}
class SimpleTest implements Cloneable {
public String name;
public SimpleTest(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
class Person implements Cloneable {
public int age;
public String name;
public Body body;
public Person(int age, String name, Body body) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
this.body = body;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Person newPerson = (Person)super.clone();
newPerson.body = (Body)body.clone();
return newPerson;
}
}
class Body implements Cloneable {
public Head head;
public Body(Head head) {
this.head = head;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Body newBody = (Body)super.clone();
newBody.head = (Head)head.clone();
return newBody;
}
}
class Head implements Cloneable {
public Face face;
public Head(Face face) {
this.face = face;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Head newHead = (Head)super.clone();
newHead.face = (Face)face.clone();
return newHead;
}
}
class Face implements Cloneable {
public Mouth mouth;
public Face(Mouth mouth) {
this.mouth = mouth;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Face newFace = (Face)super.clone();
newFace.mouth = (Mouth)mouth.clone();
return newFace;
}
}
class Mouth implements Cloneable {
public Tooth tooth;
public Mouth(Tooth tooth) {
this.tooth = tooth;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Mouth newMouth = (Mouth)super.clone();
newMouth.tooth = (Tooth)tooth.clone();
return newMouth;
}
}
class Tooth implements Cloneable {
public final int number;
public Tooth(int number) {
this.number = number;
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
public class T {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 测试Deep Clone/New 的测试代码
Person person1 = new Person(20, "Test", new Body(new Head(new Face(new Mouth(new Tooth(32))))));
Person person2 = null;
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i = 0; i < 100000000; i++)
person2 = (Person)person1.clone();
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Deep Clone : " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
System.out.println();
System.out.println("person1 == person2: " + (person1 == person2));
System.out.println();
System.out.println("person1.age == person2.age: " + (person1.age == person2.age));
System.out.println("person1.name == person2.age: " + (person1.name == person2.name));
System.out.println();
System.out.println("person1.body == person2.body: " + (person1.body == person2.body));
System.out.println("person1.body.head == person2.body.head: " + (person1.body.head == person2.body.head));
System.out.println("person1.body.head.face == person2.body.head.face: " + (person1.body.head.face == person2.body.head.face));
System.out.println("person1.body.head.face.mouth == person2.body.head.face.mouth: "
+ (person1.body.head.face.mouth == person2.body.head.face.mouth));
System.out.println("person1.body.head.face.mouth.tooth == person2.body.head.face.mouth.tooth: "
+ (person1.body.head.face.mouth.tooth == person2.body.head.face.mouth.tooth));
System.out.println("person1.body.head.face.mouth.tooth.number == person2.body.head.face.mouth.tooth.number: "
+ (person1.body.head.face.mouth.tooth.number == person2.body.head.face.mouth.tooth.number));
System.out.println();
Person person3 = null;
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i = 0; i < 100000000; i++) {
Tooth tooth = new Tooth(person1.body.head.face.mouth.tooth.number);
Mouth mouth = new Mouth(tooth);
Face face = new Face(mouth);
Head head = new Head(face);
Body body = new Body(head);
person3 = new Person(20, "Test", body);
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Deep New : " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
System.out.println();
System.out.println("person1 == person3: " + (person1 == person3));
System.out.println();
System.out.println("person1.age == person3.age: " + (person1.age == person3.age));
System.out.println("person1.name == person3.age: " + (person1.name == person3.name));
System.out.println();
System.out.println("person1.body == person3.body: " + (person1.body == person3.body));
System.out.println("person1.body.head == person3.body.head: " + (person1.body.head == person3.body.head));
System.out.println("person1.body.head.face == person3.body.head.face: " + (person1.body.head.face == person3.body.head.face));
System.out.println("person1.body.head.face.mouth == person3.body.head.face.mouth: "
+ (person1.body.head.face.mouth == person3.body.head.face.mouth));
System.out.println("person1.body.head.face.mouth.tooth == person3.body.head.face.mouth.tooth: "
+ (person1.body.head.face.mouth.tooth == person3.body.head.face.mouth.tooth));
System.out.println("person1.body.head.face.mouth.tooth.number == person3.body.head.face.mouth.tooth.number: "
+ (person1.body.head.face.mouth.tooth.number == person3.body.head.face.mouth.tooth.number));
System.out.println();
// 测试Shallow Clone/New的测试代码
SimpleTest st1 = new SimpleTest("SimpleTest");
SimpleTest st2 = null;
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i = 0; i < 100000000; i++)
st2 = (SimpleTest)st1.clone();
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Simple Shallow Clone : " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
SimpleTest st3 = null;
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i = 0; i < 100000000; i++)
st3 = new SimpleTest(st1.name);
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Simple Shallow New : " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
Test t1 = new Test("Test");
Test t2 = null;
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i = 0; i < 100000000; i++)
t2 = (Test)t1.clone();
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Complex Shallow Clone : " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
Test t3 = null;
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i = 0; i < 100000000; i++)
t3 = new Test(t1.name);
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Complex Shallow New : " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
Test t4 = null;
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i = 0; i < 100000000; i++)
t4 = t1.copy();
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Complex Shallow Copy : " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
System.out.println("t1.line0 == t2.line0 : " + (t1.line0 == t2.line0));
System.out.println("t1.line0 == t3.line0 : " + (t1.line0 == t3.line0));
System.out.println("t1.line0 == t4.line0 : " + (t1.line0 == t4.line0));
} catch(CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
T.java
Java的clone方法效率问题的更多相关文章
- Java基础——clone()方法浅析
一.clone的概念 clone顾名思义就是复制, 在Java语言中, clone方法被对象调用,所以会复制对象.所谓的复制对象,首先要分配一个和源对象同样大小的空间,在这个空间中创建一个新的对象.那 ...
- Java中clone方法的使用
什么是clone 在实际编程过程中,我们常常要遇到这种情况:有一个对象object1,在某一时刻object1中已经包含了一些有效值,此时可能会需要一个和object1完全相同新对象object2,并 ...
- 分析java中clone()方法 (转载+修改)
Java中的clone() 方法 java所有的类都是从java.lang.Object类继承而来的,而Object类提供下面的方法对对象进行复制. protected native Object c ...
- java的clone()方法
什么是"clone"? 在实际编程过程中,我们常常要遇到这种情况:有一个对象A,在某一时刻A中已经包含了一些有效值,此时可能 会需要一个和A完全相同新对象B,并且此后对B任何改动都 ...
- Java 的 clone 方法 && 浅复制和深复制
1 Java中对象的创建过程 java创建对象的方式有以下两种: (1)使用new操作符创建一个对象 (2)使用clone的方法复制一个对象,(在Java中,clone是Object类的protect ...
- Java的clone方法
现在有User类:(Getter和Setter省略) public class User implements Cloneable { private String name; private int ...
- java的 clone方法
1.java语言中没有明确提供指针的概念与用法,而实质上每个new语句返回的都是一个指针的引用,只不过在大部分情况下开发人员不需要关心如果取操作这个指针而已. 2.在java中处理基本数据类型时,都是 ...
- 详解Java中的clone方法
详解Java中的clone方法 参考:http://blog.csdn.net/zhangjg_blog/article/details/18369201/ 所谓的复制对象,首先要分配一个和源对象同样 ...
- Object类clone方法的自我理解
网上搜帖: clone()是java.lang.Object类的protected方法,实现clone方法: 1)类自身需要实现Cloneable接口 2)需重写clone()方法,最好设置修饰符mo ...
随机推荐
- [JLOI2009]神秘的生物
题目链接 题目大意 给定一个\(n*n\)的矩阵,从其中选取恰好一个连通块,使选取的格子所对应的权值和最大. \(n\leq 9\) 解题思路 由于\(n\)特别小,考虑插头dp. 和一般的插头dp不 ...
- 超长干货丨Kubernetes网络快速入门完全指南
Kubernetes网络一直是一个非常复杂的主题.本文将介绍Kubernetes实际如何创建网络以及如何为Kubernetes集群设置网络. 本文不包括如何设置Kubernetes集群.这篇文章中的所 ...
- 简单oracle查询语句转换为mongo查询语句
可以将简单的单表查询语句转换成Mongo过滤条件 列: 1. db.demo.aggregate([ {"$match": {"$and": [{"p ...
- rsync安装与配置使用 数据同步方案(centos6.5)
rsync + crond ==定时数据同步 sersync(inotify) + rsync ==实时数据同步,利用rsync实现 ##应用场景 ..1 主备服务器之间同步数据定时 = ...
- MS17_010漏洞攻击Windows7
攻击主机系统:Kali Linux 2018 目标主机系统:Windows7 x64 1.攻击主机启动Metasploit: msfconsole 2.查找MS17_010漏洞相关的信息: searc ...
- CodeForces-220B Little Elephant and Array
小象喜欢玩数组.他有一个数组a,由n个正整数组成,从1到n进行索引.让我们用索引i表示数字ai. 此外,小象对数组还有m个查询,每个查询的特征是一对整数lj和rj(1 ≤ lj ≤ rj ≤ n).对 ...
- JAVA分级测试——选课系统(补发)
博客园似乎上传图片多了之后会出现各种问题,所以只能直接上代码了 <!DOCTYPE HTML> <html lang="zh"> <head> ...
- JSP页面输入框赋值换行显示问题
<input type="hidden" id="${command.yhzlId}" value="${command.yhzx },${co ...
- 误删Django的model中的表解决办法
误删Django的model中的表解决办法 1.model里面的表格实际的操作都在migrations文件夹中,里面记录了操作过程,当在database和model中删除表格时要注意初始化数据库时会报 ...
- 一文解读RISC与CISC (转)
RISC(精简指令集计算机)和CISC(复杂指令集计算机)是当前CPU的两种架构.它们的区别在于不同的CPU设计理念和方法. 早期的CPU全部是CISC架构,它的设计目的是要用最少的机器语言指令来完成 ...
