标准库sys
sys模块的主要函数介绍,结合官方文档说明和实例。This module provides access to some variables used or maintained by the interpreter and to functions that interact strongly with the interpreter. It is always available.
以下是主要的函数的的主要功能介绍:
sys.argv 命令行参数List,第一个元素是程序本身路径sys.exit(n) 退出程序,正常退出时exit(0)sys.platform 返回操作系统平台名称sys.stdout.write('please:') val = sys.stdin.readline()[:-1] sys 模块提供了许多函数和变量来处理 Python 运行时环境的不同部分.
处理命令行参数 sys.argv
sys模块包含系统对应的功能。我们已经学习了sys.argv列表,它包含命令行参数。
在解释器启动后, argv 列表包含了传递给脚本的所有参数, 列表的第一个元素为脚本自身的名称.
sys.argv
The list of command line arguments passed to a Python script. argv[0] is the script name (it is operating system dependent whether this is a full pathname or not). If the command was executed using the -c command line option to the interpreter, argv[0] is set to the string '-c'. If no script name was passed to the Python interpreter, argv[0] is the empty string.
To loop over the standard input, or the list of files given on the command line, see the fileinput module.
import sys
print('--->',sys.argv)
print('sys.argv[0]',sys.argv[0])
print('sys.argv[1:]',sys.argv[1:])
在cmd中运行该脚本,在脚本os_func.py 后面输入 1 2 3,这些会传入sys.argv列表中。
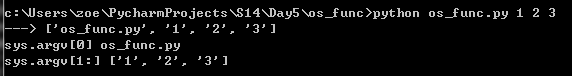
使用sys.argv的实例(转载改版为Python3.x):
import sys
def readfile(filename): #定义readfile函数,从文件中读出文件内容
'''''''''Print a file to the standard output.'''
f = open('test.txt')
while True:
line = f.readline()
if len(line) == 0:
break
print(line,)# notice comma 分别输出每行内容 f.close()
# Script starts from here
print(sys.argv)
if len(sys.argv) < 2:
print('No action specified.')
sys.exit()
if sys.argv[1].startswith('--'):
option = sys.argv[1][2:]
# fetch sys.argv[1] but without the first two characters
if option == 'version': #当命令行参数为-- version,显示版本号
print('Version 1.2')
elif option == 'help': #当命令行参数为--help时,显示相关帮助内容
print('''
This program prints files to the standard output.
Any number of files can be specified.
Options include:
--version : Prints the version number
--help : Display this help''')
else:
print('Unknown option.')
sys.exit()
else:
for filename in sys.argv[1:]: #当参数为文件名时,传入readfile,读出其内容
readfile(filename)
上面的脚本名称在我的系统文件中命名为os_func.py(虽然没对应好,但懒得改了)。同时在os_func.py文件的同一目录下,新建文件test.txt.

在CMD中运行os_func.py脚本:
1.直接运行os_func.py脚本,返回os_func.py的路径。

上面的代码执行的为是脚本中的这一段内容:

2.运行os_func.py脚本时,在后面加上参数 --version

上面的命令执行的是脚本中的当传入的参数大于等于2时,sys.argv[1]中的参数为‘--version',对字符串进行截取,判断截取的为'version'后,执行相应命令。

3.下面的命令执行原理同上2

4.在执行 os_func.py后面加上文件名(可以叠加:python os_func.py test.txt test2.txt test3.txt)会执行相应的脚本内容,读取文件内容

上面的命令执行的是脚本中的当传入的参数判断为文件名。

sys.exit([arg])
官方文档:
sys.exit([arg])
Exit from Python. This is implemented by raising the SystemExit exception, so cleanup actions specified by finally clauses of try statements are honored, and it is possible to intercept the exit attempt at an outer level.
The optional argument arg can be an integer giving the exit status (defaulting to zero), or another type of object. If it is an integer, zero is considered “successful termination” and any nonzero value is considered “abnormal termination” by shells and the like. Most systems require it to be in the range 0–127, and produce undefined results otherwise. Some systems have a convention for assigning specific meanings to specific exit codes, but these are generally underdeveloped; Unix programs generally use 2 for command line syntax errors and 1 for all other kind of errors. If another type of object is passed, None is equivalent to passing zero, and any other object is printed to stderr and results in an exit code of 1. In particular, sys.exit("some error message") is a quick way to exit a program when an error occurs.
Since exit() ultimately “only” raises an exception, it will only exit the process when called from the main thread, and the exception is not intercepted.
Changed in version 3.6: If an error occurs in the cleanup after the Python interpreter has caught SystemExit (such as an error flushing buffered data in the standard streams), the exit status is changed to 120.
可选参数[arg],默认为0,可以通过传入不同的整数或其他指定参数作为指定不同的退出状态。如果传入的是整数,0代表“成功终止”,任何非零值在shell中被认为是“异常终止”。大多数系统要求它在0 - 127范围内,否则就生成未定义的结果。有些系统有一种约定,可以为特定的退出代码分配特定的含义,但是这些通常不发达;Unix程序通常使用2来表示命令行语法错误,1用于所有其他类型的错误。如果传递了另一种类型的对象,则没有一种对象是通过0传递的,任何其他对象都被打印到stderr中,结果为1的退出码。特别是,系统。退出(“一些错误消息”)是在错误发生时退出程序的快速方法。
由于退出()最终只引发了一个异常,它只会在从主线程调用时退出进程,并且不拦截异常。
在版本3.6中更改的部分:如果在Python解释器捕获SystemExit之后的清理中出现错误(例如在标准流中的错误刷新缓冲数据),退出状态将更改为120
sys.version
A string containing the version number of the Python interpreter plus additional information on the build number and compiler used. This string is displayed when the interactive interpreter is started. Do not extract version information out of it, rather, use version_info and the functions provided by the platform module.

包含Python解释器的版本号,以及用于构建数字和编译器的附加信息的字符串。这个字符串在交互式解释器启动时显示。不要从中提取版本信息,而是使用版本信息和平台模块提供的功能提取版本信息。
sys.path
A list of strings that specifies the search path for modules. Initialized from the environment variable PYTHONPATH, plus an installation-dependent default.
As initialized upon program startup, the first item of this list, path[0], is the directory containing the script that was used to invoke the Python interpreter. If the script directory is not available (e.g. if the interpreter is invoked interactively or if the script is read from standard input), path[0] is the empty string, which directs Python to search modules in the current directory first. Notice that the script directory is inserted before the entries inserted as a result of PYTHONPATH.
A program is free to modify this list for its own purposes. Only strings and bytes should be added to sys.path; all other data types are ignored during import.
sys.path()返回指定模块搜索路径的字符串列表。从环境变量PYTHONPATH初始化,并依赖于安装的默认值。
在程序启动时初始化时,该列表的第一项(path[0])是包含用于调用Python解释器的脚本的目录。如果脚本目录不可用(例如,如果解释器是交互调用的,或者如果脚本是从标准输入中读取的),那么path[0]是空字符串,它会将Python定向到当前目录中的搜索模块。注意,脚本目录插入到插入的条目之前,是python路径的结果。

由于在cmd中运行python的交互环境,没有执行相应的python脚本,故path[0]返回的值为'[]',返回一个空字符串。
sys.maxsize-
An integer giving the maximum value a variable of type
Py_ssize_tcan take. It’s usually2**31 - 1on a 32-bit platform and2**63 - 1on a 64-bit platform.一个整数,给出了一个Py_ssize_t类型变量的最大值。在32位平台上它通常是2 * * 31 - 1,在64位平台上它通常是2 * * 63 - 1。
sys.platform
This string contains a platform identifier that can be used to append platform-specific components to sys.path, for instance.
For Unix systems, except on Linux, this is the lowercased OS name as returned by uname -s with the first part of the version as returned by uname -r appended, e.g. 'sunos5' or 'freebsd8', at the time when Python was built. Unless you want to test for a specific system version, it is therefore recommended to use the following idiom:
if sys.platform.startswith('freebsd'):
# FreeBSD-specific code here...
elif sys.platform.startswith('linux'):
# Linux-specific code here...
For other systems, the values are:
| System | platform value |
|---|---|
| Linux | 'linux' |
| Windows | 'win32' |
| Windows/Cygwin | 'cygwin' |
| Mac OS X | 'darwin' |
Changed in version 3.3: On Linux, sys.platform doesn’t contain the major version anymore. It is always 'linux', instead of 'linux2' or 'linux3'. Since older Python versions include the version number, it is recommended to always use the startswith idiom presented above.
See also
os.name has a coarser granularity. os.uname() gives system-dependent version information.
The platform module provides detailed checks for the system’s identity.
标准库sys的更多相关文章
- Python——标准库 Sys模块
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ...
- Python3 标准库:sys
import sys print(sys.argv[0]) print(sys.argv[1]) print(len(sys.argv)) print(str(sys.argv)) print(sys ...
- Python标准库sys
1.命令行参数sys.argv 我们从Python语言之模块第一部分的例子开始,看看sys.argv中到底存了些什么内容. #Filename: using_sys.py import sys i=0 ...
- A Byte of Python 笔记(12)python 标准库:sys、os,更多内容
第14章 python 标准库 Python标准库是随Python附带安装的,它包含大量极其有用的模块. sys 模块 sys 模块包含系统对应的功能.如 sys.argv 列表包含命令行参数. # ...
- python基础课程_学习笔记13:标准库:有些收藏夹——sys
标准库:有些收藏夹 sys sys这个模块可以让你访问和python解释器联系紧密的变量和函数. sys模块中一些重要的函数和变量 函数/变量 描写叙述 argv 命令行參数,包含脚本名称 exit( ...
- 介绍下Python的两个标准库 os 和 sys
import sysprint(sys.path) #python 2 中报错 ....,打印的是绝对路径(***\\python\\lib\\site-packages# 第三方库,后退一级为标准库 ...
- python练习 - 系统基本信息获取(sys标准库)+ 二维数据表格输出(tabulate库)
系统基本信息获取 描述 获取系统的递归深度.当前执行文件路径.系统最大UNICODE编码值等3个信息,并打印输出. ...
- python标准库00 学习准备
Python标准库----走马观花 python有一套很有用的标准库.标准库会随着python解释器一起安装在你的电脑上的.它是python的一个组成部分.这些标准库是python为你准备的利器,可以 ...
- 【循序渐进学Python】11.常用标准库
安装完Python之后,我们也同时获得了强大的Python标准库,通过使用这些标准库可以为我们节省大量的时间.这里是一些常用标准库的简单说明.更多的标准库的说明,可以参考Python文档 sys 模块 ...
随机推荐
- 悟懂MapReduce,不纠结!
在<谷歌 MapReduce 初探>中,我们通过统计词频的 WordCount 经典案例,对 Google 推出的 MapReduce 编程模型有了一个认识,但是那种认识,还只是停留在知道 ...
- 字符串学习笔记(二)---- StringBuffer
一.相关介绍 1.StringBuffer介绍 StringBuffer对象是字符串缓冲区对象,用于存放数据的容器 2.StringBuffer特点 StringBuffer(字符串缓冲区对象)的长度 ...
- Docker的MySQL镜像, 实行数据,配置信息,日志持久化
Docker的MySQL8镜像, 实行数据持久化 使用Docker的MySQL8.0.17实例化一个容器之后需要对其进行数据持久化操作, 使用 docker docker run -p 7797:33 ...
- git设置
1:注册码云2:点击个人主页创建私有项目3:下载git4:点击码云 头像 选择下方的设置-->点击左侧的SSH公钥-->怎样生成公钥(linux操作) window系统可以右击选择 git ...
- Azure多因素认证
什么是多重身份验证? 双重验证是需要多种验证方法的身份验证方法,可为用户登录和事务额外提供一层重要的安全保障. 它的工作原理是需要以下两种或多种验证方法: 用户知道的某样东西(通常为密码) 用户具有的 ...
- http之抽丝剥茧,深度剖析http的那些事儿
最近,小编一心扎跟学技术,毫不顾及头发的掉落速度,都快成地中海了,不过也无大碍,谁让咱是一个爱钻技术的男人呢.最近两周老是看到http,那么这个http,有哪些猫腻呢,很多同学都有这种理解,就是对于h ...
- 这些基本的 HTML5 标签你不能不知道
HTML5元素 HTML5是HTML最新的修订版本,2014年10月由万维网联盟(W3C)完成标准制定. HTML5是用来写网页的一门标记语言. 使用的时候需要在首行声明HTML,如:<!DOC ...
- 批处理 bat 查询局域网内在线电脑IP
查看自己局域网的IP和物理网卡地址可以在 WIN+R –> 打开cmd 键入 arp -a 可以看到局域网中所有的在线IP COLOR 0A CLS @ECHO Off Title 查询局域网内 ...
- protobuf总结
1.protobuf是什么? protobuf(protocol buffers)是一种语言中立,平台无关,可扩展的序列化数据的格式,可以用于通信协议,数据存储等. protobuf 相比于xml,j ...
- 8.4 StringBuilder的介绍及用法(String 和StringBuilder区别)
* StringBuilder:是一个可变的字符串.字符串缓冲区类.** String和StringBuilder的区别:* String的内容是固定的.(方法区的内容)* StringBuilder ...
