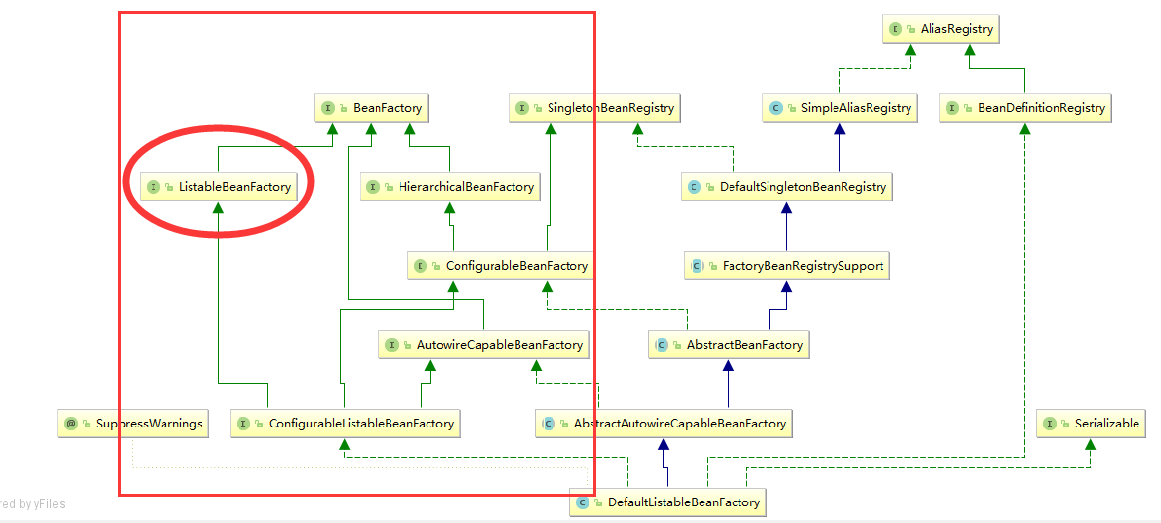
spring源码 ListableBeanFactory接口
ListableBeanFactory接口表示这些Bean是可列表的
/*
* Copyright 2002-2016 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ package org.springframework.beans.factory; import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.util.Map; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.core.ResolvableType; /**
* Extension of the {@link BeanFactory} interface to be implemented by bean factories
* that can enumerate all their bean instances, rather than attempting bean lookup
* by name one by one as requested by clients. BeanFactory implementations that
* preload all their bean definitions (such as XML-based factories) may implement
* this interface.
是BeanFactory接口的扩展,提供所有bean实例的枚举(列表),不再需要客户端通过一个个bean的name查找,BeanFactory
实现类预加载bean定义(如通过实现xml的工厂)需要实现这个接口
*
* <p>If this is a {@link HierarchicalBeanFactory}, the return values will <i>not</i>
* take any BeanFactory hierarchy into account, but will relate only to the beans
* defined in the current factory. Use the {@link BeanFactoryUtils} helper class
* to consider beans in ancestor factories too.
* 如果一样实现了HierarchicalBeanFactory,返回值不会考虑父类BeanFactory,只考虑当前factory定义的类
当然也可以使用BeanFactoryUtils辅助类来查找祖先工厂中的类。
* <p>The methods in this interface will just respect bean definitions of this factory.
* They will ignore any singleton beans that have been registered by other means like
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableBeanFactory}'s
* {@code registerSingleton} method, with the exception of
* {@code getBeanNamesOfType} and {@code getBeansOfType} which will check
* such manually registered singletons too. Of course, BeanFactory's {@code getBean}
* does allow transparent access to such special beans as well. However, in typical
* scenarios, all beans will be defined by external bean definitions anyway, so most
* applications don't need to worry about this differentiation.
*这个接口中的方法只会考虑本factory定义的Bean,这些方法会忽略ConfigurableBeanFactory的registerSingleton注册的单例bean,
getBeanNamesOfType和getBeansOfType是例外,一样会考虑手动注册的单例,当然beanFactory的getBean一样可以透明访问这些特殊bean
当然在典型情况下,所有的bean都是由external bean定义,所以引用不需要顾虑这些差别
* <p><b>NOTE:</b> With the exception of {@code getBeanDefinitionCount}
* and {@code containsBeanDefinition}, the methods in this interface
* are not designed for frequent invocation. Implementations may be slow.
*注意:getBeanDefinitionCount和ContainsBeanDefintion的实例方法因为效率比较低,并不供频繁调用的
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 16 April 2001
* @see HierarchicalBeanFactory
* @see BeanFactoryUtils
*/
public interface ListableBeanFactory extends BeanFactory { /**
* Check if this bean factory contains a bean definition with the given name.
* <p>Does not consider any hierarchy this factory may participate in,
* and ignores any singleton beans that have been registered by
* other means than bean definitions.
检查bean factory是否含有给定name的bean定义,忽略父factory和其他factory注册的单例bean
* @param beanName the name of the bean to look for
beanName要查找bean的名称
* @return if this bean factory contains a bean definition with the given name
如果bean factory包含具有给定名称的bean定义
* @see #containsBean
*/
boolean containsBeanDefinition(String beanName); /**
* Return the number of beans defined in the factory.
* <p>Does not consider any hierarchy this factory may participate in,
* and ignores any singleton beans that have been registered by
* other means than bean definitions.
返回bean factory中定义bean的数量,一样不考虑父factory和其他factory注册的单例bean
* @return the number of beans defined in the factory
返回bean factory里面定义bean的数量
*/
int getBeanDefinitionCount(); /**
* Return the names of all beans defined in this factory.
* <p>Does not consider any hierarchy this factory may participate in,
* and ignores any singleton beans that have been registered by
* other means than bean definitions.
返回bean factory中定义bean的数量,一样不考虑父factory和其他factory注册的单例Bean
* @return the names of all beans defined in this factory,
返回bean factory中定义bean的数量存在数组里,如果没有则返回空数组
* or an empty array if none defined
*/
String[] getBeanDefinitionNames(); /**
* Return the names of beans matching the given type (including subclasses),
* judging from either bean definitions or the value of {@code getObjectType}
* in the case of FactoryBeans.
* <p><b>NOTE: This method introspects top-level beans only.</b> It does <i>not</i>
* check nested beans which might match the specified type as well.
* <p>Does consider objects created by FactoryBeans, which means that FactoryBeans
* will get initialized. If the object created by the FactoryBean doesn't match,
* the raw FactoryBean itself will be matched against the type.
* <p>Does not consider any hierarchy this factory may participate in.
* Use BeanFactoryUtils' {@code beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors}
* to include beans in ancestor factories too.
* <p>Note: Does <i>not</i> ignore singleton beans that have been registered
* by other means than bean definitions.
* <p>This version of {@code getBeanNamesForType} matches all kinds of beans,
* be it singletons, prototypes, or FactoryBeans. In most implementations, the
* result will be the same as for {@code getBeanNamesForType(type, true, true)}.
* <p>Bean names returned by this method should always return bean names <i>in the
* order of definition</i> in the backend configuration, as far as possible.
* @param type the class or interface to match, or {@code null} for all bean names
* @return the names of beans (or objects created by FactoryBeans) matching
* the given object type (including subclasses), or an empty array if none
* @since 4.2
* @see #isTypeMatch(String, ResolvableType)
* @see FactoryBean#getObjectType
* @see BeanFactoryUtils#beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(ListableBeanFactory, ResolvableType)
*/
String[] getBeanNamesForType(ResolvableType type); /**
* Return the names of beans matching the given type (including subclasses),
* judging from either bean definitions or the value of {@code getObjectType}
* in the case of FactoryBeans.
* <p><b>NOTE: This method introspects top-level beans only.</b> It does <i>not</i>
* check nested beans which might match the specified type as well.
* <p>Does consider objects created by FactoryBeans, which means that FactoryBeans
* will get initialized. If the object created by the FactoryBean doesn't match,
* the raw FactoryBean itself will be matched against the type.
* <p>Does not consider any hierarchy this factory may participate in.
* Use BeanFactoryUtils' {@code beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors}
* to include beans in ancestor factories too.
* <p>Note: Does <i>not</i> ignore singleton beans that have been registered
* by other means than bean definitions.
* <p>This version of {@code getBeanNamesForType} matches all kinds of beans,
* be it singletons, prototypes, or FactoryBeans. In most implementations, the
* result will be the same as for {@code getBeanNamesForType(type, true, true)}.
* <p>Bean names returned by this method should always return bean names <i>in the
* order of definition</i> in the backend configuration, as far as possible.
获取给定类型的bean names(包括子类),通过bean定义或者FactoryBean的getObjectType判断,
注意:这个方法仅检查顶级bean,它不会检查嵌套的bean.
FactoryBean创建的bean会匹配为FactoryBean而不是原始类型。
一样不会考虑父Factory中的bean,可以使用BeanFactoryUtils中的BeanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors
其他方式注册的单例这边会纳入判断。
这个版本的getBeanNamesForType会匹配所有类型的bean,包括单例,原型,FactoryBean,在大多数实现中返回跟getBeanNamesOfType(type,true,true)一样
返回的bean names 会根据backed 配置的进行排序。
* @param type the class or interface to match, or {@code null} for all bean names
* @return the names of beans (or objects created by FactoryBeans) matching
* the given object type (including subclasses), or an empty array if none
* @see FactoryBean#getObjectType
* @see BeanFactoryUtils#beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(ListableBeanFactory, Class)
*/
String[] getBeanNamesForType(Class<?> type);
/**
* Return the names of beans matching the given type (including subclasses),
* judging from either bean definitions or the value of {@code getObjectType}
* in the case of FactoryBeans.
* <p><b>NOTE: This method introspects top-level beans only.</b> It does <i>not</i>
* check nested beans which might match the specified type as well.
* <p>Does consider objects created by FactoryBeans if the "allowEagerInit" flag is set,
* which means that FactoryBeans will get initialized. If the object created by the
* FactoryBean doesn't match, the raw FactoryBean itself will be matched against the
* type. If "allowEagerInit" is not set, only raw FactoryBeans will be checked
* (which doesn't require initialization of each FactoryBean).
* <p>Does not consider any hierarchy this factory may participate in.
* Use BeanFactoryUtils' {@code beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors}
* to include beans in ancestor factories too.
* <p>Note: Does <i>not</i> ignore singleton beans that have been registered
* by other means than bean definitions.
* <p>Bean names returned by this method should always return bean names <i>in the
* order of definition</i> in the backend configuration, as far as possible.
* @param type the class or interface to match, or {@code null} for all bean names
* @param includeNonSingletons whether to include prototype or scoped beans too
* or just singletons (also applies to FactoryBeans)
includeNonSingletons是否只要单例(包括BeanFactory)还是原型或其他作用域的Bean一样包括
* @param allowEagerInit whether to initialize <i>lazy-init singletons</i> and
* <i>objects created by FactoryBeans</i> (or by factory methods with a
* "factory-bean" reference) for the type check. Note that FactoryBeans need to be
* eagerly initialized to determine their type: So be aware that passing in "true"
* for this flag will initialize FactoryBeans and "factory-bean" references.
是否初始化懒加载的单例,FactoryBean初始化的类和工厂方法初始化的类,就是说执行这个方法会执行对应的初始化
* @return the names of beans (or objects created by FactoryBeans) matching
* the given object type (including subclasses), or an empty array if none
* @see FactoryBean#getObjectType
* @see BeanFactoryUtils#beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(ListableBeanFactory, Class, boolean, boolean)
*/
String[] getBeanNamesForType(Class<?> type, boolean includeNonSingletons, boolean allowEagerInit);
/**
* Return the bean instances that match the given object type (including
* subclasses), judging from either bean definitions or the value of
* {@code getObjectType} in the case of FactoryBeans.
* <p><b>NOTE: This method introspects top-level beans only.</b> It does <i>not</i>
* check nested beans which might match the specified type as well.
* <p>Does consider objects created by FactoryBeans, which means that FactoryBeans
* will get initialized. If the object created by the FactoryBean doesn't match,
* the raw FactoryBean itself will be matched against the type.
* <p>Does not consider any hierarchy this factory may participate in.
* Use BeanFactoryUtils' {@code beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors}
* to include beans in ancestor factories too.
* <p>Note: Does <i>not</i> ignore singleton beans that have been registered
* by other means than bean definitions.
* <p>This version of getBeansOfType matches all kinds of beans, be it
* singletons, prototypes, or FactoryBeans. In most implementations, the
* result will be the same as for {@code getBeansOfType(type, true, true)}.
* <p>The Map returned by this method should always return bean names and
* corresponding bean instances <i>in the order of definition</i> in the
* backend configuration, as far as possible.
* @param type the class or interface to match, or {@code null} for all concrete beans
* @return a Map with the matching beans, containing the bean names as
* keys and the corresponding bean instances as values
* @throws BeansException if a bean could not be created
* @since 1.1.2
* @see FactoryBean#getObjectType
* @see BeanFactoryUtils#beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(ListableBeanFactory, Class)
*/
<T> Map<String, T> getBeansOfType(Class<T> type) throws BeansException;
/**
* Return the bean instances that match the given object type (including
* subclasses), judging from either bean definitions or the value of
* {@code getObjectType} in the case of FactoryBeans.
* <p><b>NOTE: This method introspects top-level beans only.</b> It does <i>not</i>
* check nested beans which might match the specified type as well.
* <p>Does consider objects created by FactoryBeans if the "allowEagerInit" flag is set,
* which means that FactoryBeans will get initialized. If the object created by the
* FactoryBean doesn't match, the raw FactoryBean itself will be matched against the
* type. If "allowEagerInit" is not set, only raw FactoryBeans will be checked
* (which doesn't require initialization of each FactoryBean).
* <p>Does not consider any hierarchy this factory may participate in.
* Use BeanFactoryUtils' {@code beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors}
* to include beans in ancestor factories too.
* <p>Note: Does <i>not</i> ignore singleton beans that have been registered
* by other means than bean definitions.
* <p>The Map returned by this method should always return bean names and
* corresponding bean instances <i>in the order of definition</i> in the
* backend configuration, as far as possible.
* @param type the class or interface to match, or {@code null} for all concrete beans
* @param includeNonSingletons whether to include prototype or scoped beans too
* or just singletons (also applies to FactoryBeans)
* @param allowEagerInit whether to initialize <i>lazy-init singletons</i> and
* <i>objects created by FactoryBeans</i> (or by factory methods with a
* "factory-bean" reference) for the type check. Note that FactoryBeans need to be
* eagerly initialized to determine their type: So be aware that passing in "true"
* for this flag will initialize FactoryBeans and "factory-bean" references.
* @return a Map with the matching beans, containing the bean names as
* keys and the corresponding bean instances as values
* @throws BeansException if a bean could not be created
* @see FactoryBean#getObjectType
* @see BeanFactoryUtils#beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(ListableBeanFactory, Class, boolean, boolean)
*/
<T> Map<String, T> getBeansOfType(Class<T> type, boolean includeNonSingletons, boolean allowEagerInit)
throws BeansException;
/**
* Find all names of beans whose {@code Class} has the supplied {@link Annotation}
* type, without creating any bean instances yet.
* @param annotationType the type of annotation to look for
* @return the names of all matching beans
* @since 4.0
*/
String[] getBeanNamesForAnnotation(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType);
/**
* Find all beans whose {@code Class} has the supplied {@link Annotation} type,
* returning a Map of bean names with corresponding bean instances.
找到使用注解的类
* @param annotationType the type of annotation to look for
* @return a Map with the matching beans, containing the bean names as
* keys and the corresponding bean instances as values
* @throws BeansException if a bean could not be created
* @since 3.0
*/
Map<String, Object> getBeansWithAnnotation(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType) throws BeansException;
/**
* Find an {@link Annotation} of {@code annotationType} on the specified
* bean, traversing its interfaces and super classes if no annotation can be
* found on the given class itself.
查找一个类的注解,如果找不到,父类,接口使用注解也算
* @param beanName the name of the bean to look for annotations on
* @param annotationType the annotation class to look for
* @return the annotation of the given type if found, or {@code null}
* @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException if there is no bean with the given name
* @since 3.0
*/
<A extends Annotation> A findAnnotationOnBean(String beanName, Class<A> annotationType)
throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
}
spring源码 ListableBeanFactory接口的更多相关文章
- spring源码 AutowireCapableBeanFactory接口
对于想要拥有自动装配能力,并且想把这种能力暴露给外部引用的BeanFactory类需要实现此接口.正常情况下,不要使用此接口应该更倾向于使用BeanFactory或者ListableBeanFacto ...
- spring源码 HierarchicalBeanFactory接口
HierarchicalBeanFactory 表示的是这些 Bean 是有继承关系的,也就是每个Bean 有可能有父 Bean. /* * Copyright 2002-2012 the origi ...
- spring源码系列(二):IOC接口设计分析
这里主要对springIOC接口体系进行简单的概述和分析,具体每个接口详细分析在下面目录: 参考内容: <Spring技术内幕:深入解析 Spring架构与设计原理> 和 <Spri ...
- Spring源码分析——资源访问利器Resource之接口和抽象类分析
从今天开始,一步步走上源码分析的路.刚开始肯定要从简单着手.我们先从Java发展史上最强大的框架——Spring...旗下的资源抽象接口Resource开始吧. 我看了好多分析Spring源码的,每每 ...
- spring源码分析系列 (1) spring拓展接口BeanFactoryPostProcessor、BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
更多文章点击--spring源码分析系列 主要分析内容: 一.BeanFactoryPostProcessor.BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor简述与demo示例 ...
- spring源码分析系列 (3) spring拓展接口InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
更多文章点击--spring源码分析系列 主要分析内容: 一.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor简述与demo示例 二.InstantiationAwareBean ...
- spring源码分析系列 (2) spring拓展接口BeanPostProcessor
Spring更多分析--spring源码分析系列 主要分析内容: 一.BeanPostProcessor简述与demo示例 二.BeanPostProcessor源码分析:注册时机和触发点 (源码基于 ...
- Spring源码解析 - AbstractBeanFactory 实现接口与父类分析
我们先来看类图吧: 除了BeanFactory这一支的接口,AbstractBeanFactory主要实现了AliasRegistry和SingletonBeanRegistry接口. 这边主要提供了 ...
- spring源码学习之路---深入AOP(终)
作者:zuoxiaolong8810(左潇龙),转载请注明出处,特别说明:本博文来自博主原博客,为保证新博客中博文的完整性,特复制到此留存,如需转载请注明新博客地址即可. 上一章和各位一起看了一下sp ...
随机推荐
- sqlplus 登陆使用
select * from dept; input order by dname; 追加文本命令 del n 删除语句 celar buffer ; 清除缓冲区的命令 conn sys as ...
- Android加载手机磁盘上的资源---decodeFile方法的使用
一般在写Android程序时,通常会将图片资源放在/res/drawable/文件夹下,读取时,通过R.drawable.imageId即可读取图片内容,但用户在使用时,一般会想要读取存放在存储卡上的 ...
- 二、Navicat、IDEA、nopad、eclipse、excle工具使用、问题、快捷键
1.Navicat工具: 目的:本地数据库与远程数据库之间数据导入导出 步骤1:文件--新建oracle链接/mysql的连接 步骤2:工具-选项:将本地oracle的bin\oci.dll 的路径复 ...
- UOJ Contest #50: Goodbye Jihai
比赛传送门:Goodbye Jihai. \(\Huge{\mathbf{再见,己亥.\\你好,庚子!\\祝大家新春快乐!}}\) A. 新年的促销 这题如果直接做的话可能方向会想歪,方向对了其实就是 ...
- redis列表-list
Redis的list类型其实就是一个每个子元素都是string类型的双向链表,链表的最大长度是2^32.list既可以用做栈,也可以用做队列. 常用命令: 1. lpush key value [va ...
- CSS元素和文本垂直居中
div居中 1.使用绝对定位和负外边距让块级元素垂直居中 要点:必须提前知道被居中块级元素的尺寸,否则无法准确实现垂直居中. <div id="box"> <di ...
- JAVA 集合 List 分组的两种方法
CSDN日报20170219--<程序员的沟通之痛> [技术直播]揭开人工智能神秘的面纱 程序员1月书讯 云端应用征文大赛,秀绝招,赢无人机! JAVA 集合 List 分组的两种方法 2 ...
- MyEclipse 8.5整合Git,并在Github上发布项目
我们在闲暇时间想加入些团队做点属于自己有意义的东西,那Github就是为你准备的.但是用惯SVN的我们就得学习学习了. 工具/原料 myeclipse8.5 github 方法/步骤 1 下载Ecli ...
- 写的一个轻量级javascript框架的设计模式
公司一直使用jQuery框架,一些小的项目还是觉得jQuery框架太过于强大了,于是自己周末有空琢磨着写个自己的框架.谈到js的设计模式,不得不说说js的类继承机制,javascript不同于PHP可 ...
- MVC5仓库管理系统
下载
