android LinearLayout
Android的布局方式共有6种,分别是LinearLayout(线性布局)、TableLayout(表格布局)、FrameLayout(帧布局)、RelativeLayout(相对布局)、GridLayout(网格布局)以及AbsoluteLayout(绝对布局)。
LinearLayout 常用属性介绍
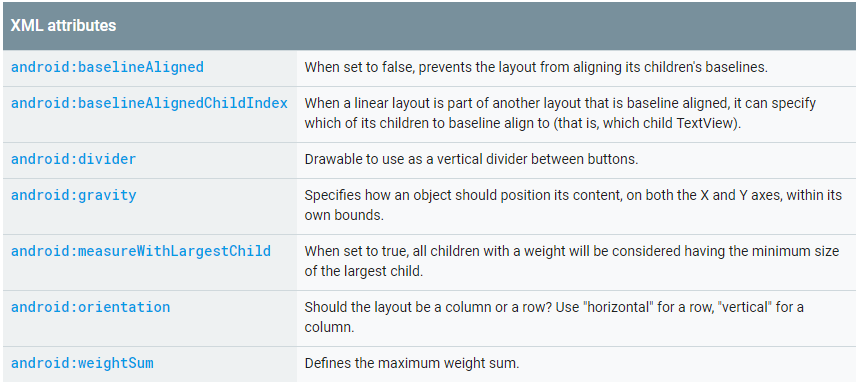
android:baselineAligned: 基准线对齐,默认为true.当设置为false时,布局文件和它的孩子的基准线不对齐。
android:baselineAlignedChildIndex:当作为layout的子控件时,设置自己的第几(0开始)个子文本(必须是文本),和外面layout内元素的基准线对其
android:measureWithLargestChild:
android:divider:分割线
android:weightSum:总权重和,即页面剩余的划分。和子控件的weight配合实现页面效果
android:orientation:horizontal(水平:0),vertical(垂直分布:1)
注意:水平不会换行,超出屏幕被隐藏
android:gravity
设置布局管理器内组件的对齐方式,该属性值可设为 top(顶部对齐) 、bottom(底部对齐) 、left(左对齐) 、right(右对齐) 、center_vertical(垂直方向居中) 、 fill_vertical(垂直方向填充) 、 center_horizontal(水平方向居中) 、 fill_horizontal(水平方向填充) 、center(垂直与水平方向都居中) 、 fill (填充)、 clip_vertical(垂直方向裁剪) 、 clip_horizontal(水平方向裁剪) 。
可同时指定多种对其方式的组合,中间用“|”连接,如下方代码设置对齐方式为 left|center_vertical 表示出现在屏幕左边且垂直居中,
<!--
第一个线性布局, 我们可以视为html中的div,用于对于整个界面进行布局
这里面 xmlns:android和xmlns:tools指定的是xml文件的命名空间,不是对布局的主要设置
但是要有
android:layout_width="match_parent"指的是当前的线性布局宽度占整个父元素,这里相对于
当前的线性布局父元素为当前的窗体,所以宽度占满窗体
android:layout_height="match_parent"指的是当前的线性布局高度占整个父元素,这里相对于
当前的线性布局父元素为当前的窗体,所以高度占满窗体
tools:context="com.example.activitylife.MainActivity":用于指定渲染上下文
android:orientation="vertical":指的是当前控件为垂直摆放
-->
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="com.example.activitylife.MainActivity"
android:orientation="vertical">
</LinearLayout>
1.android:baselineAligned 属性
baselineAligned:基准线对齐。
首先要解释什么是基准线,这个在中文中不常见,但在以字母为书写语言的其他国家非常常见,尤其是英文

如上图所示,红线就是基线(baseline),是不是很熟悉,这不就是我们经常写英文的四条线中的第三条吗。

那baselineAligned是做什么用的呢?根据官方文档,baselineAligned默认设置为true,当设置为false时,
布局文件和它的孩子的基准线不对齐。
举个栗子:
这是将baselineAligned值设置为false时,也就是不对齐。把baselineAligned值改为true,就是对齐。

2、android:baselineAlignedChildIndex属性:
线性布局(LinearLayout)中使用,设置LinearLayout中第几个(从0开始计数)子组件作为基线对齐的控件,来和LinearLayout外的基线对齐。
android:baselineAlignedChildIndex对应的view必须是可以显示文字的View
测试代码
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal"> <TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="aaa"
android:textSize="20sp"/> <!--测试LinearLayout-->
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:orientation="vertical"> <TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="fdfdfdf"/> <ImageView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@mipmap/ic_launcher"/> <TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="rgtgtgtgt"/>
</LinearLayout> <TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:text="ffsdfr"
android:textSize="40sp"/>
</LinearLayout>
1 、测试LinearLayout不设置android:baselineAlignedChildIndex时,只
![Uploading 1489473079(1)_583231.jpg . . .]
有前后TextView基线对其

2、测试LinearLayout设置android:baselineAlignedChildIndex=0,对应view为TextVIew时

3、测试LinearLayout设置android:baselineAlignedChildIndex=1,对应view为ImageView时,崩溃了,异常现象如下,不能对不是文本的进行设置基准线的对齐

4、测试LinearLayout设置android:baselineAlignedChildIndex=2,对应view为TextView时

3、weightSum 属性
weightSum属性与weight属性有很大关系,通过weightSum控制weight的最大占比。比如我们这样设置 :
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:weightSum=""
android:orientation="horizontal">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center"
android:layout_weight=""
android:background="#FF0000"
android:text="text1" /> <TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center"
android:layout_weight=""
android:background="#00FF00"
android:text="text2" />
</LinearLayout>

text1与text2本来是一样的weight,可是结果它们都没有撑满屏幕。因为weightSum="3",也就是说text1、text2占用的宽度是 (text1文本宽度)120 + (1080-240两个文本)840 / 3 = 400px ,右边还有剩余280px。如果text1与text2的weight超过了weightSum会怎样,我们设置如下看看效果 :
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:weightSum=""
android:orientation="horizontal">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center"
android:layout_weight=""
android:background="#FF0000"
android:text="text1" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center"
android:layout_weight=""
android:background="#00FF00"
android:text="text2" />
</LinearLayout>

结果发现text2的文字快到屏幕外了,说明text2的宽度超出了屏幕。其实计算方式还是一样的,它们各占剩余空间的 2/3。我们上面说过text1与text2的宽度都是120px,剩余840,那么此时text1的宽度为 120 + 840 * 2 / 3 = 680px ,两个都是 680px,那text2当然被挤到屏幕外去了。
weightSum属性可以用来控制weight属性占用剩余空间的比例。比如我们要做一个布局,一个按钮居中,它宽度是屏幕的一半,还要自适应屏幕,效果如下:

我们可以利用weightSum属性,代码如下:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:weightSum="">
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight=""
android:text="按钮" />
</LinearLayout>
运行代码看到按钮半宽居中,自适应所有分辨率的屏幕,符合要求。注意LinearLayout中设置的android:gravity="center",它让子View居中放置。
4、divider 、showDividers 属性
以往我在设置分割线时,都是新增一个View,用来显示分割线,直到我发现在LinearLayout中添加分割线的新方法。LinearLayout显示分割线主要涉及divider 、showDividers 属性 : android:divider用于设置分割线的样式,可以是xml的drawable也可以是图片。android:showDividers = "middle|end|beginning|none" 其每个选项的作用:
- middle 在每一项中间添加分割线
- end 在整体的最后一项添加分割线
- beginning 在整体的最上方添加分割线
- none 不显示分割线
我们先创建一个custom.xml的drawable ,注意设置了宽高,不然是显示不出来的:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<solid android:color="@android:color/holo_red_light" />
<size android:height="12dp" android:width="2dp"/>
</shape>
设置成android:showDividers = "beginning"时:

设置成android:showDividers = "end"时:

设置成android:showDividers = "middle"时:

还可以组合设置 ,android:showDividers="beginning|end|middle" ,显示结果:

最后如果大家发现了什么的重要的属性或巧妙的用法,也可以一起交流哈。
参考转自以下文档:
https://blog.csdn.net/chenbengang/article/details/48154057
https://www.jianshu.com/p/ae0762d2f922
https://www.jianshu.com/p/21db6618baa0
android LinearLayout的更多相关文章
- 关于android LinearLayout的比例布局(转载)
关于android LinearLayout的比例布局,主要有以下三个属性需要设置: 1,android:layout_width,android:layout_height,android:layo ...
- Android LinearLayout的android:layout_weight属性
本文主要介绍Android LinearLayout的android:layout_weight属性意义 android:layout_weight为大小权重,相当于在页面上显示的百分比,它的计算是根 ...
- Android linearlayout常用布局
用linearlayout完成这样的布局效果,这样的布局还是比较常用的,具体的xml代码如下: <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas. ...
- android LinearLayout 实现两端对齐
<?xml version="1.0″ encoding="utf-8″?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://s ...
- 关于Android LinearLayout添加分隔线的方法
目前了解的办法有两个:1.自定义一个view当作分隔线:2.使用高版本的分隔线属性 一.在需要添加分隔线的地方,添加一个view,比如ImageView,TextView等都可以,如代码,关键是设置高 ...
- android LinearLayout android:layout_weight 作用,固定比例
android 中的 LinearLayout 是线性布局有水平布局horizontal 垂直布局vertical .本文针对 水平布局horizontal 布局的weight属性做一个标记,以免 ...
- android LinearLayout和RelativeLayout实现精确布局
先明确几个概念的区别: padding margin:都是边距的含义,关键问题得明白是什么相对什么的边距padding:是控件的内容相对控件的边缘的边距. margin :是控件边缘相对父空间的边距 ...
- android linearlayout 把控件view置底部(放在页面最下方)
<LinearLayout android:id="@+id/recLayout" android:layout_width="fill_parent" ...
- android linearlayout imageview置顶摆放
在练习android时,想在Linearlayout内放一图片,使其图片置顶,预期效果是这样的: 但xml代码imageview写成这样后, <ImageView android:layout_ ...
- android LinearLayout等view如何获取button效果
我们可以给LinearLayout以及一切继承自View的控件,设置View.onClickListener监听,例如LInearLayout. 但是我们发现LinearLayout可以执行监听方法体 ...
随机推荐
- [Objective-C语言教程]类型转换(20)
类型转换是一种将变量从一种数据类型转换为另一种数据类型的方法. 例如,如果要将long值存储到简单整数(int)中,则可以将long类型转换设置为int.使用强制转换运算符将值从一种类型转换为另一种类 ...
- 使用服务器上的Jupyter notebook。
1.jupyter notebook --generate-config #产生配置文件 2.from notebook.auth import passwd #进入python环境,生成密码密文.第 ...
- day00 -----博客作业1
问题1.使用while循环输入 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 9 10 i = 0 while i<10: i+=1 if i ==7: continue print(i) 问题2 求1- ...
- JS设计模式之单体模式(Singleton)
单体模式作为一种软件开发模式在众多面向对象语言中得到了广泛的使用,在javascript中,单体模式也是使用非常广泛的,但是由于javascript语言拥有其独特的面向对象方式,导致其和一些传统面向对 ...
- 1.由于测试某个功能,需要生成500W条数据的txt,python代码如下
txt内容是手机号,数量500W,采用python代码生成,用时60S,本人技能有限,看官如果有更快的写法,欢迎留言交流. import random f = open("D:\\data. ...
- shell-007:数据库备份,本地保留7天,远程机器保留一个月
## #!/bin/bash d1=`date +%w` # 以周几有变量 d2=`date +%d` # 以每月第几天为变量 local_bakdir=/bak/mysql # 本地备份目录 rem ...
- Objective-C语法之类和对象
https://blog.csdn.net/totogo2010/article/details/7708731 Objective-C语法之类和对象 2012年07月02日 17:19:42 知行合 ...
- [转] Java中Comparator进行对象排序
[From] https://blog.51cto.com/thinklili/2063244 Java在8后引入了lambda表达式和流,使得排序方法有了变化 class User { int id ...
- Flask基本知识
@app.route('/')def hello_world(): return 'Hello World!' #route动态Route,支持字符串.整数.浮点数,/user/<int:id& ...
- dubbo SPI设计
SPI 全称为 Service Provider Interface,是一种服务发现机制.SPI 的本质是将接口实现类的全限定名配置在文件中,并由服务加载器读取配置文件,加载实现类.这样可以在运行时, ...
