python实现接口自动化
一、总述
Postman:功能强大,界面好看响应格式自主选择,缺点支持的协议单一且不能数据分离,比较麻烦的还有不是所有的公司都能上谷歌
SoupUI:支持多协议(http\soup\rest等),能实现功能和性能测试的开源接口测试工具,灵活性高可在此基础上开发脚本,缺点上手比较难
Jmeter:Java御用的接口压力测试工具,做接口功能测试有点大材小用,缺点不能生成可视化的接口测试报告
python+requests+untest
python+requests+pytest
python+HttpRunner
HttpRunner 是一款面向 HTTP(S) 协议的通用测试框架,只需编写维护一份 YAML/JSON脚本,即可实现自动化测试、性能测试、线上监控、持续集成等多种测试需求。
Requests是一个Python HTTP 库,它允许你发送纯天然的HTTP/1.1请求无需手工设置。你不需要手动为 URL 添加查询字串,也不需要对 POST 数据进行表单编码。Keep-alive 和 HTTP 连接池的功能是 100% 自动化的,一切动力都来自于根植在 Requests 内部的 urllib3。
#响应内容
r.encoding #获取当前的编码
r.encoding = 'utf-8' #设置编码
r.text #以encoding解析返回内容。字符串方式的响应体,会自动根据响应头部的字符编码进行解码。
r.content #以字节形式(二进制)返回。字节方式的响应体,会自动为你解码 gzip 和 deflate 压缩。 r.headers #以字典对象存储服务器响应头,但是这个字典比较特殊,字典键不区分大小写,若键不存在则返回None r.status_code #响应状态码
r.raw #返回原始响应体,也就是 urllib 的 response 对象,使用 r.raw.read()
r.ok # 查看r.ok的布尔值便可以知道是否登陆成功
#*特殊方法*#
r.json() #Requests中内置的JSON解码器,以json形式返回,前提返回的内容确保是json格式的,不然解析出错会抛异常
r.raise_for_status() #失败请求(非200响应)抛出异常
get(url, params=None, **kwargs)
post(url, data=None, json=None, **kwargs)
request(method, url, **kwargs)
二、requests库的用法--get
1、基本的get请求
import requests
response = requests.get('http://httpbin.org/get')
print(response.text) #以文本形式打印网页源码
# print(response.status_code) # 打印状态码
# print(response.url) # 打印请求url
# print(response.headers) # 打印头信息
# print(response.cookies) # 打印cookie信息
# print(response.content) #以二进制形式打印网页源码
结果

2、带参数的GET请求(直接将参数放在url内):
import requests
response = requests.get('http://httpbin.org/get?name=gemey&age=22')
print(response.text)
结果
3、带参数的GET请求(先将参数填写在dict中,发起请求时params参数指定为dict):
import requests
data = {
'name': 'tom',
'age': 20
}
response = requests.get('http://httpbin.org/get', params=data)
print(response.text)
4、json格式保存结果
import requests
response = requests.get('http://httpbin.org/get')
print(response.text)
print(response.json()) #response.json()方法同json.loads(response.text)
print(type(response.json()))
结果
5、二进制保存结果:
import requests
response = requests.get('http://img.ivsky.com/img/tupian/pre/201708/30/kekeersitao-002.jpg')
b = response.content
with open('F://fengjing.jpg','wb') as f:
f.write(b)
6、为请求添加头信息:
import requests
heads = {'User-Agent':"'Mozilla/5.0 ' '(Macintosh; U; Intel Mac OS X 10_6_8; en-us) AppleWebKit/534.50 ' '(KHTML, like Gecko) Version/5.1 Safari/534.50'"}
response = requests.get('http://www.baidu.com',headers=heads)
7、使用代理
代理参数也要是一个dict,这里使用requests库爬取了IP代理网站的IP与端口和类型。因为是免费的,使用的代理地址很快就失效了。
import requests
import re def get_html(url):
proxy = {
'http': '120.25.253.234:812',
'https': '163.125.222.244:8123'
}
heads = {}
heads['User-Agent'] = 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/49.0.2623.221 Safari/537.36 SE 2.X MetaSr 1.0'
req = requests.get(url, headers=heads,proxies=proxy)
html = req.text
return html def get_ipport(html):
regex = r'<td data-title="IP">(.+)</td>'
iplist = re.findall(regex, html)
regex2 = '<td data-title="PORT">(.+)</td>'
portlist = re.findall(regex2, html)
regex3 = r'<td data-title="类型">(.+)</td>'
typelist = re.findall(regex3, html)
sumray = []
for i in iplist:
for p in portlist:
for t in typelist:
pass
pass
a = t+','+i + ':' + p
sumray.append(a)
print('高匿代理')
print(sumray) if __name__ == '__main__':
url = 'http://www.kuaidaili.com/free/'
get_ipport(get_html(url))
结果:

8、获取cookie
#获取cookie
import requests response = requests.get('http://www.baidu.com') print(response.cookies)
for k,v in response.cookies.items():
print(k+':'+v)
结果:
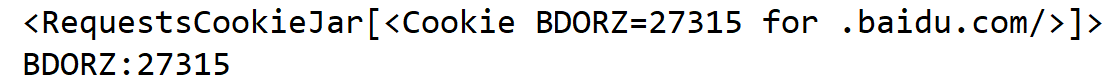
9、证书验证设置
import requests
from requests.packages import urllib3 urllib3.disable_warnings() #从urllib3中消除警告
response = requests.get('https://www.12306.cn',verify=False) #证书验证设为FALSE
print(response.status_code) 打印结果:200
10、 发送cookies到服务器
要想发送你的cookies到服务器,可以使用 cookies 参数:
import requests url = 'http://httpbin.org/cookies'
cookies = {'testCookies_1': 'Hello_Python3', 'testCookies_2': 'Hello_Requests'}# 规定空格、方括号、圆括号、等于号、逗号、双引号、斜杠、问号、@,冒号,分号等特殊符号都不能作为Cookie的内容。
r = requests.get(url, cookies=cookies)
print(r.json())
11、超时异常捕获
import requests
from requests.exceptions import ReadTimeout try:
res = requests.get('http://httpbin.org', timeout=0.1)
print(res.status_code)
except ReadTimeout:
print(timeout)
12、异常处理
在你不确定会发生什么错误时,尽量使用try...except来捕获异常
import requests
from requests.exceptions import ReadTimeout,HTTPError,RequestException try:
response = requests.get('http://www.baidu.com',timeout=0.5)
print(response.status_code)
except ReadTimeout:
print('timeout')
except HTTPError:
print('httperror')
except RequestException:
print('reqerror')
所有的requests exception: exception requests.RequestException(*args, **kwargs)
There was an ambiguous exception that occurred while handling your request. exception requests.ConnectionError(*args, **kwargs)
A Connection error occurred. exception requests.HTTPError(*args, **kwargs)
An HTTP error occurred. exception requests.URLRequired(*args, **kwargs)
A valid URL is required to make a request. exception requests.TooManyRedirects(*args, **kwargs)
Too many redirects. exception requests.ConnectTimeout(*args, **kwargs)
The request timed out while trying to connect to the remote server. Requests that produced this error are safe to retry. exception requests.ReadTimeout(*args, **kwargs)
The server did not send any data in the allotted amount of time. exception requests.Timeout(*args, **kwargs)
The request timed out. Catching this error will catch both ConnectTimeout and ReadTimeout errors.
三、requests库的用法--post
1、基本POST实例
import requests
payload = {'key1': 'value1', 'key2': 'value2'}
ret = requests.post("http://httpbin.org/post", data=payload)
print(ret.text)
2、发送请求头和数据
import requests
import json url = 'https://api.github.com/some/endpoint'
payload = {'some': 'data'}
headers = {'content-type': 'application/json'} ret = requests.post(url, data=json.dumps(payload), headers=headers) print(ret.text)
print(ret.cookies)
3、json格式请求:
import requests
import json class url_request():
def __init__(self):
''' init ''' if __name__ == '__main__':
heard = {'Content-Type': 'application/json'}
payload = {'CountryName': '中国',
'ProvinceName': '四川省',
'L1CityName': 'chengdu',
'L2CityName': 'yibing',
'TownName': '',
'Longitude': '107.33393',
'Latitude': '33.157131',
'Language': 'CN'}
r = requests.post("http://www.xxxxxx.com/CityLocation/json/LBSLocateCity", heards=heard, data=payload)
data_r = r.json()
if r.status_code!=200:
print('LBSLocateCity API Error' + str(r.status_code))
print(data_r['CityEntities'][0]['CityID']) # 打印返回json中的某个key的value
print(data_r['ResponseStatus']['Ack'])
print(json.dump(data, indent=4, sort_keys=True, ensure_ascii=False)) # 树形打印json,ensure_ascii必须设为False否则中文会显示为unicode
4、Xml请求:
import requests class url_request():
def __init__(self):
"""init""" if __name__ == '__main__':
heards = {'Content-type': 'text/xml'}
XML = '<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><soap:Envelope xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/"><soap:Body><Request xmlns="http://tempuri.org/"><jme><JobClassFullName>WeChatJSTicket.JobWS.Job.JobRefreshTicket,WeChatJSTicket.JobWS</JobClassFullName><Action>RUN</Action><Param>1</Param><HostIP>127.0.0.1</HostIP><JobInfo>1</JobInfo><NeedParallel>false</NeedParallel></jme></Request></soap:Body></soap:Envelope>'
url = 'http://jobws.push.mobile.xxxxxxxx.com/RefreshWeiXInTokenJob/RefreshService.asmx'
r = requests.post(url=url, heards=heards, data=XML)
data_r = r.text
print(data_r)
5、上传文件
使用request模块,也可以上传文件,文件的类型会自动进行处理:

import requests url = 'http://127.0.0.1:8080/upload'
files = {'file': open('/home/rxf/test.jpg', 'rb')}
#files = {'file': ('report.jpg', open('/home/lyb/sjzl.mpg', 'rb'))} #显式的设置文件名 r = requests.post(url, files=files)
print(r.text)

request更加方便的是,可以把字符串当作文件进行上传:

import requests url = 'http://127.0.0.1:8080/upload'
files = {'file': ('test.txt', b'Hello Requests.')} #必需显式的设置文件名 r = requests.post(url, files=files)
print(r.text)

6、定制头和cookie信息
header = {'user-agent': 'my-app/0.0.1''}
cookie = {'key':'value'}
r = requests.post('your url',headers=header,cookies=cookie)

import requests
import json data = {'some': 'data'}
headers = {'content-type': 'application/json','User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Ubuntu; Linux x86_64; rv:22.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/22.0'} r = requests.post('https://api.github.com/some/endpoint', data=data, headers=headers)
print(r.text)

四、综合
1、方法汇总
# HTTP请求类型
# get类型
r = requests.get('https://github.com/timeline.json')
# post类型
r = requests.post("http://m.ctrip.com/post")
# put类型
r = requests.put("http://m.ctrip.com/put")
# delete类型
r = requests.delete("http://m.ctrip.com/delete")
# head类型
r = requests.head("http://m.ctrip.com/head")
# options类型
r = requests.options("http://m.ctrip.com/get") # 获取响应内容
print(r.content) #以字节的方式去显示,中文显示为字符
print(r.text) #以文本的方式去显示 #URL传递参数
payload = {'keyword': '香港', 'salecityid': ''}
r = requests.get("http://m.ctrip.com/webapp/tourvisa/visa_list", params=payload)
print(r.url) #示例为http://m.ctrip.com/webapp/tourvisa/visa_list?salecityid=2&keyword=香港 #获取/修改网页编码
r = requests.get('https://github.com/timeline.json')
print (r.encoding) #json处理
r = requests.get('https://github.com/timeline.json')
print(r.json()) # 需要先import json # 定制请求头
url = 'http://m.ctrip.com'
headers = {'User-Agent' : 'Mozilla/5.0 (Linux; Android 4.2.1; en-us; Nexus 4 Build/JOP40D) AppleWebKit/535.19 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/18.0.1025.166 Mobile Safari/535.19'}
r = requests.post(url, headers=headers)
print (r.request.headers) #复杂post请求
url = 'http://m.ctrip.com'
payload = {'some': 'data'}
r = requests.post(url, data=json.dumps(payload)) #如果传递的payload是string而不是dict,需要先调用dumps方法格式化一下 # post多部分编码文件
url = 'http://m.ctrip.com'
files = {'file': open('report.xls', 'rb')}
r = requests.post(url, files=files) # 响应状态码
r = requests.get('http://m.ctrip.com')
print(r.status_code) # 响应头
r = requests.get('http://m.ctrip.com')
print (r.headers)
print (r.headers['Content-Type'])
print (r.headers.get('content-type')) #访问响应头部分内容的两种方式 # Cookies
url = 'http://example.com/some/cookie/setting/url'
r = requests.get(url)
r.cookies['example_cookie_name'] #读取cookies url = 'http://m.ctrip.com/cookies'
cookies = dict(cookies_are='working')
r = requests.get(url, cookies=cookies) #发送cookies #设置超时时间
r = requests.get('http://m.ctrip.com', timeout=0.001) #设置访问代理
proxies = {
"http": "http://10.10.1.10:3128",
"https": "http://10.10.1.100:4444",
}
r = requests.get('http://m.ctrip.com', proxies=proxies) #如果代理需要用户名和密码,则需要这样:
proxies = {
"http": "http://user:pass@10.10.1.10:3128/",
}
2、自动登录示例:
requests模拟登陆GitHub
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup def login_github():
"""
通过requests模块模拟浏览器登陆GitHub
:return:
"""
# 获取csrf_token
r1 = requests.get('https://github.com/login') # 获得get请求的对象
s1 = BeautifulSoup(r1.text, 'html.parser') # 使用bs4解析HTML对象
token = s1.find('input', attrs={'name': 'authenticity_token'}).get('value') # 获取登陆授权码,即csrf_token
get_cookies = r1.cookies.get_dict() # 获取get请求的cookies,post请求时必须携带 # 发送post登陆请求
'''
post登陆参数
commit Sign+in
utf8 ✓
authenticity_token E961jQMIyC9NPwL54YPj70gv2hbXWJ…fTUd+e4lT5RAizKbfzQo4eRHsfg==
login JackUpDown(用户名)
password **********(密码)
'''
r2 = requests.post(
'https://github.com/session',
data={
'commit': 'Sign+in',
'utf8': '✓',
'authenticity_token': token,
'login': 'JackUpDown',
'password': '**********'
},
cookies=get_cookies # 携带get请求的cookies
)
login_cookies = r2.cookies.get_dict() # 获得登陆成功的cookies,携带此cookies就可以访问任意GitHub页面 # 携带post cookies跳转任意页面
r3 = requests.get('https://github.com/settings/emails', cookies=login_cookies)
print(r3.text)
登录知乎
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import time import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup session = requests.Session() i1 = session.get(
url='https://www.zhihu.com/#signin',
headers={
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_10_5) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/54.0.2840.98 Safari/537.36',
}
) soup1 = BeautifulSoup(i1.text, 'lxml')
xsrf_tag = soup1.find(name='input', attrs={'name': '_xsrf'})
xsrf = xsrf_tag.get('value') current_time = time.time()
i2 = session.get(
url='https://www.zhihu.com/captcha.gif',
params={'r': current_time, 'type': 'login'},
headers={
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_10_5) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/54.0.2840.98 Safari/537.36',
}) with open('zhihu.gif', 'wb') as f:
f.write(i2.content) captcha = input('请打开zhihu.gif文件,查看并输入验证码:')
form_data = {
"_xsrf": xsrf,
'password': 'xxooxxoo',
"captcha": 'captcha',
'email': '424662508@qq.com'
}
i3 = session.post(
url='https://www.zhihu.com/login/email',
data=form_data,
headers={
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_10_5) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/54.0.2840.98 Safari/537.36',
}
) i4 = session.get(
url='https://www.zhihu.com/settings/profile',
headers={
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_10_5) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/54.0.2840.98 Safari/537.36',
}
) soup4 = BeautifulSoup(i4.text, 'lxml')
tag = soup4.find(id='rename-section')
nick_name = tag.find('span',class_='name').string
print(nick_name)
import requests, time, random, rsa, base64, re
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup as BS
import http.cookiejar as HC
from subprocess import Popen # 打开图片 home_url = "https://www.baidu.com/"
login_url = "https://passport.baidu.com/v2/api/?login" headers = {
"Host": "passport.baidu.com",
"Referer": "https://www.baidu.com/",
"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/48.0.2564.109 Safari/537.36"
} # 获取当前时间戳
def get_tt():
return str(int(time.time() * 1000)) # 随机生成callback
def get_callback():
prefix = "bd__cbs__" # callback 前缀
char = "0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"
n = random.randint(0, 2147483648)
suffix = []
while n != 0:
suffix.append(char[n % 36])
n = n // 36
suffix.reverse()
print("callback: " + (prefix + ''.join(suffix)))
return prefix + ''.join(suffix) # 随机生成gid
def get_gid():
gid = list("xxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx")
for x in range(len(gid)):
r = int(random.random() * 16)
if gid[x] == "x": # 如果当前值为x
gid[x] = hex(r).replace("0x", "").upper()
print("gid: " + "".join(gid))
return "".join(gid) def get_token():
global token_time
token_time = get_tt()
call_back = get_callback()
token_url = "https://passport.baidu.com/v2/api/?getapi&tpl=mn&apiver=v3&tt={}&class=login&gid={}&logintype=dialogLogin&callback={}".format(
token_time, gid, call_back)
response = session.get(token_url, headers=headers)
token_all = response.text.replace(call_back, "")
token_all = eval(token_all)
print(token_all)
return token_all["data"]["token"] def get_pubkey():
pubkey_callback = get_callback()
pubkey_url = "https://passport.baidu.com/v2/getpublickey?token={}&tpl=mn&apiver=v3&tt={}&gid={}&callback={}".format(
token, get_tt(), gid, pubkey_callback)
response = session.get(pubkey_url, headers=headers)
pubkey_all = eval(response.text.replace(pubkey_callback, ""))
print(pubkey_all["pubkey"], pubkey_all["key"])
return pubkey_all["pubkey"], pubkey_all["key"] # 密码rsa加密
def get_rsa_password(psw, pk):
pub = rsa.PublicKey.load_pkcs1_openssl_pem(pk.encode("utf-8"))
psw = psw.encode("utf-8")
passwd = rsa.encrypt(psw, pub)
passwd = base64.b64encode(passwd)
print(passwd.decode("utf-8"))
return passwd.decode("utf-8") session = requests.session()
session.cookies = HC.LWPCookieJar(filename="BaiDuCookies")
try:
session.cookies.load(ignore_discard=True) # 加d载cookies文件
except:
print("cookie未保存或cookie已过期")
gid = get_gid()
session.get("https://passport.baidu.com/v2/?login", headers=headers)
token = get_token()
pubkey, key = get_pubkey()
account = input("请输入您的账号:")
password = input("请输入您的密码:") postData = {
'staticpage': 'https://www.baidu.com/cache/user/html/v3Jump.html',
'charset': 'UTF-8',
'tpl': 'mn',
'subpro': '',
'apiver': 'v3',
'safeflg': '',
'u': 'https://www.baidu.com/',
'isPhone': 'false',
'detect': '',
'quick_user': '',
'logintype': 'dialogLogin',
'logLoginType': 'pc_loginDialog',
'idc': '',
'loginmerge': 'true',
'splogin': 'rate',
'mem_pass': 'on',
'crypttype': '',
'countrycode': '',
'codestring': '',
'verifycode': '',
'token': token,
'tt': get_tt(),
'gid': gid,
'username': account,
'password': get_rsa_password(password, pubkey), # 经过加密
'rsakey': key,
'ppui_logintime': str(int(get_tt()) - int(token_time)),
'callback': get_callback()
} response = session.post(login_url, postData, headers=headers)
# 如果存在codeString则获取验证码图片,再次请求
codeString = re.findall(r'codeString=(.*?)&userName', response.text)[0]
while codeString:
# 获取图片,保存图片,输入图片验证码
gif_url = "https://passport.baidu.com/cgi-bin/genimage?{}".format(codeString)
gif = session.get(gif_url, headers=headers)
with open("baidu.gif", "wb") as f:
f.write(gif.content)
Popen("baidu.gif", shell=True)
verifycode = input("验证码:")
postData["verifycode"] = verifycode
postData["codestring"] = codeString # 再次登录
relogin = session.post(login_url, postData, headers=headers)
codeString = re.findall(r'codeString=(.*?)&userName', relogin.text)[0] headers["Host"] = "www.baidu.com"
re = session.get(home_url, headers=headers)
# 保存cookies信息,以备下次直接访问首页
session.cookies.save()
# 获取首页天气信息
print("城市: " + BS(re.text, 'lxml').find("em", {"class": "show-city-name"})["data-key"])
print("气温: " + BS(re.text, 'lxml').find("em", {"class": "show-icon-temp"}).string)
1、认证机制
HTTP Basic Auth
HTTP Basic Auth简单点说明就是每次请求API时都提供用户的username和password,简言之,Basic Auth是配合RESTful API使用的最简单的认证方式,只需提供用户名密码即可,但由于有把用户名密码暴露给第三方客户端的风险,在生产环境下被使用的越来越少。因此,在开发对外开放的RESTful API时,尽量避免采用HTTP Basic Auth(事实上,很难找到用http基本身份认证方式的网站了)
import requests
r = requests.get('https://api.github.com/user', auth=('user', 'pass'))
print(r.status_code)
digest auth(摘要式身份认证)
digest auth在HTTP 1.1提出,目的是替代http 1.0提出的基本认证方式服务器收到客户端请求后返回401 UNAUTHORIZED,同时在WWW-Authenticate字段说明认证方式是Digest,其他信息还有realm域信息、nonce随机字符串、opaque透传字段(客户端会原样返回)等
import requests
r = requests.get('https://api.github.com/user', auth=('user', 'pass'))
print(r.status_code)
Cookie Auth
Cookie认证机制就是为一次请求认证在服务端创建一个Session对象,同时在客户端的浏览器端创建了一个Cookie对象;通过客户端带上来Cookie对象来与服务器端的session对象匹配来实现状态管理的。默认的,当我们关闭浏览器的时候,cookie会被删除。但可以通过修改cookie 的expire time使cookie在一定时间内有效;
OAuth(OAuth 1.0、OAuth 2.0)
OAuth(开放授权)是一个开放的授权标准,允许用户让第三方应用访问该用户在某一web服务上存储的私密的资源(如照片,视频,联系人列表),而无需将用户名和密码提供给第三方应用。
OAuth允许用户提供一个令牌,而不是用户名和密码来访问他们存放在特定服务提供者的数据。每一个令牌授权一个特定的第三方系统(例如,视频编辑网站)在特定的时段(例如,接下来的2小时内)内访问特定的资源(例如仅仅是某一相册中的视频)。这样,OAuth让用户可以授权第三方网站访问他们存储在另外服务提供者的某些特定信息,而非所有内容,这种基于OAuth的认证机制适用于个人消费者类的互联网产品,如社交类APP等应用,但是不太适合拥有自有认证权限管理的企业应用。
python处理OAuth1.0/2.0需要第三方库requests-oauthlib。
TokenAuth
使用基于 Token 的身份验证方法,在服务端不需要存储用户的登录记录。大概的流程是这样的:
1、客户端使用用户名跟密码请求登录
2、服务端收到请求,去验证用户名与密码
3、验证成功后,服务端会签发一个Token,再把这个Token发送给客户端
4、客户端收到Token以后可以把它存储起来,比如放在Cookie里
5、客户端每次向服务端请求资源的时候需要带着服务端签发的Token
6、服务端收到请求,然后去验证客户端请求里面带着的Token,如果验证成功,就向
7、客户端返回请求的数据
import requests url = "http://www.baidu.com"
response = requests.get(url)
#方法一
print(response.headers['Set-Cookie']) #方法二
print(response.cookies)
print(response.cookies.items())
print(response.cookies.items()[0][1]) #方法三
for k,v in response.cookies.items():
print(k+':'+v) #方法四
print(requests.utils.dict_from_cookiejar(response.cookies))
结果:
BDORZ=27315; max-age=86400; domain=.baidu.com; path=/
<RequestsCookieJar[<Cookie BDORZ=27315 for .baidu.com/>]>
[('BDORZ', '27315')]
27315
BDORZ:27315
{'BDORZ': '27315'}
设置cookie
#方法一:
# cookies是字典格式,这种cookie不能放在headers里
cookies = {
name1 :value1,
name2:value2
}
response = request.post(url, data=data, cookies=cookies) #方法二:使用requests.session, 通过CookieJar来处理cookie。
#将字典类型的cookie转换成cookiejar,将cookiesJar赋值给会话,cookie处理,由session自动处理cookie,报文请求的时候就不需要再加上cookie了。
cookiesJar = requests.utils.cookiejar_from_dict(manual_cookies, cookiejar=None,overwrite=True)
session = requests.session()
session.cookies=cookiesJar #方法三,headers中加cookie。
headers = {
'User-Agent':'Apache-HttpClient/4.5.2 (Java/1.8.0_66)',
'cookie':'_zap=191e4816-acf0-41ab-85ca-c54c2ff9ca1f; d_c0="ABCsEEAYPQ2PTofKIlzwxMJDdb8R-_6iVQA=|'
} response = requests.post(url,data=data,headers=headers)
#方法四:
#如果需要在请求中添加cookie,可以实例化一个RequestCookieJar的类,然后把值set进去,最后在get,post方法里面指定cookies参数就行了 import requests
from requests.cookies import RequestsCookieJar url = "http://fanyi.baidu.com/v2transapi" cookie_jar = RequestsCookieJar()
cookie_jar.set("BAIDUID", "B1CCDD4B4BC886BF99364C72C8AE1C01:FG=1", domain="baidu.com") res = requests.get(url, cookies=cookie_jar)
print res.status_code
import requests def reg():
host = "http://10.70.18.33:8083/"
url1 = host + "shopxx-mobile/register.jhtml"
r = requests.get(url1)
token = r.cookies.items()[0][1] url2 = host + "shopxx-mobile/register/send.jhtml"
headers = {
"token": token,
"Host": "10.70.18.33:8083",
"User-Agent":" Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10.11; rv:46.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/46.0",
"Accept": "application/json, text/javascript, */*; q=0.01",
"Accept-Language":"zh-CN,zh;q=0.8,en-US;q=0.5,en;q=0.3",
"Accept-Encoding": "gzip, deflate",
"Content-Type":"application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=UTF-8",
"X-Requested-With": "XMLHttpRequest",
"Connection":"keep-alive",
"Content-Length": "",
"charset":"UTF-8",
"cookie":"token=" + token
} data = {'mobile':'1851174****'}
s = requests.post(url2,data,headers=headers) print(s.status_code,s.text) if __name__ == '__main__':
reg()
4、通过cookie绕过验证码登录
为了绕过登录验证码,先手动成功登录,并抓包获取登录成功的cookie值。在代码中以保持会话的方式访问登录界面(不需要真的登录),获取cookie,然后将抓包获取到的cookie值添加到代码中的cookie里(亦即添加到session中),之后再去访问需要访问的内容。
# coding:utf-8
import requests
# 先打开登录首页,获取部分cookie
url = "https://passport.cnblogs.com/user/signin"
headers = {"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64; rv:44.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/44.0"} # get方法加个ser-Agent就可以了
s = requests.session()
r = s.get(url, headers=headers,verify=False) #获取登录页面的cookie,不需要去登陆,只要登录界面。
print(s.cookies)
# 添加登录需要的两个cookie
c = requests.cookies.RequestsCookieJar() c.set('.CNBlogsCookie', 'xxx') # 填入抓包获取的cookie
c.set('.Cnblogs.AspNetCore.Cookies','xxx') # 填入抓包获取的cookie
s.cookies.update(c)
print(s.cookies) # 登录成功后保存编辑内容
url2= "https://i.cnblogs.com/EditPosts.aspx?opt=1"
body = {"__VIEWSTATE": "",
"__VIEWSTATEGENERATOR":"FE27D343",
"Editor$Edit$txbTitle":"这是绕过登录的标题:北京-宏哥",
"Editor$Edit$EditorBody":"<p>这里是中文内容:http://www.cnblogs.com/duhong/</p>",
"Editor$Edit$Advanced$ckbPublished":"on",
"Editor$Edit$Advanced$chkDisplayHomePage":"on",
"Editor$Edit$Advanced$chkComments":"on",
"Editor$Edit$Advanced$chkMainSyndication":"on",
"Editor$Edit$lkbDraft":"存为草稿",
}
r2 = s.post(url2, data=body, verify=False)
print(r.content)
通过使用基础的测试工具,可以做简单场景的API测试;而项目进行过程中,为了解决实际的一些问题,我们会设计更加复杂的测试场景,下面列举几个实际项目中的典型场景。
场景一:API串联调用
以协议支付为例,我们知道,三方公司接入网联后,用协议支付取代代扣,而协议支付的流程中需要用户输入银行返回的验证码完成绑卡。从接口层面上看,顺序是先调用协议签约API,返回状态成功且获取到短信验证码后,再使用此短信验证码作为输入参数调用代扣API。协议签约和代扣两个API是顺序调用,而且在两次调用中间有获取手机上的短信验证码,这些过程都需要通过程序自动化实现以提高效率。
场景二:API接口加密
为保证API接口安全,系统间和系统内模块间互相访问需要进行加密处理,常用的加密方式有DES、AES、RSA、MD5等,各系统的加密方式并不一样(接口调用方和接口提供方约定好即可),意味着API测试需要支持多种自动化加密方式程。某些系统还会返回加密的响应报文,也需要识别并解密。
场景三:异步API测试
异步API指请求发出后后收到一个同步响应,但并不是最终处理结果,最终结果通过回调或者主动查询获得。对于这样的API,同步响应的验证只是第一步,后续还得继续验证DB中的值、MQ中的值、以及异步回调是否成功等。对于异步回调,我们可以模拟回调地址来验证成功与否;而对于主动查询,我们就得通过查看DB中的状态值来验证了,但是查询到结果的时间点不确定,几分钟到几小时都有可能,这就得有一个定时DB查询任务去验证。
场景四:API测试中的外部依赖
APIA调用APIB且B不可用,此时如何测试APIA需要考虑。比如支付系统对三方支付通道、对银行的依赖,并不是所有的三方都支持测试环境,解决此问题的核心思路是搭建MockServer,而且尽量做到通用性,我们开发了一套Mock系统 -aMock,通过页面录入接口信息,保存在数据库内,通过Nginx访问配置好的Mock接口,后台统一处理请求信息,然后通过URL和报文特性去匹配特定的响应信息。
python实现接口自动化的更多相关文章
- python+request接口自动化框架
python+request接口自动化框架搭建 1.数据准备2.用python获取Excel文件中测试用例数据3.通过requests测试接口4.根据接口返回的code值和Excel对比 但本章只讲整 ...
- python+pytest接口自动化(11)-测试函数、测试类/测试方法的封装
前言 在python+pytest 接口自动化系列中,我们之前的文章基本都没有将代码进行封装,但实际编写自动化测试脚本中,我们都需要将测试代码进行封装,才能被测试框架识别执行. 例如单个接口的请求代码 ...
- python+requests接口自动化完整项目设计源码
前言 有很多小伙伴吵着要完整的项目源码,完整的项目属于公司内部的代码,这个是没法分享的,违反职业道德了,就算别人分享了,也只适用于本公司内部的业务. 所以用例的代码还是得自己去一个个写,我只能分享项目 ...
- 华为测试大牛Python+Django接口自动化怎么写的?
有人喜欢创造世界,他们做了开发者:有的人喜欢开发者,他们做了测试员.什么是软件测试?软件测试就是一场本该在用户面前发生的灾难提前在自己面前发生了,这会让他们生出一种救世主的感觉,拯救了用户,也就拯救者 ...
- python+requests接口自动化完整项目设计源码(一)
原文地址https://www.cnblogs.com/yoyoketang/tag/python接口自动化/ 原文地址https://www.cnblogs.com/yoyoketang/ 原文地址 ...
- 基于Python的接口自动化-01
为什么要做接口测试 当前互联网产品迭代速度越来越快,由之前的2-3个月到个把月,再到班车制,甚至更短,每次发版之前都需要对所有功能进行回归测试,在人力资源有限的情况下,做自动化测试很有必要.由于UI更 ...
- python+requests接口自动化框架
为什么要做接口自动化框架 1.业务与配置的分离 2.数据与程序的分离:数据的变更不影响程序 3.有日志功能,实现无人值守 4.自动发送测试报告 5.不懂编程的测试人员也可以进行测试 正常接口测试的流程 ...
- python+pytest接口自动化(4)-requests发送get请求
python中用于请求http接口的有自带的urllib和第三方库requests,但 urllib 写法稍微有点繁琐,所以在进行接口自动化测试过程中,一般使用更为简洁且功能强大的 requests ...
- python+pytest接口自动化(6)-请求参数格式的确定
我们在做接口测试之前,先需要根据接口文档或抓包接口数据,搞清楚被测接口的详细内容,其中就包含请求参数的编码格式,从而使用对应的参数格式发送请求.例如某个接口规定的请求主体的编码方式为 applicat ...
- python+pytest接口自动化(9)-cookie绕过登录(保持登录状态)
在编写接口自动化测试用例或其他脚本的过程中,经常会遇到需要绕过用户名/密码或验证码登录,去请求接口的情况,一是因为有时验证码会比较复杂,比如有些图形验证码,难以通过接口的方式去处理:再者,每次请求接口 ...
随机推荐
- 使用jave2将音频wav转换成mp3格式
最近需要用到语音合成功能,网上查阅了一番,发现可以使用腾讯云的语音合成API来完成这个功能,但是腾讯云的api返回的是wav格式的音频文件,这个格式的文件有些不通用,因此需要转换成mp3格式的文件. ...
- 打开VS2015提示“重新启动处于挂起状态。请在启动Visual Studio”之前重新启动
昨晚安装了VS2015,今天打开VS2015提示[“重新启动处于挂起状态.请在启动Visual Studio”之前重新启动] 这里重新启动指的是重启电脑 解决方法: 电脑需要重启电脑
- 【简●解】POJ 1185,LG P2704【炮兵阵地】
POJ 1185,LG P2704[炮兵阵地] 状压经典入门. [传送门] POJ 1185 洛谷 P2704 [题目大意] 司令部的将军们打算在 \(N\times M\) 的网格地图上部署他们的炮 ...
- 痛苦的版本对齐(3) cygwin下的路径引用(sed解决篇)
上次问题(见http://www.cnblogs.com/yvivid/p/3546649.html),.depend信息路径错误的问题. 主要尝试了,在(虚拟机下构建)linux下编译,确实没有问题 ...
- 洛谷 P1434 [SHOI2002]滑雪
这道题适合记忆化练手 毕竟总有些大佬虐题. 这个题有几个剪枝 1.记忆化 这个不用多说了吧 剪枝就是 如果 当前点到下面一个点的目前下降的高度+1 小于 下面那个点 能下降的高度 那么反过来,这个点不 ...
- 让Selenium稳定运行的技巧
Selenium简介 Selenium是非常流行的Web自动化测试工具.它具有自动化测试用例制作简单,支持多种浏览器和不同的操作系统等优点. Selenium脚本不稳定的问题 有很多时候Seleniu ...
- zoj 1251 Box of Bricks
Box of Bricks Time Limit: 2 Seconds Memory Limit: 65536 KB Little Bob likes playing with his bo ...
- poj 3417 Network 题解
题意: 先给出一棵树,然后再给出m条边,把这m条边连上,然后剪掉两条边,一条是原边,一条是新边,问有多少种方案能使图不连通. 思路: 从原边的角度看 1.树加边,一定成环,加一条(u,v)边就有u-& ...
- [HNOI2009]梦幻布丁(链表+启发式合并)
洛谷传送门 开始一个O(n^2)思路,每次每句要改变颜色的点,改变完颜色后重新计算颜色的段数,显然拉闸. 然后呢..然后就不会了. 看了别人博客,才知道有个叫做启发式合并的东西,就是把小的合并到大的上 ...
- hdu 2438 Turn the corner [ 三分 ]
传送门 Turn the corner Time Limit: 3000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Othe ...
