[Elementary Mechanics Using Python-02]Feather in tornado
Problem
9.17 Feather in tornado.
In this project you will learn to use Newton’s laws and the force model for air resistance in a wind field to address the motion of a light object in strong winds. We start from a simple model without wind and gradually add complexity to the model, until we finally address the motion in a tornado. Motion without wind:
First, we address the motion of the feather without wind.
(a) Identify the forces acting on a feather while it is falling and draw a free-body diagram for the feather.
(b) Introduce quantitative force models for the forces, and find an expression for the acceleration of the feather. You may assume a quadratic law for air resistance.
(c) If you release the feather from rest, its velocity will tend asymptotically toward the terminal velocity, \(v_T\) . Show that the terminal velocity is \(v_T\) = \(−(mg/D)^{1/2}\), where D is the constant in the air resistance model.
(d) We release the feather from a distance h above the floor and measure the time t until the feather hits the floor. You may assume that the feather falls with a constant velocity equal to the terminal velocity. Show how you can determine D/mg by measuring the time t. Estimate D/mg when you release the feather from a height of 2.4 m above the floor and it takes 4.8 s until it hits the floor.
(e) We will now develop a more precise model where we do not assume that the velocity is constant. You release the feather from the height h at the time t = 0 s. Find the equation you have to solve to find the position of the feather as a function of time. What are the initial conditions?
(f) Write a program that solves this equation to find the velocity and position as a function of time t. Use the parameters you determined above, and test the program by ensuring that it produces the correct terminal velocity.
(g) Fig. 9.19 shows the position and velocity calculated with the program using the parameters found above. Was the approximation in part (d) reasonable? Explain your answer. Model with wind: We have now found a model that can be used to find the motion of the feather. We will now find the motion of the feather in three dimensions while it is blowing. The velocity of the wind varies in space, so that the wind velocity w is a function of the position r. We write this as w = w(r).
(h) Find an expression for the acceleration of the feather. The expression may include the wind velocity w(r). Let the z-axis correspond to the vertical direction.
(i) Assume that the feather is moving in an approximately horizontal plane—that is you may assume that the vertical acceleration is negligible. How does the wind have to blow in order for the feather to move in a circular orbit of radiusr0 with a constant speed v0?
Motion in a tornado: For a tornado with a center at the origin, the wind velocity is expected to be approximately given by the model:
\[\boldsymbol{w}(\boldsymbol{r}) = u_0\boldsymbol{r}e^{−r/R}\hat{u_θ} = u_0(-y, x,0)e^{−r/R}\hat{u_θ} , \space \space (9.79)
\]where u0 is a characteristic velocity for the wind, R is the radius of the tornado, and uˆθ is a tangential unit vector in the horizontal plane (\(\hat{u_\theta}\) is normal to r). Here, r = (x, y,z), and r = |r|. The velocity field is illustrated in Fig. 9.20.
(j) Is is possible to choose an appropriate set of initial conditions so that the feather moves in a circular path in the tornado? Explain your answer.
(k) Rewrite your program to find the velocity and position of the feather as a function of time. For the tornado you may use the values u0 = 100 m/s and R = 20 m.
(l) Find the trajectory for the feather if it is released from rest from a height of 2.4m, and in a position corresponding to r = −R i + hk. (m) The trajectory of the feather is shown in Figs. 9.20 and 9.21. Compare the results with what happended when you dropped the feather without wind. Why does the feather now take longer to reach the ground?
Solution
\((a)\)
考虑无风情况,\(\boldsymbol{w} = \boldsymbol{0}\),很容易画出受力分析图
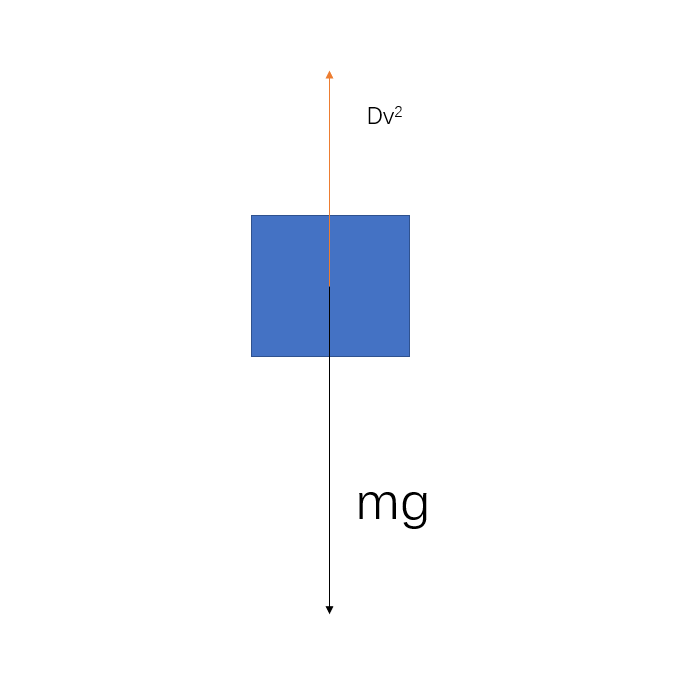
\((b)\)
由受力分析图可以简单的列出动力学方程
\]
\(\Rightarrow\)
\]
\((c)\)
我们令 \(\boldsymbol{a} = \boldsymbol{0}\), 得到方程
\]
\(\Rightarrow\)
\]
\((d)\)
由\((c)\)中公式,我们列出
\]
将\(v_T = -\sqrt[]{\frac{mg}{D}}\)带入求解,得
\]
\((e)\)
此问方程就是\((b)\)中得到的方程
\]
\((f)\)
编程实现
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
G = 9.81
H = 2.4
dt = 0.001
C = 4 # D/mg
t = np.arange(0, 5, 0.001)
a = np.zeros(5000, dtype=float)
v = np.zeros(5000, dtype=float)
x = np.zeros(5000, dtype=float)
a[0] = -G
v[0] = 0
x[0] = H
for index in range(1, 5000):
a[index] = (-1 + C*v[index-1]**2)*G
v[index] = v[index-1] + a[index-1]*dt
x[index] = x[index-1] + v[index-1]*dt
plt.subplot('211')
plt.title('$x(t)$')
ax = plt.gca()
ax.spines['right'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['top'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['bottom'].set_position(('data', 0))
plt.plot(t, x, label="$x(t)$")
plt.xlim([0, 5])
plt.ylim([0, 3])
plt.xlabel('$t[s]$')
plt.ylabel('$x[m]$')
plt.legend()
plt.subplot('313')
plt.title('$v(t)$')
ax = plt.gca()
ax.spines['right'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['top'].set_color('none')
ax.spines['bottom'].set_position(('data', 0))
plt.plot(t, v, label="$v(t)$")
plt.xlim([0, 5])
plt.ylim([-0.8, 0])
plt.xlabel('$t[s]$')
plt.ylabel('$v[m/s]$')
plt.legend()
plt.savefig('f.jpg', dpi=3000)
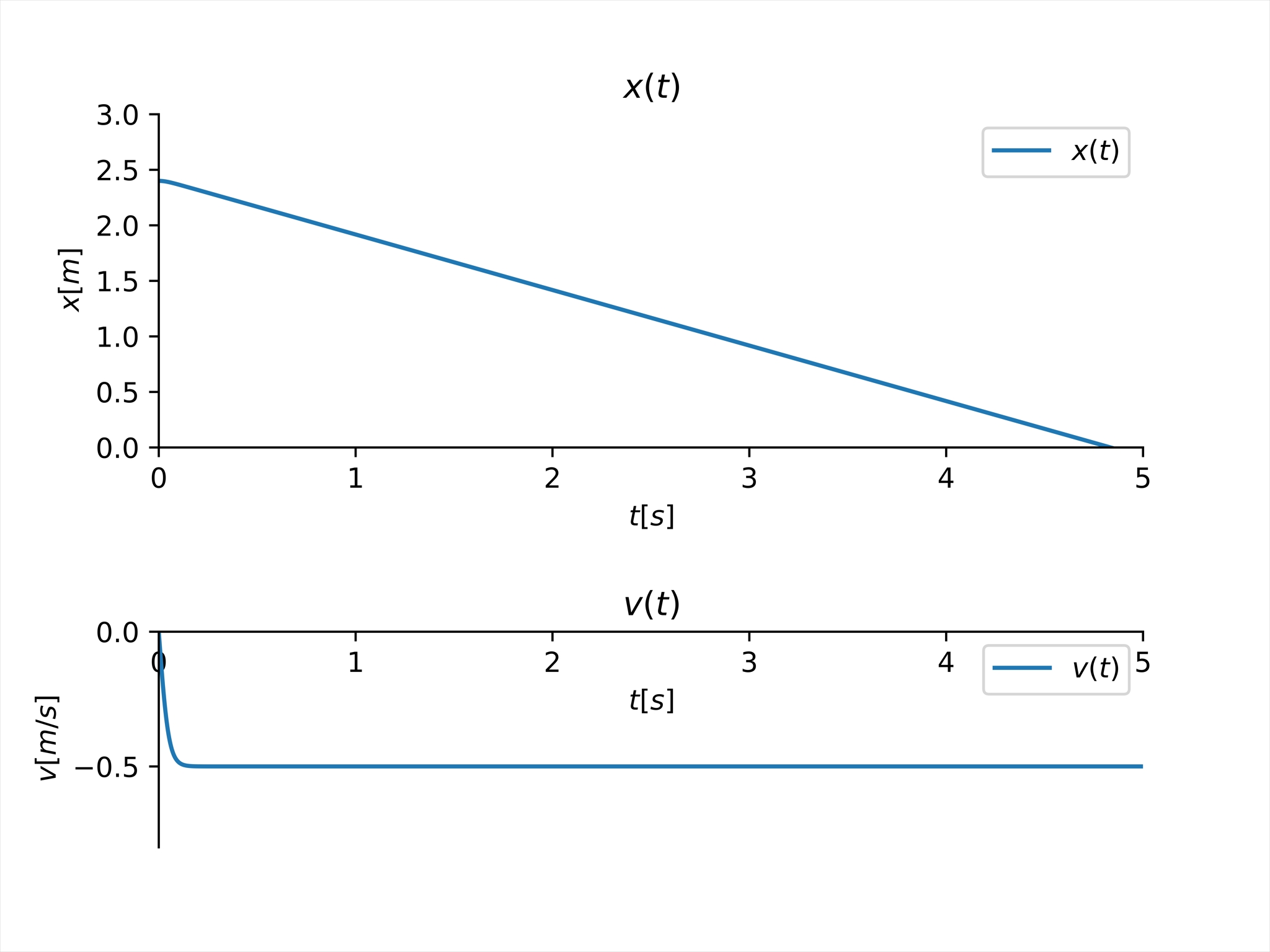
\((h)\)
考虑上风力,改为相对于风的速度
\]
\((i)\)
忽略铅锤方向加速度,\(让g \rightarrow 0, 且当\boldsymbol{a}=-\frac{v_0^2}{r_0}\hat{r}时:\\\)
\]
解出\(\boldsymbol{w}\)
\]
\((j)\)
首先列出羽毛的微分方程
\]
找到初值条件
&\boldsymbol{x}(0) = [-20, 0, 2.4] \\
&\boldsymbol{v}(0) = [0, 0, 0] \\
&\boldsymbol{a}(0) = -(\boldsymbol{k} + \frac{D}{mg}|\boldsymbol{v}(0)-\boldsymbol{w}(\boldsymbol{x}(0))|(\boldsymbol{v}(0)-\boldsymbol{w}(\boldsymbol{x}(0))))g\\
\end{align}\end{matrix}\right.
\]
编程实现
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
// 定义常量
u0 = 100
R = 20
H = 2.4
G = 9.81
k = np.array([0, 0, 1])
C = 4 # D/mg
def Len(vector):
return np.sqrt(vector[0]**2+vector[1]**2+vector[2]**2)
// 风场函数
def w(xVector, yVector, zVector=0):
rLen = Len([xVector, yVector, zVector])
return np.array([u0*np.exp(-rLen/R)*(-yVector), u0*np.exp(-rLen/R)*xVector, u0*np.exp(-rLen/R)*0])
// 加速度函数
def A(v, r):
W = w(r[0], r[1], r[2])
return -(k+C*(v - W)*Len((v - W)))*G
// 创建网格
xVector, yVector= np.meshgrid(
np.linspace(-101, 101, 100),
np.linspace(-101, 101, 100)
)
// 计算风场
uVector, vVector, wVector = w(xVector, yVector)
M = np.hypot(uVector,vVector)
// 绘制风场
plt.quiver(
xVector, yVector,
uVector, vVector,
M, pivot='mid', width=0.001
)
dt = 0.00001
tMax = 30
t = np.arange(0, tMax, dt)
x = np.zeros((int(tMax/dt), 3))
v = np.zeros((int(tMax/dt), 3))
a = np.zeros((int(tMax/dt), 3))
// 初值条件
v[0,:] = np.array([0, 0, 0])
x[0,:] = np.array([-20, 0, H])
a[0,:] = A(v[0,:], x[0,:])
// 数值积分
i = 0
for index in range(1, 3000000):
a[index,:] = A(v[index-1,:], x[index-1,:])
v[index,:] = v[index-1,:] + a[index-1,:]*dt
x[index,:] = x[index-1,:] + v[index-1,:]*dt
if x[index,2] <= 0:
i = index
print("drop at {} s".format(i*dt))
break
// 绘制羽毛轨迹
plt.plot(x[:i,0], x[:i,1], 'r', linewidth=0.5)
plt.scatter(x[:i:10000,0], x[:i:10000,1], s=0.6)
plt.xlim([-101, 101])
plt.ylim([-101, 101])
plt.axis('equal')
plt.savefig('1.jpg', dpi=3000)
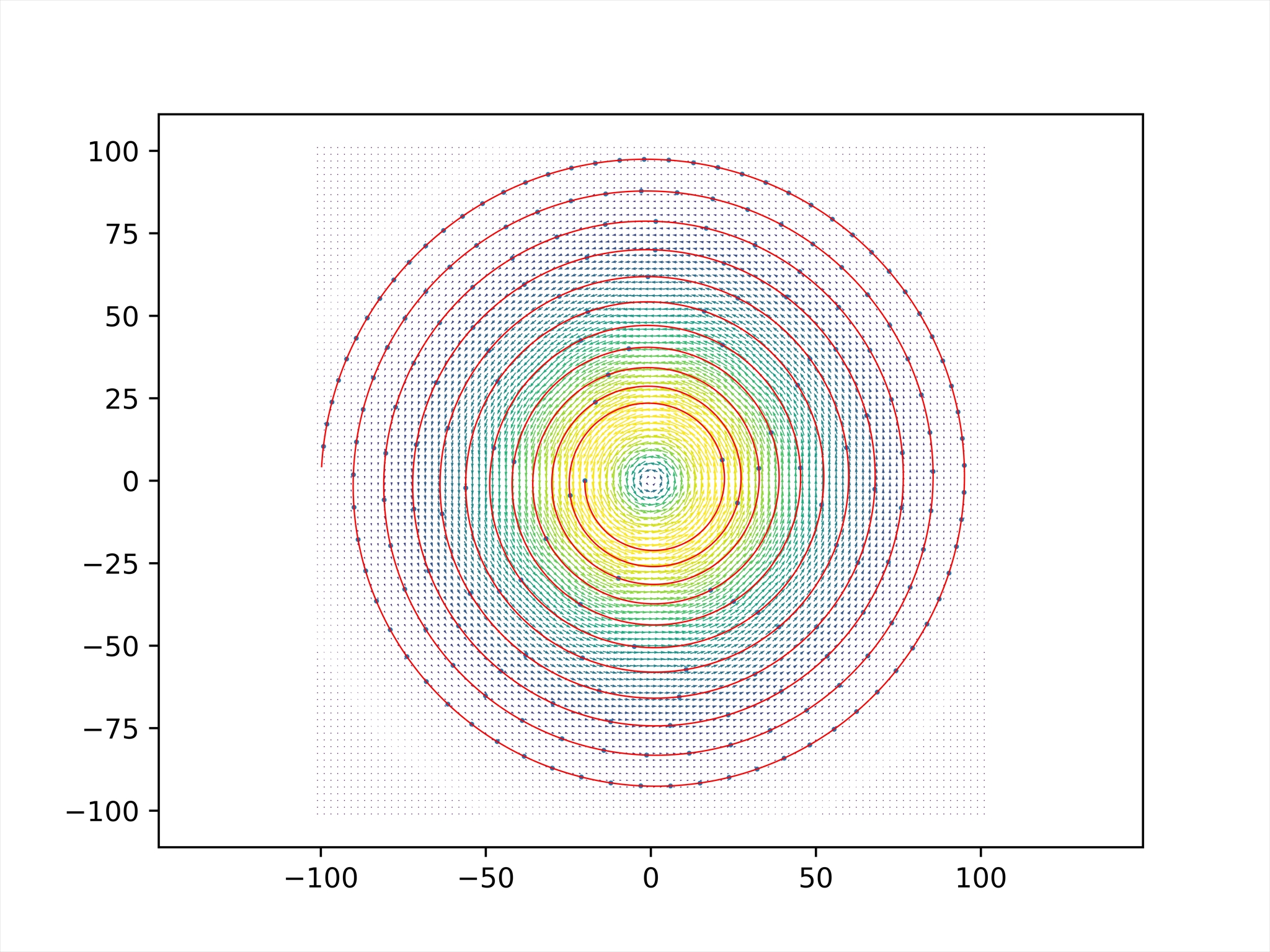
结论
在龙卷风影响下,计算出羽毛要经过 \(20.59065 s\) 落到地面,远大于无风情况下的情况,主要原因是采用了平方模型,使得空气阻力非线性。
[Elementary Mechanics Using Python-02]Feather in tornado的更多相关文章
- Python(九)Tornado web 框架
一.简介 Tornado 是 FriendFeed 使用的可扩展的非阻塞式 web 服务器及其相关工具的开源版本.这个 Web 框架看起来有些像web.py 或者 Google 的 webapp,不过 ...
- python web框架——初识tornado
一 Tornado概述 Tornado是FriendFeed使用的可扩展的非阻塞式web框架及其相关工具的开源版本.这个Web框架看起来有些像web.py或者Google的 webapp,不过为了能有 ...
- Python学习笔记17—Tornado
实例 #!/usr/bin/env Python #coding:utf-8 import tornado.httpserver import tornado.ioloop import tornad ...
- python web框架之Tornado
说Tornado之前分享几个前端不错的网站: -- Bootstrap http://www.bootcss.com/ -- Font Awesome http://fontawesome.io/ - ...
- 【Python】linux安装tornado
想写个页面,又不想用tomcat,同事说可以用tornado,试一下 1 我从网上找了个hello world类似的程序,复制粘贴运行,提示 ImportError: No module named ...
- Python Web 框架:Tornado
1.Tornado Tornado:python编写的web服务器兼web应用框架 1.1.Tornado的优势 轻量级web框架 异步非阻塞IO处理方式 出色的抗负载能力 优异的处理性能,不依赖多进 ...
- python web框架之Tornado的简单使用
python web框架有很多,比如常用的有django,flask等.今天主要介绍Tornado ,Tornado是一个用Python写的相对简单的.不设障碍的Web服务器架构,用以处理上万的同时的 ...
- 在学习python的Django\Flask\Tornado前你需要知道的,what is web?
我们都在讲web开发web开发,那到底什么是web呢? 如果你正在学习python三大主流web框架,那这些你必须要知道了 软件开发架构: C/S架构:Client/Server 客户端与服务端 ...
- python 02
函数的参数 默认参数: 函数的基本形参, 可以有默认参数, 什么是基本形参呢, 就是普通变量, 如字符串, 数字等. 并且带有默认参数的形参, 要放在后边. 传参时, 不必将所有的参数都传递, 可以只 ...
随机推荐
- Java基础(第一期)
Java基础 1.注释 Java中注释有三种: 单行注释 // 多行注释 /* */ 文本注释(用的较少) /** */ 书写注释是一个非常好的习惯 BAT 平时写代码一定要注意规范 //有趣的代码注 ...
- 在 Spring Boot 2 中致敬 JSP
新冠病毒
- [备忘] DevOps 工具上的准备清单(不断补充中……)
目录 概念 发展历程 工具清单 规划 概念 从字面上来看,"DevOps"一词是由英文 Development(开发)和 Operations (运维)组合而成,但它所代表的理念和 ...
- 交换机上禁止某个MAC地址通信
当分析出网络中某台机器中毒时而有不知道它的具体位置,我们可以通过获取其MAC地址然后在交换机上禁止其MAC来达到隔离它的效果.通过ARP表查询IP地址对应的MAC地址,再将该MAC地址加入黑名单过滤. ...
- github 无法访问
描述: 1. ping 丢失 100% 2. git 失败 Failed to connect to github.com port 443: Timed out 3.打开网站 超时 解决: http ...
- leetcode32 最长游戏括号 dp
有一说一,我觉得这题没有到困难级 要保存之前的状态,感觉是很明显的dp 思路和题解一样 class Solution { public: int longestValidParentheses(str ...
- BZOJ 3676 回文串(回文树)题解
题意: 一个回文的价值为长度 * 出现次数,问一个串中的子串的最大回文价值 思路: 回文树模板题,跑PAM,然后计算所有节点出现次数. 参考: 回文串问题的克星--Palindrome Tree(回文 ...
- sqli-libs(4) 双引号报错
经测试,发现单引号不报错,而双引号却报错了 通过查看源码,发现下图中红色的箭头,如果不知道是什么意思,我们可以复制出来看看是什么含义: <?php$id=1;$id='"' .$id. ...
- VSCode 在 Vue 导入路径中使用 @ 符号后无法正确跳转 bug
VSCode 在 Vue 导入路径中使用 @ 符号后无法正确跳转 bug bug jsconfig.json { // This file is required for VSCode to unde ...
- CSS ? Layout Module : CSS 布局模型
1 1 1 https://www.w3.org/TR/css-grid-1/ CSS Grid Layout Module Level 1 W3C Working Draft, 19 May 201 ...
