2014 UESTC暑前集训搜索专题解题报告
A.解救小Q
BFS。每次到达一个状态时看是否是在传送阵的一点上,是则传送到另一点即可。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
#define NA 100007 char mp[][]; struct status
{
int x,y;
int l;
}; int vis[][]; struct transport
{
int x1,y1; //初始点
int x2,y2; //传送目标点
int flag;
}a[]; int n,m;
int head,tail;
int pathx[]={,,,-};
int pathy[]={-,,,}; bool OK(int nx,int ny)
{
return nx>=&&ny>=&&nx<n&&ny<m;
} int bfs(int x,int y)
{
status now,next;
queue<status> que;
now.x=x;
now.y=y;
now.l=;
vis[now.x][now.y]=;
que.push(now);
while(!que.empty()) //队列非空
{
now = que.front();
que.pop();
for(int i=;i<;i++)
{
int nx=now.x+pathx[i];
int ny=now.y+pathy[i];
if(vis[nx][ny] || !OK(nx,ny))
continue;
if(mp[nx][ny]=='Q')
return now.l+;
if(mp[nx][ny]!='#')
{
if(mp[nx][ny]>='a'&&mp[nx][ny]<='z')
{
int h=mp[nx][ny]-'a';
if(a[h].x1!=nx||a[h].y1!=ny) //初始点和目标点可以互换
{
next.x=a[h].x1;
next.y=a[h].y1;
}
else
{
next.x=a[h].x2;
next.y=a[h].y2;
}
next.l=now.l+;
que.push(next);
}
else
{
next.x=nx;
next.y=ny;
next.l=now.l+;
que.push(next);
}
vis[nx][ny]=;
}
}
}
return -;
} int main()
{
int T,x,y;
int N,M;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
memset(vis,,sizeof(vis));
memset(mp,,sizeof(mp));
for(int j=;j<;j++)
a[j].flag=;
scanf("%d%d",&N,&M);
n=N;
m=M;
getchar();
for(int i=;i<N;i++)
{
for(int j=;j<M;j++)
{
scanf("%c",&mp[i][j]);
if(mp[i][j]=='L')
{
x=i;
y=j;
}
if(mp[i][j]>='a'&&mp[i][j]<='z')
{
int h=mp[i][j]-'a';
if(a[h].flag==)
{
a[h].x1=i;
a[h].y1=j;
a[h].flag=;
}
else if(a[h].flag==)
{
a[h].x2=i;
a[h].y2=j;
}
}
}
getchar();
}
printf("%d\n",bfs(x,y));
}
return ;
}
B.方老师开橙卡
每次枚举一位数,从1位数字到9位数字,满足条件则加入队列。比如21,首先1*1 = 1 和 9*9 = 81 都满足个位与21的个位相同,加入队列,下次就考虑匹配第二位,然后第三位,。。每次去除相同位数的数字(que.size()),比如去除Y,则拓展的时候枚举X,这时m=10*X+Y,看此时m^2的那一位是否与n的那一位匹配,如果匹配,则加入队列。每次如果相等,顺便判断一下是否就是n,就是的话直接与答案相比,小于答案则更新答案。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#define Mod 1000000007
using namespace std;
#define N 50007 int Scheck(ll ka,ll n)
{
while(ka && n)
{
if(ka% != n%)
return ;
ka/=;
n/=;
}
if(n == )
return ;
else
return ;
} ll Ten(int wei)
{
ll res = ;
for(int i=;i<wei;i++)
res *= ;
return res;
} ll toTen(ll tmp)
{
ll res = ;
while(tmp)
{
res *= ;
tmp /= ;
}
return res;
} ll ans;
int w[],ind; void BFS(ll n)
{
queue<ll> que;
ll m,x,y;
for(y=;y<=;y++)
{
ll ka = y*y;
if(ka% == w[])
{
if(Scheck(ka,n))
{
if(y < ans)
ans = y;
}
else
que.push(y);
}
}
int layer = ;
while(!que.empty())
{
layer++;
if(layer > || layer >= ind)
return;
ll ten = Ten(layer-);
int qsize = que.size();
while(qsize--)
{
ll tmp = que.front();
que.pop();
for(x=;x<=;x++)
{
m = ten*x+tmp;
ll m2 = m*m;
if((m2/ten)% == w[layer])
{
if(Scheck(m2,n))
{
if(m < ans)
ans = m;
}
else
que.push(m);
}
}
}
}
return;
} int main()
{
int T;
ll n;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
scanf("%lld",&n);
if(n == )
{
printf("0\n");
continue;
}
ll kn = n;
ind = ;
while(kn)
{
w[ind++] = kn%;
kn/=;
}
ans = Mod;
BFS(n);
if(ans == Mod)
puts("None");
else
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
return ;
}
C.贪吃蛇
如果存储每节身体的坐标,会爆Memory的。
考虑因为每个相邻节的坐标都是相邻的,维护一个节与前一个节的关系即可,有四种情况,可以分别用00,01,10,11来表示,这样的话就只需维护蛇头的坐标,根据01关系就可推断出整个蛇身的位置。然后就是BFS了,注意不要咬到蛇身和往自己来的方向走(如果长度为1的话就可以)。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#define Mod 1000000007
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
#define N 107 struct Point
{
int x,y;
}p[]; struct node
{
int x,y;
int num,step;
}S; char mp[][];
int vis[][][];
int R,C,K;
int EX,EY;
int dx[] = {,,,-};
int dy[] = {,,-,}; int p_to_num(Point *p)
{
int i,k;
int res = ,now = ;
for(i=;i<K;i++)
{
int sx = p[i].x;
int sy = p[i].y;
int tx = p[i+].x;
int ty = p[i+].y;
if(sx > tx && sy == ty)
k = ; //下
else if(sx == tx && sy > ty)
k = ; //右
else if(sx < tx && sy == ty)
k = ; //上
else if(sx == tx && sy < ty)
k = ; //左
k <<= now;
now += ;
res |= k;
}
return res;
} bool OK(int nx,int ny)
{
if(nx >= && nx < R && ny >= && ny < C)
return true;
return false;
} bool check(int num)
{
int i,j,k;
k = K-;
int x = ,y = ;
while(k--)
{
x += dx[num&];
y += dy[num&];
if(x == && y == )
return false;
num >>= ;
}
return true;
} int BFS(node S)
{
int i,j,k;
queue<node> que;
memset(vis,,sizeof(vis));
que.push(S);
vis[S.num][S.x][S.y] = ;
int MOD = (<<((K-)*));
while(!que.empty())
{
node tmp = que.front();
que.pop();
if(tmp.x == EX && tmp.y == EY)
return tmp.step;
for(i=;i<;i++)
{
if(K <= || ((tmp.num&) != i))
{
int nx = tmp.x + dx[i];
int ny = tmp.y + dy[i];
if(!OK(nx,ny) || mp[nx][ny] == '#')
continue;
node now;
now.num = (tmp.num << );
now.num |= (-i);
now.num %= MOD;
if(vis[now.num][nx][ny]) //状态已走过
continue;
if(!check(now.num)) //咬到蛇身
continue;
vis[now.num][nx][ny] = ;
now.x = nx;
now.y = ny;
now.step = tmp.step + ;
que.push(now);
}
}
}
return -;
} int main()
{
int i,j,k,cs = ;
while(scanf("%d%d",&R,&C)!=EOF)
{
K = ;
for(i=;i<R;i++)
{
scanf("%s",mp[i]);
for(j=;j<C;j++)
{
if(mp[i][j] == '@')
EX = i,EY = j;
if(mp[i][j] >= '' && mp[i][j] <= '')
{
k = mp[i][j] - '';
p[k].x = i,p[k].y = j;
K = max(K,k);
}
}
}
S.num = p_to_num(p);
S.x = p[].x;
S.y = p[].y;
S.step = ;
printf("Case #%d: %d\n",cs++,BFS(S));
}
return ;
}
D.方老师与素数
BFS搜索。每次改变一位(千位,百位,十位或个位),拓展状态,直到达到目标状态。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <queue>
#define Mod 1000000007
using namespace std;
#define N 10007 int u[N],c,vis[N],prime[N];
int n,a,b,flag;
struct node
{
int num,step;
}S,E; void doit()
{
int i,j;
c=;
for(i=;i<=;i++)
u[i] = ;
for(i=;i<=;i++)
{
if(u[i])
prime[c++] = i;
for(j=;j<c&&i*prime[j]<=;j++)
{
u[i*prime[j]] = ;
if(i%prime[j] == )
break;
}
}
} int change(int base,int num,int ind)
{
char ss[];
ss[] = base/ + ;
ss[] = (base/)% + ;
ss[] = (base/)% + ;
ss[] = base% + ;
ss[ind] = num + ;
ss[] = '\0';
return atoi(ss);
} int bfs(node S,int b)
{
queue<node> que;
node k;
while(!que.empty())
que.pop();
int i,j,res = ;
int ka = ;
flag = ;
memset(vis,,sizeof(vis));
que.push(S);
vis[S.num] = ;
while(!que.empty())
{
node tmp = que.front();
que.pop();
if(tmp.num == b)
{
flag = ;
return tmp.step;
}
for(i=;i<=;i++) //千位
{
int now = change(tmp.num,i,);
if(now != tmp.num && u[now] && !vis[now])
{
vis[now] = ;
k.num = now;
k.step = tmp.step + ;
que.push(k);
}
}
for(i=;i<=;i++) //百,十,个位
{
for(j=;j<=;j++)
{
int now = change(tmp.num,j,i); //i位变为j
if(now != tmp.num && u[now] && !vis[now])
{
vis[now] = ;
k.num = now;
k.step = tmp.step + ;
que.push(k);
}
}
}
}
return res;
} int main()
{
int t,i,a,b;
doit();
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
S.num = a;
S.step = ;
int res = bfs(S,b);
if(!flag)
puts("Impossible");
else
printf("%d\n",res);
}
return ;
}
E.Sticks
经典题了。
DFS+剪枝
将木棍大小从大到小排序,DFS中维护参数:
ind:当前枚举到第ind根棒子
left:要组成LEN还需left长度
remain:剩下的总长度为remain
然后剪枝,剪枝见注释。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define N 107 int a[N],vis[N];
int S,LEN,n; int DFS(int ind,int left,int remain) //当前枚举到第ind根棒子,要组成LEN还需left长度,剩下的总长度为remain
{
int i;
if(remain == LEN)
return ;
for(i=ind;i<n;i++)
{
if(!vis[i] && a[i] <= left)
{
vis[i] = ; //用这根棒子
if(a[i] < left && DFS(i+,left-a[i],remain-a[i]))
return ;
else if(a[i] == left && DFS(,LEN,remain-a[i]))
return ;
vis[i] = ; //都没成功,这根不能用
if(remain == S || a[i] == left || left == LEN) //如果一根都没用,肯定找不到了,如果不能找到一根长度为LEN的木棍,以后也不能找到了,如果这根木棍长度等于剩下的,但是DFS没成功,说明不可能找到一根或多根将其凑齐了
return ;
while(i+ < n && a[i] == a[i+]) //相同的木棍,不成功就都不成功
i++;
}
}
return ;
} int cmp(int ka,int kb)
{
return ka > kb;
} int main()
{
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF && n)
{
S = ;
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
S += a[i];
}
sort(a,a+n,cmp);
for(LEN=a[];LEN<=S;LEN++)
{
if(S%LEN == )
{
memset(vis,,sizeof(vis));
if(DFS(,LEN,S))
{
printf("%d\n",LEN);
break;
}
}
}
}
return ;
}
F.方老师与迷宫
三维的BFS,常规写法,没什么好说的。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
#define N 100007 char mp[][][];
char ss[];
int vis[][][]; struct node
{
int x,y,z;
int step;
}Sa,Ea; int sx[] = {,-,,,,};
int sy[] = {,,,-,,};
int sz[] = {,,,,,-};
int L,R,C; bool OK(int nx,int ny,int nz)
{
if(nx >= && nx < R && ny >= && ny < C && nz >= && nz < L)
return true;
return false;
} int bfs(node S,node E)
{
queue<node> que;
while(!que.empty())
que.pop();
que.push(S);
memset(vis,,sizeof(vis));
vis[S.x][S.y][S.z] = ;
while(!que.empty())
{
node tmp = que.front();
que.pop();
if(tmp.x == E.x && tmp.y == E.y && tmp.z == E.z)
return tmp.step;
for(int i=;i<;i++)
{
node now;
now.x = tmp.x + sx[i];
now.y = tmp.y + sy[i];
now.z = tmp.z + sz[i];
if(!OK(now.x,now.y,now.z) || mp[now.z][now.x][now.y] == '#' || vis[now.x][now.y][now.z])
continue;
now.step = tmp.step + ;
vis[now.x][now.y][now.z] = ;
que.push(now);
}
}
return -;
} int main()
{
int i,j,k;
while(scanf("%d%d%d",&L,&R,&C)!=EOF && (L&&R&&C))
{
for(i=;i<L;i++)
{
for(j=;j<R;j++)
{
scanf("%s",mp[i][j]);
for(k=;k<C;k++)
{
if(mp[i][j][k] == 'S')
Sa.x = j,Sa.y = k,Sa.z = i,Sa.step = ;
else if(mp[i][j][k] == 'E')
Ea.x = j,Ea.y = k,Ea.z = i,Ea.step = Mod;
}
}
getchar();
}
//printf("%d %d %d\n%d %d %d\n",S.x,S.y,S.z,E.x,E.y,E.z);
int res = bfs(Sa,Ea);
if(res != -)
printf("Escaped in %d minute(s).\n",res);
else
puts("Trapped!");
}
return ;
}
G.Eight Puzzle
把空格看做9,利用Cantor展开保存状态,BFS做,每次通过空格的移动来扩展状态,如果状态没被访问过,则加入队列。
Cantor展开(康托展开)可以求一个排列在所有这几个数的排列中的位置:
把一个整数X展开成如下形式:
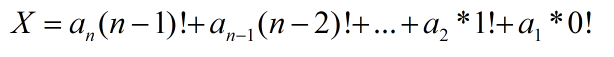
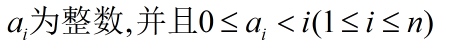
a(i)为i右边的比a(i)小的数的个数。
比如1324是{1,2,3,4}的所有排列的第三个,说明比1324小的排列有2个,0*3!+1*2!+0*1!+0*0!=2
这样可以方便的记录状态。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
#define N 370000 struct node
{
int puzzle[][];
int step;
}; int hash[N],vis[N];
int a[],b[][];
char ss[];
int mp[][] = {{,,},{,,},{,,}};
int sx[] = {,,-,};
int sy[] = {,,,-};
int fact[] = {,,,,,,,,,,}; int Cantor(int *a) //康托展开
{
int i,j,cnt;
int res = ;
for(i=;i<;i++)
{
cnt = ;
for(j=i+;j<;j++)
if(a[i] > a[j])
cnt++;
res += cnt*fact[-i-];
}
return res;
} void DB_to_SG(int *a,int b[][]) //二维转一维
{
int i,j,k = ;
for(int i=;i<;i++)
for(j=;j<;j++)
a[k++] = b[i][j];
} int HS(int b[][]) //取得排列的Cantor展开的值
{
int i,j,k,res;
DB_to_SG(a,b);
return Cantor(a);
} bool OK(int nx,int ny)
{
if(nx >= && nx < && ny >= && ny < )
return true;
return false;
} int copyDB(int (*a)[],int (*b)[]) //复制数组
{
for(int i=;i<;i++)
for(int j=;j<;j++)
a[i][j] = b[i][j];
} void BFS()
{
queue<node> que;
while(!que.empty())
que.pop();
int i,j,k;
int nx,ny;
node S;
copyDB(S.puzzle,mp);
copyDB(b,S.puzzle);
int hsb = HS(b);
vis[hsb] = ;
hash[hsb] = ;
S.step = ;
que.push(S);
while(!que.empty())
{
node tmp = que.front();
que.pop();
for(i=;i<;i++)
for(j=;j<;j++)
{
b[i][j] = tmp.puzzle[i][j];
if(b[i][j] == )
nx = i,ny = j;
}
for(k=;k<;k++)
{
int kx = nx + sx[k];
int ky = ny + sy[k];
if(!OK(kx,ky))
continue;
swap(b[nx][ny],b[kx][ky]);
int hsb = HS(b); //Cantor展开值作为状态
node now;
if(!vis[hsb])
{
copyDB(now.puzzle,b);
vis[hsb] = ;
hash[hsb] = tmp.step + ;
now.step = tmp.step + ;
que.push(now);
}
swap(b[nx][ny],b[kx][ky]);
}
}
} int main()
{
memset(hash,,sizeof(hash));
memset(vis,,sizeof(vis));
BFS();
while(gets(ss))
{
int i,j,k = ;
for(i=;i<;i++)
for(j=;j<;j++)
{
if(ss[k] == 'x')
b[i][j] = ;
else
b[i][j] = ss[k] - '';
k += ;
}
int hsb = HS(b);
if(!hsb || (hsb && hash[hsb]))
cout<<hash[hsb]<<endl;
else
puts("unsolvable");
}
return ;
}
H.一个简单的走迷宫问题
因为走的是网格线,所以先把n*m的矩阵化成(n-1)*(m-1)的网格线矩阵,然后再来走。
状态的转移有6种状态:
1.向左转
2.向右转
3.向后转 (step = 2)
4.向此时的方向走1步
5.向此时的方向走2步
6.向此时的方向走3步
然后BFS就可以了。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
#define N 100007 int mp[][],nmp[][],flag[],dis[][][];
int R,C; struct node
{
int x,y;
int dr;
int step;
bool operator<(const node &a)const
{
return step > a.step;
}
}S,E; bool OK(int nx,int ny)
{
if(nx >= && nx < R- && ny >= && ny < C-)
return true;
return false;
} int bfs(node S,node E)
{
priority_queue<node> que;
while(!que.empty())
que.pop();
que.push(S);
dis[S.dr][S.x][S.y] = ;
while(!que.empty())
{
node tmp = que.top();
que.pop();
if(tmp.x == E.x && tmp.y == E.y)
return tmp.step;
memset(flag,,sizeof(flag));
for(int i=;i<=;i++) //走的步数
{
if(i <= )
{
node now;
now.x = tmp.x;
now.y = tmp.y;
if(i == ) //向右转然后走
{
now.step = tmp.step + ;
now.dr = (tmp.dr + )%;
}
else if(i == ) //向左转然后走
{
now.step = tmp.step + ;
now.dr = (tmp.dr + )%;
}
else if(i == ) //向后转然后走
{
now.step = tmp.step + ;
now.dr = (tmp.dr + )%;
}
if(dis[now.dr][now.x][now.y] != - && now.step >= dis[now.dr][now.x][now.y])
continue;
dis[now.dr][now.x][now.y] = now.step;
que.push(now);
}
else
{
node next;
if(tmp.dr == ) //UP
{
next.x = tmp.x - i + ;
next.y = tmp.y;
}
else if(tmp.dr == ) //RIGHT
{
next.x = tmp.x;
next.y = tmp.y + i - ;
}
else if(tmp.dr == ) //DOWN
{
next.x = tmp.x + i - ;
next.y = tmp.y;
}
else if(tmp.dr == ) //LEFT
{
next.x = tmp.x;
next.y = tmp.y - i + ;
}
if(!OK(next.x,next.y) || nmp[next.x][next.y] == )
break;
next.step = tmp.step + ; //
next.dr = tmp.dr;
if(dis[next.dr][next.x][next.y] != - && next.step >= dis[next.dr][next.x][next.y])
continue;
dis[next.dr][next.x][next.y] = next.step;
que.push(next);
}
}
}
return -;
} int main()
{
int i,j;
while(scanf("%d%d",&R,&C)!=EOF && R && C)
{
memset(nmp,,sizeof(nmp));
for(i=;i<R;i++)
{
for(j=;j<C;j++)
{
scanf("%d",&mp[i][j]);
if(mp[i][j] == )
{
nmp[i][j] = ;
if(j>=)
{
nmp[i][j-] = ;
if(i>=)
nmp[i-][j-] = ;
}
if(i>=)
{
nmp[i-][j] = ;
if(j>=)
nmp[i-][j-] = ;
}
}
}
}
memset(dis,-,sizeof(dis));
scanf("%d%d%d%d%d",&S.x,&S.y,&E.x,&E.y,&S.dr);
S.x--,S.y--,E.x--,E.y--;
S.step = ;
E.dr = ,E.step = Mod;
int res = bfs(S,E);
printf("%d\n",res);
}
return ;
}
I.分割包围
这题初看没思路,结果是个水二分搜索题。
二分最小长度,可以找到满足条件的最小长度的最大值。
如何判断满足条件呢?
即在给定的最小长度下,看至少需要操作多少下才能使这些兵团的两两间隔的最小长度为该长度,然后比较操作数与题目要求的最大操作数,如果小于,则可以,如果大于,则不满足,此时减小最小长度,再判断。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#define Mod 1000000007
using namespace std;
#define N 50007 int d[N];
int x,n,m; bool check(int mid)
{
int i,j;
int cnt = ;
for(i=;i<=n+;i++)
{
for(j=i+;j<=n+;j++)
{
if(d[j]-d[i] < mid && j <= n) //如果两个间隔小于mid,则要增大,即抹除j的这个
cnt++;
else if(d[j]-d[i] < mid && j == n+)
{
cnt++;
i = Mod;
}
else
{
i = j-;
break;
}
}
}
if(cnt <= m)
return true;
return false;
} int main()
{
int i,j;
scanf("%d%d%d",&x,&n,&m);
for(i=;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&d[i]);
sort(d+,d+n+);
d[] = ;
d[n+] = x;
int mini = Mod;
for(i=;i<=n+;i++)
{
if(d[i]-d[i-] < mini)
mini = d[i]-d[i-];
}
int low = mini;
int high = x;
while(low < high)
{
int mid = (low+high+)/;
if(check(mid))
low = mid;
else
high = mid-;
}
printf("%d\n",low);
return ;
}
J.魔法少女小蟹
直接BFS肯定不行,复杂度太高。
先不考虑加加减操作,因为它们不涉及以为,很好处理。
因为一开始魔棒是在最左端,所以第i个位置被访问过了,则前面的一定都访问过。同时,我们可以直接通过和最后一位交换的方式访问最后一位。所以所有被访问的状态(标号)就只有1、12、123、1234、12345、123456、16、126、1236、12346,就10个。
所以状态记录就是dis[6][6][6][6][6][6][6][10],前6个6 代表现在的第i位是原来的第j位,第7个6 代表魔杖现在在哪,10 代表有哪些位置被访问过了。
dis表示到当前状态的步数(最小)。
BFS出来后,枚举6位数的每一位和指针位置和10种状态,看此状态是否已访问,如果已访问,表示能够到达这个状态,然后看从这个状态到目标状态还需多少步(有可能达不到),然后看dis[状态]+步数是否小于最小步数,是则更新答案。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#define Mod 1000000007
#define INT 2147483647
using namespace std;
#define N 50007 struct node
{
int p[];
int point,state;
int step;
}S; void Popy(int *p1,int *p2)
{
for(int i=;i<;i++)
p1[i] = p2[i];
} int dis[][][][][][][][];
int E[],SS[]; int min(int ka,int kb)
{
if(ka < kb)
return ka;
return kb;
} int max(int ka,int kb)
{
if(ka > kb)
return ka;
return kb;
} void BFS(node S)
{
queue<node> que;
memset(dis,-,sizeof(dis));
que.push(S);
dis[S.p[]][S.p[]][S.p[]][S.p[]][S.p[]][S.p[]][][] = ;
while(!que.empty())
{
node tmp = que.front();
que.pop();
for(int i=;i<;i++)
{
node now;
if(i == ) //与左边交换
{
swap(tmp.p[],tmp.p[tmp.point]);
Popy(now.p,tmp.p);
swap(tmp.p[],tmp.p[tmp.point]);
now.point = tmp.point;
now.state = tmp.state;
now.step = tmp.step + ;
if(dis[now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.point][now.state] == - || (dis[now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.point][now.state] != - && now.step < dis[now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.point][now.state]))
{
dis[now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.point][now.state] = now.step;
que.push(now);
}
}
else if(i == ) //与右边交换
{
swap(tmp.p[],tmp.p[tmp.point]);
Popy(now.p,tmp.p);
swap(tmp.p[],tmp.p[tmp.point]);
now.point = tmp.point;
if(tmp.state <= )
now.state = tmp.state + ;
else if(tmp.state == )
now.state = tmp.state + ;
else
now.state = tmp.state;
now.step = tmp.step + ;
if(dis[now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.point][now.state] == - || (dis[now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.point][now.state] != - && now.step < dis[now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.point][now.state]))
{
dis[now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.point][now.state] = now.step;
que.push(now);
}
}
else if(i == ) //左移
{
Popy(now.p,tmp.p);
now.point = max(,tmp.point-);
now.state = tmp.state;
now.step = tmp.step + ;
if(dis[now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.point][now.state] == - || (dis[now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.point][now.state] != - && now.step < dis[now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.point][now.state]))
{
dis[now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.point][now.state] = now.step;
que.push(now);
}
}
else if(i == ) //右移
{
Popy(now.p,tmp.p);
now.point = min(,tmp.point+);
if(tmp.state < )
now.state = tmp.state+;
else if(tmp.state == )
now.state = tmp.state;
else if(tmp.state < )
now.state = tmp.state+;
else
now.state = tmp.state-;
now.step = tmp.step + ;
if(dis[now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.point][now.state] == - || (dis[now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.point][now.state] != - && now.step < dis[now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.point][now.state]))
{
dis[now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.p[]][now.point][now.state] = now.step;
que.push(now);
}
}
}
}
} int main()
{
int a,b,i;
int h[];
int pot,status;
while(scanf("%d%d",&a,&b)!=EOF)
{
S.p[] = ; //标号。初始都在自己的位置
S.p[] = ;
S.p[] = ;
S.p[] = ;
S.p[] = ;
S.p[] = ;
S.point = ;
S.state = ;
S.step = ;
SS[] = (a/)%;
SS[] = (a/)%;
SS[] = (a/)%;
SS[] = (a/)%;
SS[] = (a/)%;
SS[] = a%;
E[] = (b/)%;
E[] = (b/)%;
E[] = (b/)%;
E[] = (b/)%;
E[] = (b/)%;
E[] = b%;
BFS(S);
int ans = Mod;
for(h[]=;h[]<=;h[]++)
{
for(h[]=;h[]<=;h[]++)
{
if(h[] != h[])
{
for(h[]=;h[]<=;h[]++)
{
if(h[] != h[] && h[] != h[])
{
for(h[]=;h[]<=;h[]++)
{
if(h[] != h[] && h[] != h[] && h[] != h[])
{
for(h[]=;h[]<=;h[]++)
{
if(h[] != h[] && h[] != h[] && h[] != h[] && h[] != h[])
{
for(h[]=;h[]<=;h[]++)
{
if(h[] != h[] && h[] != h[] && h[] != h[] && h[] != h[] && h[] != h[])
{
for(pot=;pot<=;pot++)
{
for(status=;status<;status++)
{
if(dis[h[]][h[]][h[]][h[]][h[]][h[]][pot][status] != -)
{
int cnt = ;
int t,r;
int flag = ; //No. status
if(status <= ) //1 1
{ //2 12
for(t=;t<=status+;t++) //3 123
cnt += abs(E[t]-SS[h[t]]); //4 1234
for(t;t<=;t++) //5 12345
if(E[t] != SS[h[t]]) //6 123456
{ //7 16
flag = ; //8 126
break; //9 1236
} //10 12346
if(!flag)
continue;
}
else if(status >= && status <= )
{
for(r=;r<=status-;r++)
cnt += abs(E[r]-SS[h[r]]);
for(r;r<;r++)
if(E[r] != SS[h[r]])
{
flag = ;
break;
}
if(!flag)
continue;
cnt += abs(E[]-SS[h[]]);
}
ans = min(ans,dis[h[]][h[]][h[]][h[]][h[]][h[]][pot][status]+cnt);
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
return ;
}
K.Can You Help God Wu
BFS,枚举涂法,用每个位置用0表示染上了错误的颜色,1表示染上了正确的颜色,用一个十进制数表示,最大不超过2^16.
开始的时候暴力枚举每一个矩形,每一种颜色,然后涂色,但是发现复杂度太高。TLE了。
然后改变做法,每次选一个位置的颜色进行扩展,使尽可能大的区域染上这个颜色。并且每次要将该状态的子集(1到该状态的值)也加入队列中,因为最多两行,所以考虑一行扩展和两行(一块)扩展,每次往左往右扩展染色,如果已经染好了,就跳出,表示那边已经不能再染了。直到找到目标状态(二进制位全为1)。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
#define N 250007 struct node
{
int num,step;
}S; char E[][];
int vis[];
int n,C; int BFS(node S)
{
queue<node> que;
que.push(S);
vis[S.num] = ;
int D = ((<<(*n))-);
while(!que.empty())
{
node tmp = que.front();
que.pop();
if(tmp.num == D)
return tmp.step;
int i,j,a,b;
for(i=;i<;i++)
{
for(j=;j<n;j++)
{
int pos = i*n+j;
node now;
if(tmp.num & (<<pos)) //已经是该颜色
continue;
int Num = ;
for(a=pos;a<(i==?n:*n);a++) //往右
{
if(tmp.num & (<<a)) //已经染好,不能再涂
break;
if(E[a/n][a%n] == E[pos/n][pos%n])
Num = Num | (<<a); //染色
}
for(a=pos-;a>=(i==?:n);a--) //往左
{
if(tmp.num & (<<a))
break;
if(E[a/n][a%n] == E[pos/n][pos%n])
Num = Num | (<<a);
}
for(pos=Num;pos!=;pos=Num&(pos-)) //子状态
{
if(vis[tmp.num|pos])
break;
vis[tmp.num|pos] = ;
now.num = tmp.num|pos;
now.step = tmp.step + ;
que.push(now);
}
pos = i*n+j;
if(i >= )
continue;
if(tmp.num & (<<(n+pos)))
continue;
Num = ;
for(a=pos;a<n;a++) //双行往右
{
if(tmp.num & (<<a) || tmp.num & (<<(a+n)))
break;
if(E[a/n][a%n] == E[pos/n][pos%n])
Num = Num | (<<a);
if(E[(a+n)/n][(a+n)%n] == E[pos/n][pos%n])
Num = Num | (<<(a+n));
}
for(a=pos-;a>=;a--) //双行往左
{
if(tmp.num & (<<a) || tmp.num & (<<(a+n)))
break;
if(E[a/n][a%n] == E[pos/n][pos%n])
Num = Num | (<<a);
if(E[(a+n)/n][(a+n)%n] == E[pos/n][pos%n])
Num = Num | (<<(a+n));
}
for(pos=Num;pos!=;pos=Num&(pos-)) //子状态
{
if(vis[tmp.num|pos])
continue;
vis[tmp.num|pos] = ;
now.num = tmp.num|pos;
now.step = tmp.step + ;
que.push(now);
}
}
}
}
} int main()
{
int t,cs = ,i,j;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i=;i<=;i++)
scanf("%s",E[i]);
memset(vis,,sizeof(vis));
S.num = ;
S.step = ;
int res = BFS(S);
printf("Case #%d: %d\n",cs++,res);
}
return ;
}
L.STAMPS
DFS
参数为sum:当前组合的和 和 step:当前已经用到了第几种邮票,邮票可以重复使用。限制最大搜索深度为4
如果找到答案,则根据一系列规则比较该方案是否优于答案,是则更新。出现tie则isTie置为True。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
#define N 1007 struct node
{
int deno[];
int num;
}E,tmp; int stamp[N];
int vis[N];
int n,m,S;
int isTie,flag; int Totaltype(node ka) //计算这个组合的种类数
{
memset(vis,,sizeof(vis));
int res = ;
for(int i=;i<ka.num;i++)
if(!vis[ka.deno[i]])
res++,vis[ka.deno[i]] = ;
return res;
} int Max(node ka) //找出票面价值的最大值
{
int maxi = -Mod;
for(int i=;i<ka.num;i++)
if(maxi < stamp[ka.deno[i]])
maxi = stamp[ka.deno[i]];
return maxi;
} int copyAN(int *a,int *b,int num) //复制结果
{
for(int i=;i<num;i++)
a[i] = b[i];
} void check(node &ka,node &kb) //比较函数
{
int typa = Totaltype(ka);
int typb = Totaltype(kb);
int maxa = Max(ka);
int maxb = Max(kb); if(ka.num == -Mod || (typa < typb) || (typa == typb && ka.num > kb.num) || (typa == typb && ka.num == kb.num && maxa < maxb))
{
copyAN(ka.deno,kb.deno,kb.num);
ka.num = kb.num;
isTie = ;
return;
}
if(typa == typb && ka.num == kb.num && maxa == maxb)
isTie = ;
} void DFS(int sum,int step) //sum:当前组合的和 step:当前已经用到了第几种邮票
{
if(sum == S)
{
flag = ;
check(E,tmp);
return;
} if(sum > S || tmp.num >= )
return;
for(int k=step;k<n;k++) //可用多次,所以从上次结束的位置开始枚举
{
tmp.deno[tmp.num] = k;
tmp.num++;
DFS(sum+stamp[k],k);
tmp.num--;
}
} int main()
{
int x,y,i,j;
while(scanf("%d",&x)!=EOF && x)
{
n = ;
stamp[] = x;
while(stamp[n])
{
n++;
scanf("%d",&stamp[n]);
} //stamp[n] = 0
sort(stamp,stamp+n);
while(scanf("%d",&S)!=EOF && S)
{
printf("%d ",S);
memset(E.deno,,sizeof(E.deno));
E.num = -Mod;
memset(tmp.deno,,sizeof(tmp.deno));
tmp.num = ;
flag = isTie = ;
DFS(,);
if(!flag)
puts("---- none");
else
{
sort(E.deno,E.deno+E.num);
printf("(%d):",Totaltype(E));
if(isTie)
puts(" tie");
else
{
for(i=;i<E.num;i++)
printf(" %d",stamp[E.deno[i]]);
printf("\n");
}
}
}
}
return ;
}
(2014.5.17 0:34)
2014 UESTC暑前集训搜索专题解题报告的更多相关文章
- 2014 UESTC暑前集训数据结构专题解题报告
A.Islands 这种联通块的问题一看就知道是并查集的思想. 做法:从高水位到低水位依序进行操作,这样每次都有新的块浮出水面,可以在前面的基础上进行合并集合的操作.给每个位置分配一个数字,方便合并集 ...
- 2014 UESTC暑前集训动态规划专题解题报告
A.爱管闲事 http://www.cnblogs.com/whatbeg/p/3762733.html B.轻音乐同好会 C.温泉旅馆 http://www.cnblogs.com/whatbeg/ ...
- 2014 UESTC暑前集训图论专题解题报告
A.方老师和缘分 http://www.cnblogs.com/whatbeg/p/3765621.html B.方老师和农场 http://www.cnblogs.com/whatbeg/p/376 ...
- 2014 UESTC 暑前集训队内赛(1) 解题报告
A.Planting Trees 排序+模拟 常识问题,将耗时排一个序,时间长的先种,每次判断更新最后一天的时间. 代码: #include <iostream> #include < ...
- 2014 UESTC 暑前集训队内赛(3) 部分解题报告
B.Battle for Silver 定理:完全图Kn是平面图当且仅当顶点数n<=4. 枚举所有完全图K1,K2,K3,K4,找出最大总权重. 代码: #include <iostrea ...
- 2014 UESTC 暑前集训队内赛(2) 部分解题报告
B.Cuckoo for Hashing 模拟题. 代码: #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring ...
- HDU(搜索专题) 1000 N皇后问题(深度优先搜索DFS)解题报告
前几天一直在忙一些事情,所以一直没来得及开始这个搜索专题的训练,今天做了下这个专题的第一题,皇后问题在我没有开始接受Axie的算法低强度训练前,就早有耳闻了,但一直不知道是什么类型的题目,今天一看,原 ...
- Facebook Hacker Cup 2014 Qualification Round 竞赛试题 Square Detector 解题报告
Facebook Hacker Cup 2014 Qualification Round比赛Square Detector题的解题报告.单击这里打开题目链接(国内访问需要那个,你懂的). 原题如下: ...
- 迭代加深搜索 C++解题报告 :[SCOI2005]骑士精神
题目 此题根据题目可知是迭代加深搜索. 首先应该枚举空格的位置,让空格像一个马一样移动. 但迭代加深搜索之后时间复杂度还是非常的高,根本过不了题. 感觉也想不出什么减枝,于是便要用到了乐观估计函数(O ...
随机推荐
- Jquery中的日历插件
这个插件很简单:只需要在HTML代码中引入插件如下,CLASS名和click事件函数固定! <!doctype html> <html lang="en"> ...
- (转)JavaScript二:JavaScript语言的基本语法要求
摘自:http://blog.csdn.net/erlian1992 要学习好JavaScript,首先我们要懂JavaScript语言的一些基本语法要求: 一,区分大小写 JavaScript语言区 ...
- 【position也可以很复杂】当弹出层遇上了鼠标定位(上)
前言 周五时同事有一个关于弹出层的问题没有解决,但是面临下班问题,我有点不舒服,便叫回去周六过来解决,但是上周六病了,所以请了个假,于是故事发生啦.... 今天上班时候,组员们卡到了那个地方,然后结果 ...
- 每天checklist所用到的T-CODE
1.1重点检查 作业 事务码 检查过程 检查R/3系统是否已经启动 · 登录到R/3系统 检查每日备份是否正常 DB12-Backup Logs:Overview · 检查数据库备份 · 检查数据库备 ...
- BP人工神经网络原理(转载)
- Android上的MVP:如何组织显示层的内容
MVP(Model View Presenter)模式是著名的MVC(Model View Controller)模式的一个演化版本,目前它在Android应用开发中越来越重要了,大家也都在讨论关于M ...
- Android NDK目录介绍
交叉编译 在一个平台上去编译另一个平台上可以执行的本地代码 cpu平台---arm x86 mips 操作系统平台---windows linux mac os 原理 模拟不同平台的特性去编译代码 j ...
- 【代码笔记】iOS-改变导航条标题的颜色为红色
一,效果图. 二,代码. RootViewController.m - (void)viewDidLoad { [super viewDidLoad]; // Do any additional se ...
- 列式存储(三)JFinal DB.tx()事务
上一篇中说道了列式存储中新增表单时后台接收数据问题,在存入数据库时一次插入多条数据,就要用到事务. JFinal中有个封装好的事务应用,用起来非常方便简单. 写法1: Db.tx(new IAtom( ...
- iOS-公司开发者账号的申请和注册(博主原创+亲身经历+2016年申请+附带与邓白氏公司的往来邮件截图)
不吹不黑,此篇博客真乃我的良心之作啊,希望对大家有所帮助! 链接在简书:http://www.jianshu.com/p/9de6a8eb4d88
