ThreadLocal原理解析
ThreadLocal源码分析
/*
* Copyright (c) 1997, 2013, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
* ORACLE PROPRIETARY/CONFIDENTIAL. Use is subject to license terms.
*/
package java.lang;
import java.lang.ref.*;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
import java.util.function.Supplier;
/**
* @author Josh Bloch and Doug Lea
* @since 1.2
*/
public class ThreadLocal<T> {
/**
* ThreadLocals rely on per-thread linear-probe hash maps attached
* to each thread (Thread.threadLocals and
* inheritableThreadLocals). The ThreadLocal objects act as keys,
* searched via threadLocalHashCode. This is a custom hash code
* (useful only within ThreadLocalMaps) that eliminates collisions
* in the common case where consecutively constructed ThreadLocals
* are used by the same threads, while remaining well-behaved in
* less common cases.
*/
private final int threadLocalHashCode = nextHashCode();
/**
* The next hash code to be given out. Updated atomically. Starts at
* zero.
*/
private static AtomicInteger nextHashCode =
new AtomicInteger();
/**
* The difference between successively generated hash codes - turns
* implicit sequential thread-local IDs into near-optimally spread
* multiplicative hash values for power-of-two-sized tables.
*/
private static final int HASH_INCREMENT = 0x61c88647;
/**
* Returns the next hash code.
*/
private static int nextHashCode() {
return nextHashCode.getAndAdd(HASH_INCREMENT);
}
/**
* Returns the current thread's "initial value" for this
* thread-local variable. This method will be invoked the first
* time a thread accesses the variable with the {@link #get}
* method, unless the thread previously invoked the {@link #set}
* method, in which case the {@code initialValue} method will not
* be invoked for the thread. Normally, this method is invoked at
* most once per thread, but it may be invoked again in case of
* subsequent invocations of {@link #remove} followed by {@link #get}.
*
* <p>This implementation simply returns {@code null}; if the
* programmer desires thread-local variables to have an initial
* value other than {@code null}, {@code ThreadLocal} must be
* subclassed, and this method overridden. Typically, an
* anonymous inner class will be used.
*
* @return the initial value for this thread-local
*/
protected T initialValue() {
return null;
}
/**
* Creates a thread local variable. The initial value of the variable is
* determined by invoking the {@code get} method on the {@code Supplier}.
*
* @param <S> the type of the thread local's value
* @param supplier the supplier to be used to determine the initial value
* @return a new thread local variable
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified supplier is null
* @since 1.8
*/
public static <S> ThreadLocal<S> withInitial(Supplier<? extends S> supplier) {
return new SuppliedThreadLocal<>(supplier);
}
/**
* Creates a thread local variable.
* @see #withInitial(java.util.function.Supplier)
*/
public ThreadLocal() {
}
/**
* Returns the value in the current thread's copy of this
* thread-local variable. If the variable has no value for the
* current thread, it is first initialized to the value returned
* by an invocation of the {@link #initialValue} method.
*
* @return the current thread's value of this thread-local
*/
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
return setInitialValue();
}
/**
* Variant of set() to establish initialValue. Used instead
* of set() in case user has overridden the set() method.
*
* @return the initial value
*/
private T setInitialValue() {
T value = initialValue();
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
return value;
}
/**
* Sets the current thread's copy of this thread-local variable
* to the specified value. Most subclasses will have no need to
* override this method, relying solely on the {@link #initialValue}
* method to set the values of thread-locals.
*
* @param value the value to be stored in the current thread's copy of
* this thread-local.
*/
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
}
/**
* Removes the current thread's value for this thread-local
* variable. If this thread-local variable is subsequently
* {@linkplain #get read} by the current thread, its value will be
* reinitialized by invoking its {@link #initialValue} method,
* unless its value is {@linkplain #set set} by the current thread
* in the interim. This may result in multiple invocations of the
* {@code initialValue} method in the current thread.
*
* @since 1.5
*/
public void remove() {
ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread());
if (m != null)
m.remove(this);
}
/**
* Get the map associated with a ThreadLocal. Overridden in
* InheritableThreadLocal.
*
* @param t the current thread
* @return the map
*/
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}
/**
* Create the map associated with a ThreadLocal. Overridden in
* InheritableThreadLocal.
*
* @param t the current thread
* @param firstValue value for the initial entry of the map
*/
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}
/**
* Factory method to create map of inherited thread locals.
* Designed to be called only from Thread constructor.
*
* @param parentMap the map associated with parent thread
* @return a map containing the parent's inheritable bindings
*/
static ThreadLocalMap createInheritedMap(ThreadLocalMap parentMap) {
return new ThreadLocalMap(parentMap);
}
/**
* Method childValue is visibly defined in subclass
* InheritableThreadLocal, but is internally defined here for the
* sake of providing createInheritedMap factory method without
* needing to subclass the map class in InheritableThreadLocal.
* This technique is preferable to the alternative of embedding
* instanceof tests in methods.
*/
T childValue(T parentValue) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
/**
* An extension of ThreadLocal that obtains its initial value from
* the specified {@code Supplier}.
*/
static final class SuppliedThreadLocal<T> extends ThreadLocal<T> {
private final Supplier<? extends T> supplier;
SuppliedThreadLocal(Supplier<? extends T> supplier) {
this.supplier = Objects.requireNonNull(supplier);
}
@Override
protected T initialValue() {
return supplier.get();
}
}
/**
* ThreadLocalMap is a customized hash map suitable only for
* maintaining thread local values. No operations are exported
* outside of the ThreadLocal class. The class is package private to
* allow declaration of fields in class Thread. To help deal with
* very large and long-lived usages, the hash table entries use
* WeakReferences for keys. However, since reference queues are not
* used, stale entries are guaranteed to be removed only when
* the table starts running out of space.
*/
static class ThreadLocalMap {
//类似于HASHMAP实现
}
}
- get()方法:
- set()方法:
- remove()方法:
- initialValue()方法:默认初始值的方法,子类可以实现
ThreadLocal解决的问题
- 线程内共享变量的传递问题(session中的用户登录等信息)
没有ThreadLocal的时候,一个线程在其声明周期内,可能穿过多个层级,多个方法,如果有个对象需要在此线程周期内多次调用,且是跨层级的(线程内共享),通常的做法是通过参数进行传递;而ThreadLocal将变量绑定在线程上,在一个线程周期内,无论“你身处何地”,只需通过其提供的get方法就可轻松获取到对象。极大地提高了对于“线程级变量”的访问便利性。 - 单例中有状态对象的线程安全问题(spring中的模板类的数据库连接的事务控制问题)
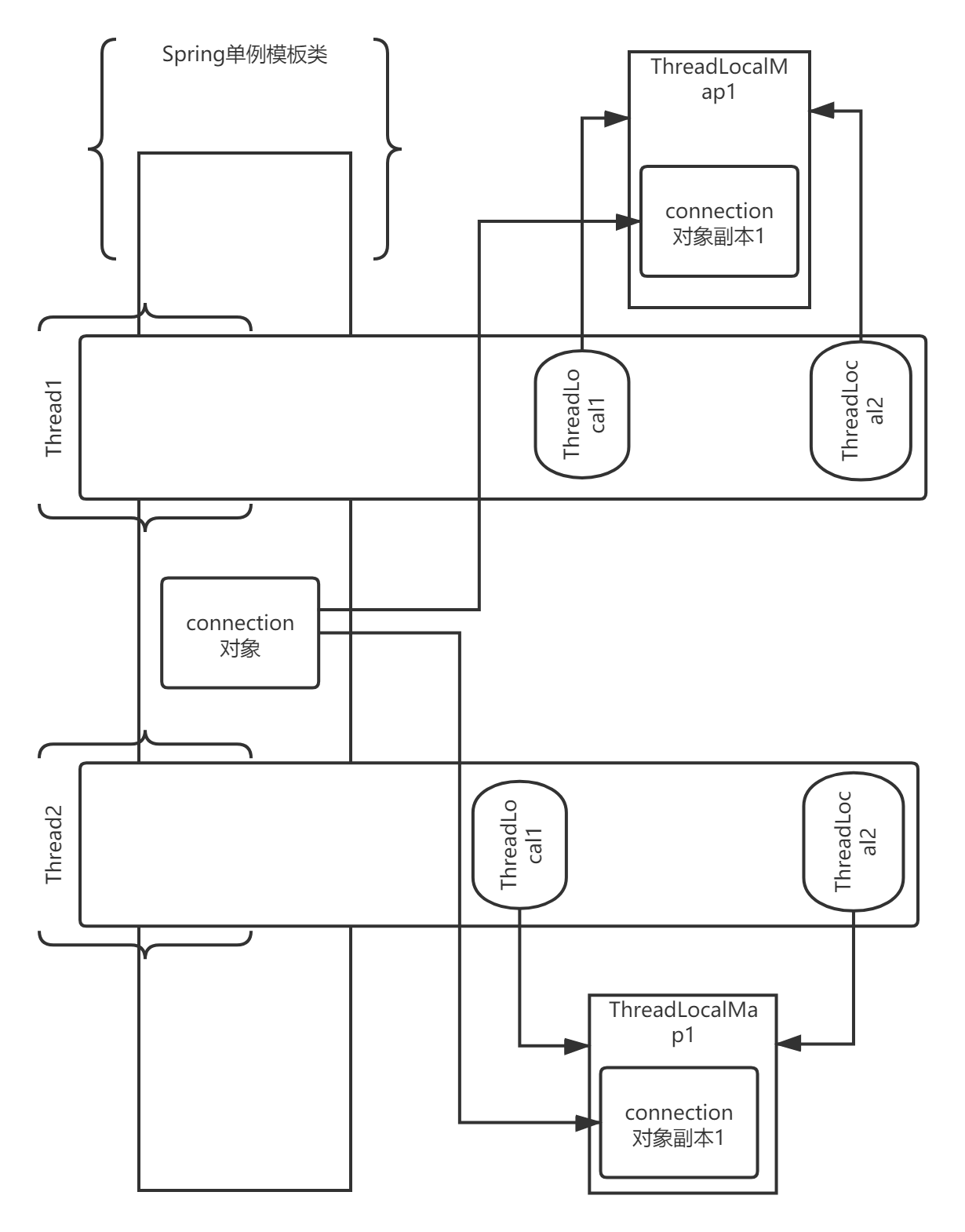
如果没有Threadlocal,Dao单例对象只能用同步锁的方式来控制连接对象的事务开启和提交的原子性操作,这大大影响了系统的并发性能,用了ThreadLocal后,在每个线程内都会维护一个connecttion对象,这样不同线程的事务操作就隔离开了,主要用了用空间换取时间的理念。
ThreadLocal的原理
ThreadLocal内部是如何为每一个线程维护变量副本的呢?
在ThreadLocal类中有一个静态内部类ThreadLocalMap(概念上类似于Map),用键值对的形式存储每一个线程的变量副本,ThreadLocalMap中元素的key为当前ThreadLocal对象,而value对应线程的变量副本,每个线程可能存在多个ThreadLocal。
ThreadLocal的几个问题
- 为什么不以线程ID为threadLocalMap中的key值?
因为threadLocalMap是跟线程绑定的,一个线程对应一个ThreadLocalMap,里面可以存储多个ThreadLocal,如果用线程ID作为KEY值,那就只能存储一个键值对啦! - ThreadLocal的内存泄漏问题
首先要理解内存泄露(memory leak)和内存溢出(out of memory)的区别。内存溢出是因为在内存中创建了大量在引用的对象,导致后续再申请内存时没有足够的内存空间供其使用。内存泄露是指程序申请完内存后,无法释放已申请的内存空间,(不再使用的对象或者变量仍占内存空间)。
根据上面Entry方法的源码,我们知道ThreadLocalMap是使用ThreadLocal的弱引用作为Key的。下图是本文介绍到的一些对象之间的引用关系图,实线表示强引用,虚线表示弱引用:

threadLocalMap设计时的对上面问题的对策:
当我们仔细读过ThreadLocalMap的源码,我们可以推断,如果在使用的ThreadLocal的过程中,显式地进行remove是个很好的编码习惯,这样是不会引起内存泄漏。
那么如果没有显式地进行remove呢?只能说如果对应线程之后调用ThreadLocal的get和set方法都有很高的概率会顺便清理掉无效对象,断开value强引用,从而大对象被收集器回收。
但无论如何,我们应该考虑到何时调用ThreadLocal的remove方法。一个比较熟悉的场景就是对于一个请求一个线程的server如tomcat,在代码中对web api作一个切面,存放一些如用户名等用户信息,在连接点方法结束后,再显式调用remove。
ThreadLocal原理解析的更多相关文章
- ThreadLocal 原理解析
1.对Thread local 理解 ThreadLocal 是为了解决线程间同步而创建的一个新的思路.简单来说就是每个线程都保存一个变量副本. 如果在Thread 内部定义一个field变量,也可以 ...
- java基础解析系列(七)---ThreadLocal原理分析
java基础解析系列(七)---ThreadLocal原理分析 目录 java基础解析系列(一)---String.StringBuffer.StringBuilder java基础解析系列(二)-- ...
- ThreadLocal系列(三)-TransmittableThreadLocal的使用及原理解析
ThreadLocal系列(三)-TransmittableThreadLocal的使用及原理解析 上一篇:ThreadLocal系列(二)-InheritableThreadLocal的使用及原理解 ...
- ThreadLocal系列(二)-InheritableThreadLocal的使用及原理解析
ThreadLocal系列之InheritableThreadLocal的使用及原理解析(源码基于java8) 上一篇:ThreadLocal系列(一)-ThreadLocal的使用及原理解析 下一篇 ...
- ThreadLocal系列(一)-ThreadLocal的使用及原理解析
ThreadLocal系列之ThreadLocal(源码基于java8) 项目中我们如果想要某个对象在程序运行中的任意位置获取到,就需要借助ThreadLocal来实现,这个对象称作线程的本地变量,下 ...
- ThreadLocal的使用及原理解析
# 基本使用 JDK的lang包下提供了ThreadLocal类,我们可以使用它创建一个线程变量,线程变量的作用域仅在于此线程内.<br />用2个示例来展示一下ThreadLocal的用 ...
- Java并发包JUC核心原理解析
CS-LogN思维导图:记录CS基础 面试题 开源地址:https://github.com/FISHers6/CS-LogN JUC 分类 线程管理 线程池相关类 Executor.Executor ...
- [原][Docker]特性与原理解析
Docker特性与原理解析 文章假设你已经熟悉了Docker的基本命令和基本知识 首先看看Docker提供了哪些特性: 交互式Shell:Docker可以分配一个虚拟终端并关联到任何容器的标准输入上, ...
- 【算法】(查找你附近的人) GeoHash核心原理解析及代码实现
本文地址 原文地址 分享提纲: 0. 引子 1. 感性认识GeoHash 2. GeoHash算法的步骤 3. GeoHash Base32编码长度与精度 4. GeoHash算法 5. 使用注意点( ...
- Web APi之过滤器执行过程原理解析【二】(十一)
前言 上一节我们详细讲解了过滤器的创建过程以及粗略的介绍了五种过滤器,用此五种过滤器对实现对执行Action方法各个时期的拦截非常重要.这一节我们简单将讲述在Action方法上.控制器上.全局上以及授 ...
随机推荐
- Linux 内核参数
/proc/sys/net/ipv4: ip_local_port_range:定义了TCP或UDP对目标发起连接所选择的本地端口范围(除ip_local_reserved_ports之外),其定义受 ...
- 数组查询includes
let arr1 = ['kk', 'jo', 'll']; if (arr1.includes("kk")) {//[ɪnˈkluːz] console.log("找到 ...
- 没有安装vs通过Rider编译Dll
没安装vs怎样生成dll? 比起VS那庞大的体积和编码效率,我还是更喜欢使用Rider(和VS的神级插件Resharper是同一家公司的产品),那么在没有安装VS的电脑上是否可以在命令行下把C#代码生 ...
- TienChin 新建业务菜单
首先是移动菜单,参考下图将菜单移动到下图结构: 我这里将系统监控,系统工具都移动到了系统管理下面,并且排了个序,将多级菜单放在了一起,这样看起来更加的清晰. 修改一下系统管理(100)与TienChi ...
- 强化学习从基础到进阶-案例与实践[1]:强化学习概述、序列决策、动作空间定义、策略价值函数、探索与利用、Gym强化学习实验
强化学习从基础到进阶-案例与实践[1]:强化学习概述.序列决策.动作空间定义.策略价值函数.探索与利用.Gym强化学习实验 1.1 强化学习概述 强化学习(reinforcement learning ...
- 从嘉手札<2024-1-29>
补一下以前的几篇日记 2018-4-6 当一个人不在纠结没有什么 而是开始珍视他所拥有的一切的时候 才算得上真正的成熟 个人的意志 不能因受到社会的压力而软弱 也不能受到自然的压力而萎缩 而应当如冬日 ...
- npm旧淘宝镜像过期,更换新淘宝镜像
1. 清空缓存 npm cache clean --force 2.设置新淘宝镜像 npm config set registry https://registry.npmmirror.com/ 3. ...
- Unity框架中的核心类
组件:Component 在Unity中,所有的游戏对象都可以挂载组件.组件控制着游戏对象的行为和外观,例如渲染.动画.碰撞检测等. 而Component就是组件的基类,提供了一些通用的方法和属性,例 ...
- P4093 [HEOI2016/TJOI2016] 序列 题解
题目链接:序列 对于 LIS 问题,很显而易见的有 dp方程为: \[dp_i=\max{dp_j}+1 \ (j<i,a_j \le a_i) \text{ dp表示以某个位置结尾的最长 LI ...
- 通过程序自动设置网卡的“internet共享”选项
操作系统 : Windows 10_x64 [版本 10.0.19042.685] Windows下可以通过网卡共享进行上网,但是需要在网卡的属性里面进行设置,需要在视窗界面进行操作,不能实现自动化. ...
