kernel_thread()和kthread_run()/kthread_create()的根本区别
0 本质区别
kthread_run()调用kthread_create(), kthread_create()加入链表后,有kthreadd()线程读取链表然后再调用kernel_thread()创建线程。
kernel_thread():实在真正的创建线程
kthread_run()/kthread_create() : 做特殊的准备工作,之后再调用kernel_thread()创建线程。
1. 函数的作用
首先要说明的是:这几个函数都是用来创建内核线程的。先看一下几个函数关系:
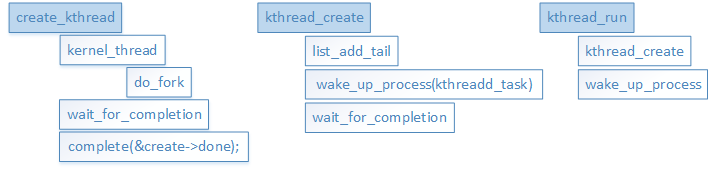
这里有两个长得很像的函数:create_kthread() 和 kthread_create()。(这不是长得像,根本就是一样的好吧,有点难记),这里只是函数封装的很像,但本质上还是kernel_thread() 和 **kthread_create()**这两个函数的区别。
从上面的函数调用便可以看出:
**kernel_thread()函数是通过调用do_fork()**函数创建的线程,而do_fork()则是在应用层fork(), vfork()和clone()函数的系统调用;此外还需要在其执行函数里调用daemonize()进行资源的释放;该线程挂接在init进程下。
kthread_create()函数是通过工作队列workqueue创建的线程,此线程挂在kthreadd线程下。
kthread_run()函数本质上是调用了kthread_create()和wake_up_process(), 就是除了挂在工作队列上后,便唤醒进行工作。
**kthread_create()**是比较推崇的创建内核线程的方式。
这几个函数在不同内核版本上有较大差别,请注意。
2. kernel_thread()
/* Create a kernel thread. *//*linux 2.6*/
int
kernel_thread(int (*fn)(void *), void * arg, unsigned long flags)
{
struct pt_regs regs;
memset(®s, 0, sizeof(regs));
/* Don't use r10 since that is set to 0 in copy_thread. */
regs.r11 = (unsigned long) fn;
regs.r12 = (unsigned long) arg;
regs.erp = (unsigned long) kernel_thread_helper;
regs.ccs = 1 << (I_CCS_BITNR + CCS_SHIFT);
/* Create the new process. */
return do_fork(flags | CLONE_VM | CLONE_UNTRACED, 0, ®s, 0, NULL, NULL);
}
在Linux2.6版本时该函数可以被驱动模块调用,因为被EXPORT_SYMBOL(kernel_thread);,但是在4.1版本没有没export,因此最好只用kthread_create()/kthread_run()来创建内核线程。
在Linux2.6版本时,非内核线程使用kernel_thread()必须在其执行函数里调用daemonize()释放资源:
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
static int Loop(void *dummy)
{
int i = 0;
daemonize("mythread");/*内核线程取的名字*/
while(i++ < 5) {
printk("current->mm = %p\n", current->mm);
printk("current->active_mm = %p\n", current->active_mm);
set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE);
schedule_timeout(10 * HZ);
}
return 0;
}
static __init int test_init(void)
{
kernel_thread(Loop, NULL, CLONE_KERNEL | SIGCHLD);
return 0;
}
static __exit int test_exit(void)
{
kernel_thread(Loop, NULL, CLONE_KERNEL | SIGCHLD);
return 0;
}
static void test_exit(void) {}
module_init(test_init);
module_exit(test_exit);
3. kthread_create()
kthread_create()函数创建的内核线程创建成功后是未被激活的,不能工作,如果需要工作,则需要使用wake_up_process()函数来唤醒。线程一旦启动起来后,会一直运行,除非该线程主动调用do_exit函数,或者其他的进程调用kthread_stop函数,本线程可以使用kthread_should_stop()来获取它其他线程kthread_stop()信号,从而实现温和的关闭方式。
/**
* kthread_create - create a kthread.
* @threadfn: the function to run until signal_pending(current).
* @data: data ptr for @threadfn.
* @namefmt: printf-style name for the thread.
*
* Description: This helper function creates and names a kernel
* thread. The thread will be stopped: use wake_up_process() to start
* it. See also kthread_run(), kthread_create_on_cpu().
*
* When woken, the thread will run @threadfn() with @data as its
* argument. @threadfn() can either call do_exit() directly if it is a
* standalone thread for which noone will **call kthread_stop(), or
* return when 'kthread_should_stop()' is true (which means
* kthread_stop() has been called). The return val**ue should be zero
* or a negative error number; it will be passed to kthread_stop().
*
* Returns a task_struct or ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM).
*/
struct task_struct *kthread_create(int (*threadfn)(void *data),
void *data,
const char namefmt[],
...)
{
struct kthread_create_info create;
create.threadfn = threadfn;
create.data = data;
init_completion(&create.started);
init_completion(&create.done);
spin_lock(&kthread_create_lock);
list_add_tail(&create.list, &kthread_create_list);
wake_up_process(kthreadd_task);/*放到了工作队列中*/
spin_unlock(&kthread_create_lock);
wait_for_completion(&create.done);
if (!IS_ERR(create.result)) {
va_list args;
va_start(args, namefmt);
vsnprintf(create.result->comm, sizeof(create.result->comm),
namefmt, args);
va_end(args);
}
return create.result;
}
4. kthread_run()
创建并唤醒该线程。 该函数基于kthread_create(),并且直接调用了wake_up_process()唤醒了该线程。因此使用kthread_run()函数创建的线程会直接开始工作。
/**
* kthread_run - create and wake a thread.
* @threadfn: the function to run until signal_pending(current).
* @data: data ptr for @threadfn.
* @namefmt: printf-style name for the thread.
*
* Description: Convenient wrapper for kthread_create() followed by
* wake_up_process(). Returns the kthread or ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM).
*/
#define kthread_run(threadfn, data, namefmt, ...) \
({ \
struct task_struct *__k \
= kthread_create(threadfn, data, namefmt, ## __VA_ARGS__); \
if (!IS_ERR(__k)) \
wake_up_process(__k); \
__k; \
})
kthread_run()创建线程:
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
static int thread_work(void *data)
{
allow_signal(SIGTERM);
current->state = TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE;
printk("New kernel thread run\n");
return 0;
}
static int __init test_init(void)
{
/* Schedule the test thread */
kthread_run (thread_work, NULL, "thread_1");
return 0;
}
static void __exit test_exit(void)
{
return;
}
MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL");
module_init(test_init);
module_exit(test_exit);
5. kthread_stop() / kthread_should_stop()
用来结束由kthread_create()创建的线程。
/**
* kthread_stop - stop a thread created by kthread_create().
* @k: thread created by kthread_create().
*
* Sets kthread_should_stop() for @k to return true, wakes it, and
* waits for it to exit. Your threadfn() must not call do_exit()
* itself if you use this function! This can also be called after
* kthread_create() instead of calling wake_up_process(): the thread
* will exit without calling threadfn().
*
* Returns the result of threadfn(), or %-EINTR if wake_up_process()
* was never called.
*/
int kthread_stop(struct task_struct *k)
{
int ret;
mutex_lock(&kthread_stop_lock);
/* It could exit after stop_info.k set, but before wake_up_process. */
get_task_struct(k);
/* Must init completion *before* thread sees kthread_stop_info.k */
init_completion(&kthread_stop_info.done);
smp_wmb();
/* Now set kthread_should_stop() to true, and wake it up. */
kthread_stop_info.k = k;
wake_up_process(k);
put_task_struct(k);
/* Once it dies, reset stop ptr, gather result and we're done. */
wait_for_completion(&kthread_stop_info.done);
kthread_stop_info.k = NULL;
ret = kthread_stop_info.err;
mutex_unlock(&kthread_stop_lock);
return ret;
}
**kthread_should_stop()**用来获取线程是否处于忙状态,如果是则返回true。之后再调用kthread_stop()完成线程的温和退出。
当然也可以直接调用kthread_stop()使线程退出。使用该函数时,线程的执行函数不得调用do_exit();
6. kthreadd() —(后续补充)
看完kthreadd()函数实现后感觉上面可能不是特别准确。。
首先这个函数kthreadd() 是上述工作队列的处理函数,从上述代码里可以看出**kthread_create()**创建线程的方法只是将工作放到工作队列中,之后实在这里做的后续处理:kthreadd是一个内核独立线程,是由do_fork()函数创建的。
kthreadd的创建:
static void noinline __init_refok rest_init(void)
__releases(kernel_lock)
{
int pid;
kernel_thread(kernel_init, NULL, CLONE_FS | CLONE_SIGHAND);/*init线程*/
numa_default_policy();
pid = kernel_thread(kthreadd, NULL, CLONE_FS | CLONE_FILES);/*kthreadd线程*/
kthreadd_task = find_task_by_pid(pid);
unlock_kernel();
/*
* The boot idle thread must execute schedule()
* at least one to get things moving:
*/
preempt_enable_no_resched();
schedule();
preempt_disable();
/* Call into cpu_idle with preempt disabled */
cpu_idle();
}
kthreadd关于工作队列的处理流程:
int kthreadd(void *unused)
{
/* Setup a clean context for our children to inherit. */
kthreadd_setup();
current->flags |= PF_NOFREEZE;
for (;;) {
set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE);
if (list_empty(&kthread_create_list))
schedule();
__set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING);
spin_lock(&kthread_create_lock);
while (!list_empty(&kthread_create_list)) {/*如果链表内有内容*/
struct kthread_create_info *create;
/*取出链表节点信息*/
create = list_entry(kthread_create_list.next, /*实现方式和container_of一样*/
struct kthread_create_info, list);
list_del_init(&create->list);
spin_unlock(&kthread_create_lock);
/*使用do_fork的方式创建线程*/
create_kthread(create);/*do_fork方式*/
spin_lock(&kthread_create_lock);
}
spin_unlock(&kthread_create_lock);
}
return 0;
}
从这段代码可以看出,工作队列的处理方式是:如果工作队列有内容,取出任务,然后创建线程(最后调用do_fork()实现的)。因此可以得出结论:内核创建线程的方式和应用层最终调用的函数是相同的,都是do_fork(); 至于为什么不直接创建而使用工作队列进程创建还不清楚原因。
kernel_thread()和kthread_run()/kthread_create()的根本区别的更多相关文章
- Linux Process Management && Process Scheduling Principle
目录 . 引言 . 进程优先级 . 进程的生命周 . 进程表示 . 进程管理相关的系统调用 . 进程调度 . 完全公平调度类 . 实时调度类 . 调度器增强 . 小结 1. 引言 在多处理器系统中,可 ...
- Linux内核线程的思考与总结
1.内核线程,只是一个称呼,实际上就是一个进程,有自己独立的TCB,参与内核调度,也参与内核抢占. 这个进程的特别之处有两点,第一.该进程没有前台.第二.永远在内核态中运行. 2.创建内核线程有两种方 ...
- 从应用到内核,分析top命令显示的进程名包含中括号"[]"的含义
背景 在执行top/ps命令的时候,在COMMAND一列,我们会发现,有些进程名被[]括起来了,例如 PID PPID USER STAT VSZ %VSZ %CPU COMMAND 1542 928 ...
- kthread_create与kernel_thread的区别【栈】
转自:http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-25513153-id-2888903.html kthread_create与kernel_thread的区别 kernel thr ...
- Linux内核多线程实现方法 —— kthread_create函数【转】
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/sharecode/article/details/40076951 Linux内核多线程实现方法 —— kthread_create函数 内核经常需要 ...
- Linux内核:kthread_create(线程)、SLEEP_MILLI_SEC
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/guowenyan001/article/details/39230181 一.代码 #include <linux/module.h> # ...
- kthread_run【转】
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/zhangxuechao_/article/details/50876397 头文件 include/linux/kthread.h 创建并启动 /** ...
- kthread_run
头文件 include/linux/kthread.h 创建并启动 /** * kthread_run - create and wake a thread. * @threadfn: the fun ...
- c#与java的区别
经常有人问这种问题,用了些时间java之后,发现这俩玩意除了一小部分壳子长的还有能稍微凑合上,基本上没什么相似之处,可以说也就是马甲层面上的相似吧,还是比较短的马甲... 一般C#多用于业务系统的开发 ...
随机推荐
- 【LeetCode】81. 搜索旋转排序数组 II
81. 搜索旋转排序数组 II 知识点:数组,二分查找: 题目描述 已知存在一个按非降序排列的整数数组 nums ,数组中的值不必互不相同. 在传递给函数之前,nums 在预先未知的某个下标 k(0 ...
- Mybatis学习笔记-CRUD
namespace namesapce中的包名需与Dao/Mapper接口的包名一致 SELCET 选择,查询语句 id:对应namespace中的方法: resultType:Sql语句执行的返回值 ...
- 利用共享内存实现比NCCL更快的集合通信
作者:曹彬 | 旷视 MegEngine 架构师 简介 从 2080Ti 这一代显卡开始,所有的民用游戏卡都取消了 P2P copy,导致训练速度显著的变慢.针对这种情况下的单机多卡训练,MegEng ...
- OI卷题记录
2021.8.2 LG3386 匈牙利算法 二分图 LG1377 笛卡尔树 题解 2021.8.3 LG2962 \(\text{Meet in middle}\) LG3389 高斯消元 高斯-约旦 ...
- 小白自学vue的第一天,加油!
一.插值的操作 1.Mustache语法 也就是双大括号(翻译过来就是胡须的意思) 2.v-once指令 加了v-once数据不会随着数据的改变而改变,只会渲染一次 3.v-html指令 可以解析HT ...
- ICCV2021 |重新思考人群中的计数和定位:一个纯粹基于点的框架
论文:Rethinking Counting and Localization in Crowds:A Purely Point-Based Framework 代码:https://github ...
- Markdown插入LaTex数学公式
本文转载自Nautilus_sailing的试试LaTeX插入数学公式,内容有所改动 今天写了一篇随笔,其中需要写几个数学式子,但是我又不想直接将公式做成图片后插入,我觉得很不美观还麻烦.但是我也不会 ...
- Notepad++的NppFTP插件连接linux操作系统
Notepad++的NppFTP插件连接linux操作系统 下载地址:https://notepad-plus-plus.org/downloads/v8.1.2/ 1.安装Npp_FTP插件 两种方 ...
- kong整合Cosul实践(3)
1. 准备工作: 需要.netcore或者java程序一套,引入consul第三方包 我这里搭建了一个.netcore的webapi项目,引入Consul第三方包,网上可查资料一堆 环境需要kong, ...
- Longhorn 云原生分布式块存储解决方案设计架构和概念
内容来源于官方 Longhorn 1.1.2 英文技术手册. 系列 Longhorn 是什么? 目录 1. 设计 1.1. Longhorn Manager 和 Longhorn Engine 1.2 ...
