V-rep学习笔记:Geometric Constraint Solver(几何约束求解)
The geometric constraint solver is slower and less precise at solving kinematic problems, but might be easier and more intuitive to use. Moreover, it allows interacting with a mechanism in a more flexible way than the inverse kinematics calculation module. Following figures illustrate the geometric constraint solver applied to a complicated mechanism:
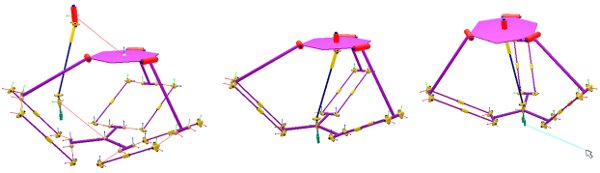
[Geometric constraint solver handling a complicated mechanism: (1) initial situation, (2) during simulation, (3) interaction with the mechanism]
V-REP's geometric constraint solver functionality operates in a similar way as the kinematics calculation module, with the difference that the solver will try to automatically identify kinematic chains, and handle them in an appropriate way (automatic constraint adjustments, loop closures, etc.). Typically, the user has to tell the solver:
- which objects (dummies) should coincide (in order to close a loop for instance)
- what mechanism has to be handled by the geometric constraint solver
- which additional constraints should be applied to the mechanism
Specifying closure constraints
Closure constraints can be seen as constraints that require two object's configurations (position and orientation) to be identical. The idea is illustrated in following figures:
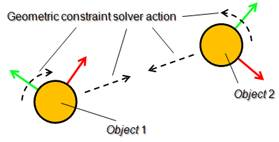
[The geometric constraint solver closure constraint]
/V-REP3/V-REP_PRO_EDU/helpFiles/en/images/gcsOp2.jpg)
[Closing action of the geometric constraint solver (1) intermediate situation, (2) final situation]
GCS会试图将closure pair的位置以及姿态重合,因此机构要有足够的自由度。对于平面机构(如铰链四杆机构)来说使用GCS保持机构闭合就不合适,可以考虑用IK,tip-target来构成闭环。The geometric constraint solver will try to overlap the position and orientation of the two objects while trying to keep the mechanism coherent (i.e. by only adjusting the joints in IK mode in the mechanism to reach that overlap situation). The objects that the geometric constraint solver uses to specify closure constraints are dummies. To this end, two dummies need to be marked as closure pair. This can be adjusted in the dummy properties by selecting the opposite dummy as Linked dummy and specifying GCS, overlap constraint for the Link type. Following figure illustrates two linked dummies specifying a geometric constraint solver closure constraint:
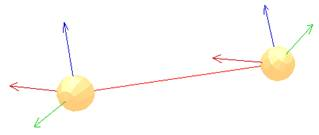
[Two linked dummies specifying a closure constraint]
Specifying the mechanism to be solved
All objects that can be reached from a given object by following a path that can go will be considered as the same mechanism:
- from one object to its parent object.
- from one object to its child objects.
- from one dummy to its linked dummy (however only links of type GCS, overlap constraint)
即按照上面3种方式从运动链(elements)上某一点开始探索,能够到达的节点都属于同一个机构。如果两个运动链没有公共的节点,但是由类型为GCS,overlap constraint的dummy相连,则这两个运动链仍属于同一个机构。Two object trees that don't share any common parent objects (referred hereafter as elements), can also be part of the same mechanism if two linked dummies join them. This is illustrated in following figure:
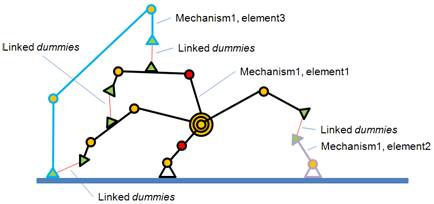
/V-REP3/V-REP_PRO_EDU/helpFiles/en/images/gcsOp4.jpg)
[One mechanism composed by 3 elements (object trees)]
The last parent object of the object that is chosen as the starting point of the mechanism exploration (path exploration) is referred to as the base object of the mechanism. When the geometric constraint solver tries to solve a mechanism, it will try to do so by keeping the base object of the mechanism in place(求解几何约束时选作base的object会固定住不动). This is important to remember. To specify a mechanism to be solved, select an object parented with the base object of the mechanism and in the geometric constraint solver dialog click insert new object. One same mechanism can only be registered once for solving. Mechanisms that do not include at least one joint in IK mode will not be handled by the solver.
Specifying additional constraints
Additional positional constraints can be specified for a mechanism. This can be done with two linked dummies that form a tip-target pair (specify GCS, tip/GCS, target as Link type in the dummy properties). Following figures illustrate two linked dummies, where one is marked as target:
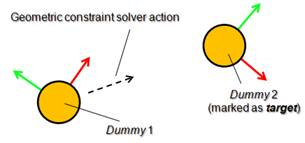
/V-REP3/V-REP_PRO_EDU/helpFiles/en/images/gcsOp5.jpg)
[The geometric constraint solver position constraint]
注意GCS, tip/GCS, target与GCS, overlap constraint的区别是:GCS, target不会被当做机构的一部分,解算时target不动tip移动到与target重合;而GCS, overlap constraint类型的dummy则属于同一个机构,解算时会同时移动直到重合。The dummy marked as target is not considered as part of the mechanism and therefore will not move during geometric constraint resolution, while the other dummy will try to reach the same position as the dummy marked as target.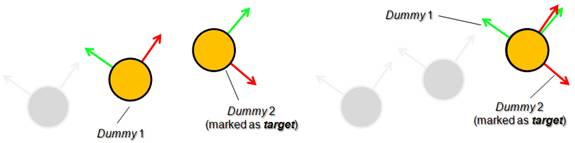
/V-REP3/V-REP_PRO_EDU/helpFiles/en/images/gcsOp6.jpg)
[Position constraint action of the geometric constraint solver (1) intermediate situation, (2) final situation]
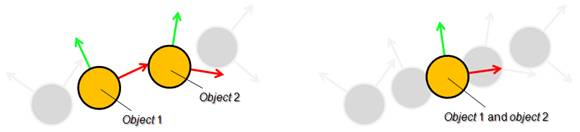
使用GCS(几何约束求解器),可以用鼠标拖动场景中的物体进行直观地控制。During simulation, a mechanism that was previously registered to be solved with the geometric constraint solver can be manipulated in a flexible way with the mouse, when the mechanism navigation mode is selected. That mode can be enabled via following API call: simSetNavigationMode. Simply click and drag any shape object that is part of the mechanism, and the solver will try to take into account that additional position constraint.
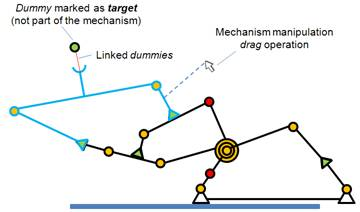
[Mechanism with two additional position constraints]
It is good practice to build your mechanism as a tree structure (i.e. where all objects in the mechanism have at least one common parent object) and have linked dummies be in charge of closing certain tree branches. By doing so you reduce the mechanism's complexity, you simplify the mechanism's scene hierarchy representation, and you will be able to handle the mechanism as a model.
下面是一个简单的例子,用鼠标选中门并按住左键拖动,可以看到门能跟着鼠标运动。修改Model browser/Models/infrastructure/doors/manual door中的场景和代码,添加一个控制球和一组Dummy(类型分别设置为GCS, tip/GCS, target),然后在Calculation Modules的Geometric Constraint Solver选项页中将根节点door设为机构的base 。最后将旋转关节设为Inverse kinematics模式,进行仿真:


代码如下:
if (sim_call_type==sim_childscriptcall_initialization) then
jointHandle=simGetObjectHandle('_doorJoint')
sphereHandle=simGetObjectHandle('manipulationSphere')
-- Retrieves the navigation and selection mode for the mouse
initialMode=simGetNavigationMode()
-- Sets the navigation and selection mode for the mouse.
simSetNavigationMode(sim_navigation_objectshift+
sim_navigation_clickselection+
sim_navigation_ctrlselection+
sim_navigation_shiftselection+
sim_navigation_camerazoomwheel+
sim_navigation_camerarotaterightbutton)
tipDummyHandle=simGetObjectHandle('tip')
-- sim_intparam_prox_sensor_select_down: Allows to enable message or callback generation when a shape
-- was clicked (down-click) in the scene. The click is a "geometric" click. This value is set to zero
-- at simulation start and simulation stop.
-- (-1: enabled for all visible shapes in the scene)
simSetInt32Parameter(sim_intparam_prox_sensor_select_down, -)
simDisplayDialog("info","You can click and drag the door",sim_dlgstyle_ok,false)
end
if (sim_call_type==sim_childscriptcall_sensing) then
-- auxiliaryData[1]: objectID
-- auxiliaryData2[1] ~ auxiliaryData2[3]: coordinates of clicked point
local message,data,data2 = simGetSimulatorMessage()
while message>- do -- (-1 if no message is available or in case of an error)
if message == sim_message_prox_sensor_select_down then
-- move manipulation sphere according the position of clicked point
simSetObjectPosition(sphereHandle,-,{data2[],data2[],data2[]})
simSetObjectPosition(tipDummyHandle,-,{data2[],data2[],data2[]})
simSetObjectParent(tipDummyHandle, data[], true)
-- select the manipulation sphere to move
simRemoveObjectFromSelection(sim_handle_all)
simAddObjectToSelection(sim_handle_single,sphereHandle)
end
message,data,data2 = simGetSimulatorMessage()
end
end
if (sim_call_type==sim_childscriptcall_cleanup) then
simRemoveObjectFromSelection(sim_handle_all) -- removes all objects from the selection
simSetInt32Parameter(sim_intparam_prox_sensor_select_down, ) -- 0: disabled
simSetNavigationMode(initialMode)
end
下面是一个修改自V-REP_PRO_EDU\scenes\constraintSolverExample.ttt的例子,用鼠标选中机构上任意杆件进行拖拽,可以看到机构能跟着一起运动而不散开:
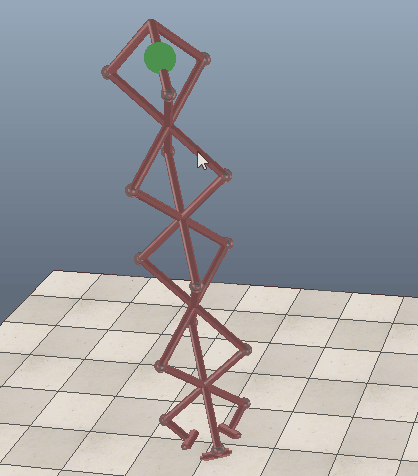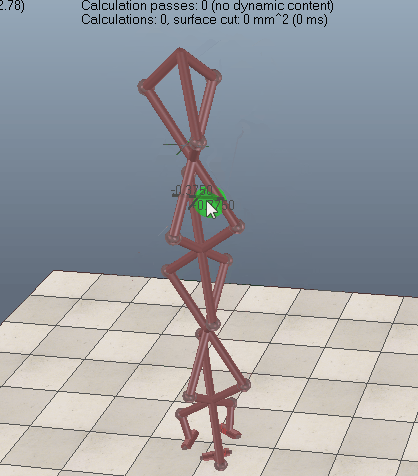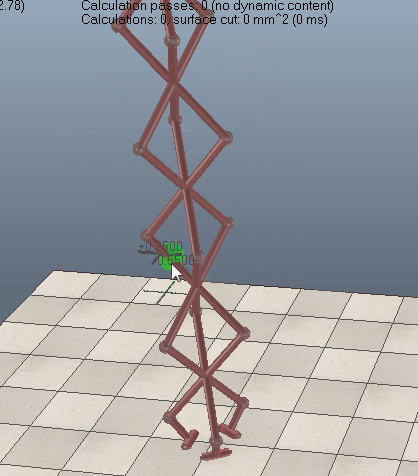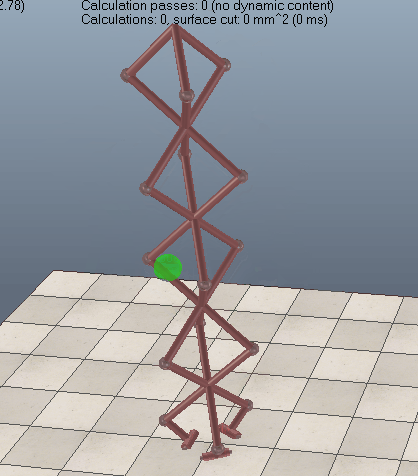
Geometric constraint solver operation
When building a mechanism that will be solved by the geometric constraint solver, make sure that the mechanism is coherent and that constraints are not impossible (i.e. that there are enough degrees of freedom for the mechanism to work). Following figures show an example of a mechanism and its resolution:
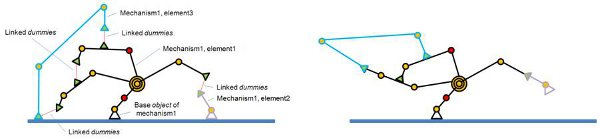
[(1) Mechanism containing 3 elements before and (2) during simulation]
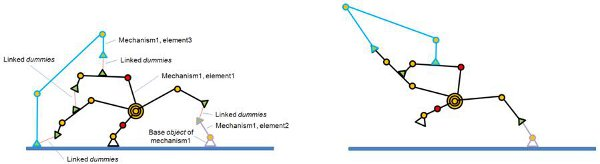
[Same mechanism, but different base object (1) before and (2) during simulation]
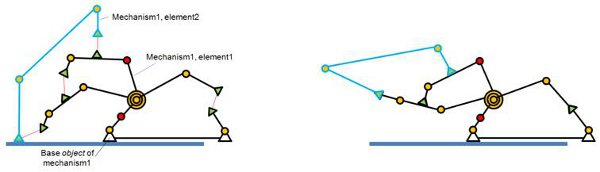
[(1) Mechanism containing 2 elements before and (2) during simulation]
参考:
Using the geometric constraint solver
Solving IK and FK for any type of mechanism
control the model using mouse in simulation mode
V-rep学习笔记:Geometric Constraint Solver(几何约束求解)的更多相关文章
- V-rep学习笔记:并联机构正逆运动学
Solving the FK problem of simple kinematic chains is trivial (just apply the desired joint values to ...
- <老友记>学习笔记
这是六个人的故事,从不服输而又有强烈控制欲的monica,未经世事的千金大小姐rachel,正直又专情的ross,幽默风趣的chandle,古怪迷人的phoebe,花心天真的joey——六个好友之间的 ...
- MySQL学习笔记一
MySQL 学习笔记 一 一.数据库简单介绍 1. 按照数据库的发展时间顺序,主要出现了以下类型数据库系统: Ø 网状型数据库 Ø 层次型数据库 Ø 关系型数据库 Ø 面向对象数据库 上面4中数据库系 ...
- 菜鸟的MySQL学习笔记(一)
本学习笔记是照搬慕课网<与MySQL的零距离接触>内容,特此感谢! 1-1 mysql的安装与配置 Windows环境下的MSI安装: 1.安装: 双击MSI文件->用户协议-> ...
- OGG学习笔记02-单向复制配置实例
OGG学习笔记02-单向复制配置实例 实验环境: 源端:192.168.1.30,Oracle 10.2.0.5 单实例 目标端:192.168.1.31,Oracle 10.2.0.5 单实例 1. ...
- Hibernate 马士兵 学习笔记 (转)
目录(?)[+] 第2课 Hibernate UML图 第3课 风格 第4课 资源 第5课 环境准备 第6课 第一个示例Hibernate HelloWorld 第7课 建立Annotation版本的 ...
- R语言与机器学习学习笔记
人工神经网络(ANN),简称神经网络,是一种模仿生物神经网络的结构和功能的数学模型或计算模型.神经网络由大量的人工神经元联结进行计算.大多数情况下人工神经网络能在外界信息的基础上改变内部结构,是一种自 ...
- 蒟蒻的长链剖分学习笔记(例题:HOTEL加强版、重建计划)
长链剖分学习笔记 说到树的链剖,大多数人都会首先想到重链剖分.的确,目前重链剖分在OI中有更加多样化的应用,但它大多时候是替代不了长链剖分的. 重链剖分是把size最大的儿子当成重儿子,顾名思义长链剖 ...
- Oracle基础学习笔记
Oracle基础学习笔记 最近找到一份实习工作,有点头疼的是,有阶段性考核,这...,实际想想看,大学期间只学过数据库原理,并没有针对某一数据库管理系统而系统的学习,这正好是一个机会,于是乎用了三天时 ...
随机推荐
- LCA算法总结
LCA问题(Least Common Ancestors,最近公共祖先问题),是指给定一棵有根树T,给出若干个查询LCA(u, v)(通常查询数量较大),每次求树T中两个顶点u和v的最近公共祖先,即找 ...
- Java的四个基本特性和对多态的理解
Java面向对象的四大基本特性:抽象.封装.继承.多态. 多态的实现方式:重载.继承.接口 Java中多态性的实现 什么是多态 面向对象的三大特性:封装.继承.多态.从一定角度来看,封装和继承几乎都是 ...
- 漂亮的CSS3提交意见输入框样式
做了个输入框样式,如图: CSS代码如下: <喎�"http://www.2cto.com/kf/ware/vc/" target="_blank" cl ...
- 大数据开发实战:Storm流计算开发
Storm是一个分布式.高容错.高可靠性的实时计算系统,它对于实时计算的意义相当于Hadoop对于批处理的意义.Hadoop提供了Map和Reduce原语.同样,Storm也对数据的实时处理提供了简单 ...
- redis调优 -- 内存碎片
最近查看了一下redis运行状况,发现公司测试服务器的redis内存不太够用,但是实际占用内存的数据量其实不大,以前也没有这种情况,之前在cache层新增了一个防刷积分任务的逻辑才会这样,搜索一下原因 ...
- 判断checkbox选中的个数
直接看例子吧: shippingAddressList 为一个集合 <c:forEach items="${shippingAddressList }" var=" ...
- POJ 1265 pick定理
pick公式:多边形的面积=多边形边上的格点数目/2+多边形内部的格点数目-1. 多边形边上的格点数目可以枚举每条边求出.如果是水平或者垂直,显然可以得到,否则则是坐标差的最大公约数减1.(注这里是不 ...
- 条件随机场 (CRF) 分词序列谈之一(转)
http://langiner.blog.51cto.com/1989264/379166 原创作品,允许转载,转载时请务必以超链接形式标明文章 原始出处 .作者信息和本声明.否则将追究法律责任.ht ...
- ES8新特性——ES8 was Released and here are its Main New Features
原文: https://hackernoon.com/es8-was-released-and-here-are-its-main-new-features-ee9c394adf66 -------- ...
- c#:对两个字符串大小比较(不使用c#/java内部的比较函数),按升序排序
题目:首先需要实现一个函数:两个字符串大小比较(不得使用c#/java系统函数)的自定义函数:之后对一个字符串数据进行按升序排序(在排序过程中使用字符串大小比较时,使用自定义的字符串大小比较函数). ...
