《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 5.19

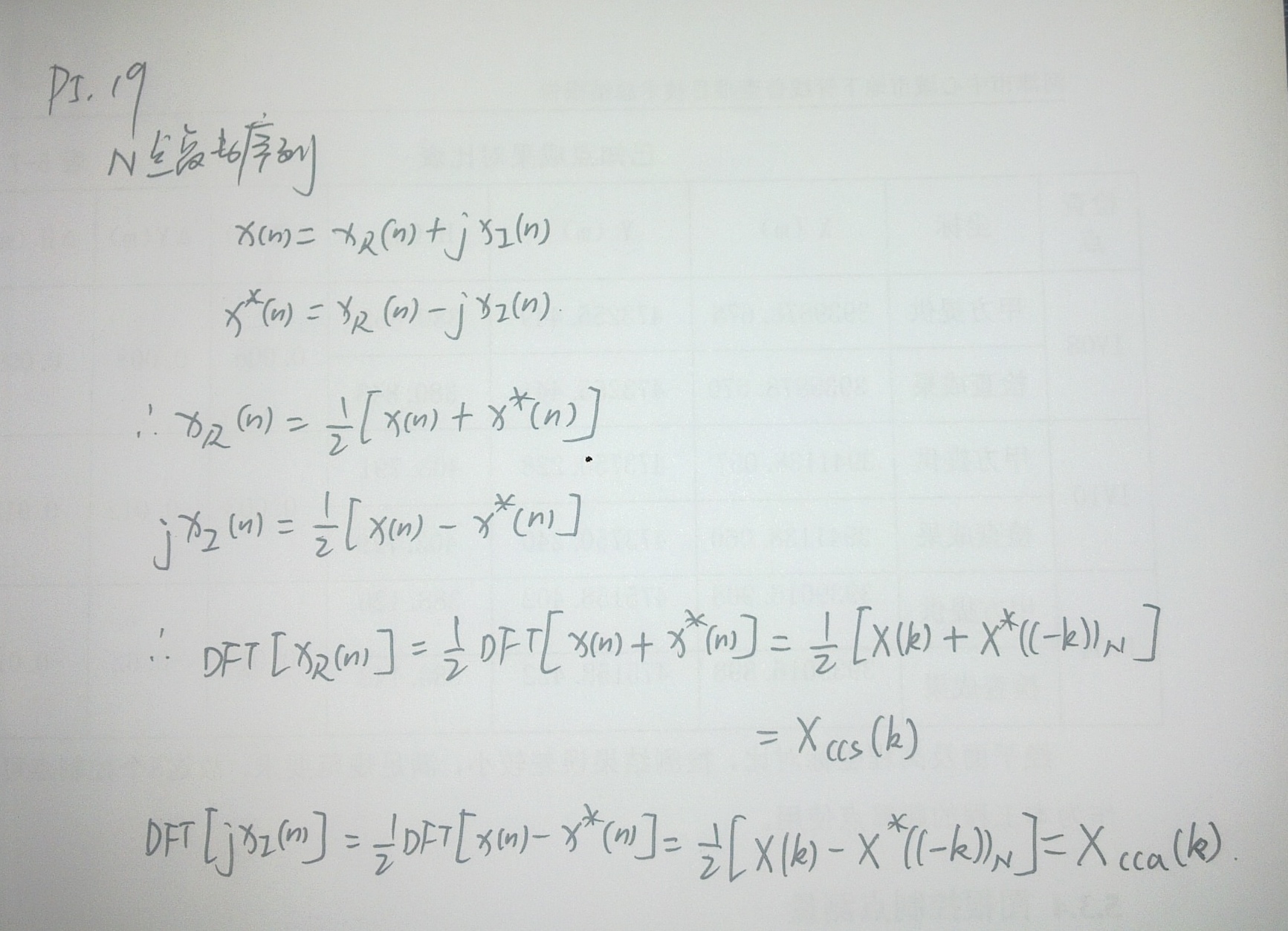
代码:
- function [X1k, X2k] = real2dft(x1, x2, N)
- %% ---------------------------------------------------------------------
- %% DFT of two Real-Valued N-Point sequence x1(n) and x2(n)
- %% ---------------------------------------------------------------------
- %% [X1, X2] = real2dft(x1, x2, N)
- %% X1k = n-point DFT of x1
- %% X2k = n-point DFT of x2
- %% x1 = sequence of length <= N
- %% x2 = sequence of length <= N
- %% N = length of DFT
- % ----------------------------------------
- % if length of x1 and x2 < N,
- % then padding zeros
- % ----------------------------------------
- if ( length(x1) < N)
- x1 = [x1 zeros(1, N-length(x1))];
- end
- if ( length(x2) < N)
- x2 = [x2 zeros(1, N-length(x2))];
- end
- x = x1 + j * x2;
- N = length(x); k = 0:(N-1);
- Xk_DFT = dft(x, N);
- Xk_DFT_fold = Xk_DFT(mod_1(-k,N)+1);
- Xk_CCS = 0.5*(Xk_DFT + conj(Xk_DFT_fold));
- Xk_CCA = 0.5*(Xk_DFT - conj(Xk_DFT_fold));
- X1k = Xk_CCS;
- X2k = Xk_CCA;
- %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
- %% Output Info about this m-file
- fprintf('\n***********************************************************\n');
- fprintf(' <DSP using MATLAB> Problem 5.19 \n\n');
- banner();
- %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
- % ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- % X(k) is N-point DFTs of N-point Complex-valued sequence x(n)
- % x(n) = xR(n) + j xI(n)
- % xR(n) and xI(n) are real and image parts of x(n);
- % DFT[xR]=Xccs(k) DFT[j*xI]=Xcca(k)
- %
- % Xccs = 0.5*[X(k)+ X*((-k))] Xcca = 0.5*[X(k) - X*((-k))]
- %
- % ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
- n = [0:39];
- x1 = cos(0.1*pi*n); % N=40 real-valued sequence
- x2 = sin(0.2*pi*n); % N=40 real-valued sequence
- x = x1 + j * x2;
- N = length(x); k = 0:(N-1);
- Xk_DFT = dft(x, N);
- Xk_DFT_fold = Xk_DFT(mod_1(-k,N)+1);
- magXk_DFT = abs( [ Xk_DFT ] ); % DFT magnitude
- angXk_DFT = angle( [Xk_DFT] )/pi; % DFT angle
- realXk_DFT = real(Xk_DFT);
- imagXk_DFT = imag(Xk_DFT);
- magXk_DFT_fold = abs( [ Xk_DFT_fold ] ); % DFT magnitude
- angXk_DFT_fold = angle( [Xk_DFT_fold] )/pi; % DFT angle
- realXk_DFT_fold = real(Xk_DFT_fold);
- imagXk_DFT_fold = imag(Xk_DFT_fold);
- % --------------------------------------------------------
- % Calculater one N-point DFT to get
- % two N-point DFT
- % --------------------------------------------------------
- [X1k_DFT, X2k_DFT] = real2dft(x1, x2, N);
- magX1k_DFT = abs( [ X1k_DFT ] ); % DFT magnitude
- angX1k_DFT = angle( [X1k_DFT] )/pi; % DFT angle
- realX1k_DFT = real(X1k_DFT);
- imagX1k_DFT = imag(X1k_DFT);
- magX2k_DFT = abs( [ X2k_DFT ] ); % DFT magnitude
- angX2k_DFT = angle( [X2k_DFT] )/pi; % DFT angle
- realX2k_DFT = real(X2k_DFT);
- imagX2k_DFT = imag(X2k_DFT);
- % -------------------------------------------------------
- % Get DFT of xR and xI directorly
- % -------------------------------------------------------
- XRk_DFT = dft(x1, N);
- XIk_DFT = dft(j*x2, N);
- magXRk_DFT = abs( [ XRk_DFT ] ); % DFT magnitude
- angXRk_DFT = angle( [XRk_DFT] )/pi; % DFT angle
- realXRk_DFT = real(XRk_DFT);
- imagXRk_DFT = imag(XRk_DFT);
- magXIk_DFT = abs( [ XIk_DFT ] ); % DFT magnitude
- angXIk_DFT = angle( [XIk_DFT] )/pi; % DFT angle
- realXIk_DFT = real(XIk_DFT);
- imagXIk_DFT = imag(XIk_DFT);
- figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'P5.19 xR(n) and xI(n)')
- set(gcf,'Color','white');
- subplot(2,1,1); stem(n, x1);
- xlabel('n'); ylabel('x1');
- title('real part of x(n), cos(0.1\pin), N=40'); grid on;
- subplot(2,1,2); stem(n, x2);
- xlabel('n'); ylabel('x2');
- title('imag part of x(n), sin(0.2\pin), N=40'); grid on;
- figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'P5.19 X(k), DFT of x(n)')
- set(gcf,'Color','white');
- subplot(2,2,1); stem(k, magXk_DFT);
- xlabel('k'); ylabel('magnitude(k)');
- title('magnitude DFT of x(n), N=40'); grid on;
- subplot(2,2,3); stem(k, angXk_DFT);
- %axis([-N/2, N/2, -0.5, 50.5]);
- xlabel('k'); ylabel('angle(k)');
- title('angle DFT of x(n), N=40'); grid on;
- subplot(2,2,2); stem(k, realXk_DFT);
- xlabel('k'); ylabel('real (k)');
- title('real DFT of x(n), N=40'); grid on;
- subplot(2,2,4); stem(k, imagXk_DFT);
- %axis([-N/2, N/2, -0.5, 50.5]);
- xlabel('k'); ylabel('imag (k)');
- title('imag DFT of x(n), N=40'); grid on;
- figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'P5.19 X((-k))_N')
- set(gcf,'Color','white');
- subplot(2,2,1); stem(k, magXk_DFT_fold);
- xlabel('k'); ylabel('magnitude(k)');
- title('magnitude X((-k)), N=40'); grid on;
- subplot(2,2,3); stem(k, angXk_DFT_fold);
- %axis([-N/2, N/2, -0.5, 50.5]);
- xlabel('k'); ylabel('angle(k)');
- title('angle X((-k)), N=40'); grid on;
- subplot(2,2,2); stem(k, realXk_DFT_fold);
- xlabel('k'); ylabel('real (k)');
- title('real X((-k)), N=40'); grid on;
- subplot(2,2,4); stem(k, imagXk_DFT_fold);
- %axis([-N/2, N/2, -0.5, 50.5]);
- xlabel('k'); ylabel('imag (k)');
- title('imag X((-k)), N=40'); grid on;
- figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'P5.19 X1(k) by real2dft')
- set(gcf,'Color','white');
- subplot(2,2,1); stem(k, magX1k_DFT);
- xlabel('k'); ylabel('magnitude(k)');
- title('magnitude, N=40'); grid on;
- subplot(2,2,3); stem(k, angX1k_DFT);
- %axis([-N/2, N/2, -0.5, 50.5]);
- xlabel('k'); ylabel('angle(k)');
- title('angle, N=40'); grid on;
- subplot(2,2,2); stem(k, realX1k_DFT);
- xlabel('k'); ylabel('real (k)');
- title('real, N=40'); grid on;
- subplot(2,2,4); stem(k, imagX1k_DFT);
- %axis([-N/2, N/2, -0.5, 50.5]);
- xlabel('k'); ylabel('imag (k)');
- title('imag, N=40'); grid on;
- figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'P5.19 X2(k) by real2dft')
- set(gcf,'Color','white');
- subplot(2,2,1); stem(k, magX2k_DFT);
- xlabel('k'); ylabel('magnitude(k)');
- title('magnitude, N=40'); grid on;
- subplot(2,2,3); stem(k, angX2k_DFT);
- %axis([-N/2, N/2, -0.5, 50.5]);
- xlabel('k'); ylabel('angle(k)');
- title('angle, N=40'); grid on;
- subplot(2,2,2); stem(k, realX2k_DFT);
- xlabel('k'); ylabel('real (k)');
- title('real, N=40'); grid on;
- subplot(2,2,4); stem(k, imagX2k_DFT);
- %axis([-N/2, N/2, -0.5, 50.5]);
- xlabel('k'); ylabel('imag (k)');
- title('imag, N=40'); grid on;
- figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'P5.19 XR(k) by direct')
- set(gcf,'Color','white');
- subplot(2,2,1); stem(k, magXRk_DFT);
- xlabel('k'); ylabel('magnitude(k)');
- title('magnitude, N=40'); grid on;
- subplot(2,2,3); stem(k, angXRk_DFT);
- %axis([-N/2, N/2, -0.5, 50.5]);
- xlabel('k'); ylabel('angle(k)');
- title('angle, N=40'); grid on;
- subplot(2,2,2); stem(k, realXRk_DFT);
- xlabel('k'); ylabel('real (k)');
- title('real, N=40'); grid on;
- subplot(2,2,4); stem(k, imagXRk_DFT);
- %axis([-N/2, N/2, -0.5, 50.5]);
- xlabel('k'); ylabel('imag (k)');
- title('imag, N=40'); grid on;
- figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'P5.19 XI(k) by direct')
- set(gcf,'Color','white');
- subplot(2,2,1); stem(k, magXIk_DFT);
- xlabel('k'); ylabel('magnitude(k)');
- title('magnitude, N=40'); grid on;
- subplot(2,2,3); stem(k, angXIk_DFT);
- %axis([-N/2, N/2, -0.5, 50.5]);
- xlabel('k'); ylabel('angle(k)');
- title('angle, N=40'); grid on;
- subplot(2,2,2); stem(k, realXIk_DFT);
- xlabel('k'); ylabel('real (k)');
- title('real, N=40'); grid on;
- subplot(2,2,4); stem(k, imagXIk_DFT);
- %axis([-N/2, N/2, -0.5, 50.5]);
- xlabel('k'); ylabel('imag (k)');
- title('imag, N=40'); grid on;
运行结果:
复数序列的实部和虚部
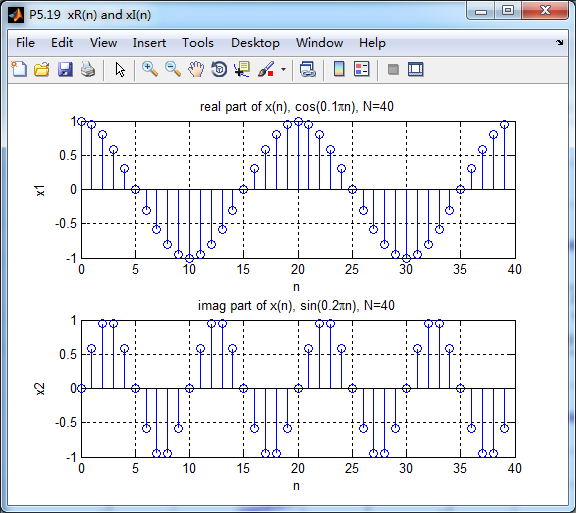
复数序列的DFT,X(k)
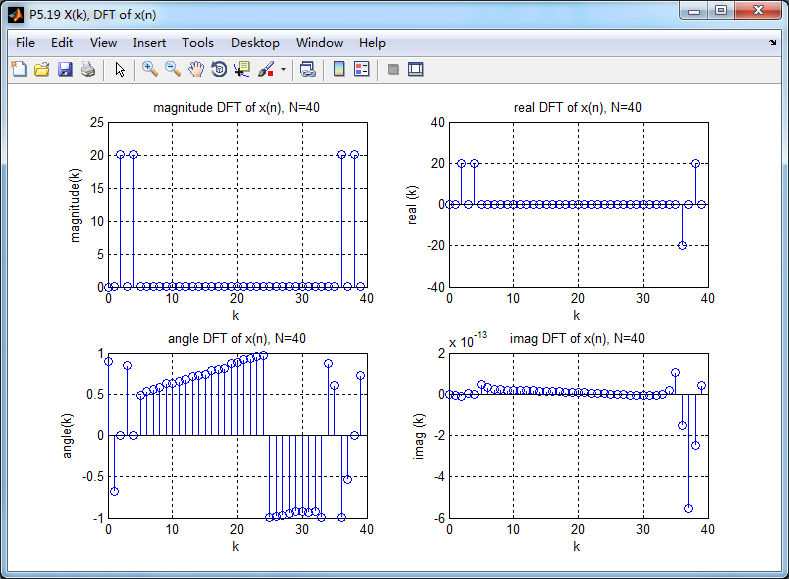
X((-k))
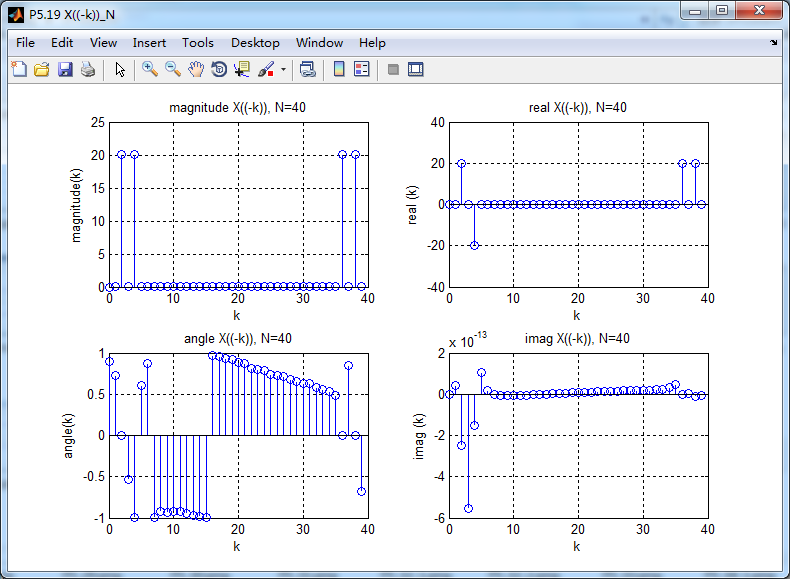
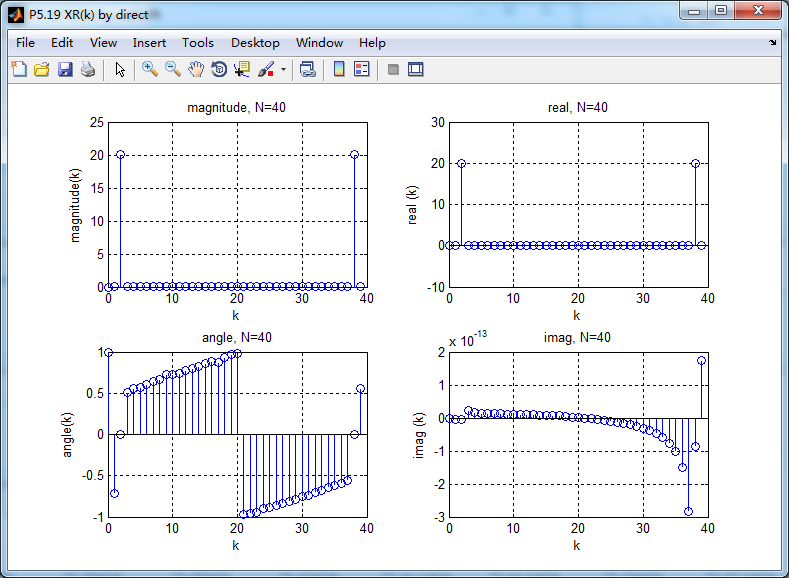
直接计算实部和虚部的DFT,XR(k)和XI(k)

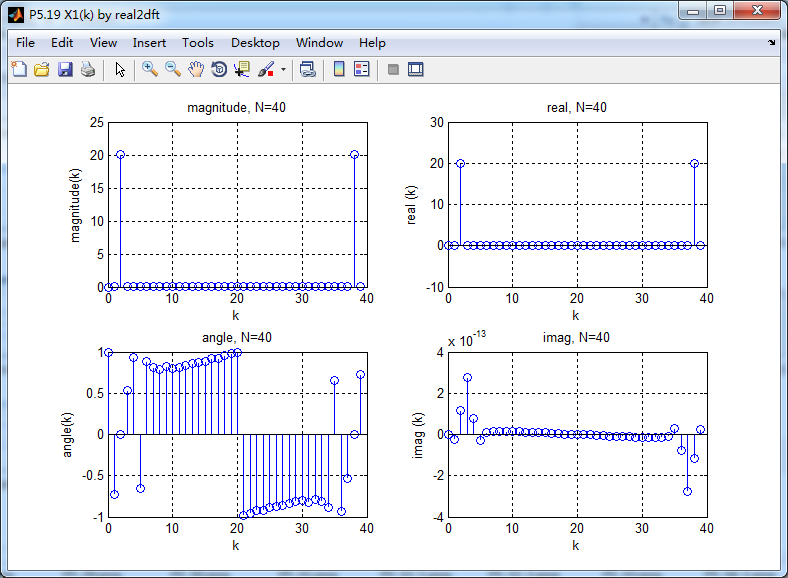
利用函数real2dft计算实部和虚部对应的DFT,Xccs(k)和Xcca(k)

结论:
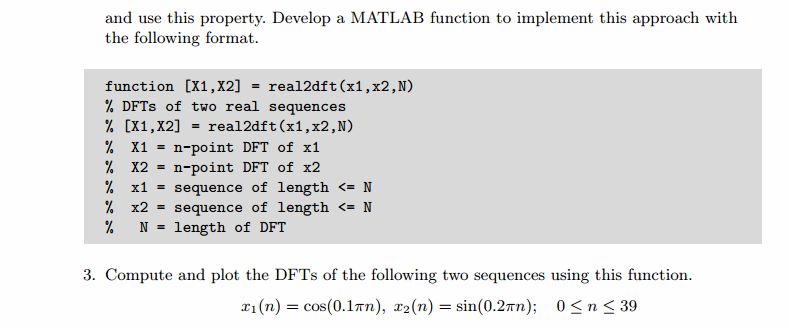
如果X(k)是N点复数序列x(n)的N点DFT,x(n)=xR(n)+jxI(n),那么有
DFT[xR]=Xccs(k) DFT[j*xI]=Xcca(k)
实部序列的DFT是复数序列的DFT的共轭圆周对称分量
虚部序列的DFT是复数序列的DFT的共轭圆周反对称分量。
《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 5.19的更多相关文章
- 《DSP using MATLAB》 Problem 3.19
先求模拟信号经过采样后,对应的数字角频率: 明显看出,第3种采样出现假频了.DTFT是以2π为周期的,所以假频出现在10π-2kπ=0处. 代码: %% ----------------------- ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 2.19
代码: %% ------------------------------------------------------------------------ %% Output Info about ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 8.19
代码: %% ------------------------------------------------------------------------ %% Output Info about ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 7.16
使用一种固定窗函数法设计带通滤波器. 代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 5.18
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% O ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 5.5
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 5.4
代码: %% ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ %% Output In ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 5.3
这段时间爬山去了,山中林密荆棘多,沟谷纵横,体力增强不少. 代码: %% +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ ...
- 《DSP using MATLAB》Problem 4.23
代码: %% ------------------------------------------------------------------------ %% Output Info about ...
随机推荐
- shell 通配符
Bash中的通配符 '?' 匹配一个任意字符 '*' 匹配0个或任意多个字符,也就是可以匹配任何内容 '[]' 匹配括号中任意一个字符.例如[abc]代表一定匹配一个字符,或者是a,或者是b,或者是c ...
- python-第一类对象,闭包,迭代器
# def fn(): # print("我叫fn") # fn() # print(fn) # <function fn at 0x0000000001D12E18> ...
- sqlalchemy(二)简单的连接示例
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import sqlalchemy from sqlalchemy import create_engine from sqlalchemy.ext.d ...
- [Leetcode 739]*还有几天会升温 Daily Temperatures
[题目] Given a list of daily temperatures T, return a list such that, for each day in the input, tells ...
- Android system :灯光系统_HAL_lights
一.android灯光系统框架: Java: frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/lights/LightsService.ja ...
- Java集合(续)
java学习笔记 --- 集合 1.定义:集合是一种容器,专门用来存储对象 数组和集合的区别? A:长度区别 数组的长度固定 集合长度可变 B:内容不同 数组存储的是同一 ...
- shell中环境变量
Linux中环境变量包括系统级和用户级,系统级的环境变量是每个登录到系统的用户都要读取的系统变量,而用户级的环境变量则是该用户使用系统时加载的环境变量. 所以管理环境变量的文件也分为系统级和用户级的, ...
- elasticsearch学习笔记——安装,初步使用
前言 久仰elasticsearch大名,近年来,fackbook,baidu等大型网站的搜索功能均开始采用elasticsearch,足见其在处理大数据和高并发搜索中的卓越性能.不少其他网站也开始将 ...
- FCC JS基础算法题(7):Chunky Monkey(分割数组)
题目描述: 把一个数组arr按照指定的数组大小size分割成若干个数组块. 例如:chunk([1,2,3,4],2)=[[1,2],[3,4]]; chunk([1,2,3,4,5],2)=[[1, ...
- 3--Python入门--Python数据集合类型--元组
在基础数据类型的基础上,Python有6中数据集合的类型: 列表list,最常用的数据类型,以[]为标识 元组tuple,和list很相似,但是不能二次赋值,用()标识 集合set,和list类似,但 ...
