<Scala><For beginners>
Scala Overview
Scala is object-oriented
- Scala is a pure object-oriented language in the sense that every value is an object. Types and behavior of objects are described by classes and traits. Classes are extended by subclassing and a flexible mixin-based composition mechanism as a clean replacement for multiple inheritance.
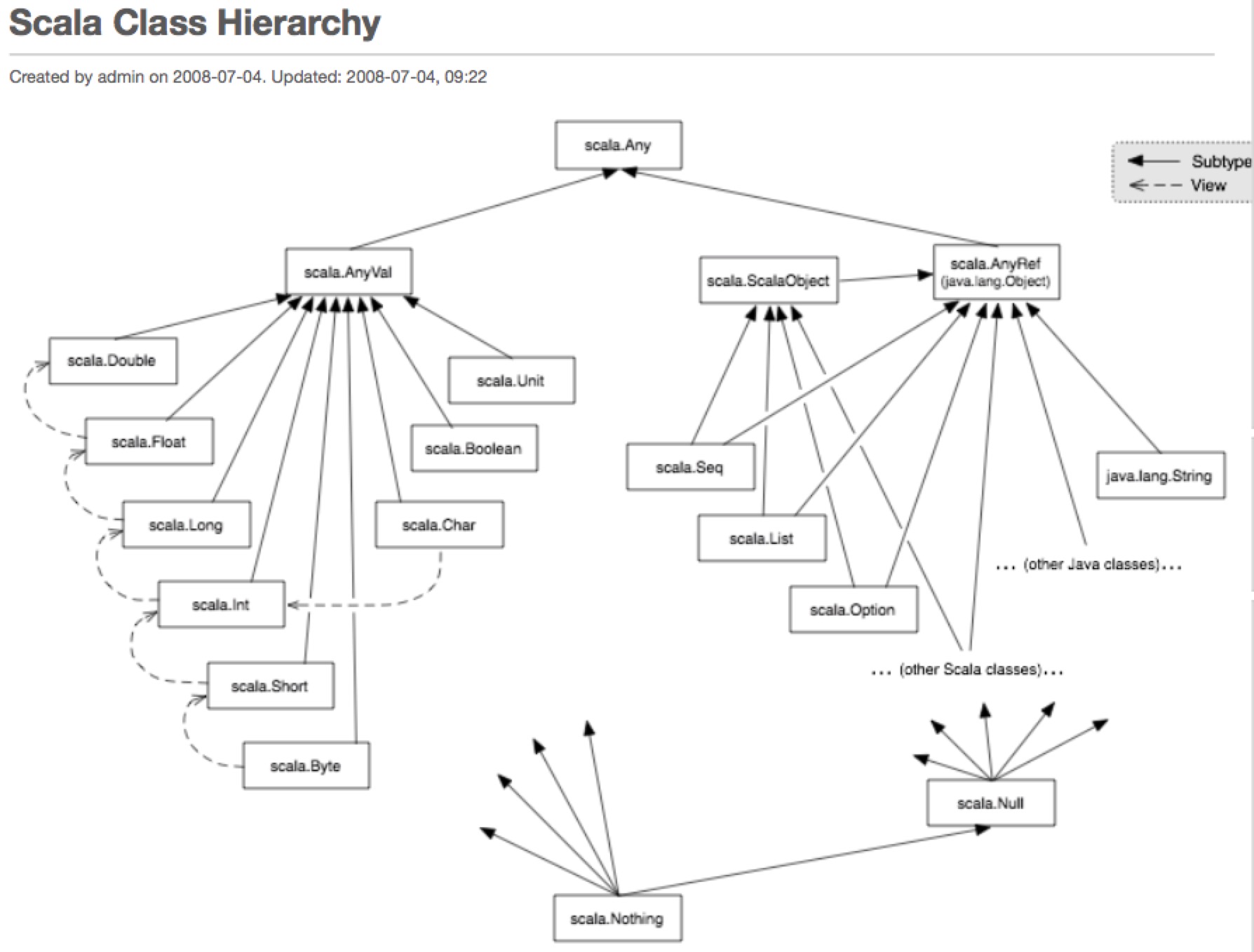
- Every user-defined class in Scala implicitly extends the trait scala.ScalaObject.
- If Scala is used in the context of a Java runtime environment, then scala.AnyRef corresponds to java.lang.Object.
Scala is Functional
- Scala is also a functional language in the sense that every function is a value.
- Scala provides a lightweight syntax for defining anonymous functions, it supports higher-order functions, it allows functions to be nested, and supports currying.
- Scala's case classes and its built-in support for pattern matching model algebraic types used in many functional programming languages.
Anonymous Function Syntax
- eg:
- (x: Int) => x + 1
This is a shorthand for the following anonymous class definition:
- new Function1[Int, Int] {
- def apply(x: Int): Int = x + 1
- }
- (x: Int) => x + 1
It is also possible to define functions with multiple parameters:
- (x: Int, y: Int) => "(" + x + ", " + y + ")"
or even with no parameter:
- () => { System.getProperty("user.dir") }
Higher-Order Functions
- Higher-order functions are those who can take functions as parameters, or whose result is a function.
- Eg: Function apply which takes another function f and a value v and applies function f to v:
def apply(f: Int => String, v: Int) = f(v) - A more complicated example:
- class Decorator(left: String, right: String) {
- def layout[A](x: A) = left + x.toString() + right
- }
- object FunTest extends Application {
- def apply(f: Int => String, v: Int) = f(v)
- val decorator = new Decorator("[", "]")
- println(apply(decorator.layout, 7))
- }
- class Decorator(left: String, right: String) {
In this example, the method decorator.layout is coerced automatically to a value of type Int => String as required by method apply. Please note that the method decorator.layout is a polymorphic method(i.e. it abstracts over some of its signature types) and the Scala compiler has to instantiate its method type first appropriately.
Nested Functions
- In Scala it is possible to nest function definitions.
- Eg:
- object FilterTest extends Application {
- def filter(xs: List[Int], threshold: Int) = {
- def process(ys: List[Int]): List[Int] =
- if (ys.isEmpty) ys
- else if (ys.head < threshold) ys.head :: process(ys.tail)
- else process(ys.tail)
- process(xs)
- }
- println(filter(List(1, 9, 2, 8, 3, 7, 4), 5))
- }
- object FilterTest extends Application {
Currying
- Methods may define multiple parameter lists. When a method is called with a fewer number of parameter lists, then this will yield a function taking the missing parameter lists as its arguments.
- Eg:
- object CurryTest extends Application {
- def filter(xs: List[Int], p: Int => Boolean): List[Int] =
- if (xs.isEmpty) xs
- else if (p(xs.head)) xs.head :: filter(xs.tail, p)
- else filter(xs.tail, p)
- def modN(n: Int)(x: Int) = ((x % n) == 0)
- val nums = List(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8)
- println(filter(nums, modN(2)))
- println(filter(nums, modN(3)))
- }
Note that method modN is partially applied in the two filter calls; i.e. only its first argument is actually applied. The term modN(2) yields a function of type Int => Boolean and is thus a possible candidate for the second argument of function filter.
- object CurryTest extends Application {
Case Classes
- Case classes are regular classes which export their constructor parameters and which provide a recursive decomposition mechanism via pattern matching.
- An example for a class hierarchy which consists of an abstract super class Term and three concrete case classes Var, Fun and App.
- abstract class Term
- case class Var(name: String) extends Term
- case class Fun(arg: String, body: Term) extends Term
- case class App(f: Term, v: Term) extends Term
- abstract class Term
- This class hierarchy can be used to represent terms of the untyped lambda calculus.
- To facilitate the construction of case class instances, Scala does not require that the
newprimitive is used. - The main benefits of case class:
- Dont need new when initialization;
- better toString() method;
- with equals() & hashCode() default;
- with Serializable default;
- The constructor parameters are public(can be access directly);
- Support pattern matching;(It makes only sense to define case classes if pattern matching is used to decompose data stuctures.)
- For better understanding of case class, u should know pattern matching first:
- For javaer, switch is some kind of pm, but it's easy for programmer to forget 'break';
- But in scala: [Scala has a built-in general pattern matching mechanism. It allows to match on any sort of data with a first-match policy. ]
- object PatternMatchingTest extends App {
- for (i <- 1 to 100) {
- i match {
- case 10 => println(10)
- case 50 => println(50)
- case _ =>
- }
- }
- }
- object PatternMatchingTest extends App {
Case class can be seen as a special class that have been optimized for pattern matching
- .
- abstract class Person
- case class Student(name: String, age: Int, studentNo: Int) extends Person
- case class Teacher(name: Stirng, age: Int, teacherNo: Int) extends Person
- case class Nobody(name: String) extends Person
- object CaseClassDemo {
- def main(agrs: Array[String]): Unit = {
- // case class will generate apply method, this can reduce 'new'
- val p: Person = Student("john", 18, 1024)
- // match case
- p match {
- case Student(name, age, studentNo) => println(name + ":" + age + ":" + studentNo)
- case Teacher(name,age,teacherNo)=>println(name+":"+age+":"+teacherNo)
- case Nobody(name)=>println(name)
- }
- }
- }
当一个类被声明为case class时,scala会帮我们做以下几件事情:
- 自动创建伴生对象,同时在其内实现子apply方法,因为在使用时不用显式new;
- 伴生对象内同时实现了upapply(),从而可以将case class用于模式匹配,具体之后在extractor会介绍;
- 实现toString(), hashCode(), copy(), equals()
Extractor Objects
- In scala, patterns can be defined independently of case classess. To this end, a method named unapply is defined to yield a so-called extractor.
For instance, the following code defines an extractor object `Twice`.
- object Twice {
- def apply(x: Int): Int = x * 2
- def unapply(z: Int): Option[Int] = if (z % 2) == 0 Some(z / 2) else None
- }
- object TwiceTest extends Application {
- val x = Twice(21)
- x match { case Twice(n) => Console.println(n) }
- }
There are two syntactic conventions at work here:
- The pattern case Twice(n) will cause an invocation of Twice.unapply, which is used to match even number; the return value of the unapply signals whether the argument has matched or not, and any sub-values that can be used for further matching. Here, the sub-value is z/2.
- The apply method is not necessary for pattern matching. It is only used to mimick a constructor. val x = Twice(21) expands to val x = Twice.apply(21).
- The return type of an unapply should be chosen as follows:
- If it is just a test, return a Boolean.
- If it returns a single sub-value of type T, return a Option[T].
- If u want to return several sub-values T1, ..., Tn, group them in an optional tuple Option[(T1, ..., Tn)].
- Extractor: 提取器是从传递给它的对象中提取出构造该对象的参数。Scala提取器是一个带有unapply方法的对象。unapply方法算是apply方法的反向操作:unapply方法接受一个对象,然后从对象中提取值,提取的值通常是用来构造该对象的值。
Scala is statically typed
- Scala is equipped with an expressive type system that enforces statically that abstractions are used in a safe and coherent manner.
- In particular, the type system supports:
- generic classes
- variance annotations
- upper and lower type bounds
- inner classes and abstract types as object members
- compound types
- explicitly typed self references
- vies
- polymorphic methods
Generic classes
- Scala has built-in support for classes parameterized with types. Such generic classes are particularly useful for the development of collection classes.
- Eg:
- class Stack[T] {
- var elems: List[T] = Nil
- def push(x: T) { elems = x :: elems }
- def top: T = elems.head
- def pop() { elems = elems.tail }
- }
The use of type parameters allows to check that only legal elements(that of type T) are pushed onto the stack.
- class Stack[T] {
- Note that subtyping of generic types is invariant. This means that if we have a stack of characters of type Stack[Char] then it cannot be used as an integer stack of type Stack[Int].
Variances
- Scala supports variance annotations of type parameters of generic classes.
<Scala><For beginners>的更多相关文章
- 简单物联网:外网访问内网路由器下树莓派Flask服务器
最近做一个小东西,大概过程就是想在教室,宿舍控制实验室的一些设备. 已经在树莓上搭了一个轻量的flask服务器,在实验室的路由器下,任何设备都是可以访问的:但是有一些限制条件,比如我想在宿舍控制我种花 ...
- 利用ssh反向代理以及autossh实现从外网连接内网服务器
前言 最近遇到这样一个问题,我在实验室架设了一台服务器,给师弟或者小伙伴练习Linux用,然后平时在实验室这边直接连接是没有问题的,都是内网嘛.但是回到宿舍问题出来了,使用校园网的童鞋还是能连接上,使 ...
- 外网访问内网Docker容器
外网访问内网Docker容器 本地安装了Docker容器,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地Docker容器? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装并启动Docker容器 ...
- 外网访问内网SpringBoot
外网访问内网SpringBoot 本地安装了SpringBoot,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地SpringBoot? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装Java 1 ...
- 外网访问内网Elasticsearch WEB
外网访问内网Elasticsearch WEB 本地安装了Elasticsearch,只能在局域网内访问其WEB,怎样从外网也能访问本地Elasticsearch? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. ...
- 怎样从外网访问内网Rails
外网访问内网Rails 本地安装了Rails,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地Rails? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装并启动Rails 默认安装的Rails端口 ...
- 怎样从外网访问内网Memcached数据库
外网访问内网Memcached数据库 本地安装了Memcached数据库,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地Memcached数据库? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装 ...
- 怎样从外网访问内网CouchDB数据库
外网访问内网CouchDB数据库 本地安装了CouchDB数据库,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地CouchDB数据库? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装并启动Cou ...
- 怎样从外网访问内网DB2数据库
外网访问内网DB2数据库 本地安装了DB2数据库,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地DB2数据库? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装并启动DB2数据库 默认安装的DB2 ...
- 怎样从外网访问内网OpenLDAP数据库
外网访问内网OpenLDAP数据库 本地安装了OpenLDAP数据库,只能在局域网内访问,怎样从外网也能访问本地OpenLDAP数据库? 本文将介绍具体的实现步骤. 1. 准备工作 1.1 安装并启动 ...
随机推荐
- canvas学习之树叶动画
项目地址:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1geJgqen 今天用canvas做了一个树叶发芽到凋落的动画,当然还有很多不完善的地方,不过也让我体会到了,做动画技术占2分,算法占8分.这 ...
- drf 生成接口文档
REST framework可以自动帮助我们生成接口文档.接口文档以网页的方式呈现. 自动接口文档能生成的是继承自APIView及其子类的视图. 一.安装依赖 REST framewrok生成接口文档 ...
- Linux中安装Mysql授权远程访问
一.直接授权 mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'root'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'youpassword' WITH GRANT OP ...
- 廖雪峰网站:学习python函数—函数参数(三)
1.*args # 位置参数,计算x2的函数 def power(x): return x * x p = power(5) print(p) # 把power(x)修改为power(x, n),用来 ...
- php 中输入输出提交
</head> <body> 输出的两个位置 <? echo $_POST['sub']; ?> <form action="" meth ...
- Git Diff 格式分析
参考: http://stackoverflow.com/questions/2529441/how-to-read-the-output-from-git-diff https://www.git- ...
- MySQL5.6复制技术(4)-MySQL主从复制过滤参数
复制的过滤主要有2种方式: 在主服务器在把事件从进二制日志中过滤掉,相关的参数是:binlog_do_db和binlog_ignore_db. 在从服务器上把事件从中继日志中过滤掉,相关的参数是re ...
- spring cloud服务发现注解之@EnableDiscoveryClient与@EnableEurekaClient
使用服务发现的时候提到了两种注解,一种为@EnableDiscoveryClient,一种为@EnableEurekaClient,用法上基本一致,今天就来讲下两者,下文是从stackoverflow ...
- ActiveMQ 事务和XA
1. 客户端怎样显式地使用事务? producer 开启事务(代码片段): ActiveMQSession session = (ActiveMQSession)connection.createSe ...
- VSS+SourceAnywhere for VSS搭建版本控制系统教程
VSS:Microsoft Visual Source Safe,本教程使用VSS2005(好像2005就是官方更新的最后一版了). SourceAnywhere for VSS:分为服务端和客户端: ...
