3 爬虫解析 Xpath 和 BeautifulSoup
1.正则表达式
单字符:
. : 除换行以外所有字符
[] :[aoe] [a-w] 匹配集合中任意一个字符
\d :数字 [-]
\D : 非数字
\w :数字、字母、下划线、中文
\W : 非\w
\s :所有的空白字符包,括空格、制表符、换页符等等。等价于 [ \f\n\r\t\v]。
\S : 非空白
数量修饰:
* : 任意多次 >=
+ : 至少1次 >=
? : 可有可无 0次或者1次
{m} :固定m次 hello{,}
{m,} :至少m次
{m,n} :m-n次
边界:
$ : 以某某结尾
^ : 以某某开头
分组:
(ab)
贪婪模式: .*
非贪婪(惰性)模式: .*? re.I : 忽略大小写
re.M :多行匹配
re.S :单行匹配 re.sub(正则表达式, 替换内容, 字符串)
2.Xpath解析
测试页面:
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>测试bs4</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<p>百里守约</p>
</div>
<div class="song">
<p>李清照</p>
<p>王安石</p>
<p>苏轼</p>
<p>柳宗元</p>
<a href="http://www.song.com/" title="赵匡胤" target="_self">
<span>this is span</span>
宋朝是最强大的王朝,不是军队的强大,而是经济很强大,国民都很有钱</a>
<a href="" class="du">总为浮云能蔽日,长安不见使人愁</a>
<img src="http://www.baidu.com/meinv.jpg" alt="" />
</div>
<div class="tang">
<ul>
<li><a href="http://www.baidu.com" title="qing">清明时节雨纷纷,路上行人欲断魂,借问酒家何处有,牧童遥指杏花村</a></li>
<li><a href="http://www.163.com" title="qin">秦时明月汉时关,万里长征人未还,但使龙城飞将在,不教胡马度阴山</a></li>
<li><a href="http://www.126.com" alt="qi">岐王宅里寻常见,崔九堂前几度闻,正是江南好风景,落花时节又逢君</a></li>
<li><a href="http://www.sina.com" class="du">杜甫</a></li>
<li><a href="http://www.dudu.com" class="du">杜牧</a></li>
<li><b>杜小月</b></li>
<li><i>度蜜月</i></li>
<li><a href="http://www.haha.com" id="feng">凤凰台上凤凰游,凤去台空江自流,吴宫花草埋幽径,晋代衣冠成古丘</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
</html>
xpath 的使用:
1.下载:pip install lxml
2.导包:from lxml import etree 3.将html文档或者xml文档转换成一个etree对象,然后调用对象中的方法查找指定的节点 2.1 本地文件:tree = etree.parse(文件名)
tree.xpath("xpath表达式") 2.2 网络数据:tree = etree.HTML(网页内容字符串)
tree.xpath("xpath表达式")
xpath 表达式:
'''
属性定位:
#找到class属性值为song的div标签
//div[@class="song"]
层级&索引定位:
#找到class属性值为tang的div的直系子标签ul下的第二个子标签li下的直系子标签a
//div[@class="tang"]/ul/li[2]/a
逻辑运算:
#找到href属性值为空且class属性值为du的a标签
//a[@href="" and @class="du"]
模糊匹配:
//div[contains(@class, "ng")]
//div[starts-with(@class, "ta")]
取文本:
# /表示获取某个标签下的文本内容
# //表示获取某个标签下的文本内容和所有子标签下的文本内容
//div[@class="song"]/p[1]/text()
//div[@class="tang"]//text()
取属性:
//div[@class="tang"]//li[2]/a/@href
'''
#从本地文件中获取
etree1 = etree.parse("xpath.html")
#网页字符串
etree2=etree.HTML(doc) # 1 属性定位 @ # //表示文档 / 表示下一层
# res1 =etree1.xpath('//a[@id="feng"]/text()')
#['凤凰台上凤凰游,凤去台空江自流,吴宫花草埋幽径,晋代衣冠成古丘']
# res2 =etree2.xpath('//a[@id="feng"]/text()')
#['凤凰台上凤凰游,凤去台空江自流,吴宫花草埋幽径,晋代衣冠成古丘']
# res = etree1.xpath('//div[@class="tang"]/ul/li/b/text()') #['杜小月']
# res = etree1.xpath('//a[@title="赵匡胤"]/@href') #['http://www.song.com/'] #2 层级定位和索引
# res = etree1.xpath('//div[@class="tang"]/ul/li[2]/a/@href') #3模糊匹配
# res = etree1.xpath('//a[starts-with(@title,"qin")]/@href')
# res = etree1.xpath('//a[contains(@title,"qin")]/@href') #4 逻辑运算:
# res = etree1.xpath('//a[@href="" and @class="du"]/text()') # print(res)
3.Beautiful Soup
Beautiful Soup 是一个可以从HTML或XML文件中提取数据的Python库。
提供一些简单的、python式的函数用来处理导航、搜索、修改分析树等功能。
安装:
pip3 install beautifulsoup4
解析器
Beautiful Soup支持Python标准库中的HTML解析器,还支持一些第三方的解析器,
如果我们不安装它,则 Python 会使用 Python默认的解析器,lxml 解析器更加强大,速度更快,推荐安装。
pip3 install lxml
html5lib 纯Python实现的 , html5lib的解析方式与浏览器相同
pip install html5lib
解析器对比:
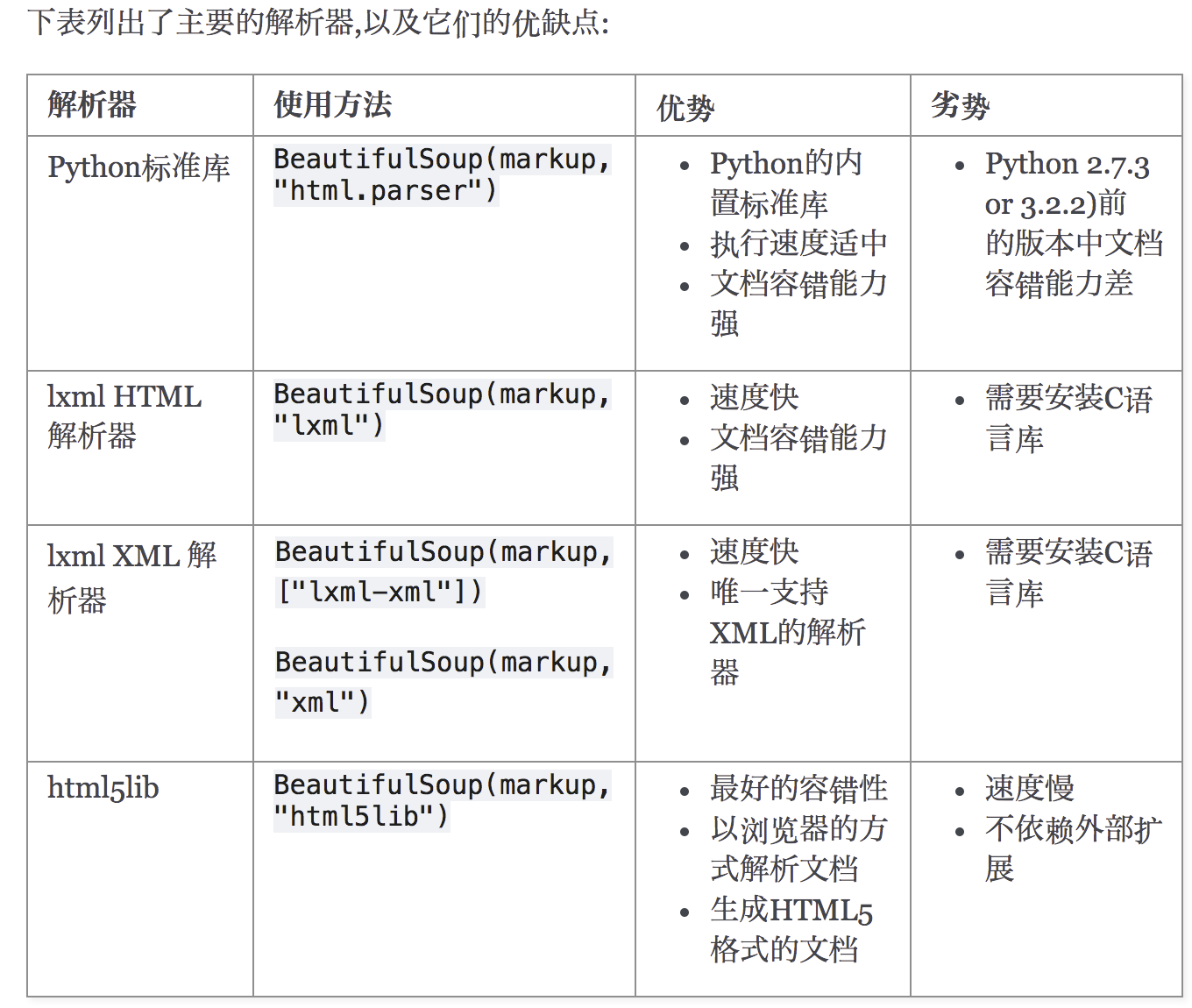
beautifulsoup语法:
1.使用流程
- 导包:from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
- 使用方式:可以将一个html文档,转化为BeautifulSoup对象,然后通过对象的方法或者属性去查找指定的节点内容
(1)转化本地文件:
- soup = BeautifulSoup(open('本地文件'), 'lxml')
(2)转化网络文件:
- soup = BeautifulSoup('字符串类型或者字节类型', 'lxml')
(3)打印soup对象显示内容为html文件中的内容
2.用法
(1)根据标签名查找
- soup.a 只能找到第一个符合要求的标签 (找到第一个a标签)
(2)获取属性
- soup.a.attrs 获取a所有的属性和属性值,返回一个字典
- soup.a.attrs['href'] 获取href属性
- soup.a['href'] 也可简写为这种形式
(3)获取内容
- soup.a.string (标签套标签并列标签情况文本内容获取获取不到,一个的话可以获取到)
- soup.a.text (可以获取到标签套标签并列的标签中的文档,可以拿到并拼接一起)
- soup.a.get_text() (和.text 相同)
【注意】如果标签还有标签,那么string获取到的结果为None,而其它两个,可以获取文本内容
(4)find:找到第一个符合要求的标签(可以带其他参数)
- soup.find('a') 找到第一个符合要求的
- soup.find('a', title="xxx")
- soup.find('a', alt="xxx")
- soup.find('a', class_="xxx")
- soup.find('a', id="xxx")
(5)find_all:找到所有符合要求的标签
- soup.find_all('a')
- soup.find_all(['a','b']) 找到所有的a和b标签
- soup.find_all('a', limit=2) 限制前两个
(6)根据选择器选择指定的内容
select:soup.select('#feng')
- 常见的选择器:标签选择器(a)、类选择器(.)、id选择器(#)、层级选择器
- 层级选择器:
div .dudu #lala .meme .xixi 下面好多级
div > p > a > .lala 只能是下面一级
【注意】select选择器返回永远是列表,需要通过下标提取指定的对象
重点方法:
1.find_all()
#搜索文档树:BeautifulSoup定义了很多搜索方法,这里着重介绍2个: find() 和 find_all() .其它方法的参数和用法类似
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p id="my p" class="title"><b id="bbb" class="boldest">The Dormouse's story</b>
</p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> <p class="story">...</p>
""" from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup=BeautifulSoup(html_doc,'lxml') #1、name的五种过滤器: 字符串、正则表达式、列表、True、方法
#1.1、字符串:即标签名
print(soup.find_all('b')) #1.2、正则表达式
import re
print(soup.find_all(re.compile('^b'))) #找出b开头的标签,结果有body和b标签 #1.3、列表:如果传入列表参数,Beautiful Soup会将与列表中任一元素匹配的内容返回.下面代码找到文档中所有<a>标签和<b>标签:
print(soup.find_all(['a','b'])) #1.4、True:可以匹配任何值,下面代码查找到所有的tag,但是不会返回字符串节点
print(soup.find_all(True))
for tag in soup.find_all(True):
print(tag.name) #1.5、方法:如果没有合适过滤器,那么还可以定义一个方法,方法只接受一个元素参数 ,如果这个方法返回 True 表示当前元素匹配并且被找到,如果不是则反回 False
def has_class_but_no_id(tag):
return tag.has_attr('class') and not tag.has_attr('id')
print(soup.find_all(has_class_but_no_id)) #2、按照类名查找,注意关键字是class_,class_=value,value可以是五种选择器之一
print(soup.find_all('a',class_='sister')) #查找类为sister的a标签
print(soup.find_all('a',class_='sister ssss')) #查找类为sister和sss的a标签,顺序错误也匹配不成功
print(soup.find_all(class_=re.compile('^sis'))) #查找类为sister的所有标签 #3、attrs
print(soup.find_all('p',attrs={'class':'story'})) #4、text: 值可以是:字符,列表,True,正则
print(soup.find_all(text='Elsie'))
print(soup.find_all('a',text='Elsie')) #5、limit参数:如果文档树很大那么搜索会很慢.如果我们不需要全部结果,可以使用 limit 参数限制返回结果的数量.效果与SQL中的limit关键字类似,当搜索到的结果数量达到 limit 的限制时,就停止搜索返回结果
print(soup.find_all('a',limit=2)) #6、recursive:调用tag的 find_all() 方法时,Beautiful Soup会检索当前tag的所有子孙节点,如果只想搜索tag的直接子节点,可以使用参数 recursive=False .
print(soup.html.find_all('a'))
print(soup.html.find_all('a',recursive=False)) '''
像调用 find_all() 一样调用tag
find_all() 几乎是Beautiful Soup中最常用的搜索方法,所以我们定义了它的简写方法. BeautifulSoup 对象和 tag 对象可以被当作一个方法来使用,
这个方法的执行结果与调用这个对象的 find_all() 方法相同,下面两行代码是等价的: soup.find_all("a")
soup("a") 这两行代码也是等价的: soup.title.find_all(text=True)
soup.title(text=True) '''
2、find( name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs )
find_all() 方法将返回文档中符合条件的所有tag,尽管有时候我们只想得到一个结果.比如文档中只有一个<body>标签,那么使用 find_all() 方法来查找<body>标签就不太合适, 使用 find_all 方法并设置 limit=1 参数不如直接使用 find() 方法.下面两行代码是等价的:
soup.find_all('title', limit=1)
# [<title>The Dormouse's story</title>]
soup.find('title')
# <title>The Dormouse's story</title>
唯一的区别是 find_all() 方法的返回结果是值包含一个元素的列表,而 find() 方法直接返回结果.
find_all() 方法没有找到目标是返回空列表, find() 方法找不到目标时,返回 None .
print(soup.find("nosuchtag"))
# None
soup.head.title 是 tag的名字方法的简写.这个简写的原理就是多次调用当前tag的 find() 方法:
soup.head.title
# <title>The Dormouse's story</title>
soup.find("head").find("title")
# <title>The Dormouse's story</title>
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import re
html_doc ="""
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body> <p id="my p" class="title"><b id="bbb" class="boldest">The Dormouse's story</b><span>123</span></p>
<p class="story" name="deng">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> <p class="story">...</p>
"""
doc2="""
<div class="c1">
<p>123</p>
<p>345</p>
<div> </div>
</div>
"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc,"lxml")
# 1.拿到第一个a标签对象
res =soup.a
# print(res) # 第一个a标签对象 #2.获取标签对象属性:
# print(soup.a.attrs) # 拿到第一个a标签对象的所有属性
# print(soup.a.attrs["id"]) #
# print(soup.a.attrs.get("id"))
# print(soup.a["id"]) # 简写 #3.文本操作
# print(soup.a.text) #Elsie
# print(soup.a.get_text()) #Elsie
# print(soup.a.string)
# print(soup.p.text) #The Dormouse's story123
# print(soup.p.string) # None #4. find_all()
#name参数:四种name过滤器
# print(soup.find_all("a")) # 找所有a标签
# print(soup.find_all(["a","b"])) # 找所有a标签和b标签
# print(soup.find_all(re.compile("^b"))) # 找到所有 以 b开头的标签
#参数为函数名 # def has_class_but_no_id(tag):
# return tag.has_attr('class') and not tag.has_attr('id')
# print(soup.find_all(has_class_but_no_id)) # name=has_class_but_no_id # 1.属性参数:
# print(soup.find_all(attrs={"class":"sister"}))
# 简写
# print(soup.find_all('a',id="link2")) #
# print(soup.find_all("a",class_="sister")) #2 文本参数
# print(soup.find_all("a",text="Tillie")) #3.limit参数
# print(soup.find_all("a",limit=2)) # 找到所有a标签取前2条
#4 recursive参数
# print(soup.find_all(recursive=True)) # 深度查询
# print(soup.find_all(recursive=False)) # 局部查 #5.find 等同于 soup.a # print(soup.find("a")) # 等同于 soup.a
# find参数和find_all完全一样 ############select######## # 这个selector等同于css选择器
# print(soup.select(".sister"))
# print(soup.select("#link1"))
# print(soup.select("[name='deng']"))
# for i in soup.select("body a"):
# print(i["id"])
例子
3 爬虫解析 Xpath 和 BeautifulSoup的更多相关文章
- 爬虫 解析库re,Beautifulsoup,
re模块 点我回顾 Beautifulsoup模块 #安装 Beautiful Soup pip install beautifulsoup4 #安装解析器 Beautiful Soup支持Pytho ...
- python爬虫解析库之Beautifulsoup模块
一 介绍 Beautiful Soup 是一个可以从HTML或XML文件中提取数据的Python库.它能够通过你喜欢的转换器实现惯用的文档导航,查找,修改文档的方式.Beautiful Soup会 ...
- 【爬虫入门手记03】爬虫解析利器beautifulSoup模块的基本应用
[爬虫入门手记03]爬虫解析利器beautifulSoup模块的基本应用 1.引言 网络爬虫最终的目的就是过滤选取网络信息,因此最重要的就是解析器了,其性能的优劣直接决定这网络爬虫的速度和效率.Bea ...
- 【网络爬虫入门03】爬虫解析利器beautifulSoup模块的基本应用
[网络爬虫入门03]爬虫解析利器beautifulSoup模块的基本应用 1.引言 网络爬虫最终的目的就是过滤选取网络信息,因此最重要的就是解析器了,其性能的优劣直接决定这网络爬虫的速度和效率.B ...
- python网络爬虫之解析网页的BeautifulSoup(爬取电影图片)[三]
目录 前言 一.BeautifulSoup的基本语法 二.爬取网页图片 扩展学习 后记 前言 本章同样是解析一个网页的结构信息 在上章内容中(python网络爬虫之解析网页的正则表达式(爬取4k动漫图 ...
- Xpath re bs4 等爬虫解析器的性能比较
xpath re bs4 等爬虫解析器的性能比较 本文原始地址:https://sitoi.cn/posts/23470.html 思路 测试网站地址:http://baijiahao.baidu.c ...
- 第三百三十六节,web爬虫讲解2—urllib库中使用xpath表达式—BeautifulSoup基础
第三百三十六节,web爬虫讲解2—urllib库中使用xpath表达式—BeautifulSoup基础 在urllib中,我们一样可以使用xpath表达式进行信息提取,此时,你需要首先安装lxml模块 ...
- 爬虫解析之css,xpath语法
一.xpath语法 xpath实例文档 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?> <bookst ...
- python爬虫:XPath语法和使用示例
python爬虫:XPath语法和使用示例 XPath(XML Path Language)是一门在XML文档中查找信息的语言,可以用来在XML文档中对元素和属性进行遍历. 选取节点 XPath使用路 ...
随机推荐
- CentOS 安装 MongoDB
一.安装mongodb 本文介绍的安装方式是以二进制方式离线安装,相当于windows"绿色"安装版本的概念. 下载mongodb: # https://www.mongodb.c ...
- NodeJs 在window中安装使用
Nodejs: 官网下载长期版本zip格式解压 D:\Program Files\nodejs 查看版本 D:\Git\SpringBootDemo (master) $ node -v v8.11. ...
- fhqtreap初探
介绍 fhqtreap为利用分裂和合并来满足平衡树的性质,不需要旋转操作的一种平衡树. 并且利用函数式编程可以极大的简化代码量. (题目是抄唐神的来着) 核心操作 (均为按位置分裂合并) struct ...
- 题解——Codeforces Round #507 (based on Olympiad of Metropolises) T2(模拟)
T2还是模拟 枚举一下第一个放哪里 然后贪心的反转即可 虽然我也不会证,但是这题肯定有解qwq #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> # ...
- 【C#】神奇的yeild
直接出栗子: class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { foreach (var item in FilterWithoutYield) { ...
- Latex: 解决 The gutter between columns is x inches wide (on page x), but should be at least 0.2 inches. 问题
参考: Sample_WCCI.tex Latex: 解决 The gutter between columns is x inches wide (on page x), but should be ...
- python爬虫训练——正则表达式+BeautifulSoup爬图片
这次练习爬 传送门 这贴吧里的美食图片. 如果通过img标签和class属性的话,用BeautifulSoup能很简单的解决,但是这次用一下正则表达式,我这也是参考了该博主的博文:传送门 所有图片的s ...
- Android之使用传感器获取相应数据
Android的大部分手机中都有传感器,传感器类型有方向.加速度(重力).光线.磁场.距离(临近性).温度等. 方向传感器: Sensor.TYPE_ORIENTATION 加速度(重力)传感器: ...
- WinForm 拖动、移动窗体
private const int WM_NCLBUTTONDOWN = 0XA1; private const int HTCAPTION = 2; [System.Runtime.InteropS ...
- hdu 6134 Battlestation Operational 莫比乌斯反演
Battlestation Operational Time Limit: 6000/3000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Jav ...
