More 3D Graphics (rgl) for Classification with Local Logistic Regression and Kernel Density Estimates (from The Elements of Statistical Learning)(转)
This post builds on a previous post, but can be read and understood independently.
As part of my course on statistical learning, we created 3D graphics to foster a more intuitive understanding of the various methods that are used to relax the assumption of linearity (in the predictors) in regression and classification methods.
The authors of our text (The Elements of Statistical Learning, 2nd Edition) provide a Mixture Simulation data set that has two continuous predictors and a binary outcome. This data is used to demonstrate classification procedures by plotting classification boundaries in the two predictors, which are determined by one or more surfaces (e.g., a probability surface such as that produced by logistic regression, or multiple intersecting surfaces as in linear discriminant analysis). In our class laboratory, we used the R package rgl to create a 3D representation of these surfaces for a variety of semiparametric classification procedures.
Chapter 6 presents local logistic regression and kernel density classification, among other kernel (local) classification and regression methods. Below is the code and graphic (a 2D projection) associated with the local linear logistic regression in these data:
- library(rgl)
- load(url("http://statweb.stanford.edu/~tibs/ElemStatLearn/datasets/ESL.mixture.rda"))
- dat <- ESL.mixture
- ddat <- data.frame(y=dat$y, x1=dat$x[,1], x2=dat$x[,2])
- ## create 3D graphic, rotate to view 2D x1/x2 projection
- par3d(FOV=1,userMatrix=diag(4))
- plot3d(dat$xnew[,1], dat$xnew[,2], dat$prob, type="n",
- xlab="x1", ylab="x2", zlab="",
- axes=FALSE, box=TRUE, aspect=1)
- ## plot points and bounding box
- x1r <- range(dat$px1)
- x2r <- range(dat$px2)
- pts <- plot3d(dat$x[,1], dat$x[,2], 1,
- type="p", radius=0.5, add=TRUE,
- col=ifelse(dat$y, "orange", "blue"))
- lns <- lines3d(x1r[c(1,2,2,1,1)], x2r[c(1,1,2,2,1)], 1)
- ## draw Bayes (True) classification boundary in blue
- dat$probm <- with(dat, matrix(prob, length(px1), length(px2)))
- dat$cls <- with(dat, contourLines(px1, px2, probm, levels=0.5))
- pls0 <- lapply(dat$cls, function(p) lines3d(p$x, p$y, z=1, color="blue"))
- ## compute probabilities plot classification boundary
- ## associated with local linear logistic regression
- probs.loc <-
- apply(dat$xnew, 1, function(x0) {
- ## smoothing parameter
- l <- 1/2
- ## compute (Gaussian) kernel weights
- d <- colSums((rbind(ddat$x1, ddat$x2) - x0)^2)
- k <- exp(-d/2/l^2)
- ## local fit at x0
- fit <- suppressWarnings(glm(y ~ x1 + x2, data=ddat, weights=k,
- family=binomial(link="logit")))
- ## predict at x0
- as.numeric(predict(fit, type="response", newdata=as.data.frame(t(x0))))
- })
- dat$probm.loc <- with(dat, matrix(probs.loc, length(px1), length(px2)))
- dat$cls.loc <- with(dat, contourLines(px1, px2, probm.loc, levels=0.5))
- pls <- lapply(dat$cls.loc, function(p) lines3d(p$x, p$y, z=1))
- ## plot probability surface and decision plane
- sfc <- surface3d(dat$px1, dat$px2, probs.loc, alpha=1.0,
- color="gray", specular="gray")
- qds <- quads3d(x1r[c(1,2,2,1)], x2r[c(1,1,2,2)], 0.5, alpha=0.4,
- color="gray", lit=FALSE)
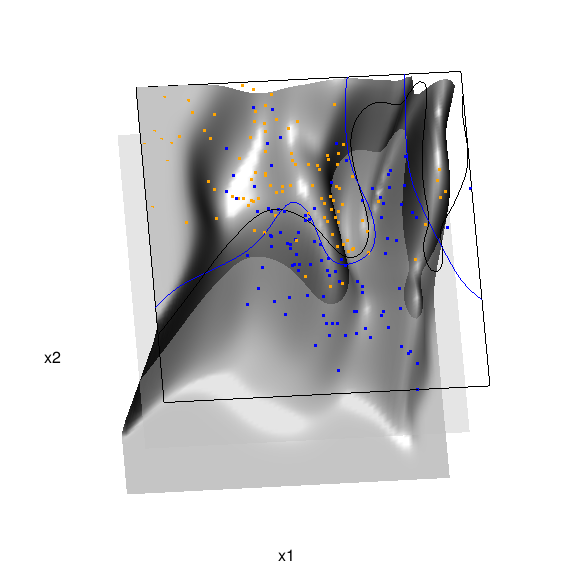
In the above graphic, the solid blue line represents the true Bayes decision boundary (i.e., {x: Pr("orange"|x) = 0.5}), which is computed from the model used to simulate these data. The probability surface (generated by the local logistic regression) is represented in gray, and the corresponding Bayes decision boundary occurs where the plane f(x) = 0.5 (in light gray) intersects with the probability surface. The solid black line is a projection of this intersection. Here is a link to the interactive version of this graphic: local logistic regression.
Below is the code and graphic associated with the kernel density classification (note: this code below should only be executed after the above code, since the 3D graphic is modified, rather than created anew):
- ## clear the surface, decision plane, and decision boundary
- pop3d(id=sfc); pop3d(id=qds)
- for(pl in pls) pop3d(id=pl)
- ## kernel density classification
- ## compute kernel density estimates for each class
- dens.kde <-
- lapply(unique(ddat$y), function(uy) {
- apply(dat$xnew, 1, function(x0) {
- ## subset to current class
- dsub <- subset(ddat, y==uy)
- ## smoothing parameter
- l <- 1/2
- ## kernel density estimate at x0
- mean(dnorm(dsub$x1-x0[1], 0, l)*dnorm(dsub$x2-x0[2], 0, l))
- })
- })
- ## compute prior for each class (sample proportion)
- prir.kde <- table(ddat$y)/length(dat$y)
- ## compute posterior probability Pr(y=1|x)
- probs.kde <- prir.kde[2]*dens.kde[[2]]/
- (prir.kde[1]*dens.kde[[1]]+prir.kde[2]*dens.kde[[2]])
- ## plot classification boundary associated
- ## with kernel density classification
- dat$probm.kde <- with(dat, matrix(probs.kde, length(px1), length(px2)))
- dat$cls.kde <- with(dat, contourLines(px1, px2, probm.kde, levels=0.5))
- pls <- lapply(dat$cls.kde, function(p) lines3d(p$x, p$y, z=1))
- ## plot probability surface and decision plane
- sfc <- surface3d(dat$px1, dat$px2, probs.kde, alpha=1.0,
- color="gray", specular="gray")
- qds <- quads3d(x1r[c(1,2,2,1)], x2r[c(1,1,2,2)], 0.5, alpha=0.4,
- color="gray", lit=FALSE)
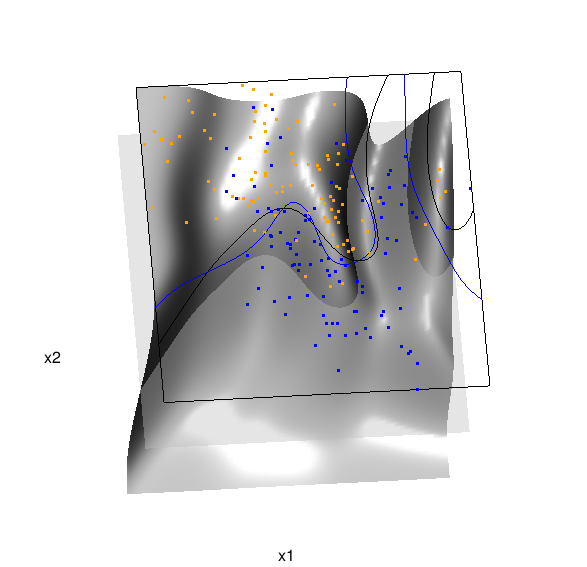
Here are links to the interactive versions of both graphics: local logistic regression, kernel density classification
This entry was posted in Technical and tagged data, graphics, programming, R, statistics on February 7, 2015.
More 3D Graphics (rgl) for Classification with Local Logistic Regression and Kernel Density Estimates (from The Elements of Statistical Learning)(转)的更多相关文章
- Some 3D Graphics (rgl) for Classification with Splines and Logistic Regression (from The Elements of Statistical Learning)(转)
This semester I'm teaching from Hastie, Tibshirani, and Friedman's book, The Elements of Statistical ...
- 李宏毅机器学习笔记3:Classification、Logistic Regression
李宏毅老师的机器学习课程和吴恩达老师的机器学习课程都是都是ML和DL非常好的入门资料,在YouTube.网易云课堂.B站都能观看到相应的课程视频,接下来这一系列的博客我都将记录老师上课的笔记以及自己对 ...
- Logistic Regression Using Gradient Descent -- Binary Classification 代码实现
1. 原理 Cost function Theta 2. Python # -*- coding:utf8 -*- import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplo ...
- Classification week2: logistic regression classifier 笔记
华盛顿大学 machine learning: Classification 笔记. linear classifier 线性分类器 多项式: Logistic regression & 概率 ...
- Classification and logistic regression
logistic 回归 1.问题: 在上面讨论回归问题时.讨论的结果都是连续类型.但假设要求做分类呢?即讨论结果为离散型的值. 2.解答: 假设: 当中: g(z)的图形例如以下: 由此可知:当hθ( ...
- Android Programming 3D Graphics with OpenGL ES (Including Nehe's Port)
https://www3.ntu.edu.sg/home/ehchua/programming/android/Android_3D.html
- Logistic Regression and Classification
分类(Classification)与回归都属于监督学习,两者的唯一区别在于,前者要预测的输出变量\(y\)只能取离散值,而后者的输出变量是连续的.这些离散的输出变量在分类问题中通常称之为标签(Lab ...
- Logistic Regression求解classification问题
classification问题和regression问题类似,区别在于y值是一个离散值,例如binary classification,y值只取0或1. 方法来自Andrew Ng的Machine ...
- 分类和逻辑回归(Classification and logistic regression)
分类问题和线性回归问题问题很像,只是在分类问题中,我们预测的y值包含在一个小的离散数据集里.首先,认识一下二元分类(binary classification),在二元分类中,y的取值只能是0和1.例 ...
随机推荐
- 最新windows 0day漏洞利用
利用视屏:https://v.qq.com/iframe/player.html?vid=g0393qtgvj0&tiny=0&auto=0 使用方法 环境搭建 注意,必须安装32位p ...
- 【理论篇】Percona XtraBackup 恢复单表
小明在某次操作中,误操作导致误删除了某个表,需要立即进行数据恢复. 如果是数据量较小的实例,并且有备份,即便是全备,做一次全量恢复,然后单表导出导入,虽然麻烦一点,却也花不了多少时间:如果是数据量大的 ...
- IT职场经纬 |阿里web前端面试考题,你能答出来几个?
有很多小伙伴们特别关心面试Web前端开发工程师时,面试官都会问哪些问题.今天小卓把收集来的"阿里Web前端开发面试题"整理贴出来分享给大家伙看看,赶紧收藏起来做准备吧~~ 一.CS ...
- 远程SSH连接服务与基本排错
为什么要远程连接Linux系统?? 在实际的工作场景中,虚拟机界面或物理服务器本地的窗口都是很少能够接触到的,因为服务器装完系统后,都要拉到IDC机房托管,如果是购买了云主机,更碰不到服务器本地显示器 ...
- DirectFB 之 通过多Window实现多元素处理
图像 设计 采用多window的方式实现显示,因为每个window可以独立的属性,比如刷新频率,也是我们最关注的 示例 /*************************************** ...
- phpmyadmin 免登陆
第一步: 打开 phpmyadmin/libraries/plugins/auth/AuthenticationCookie.class.php 找到 authCheck 和 authSetUser ...
- ICDM评选:数据挖掘十大经典算法
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/aladdina/article/details/4141177 国际权威的学术组织the IEEE International Conferenc ...
- 封装类(Merry May Day to all you who are burried in work ~)---2017-05-01
1.为什么要使用封装类? (1) 可以多个地方调用,避免代码的冗余 (2)面向对象三大特点之一,安全性高 2.代码及注意点? <?php class DB //文件名为:DB.class.php ...
- Python魔法方法总结及注意事项
1.何为魔法方法: Python中,一定要区分开函数和方法的含义: 1.函数:类外部定义的,跟类没有直接关系的:形式: def func(*argv): 2.方法:class内部定义的函数(对象的方法 ...
- Java提高(一)---- HashMap
阅读博客 1, java提高篇(二三)-----HashMap 这一篇由chenssy发表于2014年1月,是根据JDK1.6的源码讲的. 2,Java类集框架之HashMap(JDK1.8)源码剖析 ...
