高性能相关、Scrapy框架
高性能相关
在编写爬虫时,性能的消耗主要在IO请求中,当单进程单线程模式下请求URL时必然会引起等待,从而使得请求整体变慢。
import requests def fetch_async(url):
response = requests.get(url)
return response url_list = ['http://www.github.com', 'http://www.bing.com'] for url in url_list:
fetch_async(url)
1.同步执行
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
import requests def fetch_async(url):
response = requests.get(url)
return response url_list = ['http://www.github.com', 'http://www.bing.com']
pool = ThreadPoolExecutor(5)
for url in url_list:
pool.submit(fetch_async, url)
pool.shutdown(wait=True)
2.多线程执行
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
import requests def fetch_async(url):
response = requests.get(url)
return response def callback(future):
print(future.result()) url_list = ['http://www.github.com', 'http://www.bing.com']
pool = ThreadPoolExecutor(5)
for url in url_list:
v = pool.submit(fetch_async, url)
v.add_done_callback(callback)
pool.shutdown(wait=True)
2.多线程+回调函数执行
from concurrent.futures import ProcessPoolExecutor
import requests def fetch_async(url):
response = requests.get(url)
return response url_list = ['http://www.github.com', 'http://www.bing.com']
pool = ProcessPoolExecutor(5)
for url in url_list:
pool.submit(fetch_async, url)
pool.shutdown(wait=True)
3.多进程执行
from concurrent.futures import ProcessPoolExecutor
import requests def fetch_async(url):
response = requests.get(url)
return response def callback(future):
print(future.result()) url_list = ['http://www.github.com', 'http://www.bing.com']
pool = ProcessPoolExecutor(5)
for url in url_list:
v = pool.submit(fetch_async, url)
v.add_done_callback(callback)
pool.shutdown(wait=True)
3.多进程+回调函数执行
通过上述代码均可以完成对请求性能的提高,对于多线程和多进行的缺点是在IO阻塞时会造成了线程和进程的浪费,所以异步IO回事首选:
import asyncio @asyncio.coroutine
def func1():
print('before...func1......')
yield from asyncio.sleep(5)
print('end...func1......') tasks = [func1(), func1()] loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.gather(*tasks))
loop.close()
1.asyncio示例1
import asyncio @asyncio.coroutine
def fetch_async(host, url='/'):
print(host, url)
reader, writer = yield from asyncio.open_connection(host, 80) request_header_content = """GET %s HTTP/1.0\r\nHost: %s\r\n\r\n""" % (url, host,)
request_header_content = bytes(request_header_content, encoding='utf-8') writer.write(request_header_content)
yield from writer.drain()
text = yield from reader.read()
print(host, url, text)
writer.close() tasks = [
fetch_async('www.cnblogs.com', '/wupeiqi/'),
fetch_async('dig.chouti.com', '/pic/show?nid=4073644713430508&lid=10273091')
] loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
results = loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.gather(*tasks))
loop.close()
1.asyncio示例2
import aiohttp
import asyncio @asyncio.coroutine
def fetch_async(url):
print(url)
response = yield from aiohttp.request('GET', url)
# data = yield from response.read()
# print(url, data)
print(url, response)
response.close() tasks = [fetch_async('http://www.google.com/'), fetch_async('http://www.chouti.com/')] event_loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
results = event_loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.gather(*tasks))
event_loop.close()
2.asyncio + aiohttp
import asyncio
import requests @asyncio.coroutine
def fetch_async(func, *args):
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
future = loop.run_in_executor(None, func, *args)
response = yield from future
print(response.url, response.content) tasks = [
fetch_async(requests.get, 'http://www.cnblogs.com/wupeiqi/'),
fetch_async(requests.get, 'http://dig.chouti.com/pic/show?nid=4073644713430508&lid=10273091')
] loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
results = loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.gather(*tasks))
loop.close()
3.asyncio + requests
import gevent import requests
from gevent import monkey monkey.patch_all() def fetch_async(method, url, req_kwargs):
print(method, url, req_kwargs)
response = requests.request(method=method, url=url, **req_kwargs)
print(response.url, response.content) # ##### 发送请求 #####
gevent.joinall([
gevent.spawn(fetch_async, method='get', url='https://www.python.org/', req_kwargs={}),
gevent.spawn(fetch_async, method='get', url='https://www.yahoo.com/', req_kwargs={}),
gevent.spawn(fetch_async, method='get', url='https://github.com/', req_kwargs={}),
]) # ##### 发送请求(协程池控制最大协程数量) #####
# from gevent.pool import Pool
# pool = Pool(None)
# gevent.joinall([
# pool.spawn(fetch_async, method='get', url='https://www.python.org/', req_kwargs={}),
# pool.spawn(fetch_async, method='get', url='https://www.yahoo.com/', req_kwargs={}),
# pool.spawn(fetch_async, method='get', url='https://www.github.com/', req_kwargs={}),
# ])
4.gevent + requests
import grequests request_list = [
grequests.get('http://httpbin.org/delay/1', timeout=0.001),
grequests.get('http://fakedomain/'),
grequests.get('http://httpbin.org/status/500')
] # ##### 执行并获取响应列表 #####
# response_list = grequests.map(request_list)
# print(response_list) # ##### 执行并获取响应列表(处理异常) #####
# def exception_handler(request, exception):
# print(request,exception)
# print("Request failed") # response_list = grequests.map(request_list, exception_handler=exception_handler)
# print(response_list)
5.grequests
from twisted.web.client import getPage, defer
from twisted.internet import reactor def all_done(arg):
reactor.stop() def callback(contents):
print(contents) deferred_list = [] url_list = ['http://www.bing.com', 'http://www.baidu.com', ]
for url in url_list:
deferred = getPage(bytes(url, encoding='utf8'))
deferred.addCallback(callback)
deferred_list.append(deferred) dlist = defer.DeferredList(deferred_list)
dlist.addBoth(all_done) reactor.run()
6.Twisted示例
from tornado.httpclient import AsyncHTTPClient
from tornado.httpclient import HTTPRequest
from tornado import ioloop def handle_response(response):
"""
处理返回值内容(需要维护计数器,来停止IO循环),调用 ioloop.IOLoop.current().stop()
:param response:
:return:
"""
if response.error:
print("Error:", response.error)
else:
print(response.body) def func():
url_list = [
'http://www.baidu.com',
'http://www.bing.com',
]
for url in url_list:
print(url)
http_client = AsyncHTTPClient()
http_client.fetch(HTTPRequest(url), handle_response) ioloop.IOLoop.current().add_callback(func)
ioloop.IOLoop.current().start()
7.Tornado
from twisted.internet import reactor
from twisted.web.client import getPage
import urllib.parse def one_done(arg):
print(arg)
reactor.stop() post_data = urllib.parse.urlencode({'check_data': 'adf'})
post_data = bytes(post_data, encoding='utf8')
headers = {b'Content-Type': b'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'}
response = getPage(bytes('http://dig.chouti.com/login', encoding='utf8'),
method=bytes('POST', encoding='utf8'),
postdata=post_data,
cookies={},
headers=headers)
response.addBoth(one_done) reactor.run()
Twisted更多
以上均是Python内置以及第三方模块提供异步IO请求模块,使用简便大大提高效率,而对于异步IO请求的本质则是【非阻塞Socket】+【IO多路复用】:
import select
import socket
import time class AsyncTimeoutException(TimeoutError):
"""
请求超时异常类
""" def __init__(self, msg):
self.msg = msg
super(AsyncTimeoutException, self).__init__(msg) class HttpContext(object):
"""封装请求和相应的基本数据""" def __init__(self, sock, host, port, method, url, data, callback, timeout=5):
"""
sock: 请求的客户端socket对象
host: 请求的主机名
port: 请求的端口
port: 请求的端口
method: 请求方式
url: 请求的URL
data: 请求时请求体中的数据
callback: 请求完成后的回调函数
timeout: 请求的超时时间
"""
self.sock = sock
self.callback = callback
self.host = host
self.port = port
self.method = method
self.url = url
self.data = data self.timeout = timeout self.__start_time = time.time()
self.__buffer = [] def is_timeout(self):
"""当前请求是否已经超时"""
current_time = time.time()
if (self.__start_time + self.timeout) < current_time:
return True def fileno(self):
"""请求sockect对象的文件描述符,用于select监听"""
return self.sock.fileno() def write(self, data):
"""在buffer中写入响应内容"""
self.__buffer.append(data) def finish(self, exc=None):
"""在buffer中写入响应内容完成,执行请求的回调函数"""
if not exc:
response = b''.join(self.__buffer)
self.callback(self, response, exc)
else:
self.callback(self, None, exc) def send_request_data(self):
content = """%s %s HTTP/1.0\r\nHost: %s\r\n\r\n%s""" % (
self.method.upper(), self.url, self.host, self.data,) return content.encode(encoding='utf8') class AsyncRequest(object):
def __init__(self):
self.fds = []
self.connections = [] def add_request(self, host, port, method, url, data, callback, timeout):
"""创建一个要请求"""
client = socket.socket()
client.setblocking(False)
try:
client.connect((host, port))
except BlockingIOError as e:
pass
# print('已经向远程发送连接的请求')
req = HttpContext(client, host, port, method, url, data, callback, timeout)
self.connections.append(req)
self.fds.append(req) def check_conn_timeout(self):
"""检查所有的请求,是否有已经连接超时,如果有则终止"""
timeout_list = []
for context in self.connections:
if context.is_timeout():
timeout_list.append(context)
for context in timeout_list:
context.finish(AsyncTimeoutException('请求超时'))
self.fds.remove(context)
self.connections.remove(context) def running(self):
"""事件循环,用于检测请求的socket是否已经就绪,从而执行相关操作"""
while True:
r, w, e = select.select(self.fds, self.connections, self.fds, 0.05) if not self.fds:
return for context in r:
sock = context.sock
while True:
try:
data = sock.recv(8096)
if not data:
self.fds.remove(context)
context.finish()
break
else:
context.write(data)
except BlockingIOError as e:
break
except TimeoutError as e:
self.fds.remove(context)
self.connections.remove(context)
context.finish(e)
break for context in w:
# 已经连接成功远程服务器,开始向远程发送请求数据
if context in self.fds:
data = context.send_request_data()
context.sock.sendall(data)
self.connections.remove(context) self.check_conn_timeout() if __name__ == '__main__':
def callback_func(context, response, ex):
"""
:param context: HttpContext对象,内部封装了请求相关信息
:param response: 请求响应内容
:param ex: 是否出现异常(如果有异常则值为异常对象;否则值为None)
:return:
"""
print(context, response, ex) obj = AsyncRequest()
url_list = [
{'host': 'www.google.com', 'port': 80, 'method': 'GET', 'url': '/', 'data': '', 'timeout': 5,
'callback': callback_func},
{'host': 'www.baidu.com', 'port': 80, 'method': 'GET', 'url': '/', 'data': '', 'timeout': 5,
'callback': callback_func},
{'host': 'www.bing.com', 'port': 80, 'method': 'GET', 'url': '/', 'data': '', 'timeout': 5,
'callback': callback_func},
]
for item in url_list:
print(item)
obj.add_request(**item) obj.running()
史上最牛逼的异步IO模块
Scrapy
Scrapy是一个为了爬取网站数据,提取结构性数据而编写的应用框架。 其可以应用在数据挖掘,信息处理或存储历史数据等一系列的程序中。
其最初是为了页面抓取 (更确切来说, 网络抓取 )所设计的, 也可以应用在获取API所返回的数据(例如 Amazon Associates Web Services ) 或者通用的网络爬虫。Scrapy用途广泛,可以用于数据挖掘、监测和自动化测试。
Scrapy 使用了 Twisted异步网络库来处理网络通讯。整体架构大致如下:
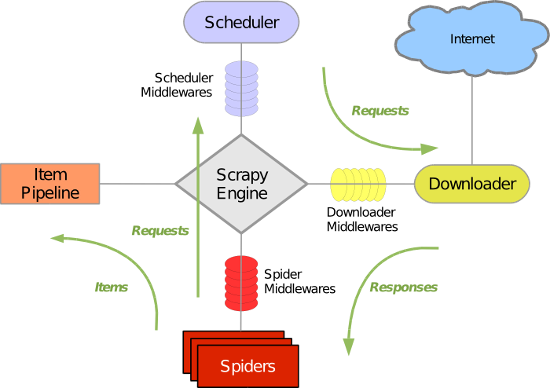
Scrapy主要包括了以下组件:
- 引擎(Scrapy)
用来处理整个系统的数据流处理, 触发事务(框架核心) - 调度器(Scheduler)
用来接受引擎发过来的请求, 压入队列中, 并在引擎再次请求的时候返回. 可以想像成一个URL(抓取网页的网址或者说是链接)的优先队列, 由它来决定下一个要抓取的网址是什么, 同时去除重复的网址 - 下载器(Downloader)
用于下载网页内容, 并将网页内容返回给蜘蛛(Scrapy下载器是建立在twisted这个高效的异步模型上的) - 爬虫(Spiders)
爬虫是主要干活的, 用于从特定的网页中提取自己需要的信息, 即所谓的实体(Item)。用户也可以从中提取出链接,让Scrapy继续抓取下一个页面 - 项目管道(Pipeline)
负责处理爬虫从网页中抽取的实体,主要的功能是持久化实体、验证实体的有效性、清除不需要的信息。当页面被爬虫解析后,将被发送到项目管道,并经过几个特定的次序处理数据。 - 下载器中间件(Downloader Middlewares)
位于Scrapy引擎和下载器之间的框架,主要是处理Scrapy引擎与下载器之间的请求及响应。 - 爬虫中间件(Spider Middlewares)
介于Scrapy引擎和爬虫之间的框架,主要工作是处理蜘蛛的响应输入和请求输出。 - 调度中间件(Scheduler Middewares)
介于Scrapy引擎和调度之间的中间件,从Scrapy引擎发送到调度的请求和响应。
Scrapy运行流程大概如下:
- 引擎从调度器中取出一个链接(URL)用于接下来的抓取
- 引擎把URL封装成一个请求(Request)传给下载器
- 下载器把资源下载下来,并封装成应答包(Response)
- 爬虫解析Response
- 解析出实体(Item),则交给实体管道进行进一步的处理
- 解析出的是链接(URL),则把URL交给调度器等待抓取
一、安装
Linux
pip3 install scrapy Windows
a. pip3 install wheel
b. 下载twisted http://www.lfd.uci.edu/~gohlke/pythonlibs/#twisted
c. 进入下载目录,执行 pip3 install Twisted‑17.1.0‑cp35‑cp35m‑win_amd64.whl
d. pip3 install scrapy
e. 下载并安装pywin32:https://sourceforge.net/projects/pywin32/files/
二、基本使用
1. 基本命令
1. scrapy startproject 项目名称
- 在当前目录中创建中创建一个项目文件(类似于Django) 2. scrapy genspider [-t template] <name> <domain>
- 创建爬虫应用
如:
scrapy gensipider -t basic oldboy oldboy.com
scrapy gensipider -t xmlfeed autohome autohome.com.cn
PS:
查看所有命令:scrapy gensipider -l
查看模板命令:scrapy gensipider -d 模板名称 3. scrapy list
- 展示爬虫应用列表 4. scrapy crawl 爬虫应用名称
- 运行单独爬虫应用
2.项目结构以及爬虫应用简介
project_name/
scrapy.cfg
project_name/
__init__.py
items.py
pipelines.py
settings.py
spiders/
__init__.py
爬虫1.py
爬虫2.py
爬虫3.py
文件说明:
- scrapy.cfg 项目的主配置信息。(真正爬虫相关的配置信息在settings.py文件中)
- items.py 设置数据存储模板,用于结构化数据,如:Django的Model
- pipelines 数据处理行为,如:一般结构化的数据持久化
- settings.py 配置文件,如:递归的层数、并发数,延迟下载等
- spiders 爬虫目录,如:创建文件,编写爬虫规则
注意:一般创建爬虫文件时,以网站域名命名
import scrapy class XiaoHuarSpider(scrapy.spiders.Spider):
name = "xiaohuar" # 爬虫名称 *****
allowed_domains = ["xiaohuar.com"] # 允许的域名
start_urls = [
"http://www.xiaohuar.com/hua/", # 其实URL
] def parse(self, response):
# 访问起始URL并获取结果后的回调函数
爬虫1.py
3. 小试牛刀
import scrapy
from scrapy.selector import HtmlXPathSelector
from scrapy.http.request import Request class DigSpider(scrapy.Spider):
# 爬虫应用的名称,通过此名称启动爬虫命令
name = "dig" # 允许的域名
allowed_domains = ["chouti.com"] # 起始URL
start_urls = [
'http://dig.chouti.com/',
] has_request_set = {} def parse(self, response):
print(response.url) hxs = HtmlXPathSelector(response)
page_list = hxs.select('//div[@id="dig_lcpage"]//a[re:test(@href, "/all/hot/recent/\d+")]/@href').extract()
for page in page_list:
page_url = 'http://dig.chouti.com%s' % page
key = self.md5(page_url)
if key in self.has_request_set:
pass
else:
self.has_request_set[key] = page_url
obj = Request(url=page_url, method='GET', callback=self.parse)
yield obj @staticmethod
def md5(val):
import hashlib
ha = hashlib.md5()
ha.update(bytes(val, encoding='utf-8'))
key = ha.hexdigest()
return key
执行此爬虫文件,则在终端进入项目目录执行如下命令:
scrapy crawl dig --nolog
对于上述代码重要之处在于:
- Request是一个封装用户请求的类,在回调函数中yield该对象表示继续访问
- HtmlXpathSelector用于结构化HTML代码并提供选择器功能
4. 选择器
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
from scrapy.selector import Selector, HtmlXPathSelector
from scrapy.http import HtmlResponse
html = """<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head lang="en">
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li class="item-"><a id='i1' href="link.html">first item</a></li>
<li class="item-0"><a id='i2' href="llink.html">first item</a></li>
<li class="item-1"><a href="llink2.html">second item<span>vv</span></a></li>
</ul>
<div><a href="llink2.html">second item</a></div>
</body>
</html>
"""
response = HtmlResponse(url='http://example.com', body=html,encoding='utf-8')
# hxs = HtmlXPathSelector(response)
# print(hxs)
# hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a')
# print(hxs)
# hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[2]')
# print(hxs)
# hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[@id]')
# print(hxs)
# hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[@id="i1"]')
# print(hxs)
# hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[@href="link.html"][@id="i1"]')
# print(hxs)
# hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[contains(@href, "link")]')
# print(hxs)
# hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[starts-with(@href, "link")]')
# print(hxs)
# hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[re:test(@id, "i\d+")]')
# print(hxs)
# hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[re:test(@id, "i\d+")]/text()').extract()
# print(hxs)
# hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[re:test(@id, "i\d+")]/@href').extract()
# print(hxs)
# hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('/html/body/ul/li/a/@href').extract()
# print(hxs)
# hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//body/ul/li/a/@href').extract_first()
# print(hxs) # ul_list = Selector(response=response).xpath('//body/ul/li')
# for item in ul_list:
# v = item.xpath('./a/span')
# # 或
# # v = item.xpath('a/span')
# # 或
# # v = item.xpath('*/a/span')
# print(v)
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import scrapy
from scrapy.selector import HtmlXPathSelector
from scrapy.http.request import Request
from scrapy.http.cookies import CookieJar
from scrapy import FormRequest class ChouTiSpider(scrapy.Spider):
# 爬虫应用的名称,通过此名称启动爬虫命令
name = "chouti"
# 允许的域名
allowed_domains = ["chouti.com"] cookie_dict = {}
has_request_set = {} def start_requests(self):
url = 'http://dig.chouti.com/'
# return [Request(url=url, callback=self.login)]
yield Request(url=url, callback=self.login) def login(self, response):
cookie_jar = CookieJar()
cookie_jar.extract_cookies(response, response.request)
for k, v in cookie_jar._cookies.items():
for i, j in v.items():
for m, n in j.items():
self.cookie_dict[m] = n.value req = Request(
url='http://dig.chouti.com/login',
method='POST',
headers={'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=UTF-8'},
body='phone=8615131255089&password=pppppppp&oneMonth=1',
cookies=self.cookie_dict,
callback=self.check_login
)
yield req def check_login(self, response):
req = Request(
url='http://dig.chouti.com/',
method='GET',
callback=self.show,
cookies=self.cookie_dict,
dont_filter=True
)
yield req def show(self, response):
# print(response)
hxs = HtmlXPathSelector(response)
news_list = hxs.select('//div[@id="content-list"]/div[@class="item"]')
for new in news_list:
# temp = new.xpath('div/div[@class="part2"]/@share-linkid').extract()
link_id = new.xpath('*/div[@class="part2"]/@share-linkid').extract_first()
yield Request(
url='http://dig.chouti.com/link/vote?linksId=%s' %(link_id,),
method='POST',
cookies=self.cookie_dict,
callback=self.do_favor
) page_list = hxs.select('//div[@id="dig_lcpage"]//a[re:test(@href, "/all/hot/recent/\d+")]/@href').extract()
for page in page_list: page_url = 'http://dig.chouti.com%s' % page
import hashlib
hash = hashlib.md5()
hash.update(bytes(page_url,encoding='utf-8'))
key = hash.hexdigest()
if key in self.has_request_set:
pass
else:
self.has_request_set[key] = page_url
yield Request(
url=page_url,
method='GET',
callback=self.show
) def do_favor(self, response):
print(response.text)
示例:自动登陆抽屉并点赞
注意:settings.py中设置DEPTH_LIMIT = 1来指定“递归”的层数。
5. 格式化处理
上述实例只是简单的处理,所以在parse方法中直接处理。如果对于想要获取更多的数据处理,则可以利用Scrapy的items将数据格式化,然后统一交由pipelines来处理。
import scrapy
from scrapy.selector import HtmlXPathSelector
from scrapy.http.request import Request
from scrapy.http.cookies import CookieJar
from scrapy import FormRequest class XiaoHuarSpider(scrapy.Spider):
# 爬虫应用的名称,通过此名称启动爬虫命令
name = "xiaohuar"
# 允许的域名
allowed_domains = ["xiaohuar.com"] start_urls = [
"http://www.xiaohuar.com/list-1-1.html",
]
# custom_settings = {
# 'ITEM_PIPELINES':{
# 'spider1.pipelines.JsonPipeline': 100
# }
# }
has_request_set = {} def parse(self, response):
# 分析页面
# 找到页面中符合规则的内容(校花图片),保存
# 找到所有的a标签,再访问其他a标签,一层一层的搞下去 hxs = HtmlXPathSelector(response) items = hxs.select('//div[@class="item_list infinite_scroll"]/div')
for item in items:
src = item.select('.//div[@class="img"]/a/img/@src').extract_first()
name = item.select('.//div[@class="img"]/span/text()').extract_first()
school = item.select('.//div[@class="img"]/div[@class="btns"]/a/text()').extract_first()
url = "http://www.xiaohuar.com%s" % src
from ..items import XiaoHuarItem
obj = XiaoHuarItem(name=name, school=school, url=url)
yield obj urls = hxs.select('//a[re:test(@href, "http://www.xiaohuar.com/list-1-\d+.html")]/@href')
for url in urls:
key = self.md5(url)
if key in self.has_request_set:
pass
else:
self.has_request_set[key] = url
req = Request(url=url,method='GET',callback=self.parse)
yield req @staticmethod
def md5(val):
import hashlib
ha = hashlib.md5()
ha.update(bytes(val, encoding='utf-8'))
key = ha.hexdigest()
return key
spiders/xiahuar.py
import scrapy class XiaoHuarItem(scrapy.Item):
name = scrapy.Field()
school = scrapy.Field()
url = scrapy.Field()
items
import json
import os
import requests class JsonPipeline(object):
def __init__(self):
self.file = open('xiaohua.txt', 'w') def process_item(self, item, spider):
v = json.dumps(dict(item), ensure_ascii=False)
self.file.write(v)
self.file.write('\n')
self.file.flush()
return item class FilePipeline(object):
def __init__(self):
if not os.path.exists('imgs'):
os.makedirs('imgs') def process_item(self, item, spider):
response = requests.get(item['url'], stream=True)
file_name = '%s_%s.jpg' % (item['name'], item['school'])
with open(os.path.join('imgs', file_name), mode='wb') as f:
f.write(response.content)
return item
pipelines
ITEM_PIPELINES = {
'spider1.pipelines.JsonPipeline': 100,
'spider1.pipelines.FilePipeline': 300,
}
# 每行后面的整型值,确定了他们运行的顺序,item按数字从低到高的顺序,通过pipeline,通常将这些数字定义在0-1000范围内。
settings
对于pipeline可以做更多,如下:
from scrapy.exceptions import DropItem class CustomPipeline(object):
def __init__(self,v):
self.value = v def process_item(self, item, spider):
# 操作并进行持久化 # return表示会被后续的pipeline继续处理
return item # 表示将item丢弃,不会被后续pipeline处理
# raise DropItem() @classmethod
def from_crawler(cls, crawler):
"""
初始化时候,用于创建pipeline对象
:param crawler:
:return:
"""
val = crawler.settings.getint('MMMM')
return cls(val) def open_spider(self,spider):
"""
爬虫开始执行时,调用
:param spider:
:return:
"""
print('') def close_spider(self,spider):
"""
爬虫关闭时,被调用
:param spider:
:return:
"""
print('')
自定义pipeline
6.中间件
class SpiderMiddleware(object):
def process_spider_input(self,response, spider):
"""
下载完成,执行,然后交给parse处理
:param response:
:param spider:
:return:
"""
pass
def process_spider_output(self,response, result, spider):
"""
spider处理完成,返回时调用
:param response:
:param result:
:param spider:
:return: 必须返回包含 Request 或 Item 对象的可迭代对象(iterable)
"""
return result
def process_spider_exception(self,response, exception, spider):
"""
异常调用
:param response:
:param exception:
:param spider:
:return: None,继续交给后续中间件处理异常;含 Response 或 Item 的可迭代对象(iterable),交给调度器或pipeline
"""
return None
def process_start_requests(self,start_requests, spider):
"""
爬虫启动时调用
:param start_requests:
:param spider:
:return: 包含 Request 对象的可迭代对象
"""
return start_requests
爬虫中间件
class DownMiddleware1(object):
def process_request(self, request, spider):
"""
请求需要被下载时,经过所有下载器中间件的process_request调用
:param request:
:param spider:
:return:
None,继续后续中间件去下载;
Response对象,停止process_request的执行,开始执行process_response
Request对象,停止中间件的执行,将Request重新调度器
raise IgnoreRequest异常,停止process_request的执行,开始执行process_exception
"""
pass def process_response(self, request, response, spider):
"""
spider处理完成,返回时调用
:param response:
:param result:
:param spider:
:return:
Response 对象:转交给其他中间件process_response
Request 对象:停止中间件,request会被重新调度下载
raise IgnoreRequest 异常:调用Request.errback
"""
print('response1')
return response def process_exception(self, request, exception, spider):
"""
当下载处理器(download handler)或 process_request() (下载中间件)抛出异常
:param response:
:param exception:
:param spider:
:return:
None:继续交给后续中间件处理异常;
Response对象:停止后续process_exception方法
Request对象:停止中间件,request将会被重新调用下载
"""
return None
下载器中间件
7. 自定制命令
- 在spiders同级创建任意目录,如:commands
- 在其中创建 crawlall.py 文件 (此处文件名就是自定义的命令)
from scrapy.commands import ScrapyCommand
from scrapy.utils.project import get_project_settings class Command(ScrapyCommand): requires_project = True def syntax(self):
return '[options]' def short_desc(self):
return 'Runs all of the spiders' def run(self, args, opts):
spider_list = self.crawler_process.spiders.list()
for name in spider_list:
self.crawler_process.crawl(name, **opts.__dict__)
self.crawler_process.start()
crawlall.py
- 在settings.py 中添加配置 COMMANDS_MODULE = '项目名称.目录名称'
- 在项目目录执行命令:scrapy crawlall
8. 自定义扩展
自定义扩展时,利用信号在指定位置注册制定操作
from scrapy import signals class MyExtension(object):
def __init__(self, value):
self.value = value @classmethod
def from_crawler(cls, crawler):
val = crawler.settings.getint('MMMM')
ext = cls(val) crawler.signals.connect(ext.spider_opened, signal=signals.spider_opened)
crawler.signals.connect(ext.spider_closed, signal=signals.spider_closed) return ext def spider_opened(self, spider):
print('open') def spider_closed(self, spider):
print('close')
9. 避免重复访问
scrapy默认使用 scrapy.dupefilter.RFPDupeFilter 进行去重,相关配置有:
DUPEFILTER_CLASS = 'scrapy.dupefilter.RFPDupeFilter'
DUPEFILTER_DEBUG = False
JOBDIR = "保存范文记录的日志路径,如:/root/" # 最终路径为 /root/requests.seen
class RepeatUrl:
def __init__(self):
self.visited_url = set() @classmethod
def from_settings(cls, settings):
"""
初始化时,调用
:param settings:
:return:
"""
return cls() def request_seen(self, request):
"""
检测当前请求是否已经被访问过
:param request:
:return: True表示已经访问过;False表示未访问过
"""
if request.url in self.visited_url:
return True
self.visited_url.add(request.url)
return False def open(self):
"""
开始爬去请求时,调用
:return:
"""
print('open replication') def close(self, reason):
"""
结束爬虫爬取时,调用
:param reason:
:return:
"""
print('close replication') def log(self, request, spider):
"""
记录日志
:param request:
:param spider:
:return:
"""
print('repeat', request.url)
自定义URL去重操作
10.其他
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Scrapy settings for step8_king project
#
# For simplicity, this file contains only settings considered important or
# commonly used. You can find more settings consulting the documentation:
#
# http://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/settings.html
# http://scrapy.readthedocs.org/en/latest/topics/downloader-middleware.html
# http://scrapy.readthedocs.org/en/latest/topics/spider-middleware.html # 1. 爬虫名称
BOT_NAME = 'step8_king' # 2. 爬虫应用路径
SPIDER_MODULES = ['step8_king.spiders']
NEWSPIDER_MODULE = 'step8_king.spiders' # Crawl responsibly by identifying yourself (and your website) on the user-agent
# 3. 客户端 user-agent请求头
# USER_AGENT = 'step8_king (+http://www.yourdomain.com)' # Obey robots.txt rules
# 4. 禁止爬虫配置
# ROBOTSTXT_OBEY = False # Configure maximum concurrent requests performed by Scrapy (default: 16)
# 5. 并发请求数
# CONCURRENT_REQUESTS = 4 # Configure a delay for requests for the same website (default: 0)
# See http://scrapy.readthedocs.org/en/latest/topics/settings.html#download-delay
# See also autothrottle settings and docs
# 6. 延迟下载秒数
# DOWNLOAD_DELAY = 2 # The download delay setting will honor only one of:
# 7. 单域名访问并发数,并且延迟下次秒数也应用在每个域名
# CONCURRENT_REQUESTS_PER_DOMAIN = 2
# 单IP访问并发数,如果有值则忽略:CONCURRENT_REQUESTS_PER_DOMAIN,并且延迟下次秒数也应用在每个IP
# CONCURRENT_REQUESTS_PER_IP = 3 # Disable cookies (enabled by default)
# 8. 是否支持cookie,cookiejar进行操作cookie
# COOKIES_ENABLED = True
# COOKIES_DEBUG = True # Disable Telnet Console (enabled by default)
# 9. Telnet用于查看当前爬虫的信息,操作爬虫等...
# 使用telnet ip port ,然后通过命令操作
# TELNETCONSOLE_ENABLED = True
# TELNETCONSOLE_HOST = '127.0.0.1'
# TELNETCONSOLE_PORT = [6023,] # 10. 默认请求头
# Override the default request headers:
# DEFAULT_REQUEST_HEADERS = {
# 'Accept': 'text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8',
# 'Accept-Language': 'en',
# } # Configure item pipelines
# See http://scrapy.readthedocs.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html
# 11. 定义pipeline处理请求
# ITEM_PIPELINES = {
# 'step8_king.pipelines.JsonPipeline': 700,
# 'step8_king.pipelines.FilePipeline': 500,
# } # 12. 自定义扩展,基于信号进行调用
# Enable or disable extensions
# See http://scrapy.readthedocs.org/en/latest/topics/extensions.html
# EXTENSIONS = {
# # 'step8_king.extensions.MyExtension': 500,
# } # 13. 爬虫允许的最大深度,可以通过meta查看当前深度;0表示无深度
# DEPTH_LIMIT = 3 # 14. 爬取时,0表示深度优先Lifo(默认);1表示广度优先FiFo # 后进先出,深度优先
# DEPTH_PRIORITY = 0
# SCHEDULER_DISK_QUEUE = 'scrapy.squeue.PickleLifoDiskQueue'
# SCHEDULER_MEMORY_QUEUE = 'scrapy.squeue.LifoMemoryQueue'
# 先进先出,广度优先 # DEPTH_PRIORITY = 1
# SCHEDULER_DISK_QUEUE = 'scrapy.squeue.PickleFifoDiskQueue'
# SCHEDULER_MEMORY_QUEUE = 'scrapy.squeue.FifoMemoryQueue' # 15. 调度器队列
# SCHEDULER = 'scrapy.core.scheduler.Scheduler'
# from scrapy.core.scheduler import Scheduler # 16. 访问URL去重
# DUPEFILTER_CLASS = 'step8_king.duplication.RepeatUrl' # Enable and configure the AutoThrottle extension (disabled by default)
# See http://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/autothrottle.html """
17. 自动限速算法
from scrapy.contrib.throttle import AutoThrottle
自动限速设置
1. 获取最小延迟 DOWNLOAD_DELAY
2. 获取最大延迟 AUTOTHROTTLE_MAX_DELAY
3. 设置初始下载延迟 AUTOTHROTTLE_START_DELAY
4. 当请求下载完成后,获取其"连接"时间 latency,即:请求连接到接受到响应头之间的时间
5. 用于计算的... AUTOTHROTTLE_TARGET_CONCURRENCY
target_delay = latency / self.target_concurrency
new_delay = (slot.delay + target_delay) / 2.0 # 表示上一次的延迟时间
new_delay = max(target_delay, new_delay)
new_delay = min(max(self.mindelay, new_delay), self.maxdelay)
slot.delay = new_delay
""" # 开始自动限速
# AUTOTHROTTLE_ENABLED = True
# The initial download delay
# 初始下载延迟
# AUTOTHROTTLE_START_DELAY = 5
# The maximum download delay to be set in case of high latencies
# 最大下载延迟
# AUTOTHROTTLE_MAX_DELAY = 10
# The average number of requests Scrapy should be sending in parallel to each remote server
# 平均每秒并发数
# AUTOTHROTTLE_TARGET_CONCURRENCY = 1.0 # Enable showing throttling stats for every response received:
# 是否显示
# AUTOTHROTTLE_DEBUG = True # Enable and configure HTTP caching (disabled by default)
# See http://scrapy.readthedocs.org/en/latest/topics/downloader-middleware.html#httpcache-middleware-settings """
18. 启用缓存
目的用于将已经发送的请求或相应缓存下来,以便以后使用 from scrapy.downloadermiddlewares.httpcache import HttpCacheMiddleware
from scrapy.extensions.httpcache import DummyPolicy
from scrapy.extensions.httpcache import FilesystemCacheStorage
"""
# 是否启用缓存策略
# HTTPCACHE_ENABLED = True # 缓存策略:所有请求均缓存,下次在请求直接访问原来的缓存即可
# HTTPCACHE_POLICY = "scrapy.extensions.httpcache.DummyPolicy"
# 缓存策略:根据Http响应头:Cache-Control、Last-Modified 等进行缓存的策略
# HTTPCACHE_POLICY = "scrapy.extensions.httpcache.RFC2616Policy" # 缓存超时时间
# HTTPCACHE_EXPIRATION_SECS = 0 # 缓存保存路径
# HTTPCACHE_DIR = 'httpcache' # 缓存忽略的Http状态码
# HTTPCACHE_IGNORE_HTTP_CODES = [] # 缓存存储的插件
# HTTPCACHE_STORAGE = 'scrapy.extensions.httpcache.FilesystemCacheStorage' """
19. 代理,需要在环境变量中设置
from scrapy.contrib.downloadermiddleware.httpproxy import HttpProxyMiddleware 方式一:使用默认
os.environ
{
http_proxy:http://root:woshiniba@192.168.11.11:9999/
https_proxy:http://192.168.11.11:9999/
}
方式二:使用自定义下载中间件 def to_bytes(text, encoding=None, errors='strict'):
if isinstance(text, bytes):
return text
if not isinstance(text, six.string_types):
raise TypeError('to_bytes must receive a unicode, str or bytes '
'object, got %s' % type(text).__name__)
if encoding is None:
encoding = 'utf-8'
return text.encode(encoding, errors) class ProxyMiddleware(object):
def process_request(self, request, spider):
PROXIES = [
{'ip_port': '111.11.228.75:80', 'user_pass': ''},
{'ip_port': '120.198.243.22:80', 'user_pass': ''},
{'ip_port': '111.8.60.9:8123', 'user_pass': ''},
{'ip_port': '101.71.27.120:80', 'user_pass': ''},
{'ip_port': '122.96.59.104:80', 'user_pass': ''},
{'ip_port': '122.224.249.122:8088', 'user_pass': ''},
]
proxy = random.choice(PROXIES)
if proxy['user_pass'] is not None:
request.meta['proxy'] = to_bytes("http://%s" % proxy['ip_port'])
encoded_user_pass = base64.encodestring(to_bytes(proxy['user_pass']))
request.headers['Proxy-Authorization'] = to_bytes('Basic ' + encoded_user_pass)
print "**************ProxyMiddleware have pass************" + proxy['ip_port']
else:
print "**************ProxyMiddleware no pass************" + proxy['ip_port']
request.meta['proxy'] = to_bytes("http://%s" % proxy['ip_port']) DOWNLOADER_MIDDLEWARES = {
'step8_king.middlewares.ProxyMiddleware': 500,
} """ """
20. Https访问
Https访问时有两种情况:
1. 要爬取网站使用的可信任证书(默认支持)
DOWNLOADER_HTTPCLIENTFACTORY = "scrapy.core.downloader.webclient.ScrapyHTTPClientFactory"
DOWNLOADER_CLIENTCONTEXTFACTORY = "scrapy.core.downloader.contextfactory.ScrapyClientContextFactory" 2. 要爬取网站使用的自定义证书
DOWNLOADER_HTTPCLIENTFACTORY = "scrapy.core.downloader.webclient.ScrapyHTTPClientFactory"
DOWNLOADER_CLIENTCONTEXTFACTORY = "step8_king.https.MySSLFactory" # https.py
from scrapy.core.downloader.contextfactory import ScrapyClientContextFactory
from twisted.internet.ssl import (optionsForClientTLS, CertificateOptions, PrivateCertificate) class MySSLFactory(ScrapyClientContextFactory):
def getCertificateOptions(self):
from OpenSSL import crypto
v1 = crypto.load_privatekey(crypto.FILETYPE_PEM, open('/Users/wupeiqi/client.key.unsecure', mode='r').read())
v2 = crypto.load_certificate(crypto.FILETYPE_PEM, open('/Users/wupeiqi/client.pem', mode='r').read())
return CertificateOptions(
privateKey=v1, # pKey对象
certificate=v2, # X509对象
verify=False,
method=getattr(self, 'method', getattr(self, '_ssl_method', None))
)
其他:
相关类
scrapy.core.downloader.handlers.http.HttpDownloadHandler
scrapy.core.downloader.webclient.ScrapyHTTPClientFactory
scrapy.core.downloader.contextfactory.ScrapyClientContextFactory
相关配置
DOWNLOADER_HTTPCLIENTFACTORY
DOWNLOADER_CLIENTCONTEXTFACTORY """ """
21. 爬虫中间件
class SpiderMiddleware(object): def process_spider_input(self,response, spider):
'''
下载完成,执行,然后交给parse处理
:param response:
:param spider:
:return:
'''
pass def process_spider_output(self,response, result, spider):
'''
spider处理完成,返回时调用
:param response:
:param result:
:param spider:
:return: 必须返回包含 Request 或 Item 对象的可迭代对象(iterable)
'''
return result def process_spider_exception(self,response, exception, spider):
'''
异常调用
:param response:
:param exception:
:param spider:
:return: None,继续交给后续中间件处理异常;含 Response 或 Item 的可迭代对象(iterable),交给调度器或pipeline
'''
return None def process_start_requests(self,start_requests, spider):
'''
爬虫启动时调用
:param start_requests:
:param spider:
:return: 包含 Request 对象的可迭代对象
'''
return start_requests 内置爬虫中间件:
'scrapy.contrib.spidermiddleware.httperror.HttpErrorMiddleware': 50,
'scrapy.contrib.spidermiddleware.offsite.OffsiteMiddleware': 500,
'scrapy.contrib.spidermiddleware.referer.RefererMiddleware': 700,
'scrapy.contrib.spidermiddleware.urllength.UrlLengthMiddleware': 800,
'scrapy.contrib.spidermiddleware.depth.DepthMiddleware': 900, """
# from scrapy.contrib.spidermiddleware.referer import RefererMiddleware
# Enable or disable spider middlewares
# See http://scrapy.readthedocs.org/en/latest/topics/spider-middleware.html
SPIDER_MIDDLEWARES = {
# 'step8_king.middlewares.SpiderMiddleware': 543,
} """
22. 下载中间件
class DownMiddleware1(object):
def process_request(self, request, spider):
'''
请求需要被下载时,经过所有下载器中间件的process_request调用
:param request:
:param spider:
:return:
None,继续后续中间件去下载;
Response对象,停止process_request的执行,开始执行process_response
Request对象,停止中间件的执行,将Request重新调度器
raise IgnoreRequest异常,停止process_request的执行,开始执行process_exception
'''
pass def process_response(self, request, response, spider):
'''
spider处理完成,返回时调用
:param response:
:param result:
:param spider:
:return:
Response 对象:转交给其他中间件process_response
Request 对象:停止中间件,request会被重新调度下载
raise IgnoreRequest 异常:调用Request.errback
'''
print('response1')
return response def process_exception(self, request, exception, spider):
'''
当下载处理器(download handler)或 process_request() (下载中间件)抛出异常
:param response:
:param exception:
:param spider:
:return:
None:继续交给后续中间件处理异常;
Response对象:停止后续process_exception方法
Request对象:停止中间件,request将会被重新调用下载
'''
return None 默认下载中间件
{
'scrapy.contrib.downloadermiddleware.robotstxt.RobotsTxtMiddleware': 100,
'scrapy.contrib.downloadermiddleware.httpauth.HttpAuthMiddleware': 300,
'scrapy.contrib.downloadermiddleware.downloadtimeout.DownloadTimeoutMiddleware': 350,
'scrapy.contrib.downloadermiddleware.useragent.UserAgentMiddleware': 400,
'scrapy.contrib.downloadermiddleware.retry.RetryMiddleware': 500,
'scrapy.contrib.downloadermiddleware.defaultheaders.DefaultHeadersMiddleware': 550,
'scrapy.contrib.downloadermiddleware.redirect.MetaRefreshMiddleware': 580,
'scrapy.contrib.downloadermiddleware.httpcompression.HttpCompressionMiddleware': 590,
'scrapy.contrib.downloadermiddleware.redirect.RedirectMiddleware': 600,
'scrapy.contrib.downloadermiddleware.cookies.CookiesMiddleware': 700,
'scrapy.contrib.downloadermiddleware.httpproxy.HttpProxyMiddleware': 750,
'scrapy.contrib.downloadermiddleware.chunked.ChunkedTransferMiddleware': 830,
'scrapy.contrib.downloadermiddleware.stats.DownloaderStats': 850,
'scrapy.contrib.downloadermiddleware.httpcache.HttpCacheMiddleware': 900,
} """
# from scrapy.contrib.downloadermiddleware.httpauth import HttpAuthMiddleware
# Enable or disable downloader middlewares
# See http://scrapy.readthedocs.org/en/latest/topics/downloader-middleware.html
# DOWNLOADER_MIDDLEWARES = {
# 'step8_king.middlewares.DownMiddleware1': 100,
# 'step8_king.middlewares.DownMiddleware2': 500,
# }
settings
11.TinyScrapy
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import types
from twisted.internet import defer
from twisted.web.client import getPage
from twisted.internet import reactor class Request(object):
def __init__(self, url, callback):
self.url = url
self.callback = callback
self.priority = 0 class HttpResponse(object):
def __init__(self, content, request):
self.content = content
self.request = request class ChouTiSpider(object): def start_requests(self):
url_list = ['http://www.cnblogs.com/', 'http://www.bing.com']
for url in url_list:
yield Request(url=url, callback=self.parse) def parse(self, response):
print(response.request.url)
# yield Request(url="http://www.baidu.com", callback=self.parse) from queue import Queue
Q = Queue() class CallLaterOnce(object):
def __init__(self, func, *a, **kw):
self._func = func
self._a = a
self._kw = kw
self._call = None def schedule(self, delay=0):
if self._call is None:
self._call = reactor.callLater(delay, self) def cancel(self):
if self._call:
self._call.cancel() def __call__(self):
self._call = None
return self._func(*self._a, **self._kw) class Engine(object):
def __init__(self):
self.nextcall = None
self.crawlling = []
self.max = 5
self._closewait = None def get_response(self,content, request):
response = HttpResponse(content, request)
gen = request.callback(response)
if isinstance(gen, types.GeneratorType):
for req in gen:
req.priority = request.priority + 1
Q.put(req) def rm_crawlling(self,response,d):
self.crawlling.remove(d) def _next_request(self,spider):
if Q.qsize() == 0 and len(self.crawlling) == 0:
self._closewait.callback(None) if len(self.crawlling) >= 5:
return
while len(self.crawlling) < 5:
try:
req = Q.get(block=False)
except Exception as e:
req = None
if not req:
return
d = getPage(req.url.encode('utf-8'))
self.crawlling.append(d)
d.addCallback(self.get_response, req)
d.addCallback(self.rm_crawlling,d)
d.addCallback(lambda _: self.nextcall.schedule()) @defer.inlineCallbacks
def crawl(self):
spider = ChouTiSpider()
start_requests = iter(spider.start_requests())
flag = True
while flag:
try:
req = next(start_requests)
Q.put(req)
except StopIteration as e:
flag = False self.nextcall = CallLaterOnce(self._next_request,spider)
self.nextcall.schedule() self._closewait = defer.Deferred()
yield self._closewait @defer.inlineCallbacks
def pp(self):
yield self.crawl() _active = set()
obj = Engine()
d = obj.crawl()
_active.add(d) li = defer.DeferredList(_active)
li.addBoth(lambda _,*a,**kw: reactor.stop()) reactor.run()
参考版
更多文档参见:http://scrapy-chs.readthedocs.io/zh_CN/latest/index.html
高性能相关、Scrapy框架的更多相关文章
- 爬虫相关-scrapy框架介绍
性能相关-进程.线程.协程 在编写爬虫时,性能的消耗主要在IO请求中,当单进程单线程模式下请求URL时必然会引起等待,从而使得请求整体变慢. 串行执行 import requests def fetc ...
- python自动化开发-[第二十四天]-高性能相关与初识scrapy
今日内容概要 1.高性能相关 2.scrapy初识 上节回顾: 1. Http协议 Http协议:GET / http1.1/r/n...../r/r/r/na=1 TCP协议:sendall(&qu ...
- day37 爬虫2(web微信、高性能相关、Scrapy)
s16day37 爬虫2 参考博客:http://www.cnblogs.com/wupeiqi/articles/6229292.html 课堂代码:https://github.com/liyon ...
- python 爬虫相关含Scrapy框架
1.从酷狗网站爬取 新歌首发的新歌名字.播放时长.链接等 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup as BS import requests import re import js ...
- 爬虫基础(五)-----scrapy框架简介
---------------------------------------------------摆脱穷人思维 <五> :拓展自己的视野,适当做一些眼前''无用''的事情,防止进入只关 ...
- 爬虫(九)scrapy框架简介和基础应用
概要 scrapy框架介绍 环境安装 基础使用 一.什么是Scrapy? Scrapy是一个为了爬取网站数据,提取结构性数据而编写的应用框架,非常出名,非常强悍.所谓的框架就是一个已经被集成了各种功能 ...
- 10.scrapy框架简介和基础应用
今日概要 scrapy框架介绍 环境安装 基础使用 今日详情 一.什么是Scrapy? Scrapy是一个为了爬取网站数据,提取结构性数据而编写的应用框架,非常出名,非常强悍.所谓的框架就是一个已经被 ...
- 5、爬虫系列之scrapy框架
一 scrapy框架简介 1 介绍 (1) 什么是Scrapy? Scrapy是一个为了爬取网站数据,提取结构性数据而编写的应用框架,非常出名,非常强悍.所谓的框架就是一个已经被集成了各种功能(高性能 ...
- scrapy框架简介和基础应用
scrapy框架介绍 环境安装 基础使用 一.什么是Scrapy? Scrapy是一个为了爬取网站数据,提取结构性数据而编写的应用框架,非常出名,非常强悍.所谓的框架就是一个已经被集成了各种功能(高性 ...
随机推荐
- selenium webdriver API详解(一)
本系列主要讲解webdriver常用的API使用方法(注意:使用前请确认环境是否安装成功,浏览器驱动是否与谷歌浏览器版本对应) 一:打开某个网址:get() from selenium import ...
- 2018 ACM-ICPC World Finals - Beijing F.Go with the Flow
先枚举所有的列长度 对于每种列长度,然后里面用dp算 #include <algorithm> #include <cmath> #include <cstdio> ...
- 001 -js对时间日期的排序
001-JS对时间日期的排序 最近在做公司的项目时间,产品给了一个很简单的页面,让帮忙写一下.首先看一下产品的需求: 需要对该列表进行排序 思路:(1)可以在数据库写sql语句的时间直接一个DESC按 ...
- Python 中的实用数据挖掘
本文是 2014 年 12 月我在布拉格经济大学做的名为‘ Python 数据科学’讲座的笔记.欢迎通过 @RadimRehurek 进行提问和评论. 本次讲座的目的是展示一些关于机器学习的高级概念. ...
- nginx 根据get参数重定向(根据电视访问的mac地址传递的值,来重定向访问别的url地址,这样就可以进行单台的测试环境。。)
背景是这样的: 公司要做所有客户端的迁移到别的云平台,但又担心会有问题,所以考虑分批次迁移过去,这样就需要迁移部分用户,因为客户端刷但都是统一但rom包,不能轻易发生改动,所以决定用重定向方式将部分客 ...
- sprint1_11.15燃尽图(第二天)
找相关的图片资料用于做点餐系统的界面 燃尽图:
- 模仿qq列表信息滑动删除效果
这个效果的完成主要分为两个部分 自定义view作为listview的列表项 一个view里面包括 显示头像,名字,消息内容等的contentView和滑动才能显示出来的删除,置顶的右边菜单menuVi ...
- Programming Protocol-Independent Packet Processors
引言 OpenFlow协议固定的包头域数目,使得南向协议过于死板. P4可以实现自定义包头,增加灵活性. P4是OpenFlow未来发展的方向. We propose P4 as a strawman ...
- 周总结<4>
经过了一周的学习,我们在html以及C语言方面又有的新的知识点的学习. html 自习表格,函数等 C语言 哈弗曼编码 Html案例: 一. <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC &quo ...
- Ubuntu系统升级内核方法
一.查看内核版本 $ uname-sr //查看内核版本 二.去Ubuntu网站http://kernel.ubuntu.com/~kernel-ppa/mainline/下载所需版本的deb文件 w ...
