Binder中的asInterface解析
在使用AIDL通信的时候,在Stub类中都会生成一个asInterface函数,以《Android开发艺术探索》中的例子来分析,其生成的asInterface函数源码为:
/**
* Cast an IBinder object into an com.willhua.demoaidl.aidl.IBookManager
* interface, generating a proxy if needed.
*/
public static com.willhua.demoaidl.aidl.IBookManager asInterface(
android.os.IBinder obj) {
if ((obj == null)) {
return null;
}
android.os.IInterface iin = obj.queryLocalInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
if (((iin != null) && (iin instanceof com.willhua.demoaidl.aidl.IBookManager))) {
return ((com.willhua.demoaidl.aidl.IBookManager) iin);
}
return new com.willhua.demoaidl.aidl.IBookManager.Stub.Proxy(obj);
}
我们知道asInterface的作用是根据调用是否属于同进程而返回不同的实例对象,但是对于该过程是怎么进行的,返回的到底是什么东西,可能很多童鞋不是很清楚,就这个问题分享一点我的理解。显然,通过代码可知,决定返回何种对象的关键在obj.queryLocalInterface(DESCRIPTOR)的返回结果。
下面我们通过实际DEMO来了解其过程。代码基于《Android开发艺术探索》中的例子。
DEMO中有主要有两个东西,一个就是MainActivity,一个就是BookService,MainActivity会去bind BookService,而BookService通过在Manifest中设置android:process而使之分别与MainActivity运行在同进程和异进程。
主要代码:
public class BookService extends Service {
private Binder mBinder = new IBookManager.Stub() {
...
};
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
LOG("BookService onBind mBinder:" +mBinder.getClass().getName() + " Process:" + Process.myPid());
return mBinder;
}
}
public class MainActivity extends Activity{
private IBookManager mService;
private Button mQuery;
private TextView mOutInfo;
...
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
connectService();
}
private void connectService(){
Intent intent = new Intent(getApplicationContext(), BookService.class);
bindService(intent, new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
LOG("onServiceConnected " + service);
mService = IBookManager.Stub.asInterface(service);
}
}, BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
...
}
public static abstract class Stub extends android.os.Binder implements
com.willhua.demoaidl.aidl.IBookManager {
private static final java.lang.String DESCRIPTOR = "com.willhua.demoaidl.aidl.IBookManager"; /** Construct the stub at attach it to the interface. */
public Stub() {
this.attachInterface(this, DESCRIPTOR);
} /**
* Cast an IBinder object into an com.willhua.demoaidl.aidl.IBookManager
* interface, generating a proxy if needed.
*/
public static com.willhua.demoaidl.aidl.IBookManager asInterface(
android.os.IBinder obj) {
if ((obj == null)) {
return null;
}
android.os.IInterface iin = obj.queryLocalInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
if (((iin != null) && (iin instanceof com.willhua.demoaidl.aidl.IBookManager))) {
return ((com.willhua.demoaidl.aidl.IBookManager) iin);
}
return new com.willhua.demoaidl.aidl.IBookManager.Stub.Proxy(obj);
}
...
}
androd.os.Binder部分源码:
public class Binder implements IBinder {
//...
/**
* Convenience method for associating a specific interface with the Binder.
* After calling, queryLocalInterface() will be implemented for you
* to return the given owner IInterface when the corresponding
* descriptor is requested.
*/
public void attachInterface(IInterface owner, String descriptor) {
mOwner = owner;
mDescriptor = descriptor;
}
/**
* Use information supplied to attachInterface() to return the
* associated IInterface if it matches the requested
* descriptor.
*/
public IInterface queryLocalInterface(String descriptor) {
if (mDescriptor.equals(descriptor)) {
return mOwner;
}
return null;
}
//...
final class BinderProxy implements IBinder {
//...
public IInterface queryLocalInterface(String descriptor) {
return null;
}
//...
}
}
通过LOG,我们发现,在onServiceConnected函数中,如果MainActivity与BookService同进程,则打印的log为:

如果MainActivity与BookService异进程,及MainActivity跨进程绑定BookService服务,则打印的log为:
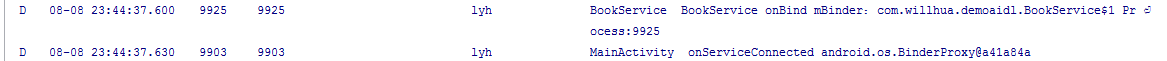
先分析同进程,
在同进程中,onServiceConnected接收得到的service对象的类型为BookServices$1,我们知道$表示的是BookServices中的内部类,而在BookServices的定义中,我们只在mBinder的初始化中定义了一个IBookManager.Stub()的子类,即同进程时,在onServiceConnected接收到的是IBookManager.Stub()类型。而IBookManager.Stub() extenders android.os.Binder implements IBookManager,其queryLocalInterface方法来源于超类android.os.Binder。对于方法中传入的descriptor,通过asInterface的代码可知就是Stub中定义的DESCRIPTOR,而Binder中定义的mDescriptor,其赋值过程是在attachInterface函数中,而attachInterface函数是在Stub的构造函数中被调用,其调用为
this.attachInterface(this, DESCRIPTOR);
而在onServiceConnected中的调用为:
mService = IBookManager.Stub.asInterface(service);
注意sercice为IBookManager.Stub,从而我们可以知道,
if (mDescriptor.equals(descriptor))
判断语句中的mDescriptor和descriptor都为IBookManager.Stub中定义的DESCRIPTOR,则queryLocalInterface返回的是mOwer。那么mOwer又是什么呢?细心的童鞋估计已经知道答案,在Stub的构造函数调用中attachInterface的时候,已经给mOwer赋值,且赋值为this,即该Stub对象本身!再回去对照asInterface的逻辑,我们即可以得出结论:同进程时,调用asInterface返回的是Stub对象,其实就是在onBind中返回的mBinder。
再来分析跨进程调用的情形
由上面的log可知,跨进程调用时,onSericeConnected中接收到的service为android.os.BinderProxy类型,而上面的源码已经给出,BinderProxy为final类,且其queryLocalInterface方法直接返回的null,结合asInterface的代码逻辑,就知道它返回的为IBookManager.Stub.Proxy对象,得出结论:同进程时,调用asInterface返回的是Stub.Proxy对象。
至此,开篇提到的问题应该已经明了。但其实又引出了一个新的问题:为什么跨进程调时,在onServiceConnected中接收到的是os.BinderProxy,而同进程调用时接收到的是IBookManager.Stub?
且听下回。。。
Binder中的asInterface解析的更多相关文章
- Android系统进程间通信(IPC)机制Binder中的Client获得Server远程接口过程源代码分析
文章转载至CSDN社区罗升阳的安卓之旅,原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/luoshengyang/article/details/6633311 在上一篇文章中,我 们分析了And ...
- Android系统进程间通信(IPC)机制Binder中的Server启动过程源代码分析
文章转载至CSDN社区罗升阳的安卓之旅,原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/luoshengyang/article/details/6629298 在前面一篇文章浅谈Android系 ...
- java中采用dom4j解析xml文件
一.前言 在最近的开发中用到了dom4j来解析xml文件,以前听说过来解析xml文件的几种标准方式:但是从来的没有应用过来,所以可以在google中搜索dmo4j解析xml文件的方式,学习一下dom4 ...
- 转:在java中使用dom4j解析xml
JAVA 使用Dom4j 解析XML Java DOM4J Parser - Parse XML Document Dom4j下载及使用Dom4j读写XML简介 在java中使用dom4j解析xml ...
- Android中的XML解析
在安卓中主要有三种XML文档解析方式:DOM(Document Object Model), SAX(Simple API for XML), PULL 他们的主要特点如下表: 特点 主要类 DO ...
- Android中使用Gson解析JSON数据的两种方法
Json是一种类似于XML的通用数据交换格式,具有比XML更高的传输效率;本文将介绍两种方法解析JSON数据,需要的朋友可以参考下 Json是一种类似于XML的通用数据交换格式,具有比XML更高的 ...
- julia与python中的列表解析.jl
julia与python中的列表解析.jl #=julia与python中的列表解析.jl 2016年3月16日 07:30:47 codegay julia是一门很年轻的科学计算语言 julia文档 ...
- Hadoop中的InputFormat解析
1.InputFormat InputFormat是Hadoop平台上Mapreduce输入的规范,仅有两个抽象方法. List<InputSplit> getSplits(), 获取由输 ...
- Kakfa揭秘 Day4 Kafka中分区深度解析
Kakfa揭秘 Day4 Kafka中分区深度解析 今天主要谈Kafka中的分区数和consumer中的并行度.从使用Kafka的角度说,这些都是至关重要的. 分区原则 Partition代表一个to ...
随机推荐
- UI自动化测试框架(项目实战)python、Selenium(日志、邮件、pageobject)
其实百度UI自动化测试框架,会出来很多相关的信息,不过就没有找到纯项目的,无法拿来使用的:所以我最近就写了一个简单,不过可以拿来在真正项目中可以使用的测试框架. 项目的地址:https://githu ...
- final .....finally ...... 和Finalize ......区别
一.性质不同 ()final为关键字: ()finalize()为方法: ()finally为为区块标志,用于try语句中: 二.作用 ()final为用于标识常量的关键字,final标识的关键字存储 ...
- C语言编译过程
GCC编译C源码有四个步骤: 预处理-----> 编译 ----> 汇编 ----> 链接 一. 编译和链接的流程 C语言的编译链接过程要把我们编写的一个c程序(源代码)转换成可以在 ...
- mysql,命令导入\导出表结构或数据
在命令行下mysql的数据导出有个很好用命令mysqldump,它的参数有一大把,可以这样查看: mysqldump 最常用的: mysqldump -uroot -pmysql databasefo ...
- MySQL建表规范与常见问题
一. 表设计 库名.表名.字段名必须使用小写字母,“_”分割. 库名.表名.字段名必须不超过12个字符. 库名.表名.字段名见名知意,建议使用名词而不是动词. 建议使用InnoDB存储引擎. 存储精确 ...
- linux下查找java进程占用CPU过高原因
1. 查找进程 top查看进程占用资源情况 明显看出java的两个进程22714,12406占用过高cpu. 2.查找线程 使用top -H -p <pid>查看线程占用情况 3. ...
- Medoo个人修改版
Medoo是一款轻量级的php数据库操作类,下面不会介绍Medoo的使用方法,想学习Medoo请前往官网自学:http://medoo.in/ 在接触Medoo之前,一直是用自己写的php数据库操作类 ...
- jQuery Countdown Timer 倒计时效果
这个一款简单的 jQuery 倒计时插件,用于显示剩余的天数,小时,分钟和秒.倒计时功能是非常有用的一个小功能,可以告诉用户多久以后您的网站将会发布或者关闭进行维护,还可以用于举办活动的开始和停止的倒 ...
- PS教程:20个新鲜出炉的 Photoshop 中级教程
Photoshop 实例教程是提高 Photoshop 技能的最佳学习途径.今天,我向大家分享最新20个 Photoshop 进阶教程,提高你的图片处理技巧,制作时尚的效果.这些教程可以帮助把你的想法 ...
- easyui1.3.2中使用1.3.6或1.4.x的calendar
首先在1.3.2中calendar控件不支持日历某天的颜色进行改变,和自定义回调函数 Name Type Description Default width number The width of c ...
