[C2] 逻辑回归(Logistic Regression)
逻辑回归(Logistic Regression)
假设函数(Hypothesis Function)
\(h_\theta(x)=g(\theta^Tx)=g(z)=\frac{1}{1+e^{-z}}=\frac{1}{1+e^{\theta^Tx}}\)
g函数称为 Sigmoid Function 或 Logistic Function, 它可以使得 \(0 \leq h_\theta (x) \leq 1\).
The following image shows us what the sigmoid function looks like:
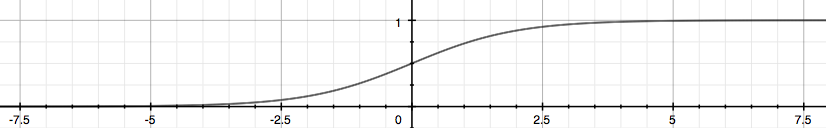
\(h_\theta(x)\) 用来估计基于输入特征值x,y=1的可能性。 正式的写法为:
\(h_\theta(x)=P(y=1|x;\theta)=1-P(y=0|x;\theta)\)
因为
\(z=0,e^0=1 \implies g(z) = \frac{1}{2}\)
\(z \to \infty,e^{-\infty} \to 0 \implies g(z) = 1\)
\(z \to - \infty,e^{\infty} \to \infty \implies g(z) = 0\)
所以
当 \(h_\theta(x) \geq 0.5\) 或 \(z \geq 0\) 时,y=1
当 \(h_\theta(x) < 0.5\) 或 \(z < 0\) 时,y=0
另外
The input to the sigmoid function g(z) (e.g. \(\theta^T X\)) doesn't need to be linear, and could be a function that describes a circle (e.g. \(z = \theta_0 + \theta_1 x_1^2 +\theta_2 x_2^2\)) or any shape to fit our data.
代价函数(Cost Function)
We cannot use the same cost function that we use for linear regression because the Logistic Function will cause the output to be wavy, causing many local optima. In other words, it will not be a convex function.
Instead, our cost function for logistic regression looks like:
\(J(\theta)=\frac{1}{m} \sum\limits_{i=1}^m Cost(h_\theta(x^{(i)}),y^{(i)})\)
\(\begin{cases} Cost(h_\theta(x),y)=-log(h_\theta(x)) & \quad \text{if y = 1} \\ \\ Cost(h_\theta(x),y)=-log(1-h_\theta(x)) & \quad \text{if y = 0} \end{cases}\)
When y = 1, we get the following plot for \(J(\theta)\) vs \(h_\theta (x)\):

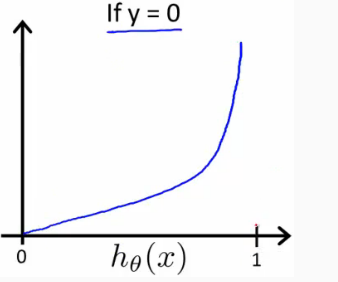
Similarly, when y = 0, we get the following plot for J(θ) vs hθ(x):
If our correct answer 'y' is 1, then the cost function will be 0 if our hypothesis function outputs 1. If our hypothesis approaches 0, then the cost function will approach infinity.
当 \(y=1\) 时,若 \(h_\theta(x)=1\) ,则 \(Cost=0\) ,若 \(h_\theta(x)=0\) ,则 \(Cost \to \infty\);
If our correct answer 'y' is 0, then the cost function will be 0 if our hypothesis function also outputs 0. If our hypothesis approaches 1, then the cost function will approach infinity.
当 \(y=0\) 时,若 \(h_\theta(x)=0\) ,则 \(Cost=0\) ,若 \(h_\theta(x)=1\) ,则 \(Cost \to \infty\)。
Note that writing the cost function in this way guarantees that J(θ) is convex for logistic regression.
这种代价函数的表示方法可以确保逻辑回归的 \(J(\theta)\) 是凸函数,所以可以使用梯度下降求解 \(\theta\)
将 \(Cost \Big(h_\theta(x),y \Big)\) 简化可得(We can compress our cost function's two conditional cases into one case):
\(Cost \Big(h_\theta(x),y \Big)=-y \cdot log \Big(h_\theta(x) \Big) - (1-y) \cdot log \Big(1-h_\theta(x) \Big)\)
最终的代价函数为(We can fully write out our entire cost function as follows):
\(J(\theta)=-\frac{1}{m} \sum\limits_{i=1}^m \Bigg[ y^{(i)} \cdot log \bigg(h_\theta(x^{(i)}) \bigg) + (1-y^{(i)}) \cdot log \bigg(1-h_\theta(x^{(i)}) \bigg) \Bigg]\)
向量化表示为(A vectorized implementation is):
\(\overrightarrow{h}=g(X \overrightarrow{\theta})\)
\(J(\theta)=\frac{1}{m} \cdot \Big( -\overrightarrow{y}^T \cdot log(\overrightarrow{h}) - (1- \overrightarrow{y})^T \cdot log(1- \overrightarrow{h}) \Big)\)
梯度下降(Gradient Descent)
重复,直到收敛(Repeat until convergence):
\(\theta_j := \theta_j - \alpha\frac{\partial}{\partial\theta_j}J(\theta_0,\theta_1,···\theta_n)\), 其中 \(\frac{\partial}{\partial\theta_j}J(\theta_0,\theta_1,···\theta_n)\) 计算方法为对 \(\theta_j\) 求偏导数(partial derivative)
即(We can work out the derivative part using calculus to get):
\(\theta_j := \theta_j - \alpha\frac{1}{m}\sum\limits_{i = 1}^{m}\biggl(h_\theta(x^{(i)}) - y^{(i)}\biggl)\cdot x_j^{(i)}\)
同时更新(simultaneously update)\(\theta_j\), for j = 0, 1 ..., n
另外, \(x_0^{(i)} \equiv 1\)
向量化表示为(A vectorized implementation is):
\(\theta := \theta - \frac{\alpha}{m} X^T \Big( g(X\theta) - \overrightarrow{y} \Big)\)
Advanced Optimization for Gradient Descent
除了梯度下降法外,还有其他方法计算 \(\overrightarrow{\theta}\) :
- 共轭梯度法(Conjugate gradient)
- 变长度法(BFGS)
- 限制尺度法(L-BFGS)
优点是,无需手动选择学习速率 \(\alpha\) , 以及收敛速度更快。缺点是更加的复杂。
Octave 中已经有提供该方法(fminunc),要调用 fminunc 方法来计算 \(\overrightarrow{\theta}\),需先计算 \(J(\theta)\) 和 \(\frac{\alpha}{\alpha \theta_j}J(\theta)\)
可以写一个简单的函数返回这两个值
function [jVal, gradient] = costFunction(theta)
jVal = [...code to compute J(theta)...];
gradient = [...code to compute derivative of J(theta)...];
end
然后使用Octave的“fminunc()”优化算法以及“optimset()”函数来创建一个包含要发送到“fminunc()”的“options“对象。
options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 100);
initialTheta = zeros(2,1); % our initial vector of theta values
[optTheta, functionVal, exitFlag] = fminunc(@costFunction, initialTheta, options);
多元分类(Multiclass Classification: One-vs-all)
对于多元分类的情况,即 y = {0,1...n},我们可以把问题分解为 n+1 个二元分类的问题。 +1 是因为索引是从0开始的。
$y \in $ {0,1...n}
\(h_\theta^{(0)}(x)=P(y=0|x;\theta)\)
\(h_\theta^{(1)}(x)=P(y=1|x;\theta)\)
\(...\)
\(h_\theta^{(n)}(x)=P(y=n|x;\theta)\)
\(prediction=\max\limits_i(h_\theta^{(i)}(x))\)
我们基本上是选择一个类,然后把所有其他类都放到第二类中。重复这样做,对每种情况应用二元逻辑回归,然后使用返回最大值的假设作为我们的预测。
The following image shows how one could classify 3 classes:

To summarize:
Train a logistic regression classifier \(h_\theta(x)\) for each class to predict the probability that  y = i .
To make a prediction on a new x, pick the class that maximizes \(h_\theta (x)\)
程序代码
直接查看Logistic Regression.ipynb可点击
获取源码以其他文件,可点击右上角 Fork me on GitHub 自行 Clone。
[C2] 逻辑回归(Logistic Regression)的更多相关文章
- 机器学习总结之逻辑回归Logistic Regression
机器学习总结之逻辑回归Logistic Regression 逻辑回归logistic regression,虽然名字是回归,但是实际上它是处理分类问题的算法.简单的说回归问题和分类问题如下: 回归问 ...
- 机器学习(四)--------逻辑回归(Logistic Regression)
逻辑回归(Logistic Regression) 线性回归用来预测,逻辑回归用来分类. 线性回归是拟合函数,逻辑回归是预测函数 逻辑回归就是分类. 分类问题用线性方程是不行的 线性方程拟合的是连 ...
- 机器学习入门11 - 逻辑回归 (Logistic Regression)
原文链接:https://developers.google.com/machine-learning/crash-course/logistic-regression/ 逻辑回归会生成一个介于 0 ...
- Coursera公开课笔记: 斯坦福大学机器学习第六课“逻辑回归(Logistic Regression)” 清晰讲解logistic-good!!!!!!
原文:http://52opencourse.com/125/coursera%E5%85%AC%E5%BC%80%E8%AF%BE%E7%AC%94%E8%AE%B0-%E6%96%AF%E5%9D ...
- 机器学习方法(五):逻辑回归Logistic Regression,Softmax Regression
欢迎转载,转载请注明:本文出自Bin的专栏blog.csdn.net/xbinworld. 技术交流QQ群:433250724,欢迎对算法.技术.应用感兴趣的同学加入. 前面介绍过线性回归的基本知识, ...
- 机器学习 (三) 逻辑回归 Logistic Regression
文章内容均来自斯坦福大学的Andrew Ng教授讲解的Machine Learning课程,本文是针对该课程的个人学习笔记,如有疏漏,请以原课程所讲述内容为准.感谢博主Rachel Zhang 的个人 ...
- ML 逻辑回归 Logistic Regression
逻辑回归 Logistic Regression 1 分类 Classification 首先我们来看看使用线性回归来解决分类会出现的问题.下图中,我们加入了一个训练集,产生的新的假设函数使得我们进行 ...
- 逻辑回归(Logistic Regression)详解,公式推导及代码实现
逻辑回归(Logistic Regression) 什么是逻辑回归: 逻辑回归(Logistic Regression)是一种基于概率的模式识别算法,虽然名字中带"回归",但实际上 ...
- 逻辑回归 Logistic Regression
逻辑回归(Logistic Regression)是广义线性回归的一种.逻辑回归是用来做分类任务的常用算法.分类任务的目标是找一个函数,把观测值匹配到相关的类和标签上.比如一个人有没有病,又因为噪声的 ...
随机推荐
- oracle中utl_raw
RAW,类似于CHAR,声明方式RAW(L),L为长度,以字节为单位,作为数据库列最大2000,作为变量最大32767字节.LONG RAW,类似于LONG,作为数据库列最大存储2G字节的数据,作为变 ...
- MYSQL ERROR:1130 解决
MYSQL ERROR:1130 解决 ERROR 1130: Host '127.0.0.7' is not allowed to connect to this MySQL server 解决 ...
- 《Java面试全解析》505道面试题详解
<Java面试全解析>是我在 GitChat 发布的一门电子书,全书总共有 15 万字和 505 道 Java 面试题解析,目前来说应该是最实用和最全的 Java 面试题解析了. 我本人是 ...
- beego安装错误处理
1. 安装beego时无法安装go依赖包 解决办法: $vim ~/.bashrc export GOPROXY=https://goproxy.io $source ~/.bashrc$go get ...
- postgresql 笔记
客户端GUI 在官网下载一个,在安装的时候,不安装 server 端,会在客户端 安装一个 pgadmin .
- java(二)变量
基础数据类型: 数值型:整型(byte.short.int.long).浮点型(float.double)java各整数类型有固定的表数范围和字段长度,不受具体os的影响,以保持java的可移植性:j ...
- python笔记:配置虚拟开发环境
问题 有的时候开发不同的业务,所需要的环境不一样.一直在同一个环境中开发时候,不同的包版本升级可能会导致另外的业务不能正常工作.另外,有的github上的项目需要的开发环境与你使用的环境不同,冒然的按 ...
- MySQL UNSIGNED和ZEROFILL属性
UNSIGNED 这个属性就是标记数字类型是无符号的,和C/C++语言中的unsigned含义是一样的,int signed的类型范围是-2147483648~2147483648,而int unsi ...
- python 实例方法、静态方法、类方法
class Date: #构造函数 def __init__(self, year, month, day): self.year = year self.month = month self.day ...
- gitlab的安装配置与简单使用
安装 gitlab,建议系统内存 6G ,不然会报错. 一.如何安装 gitlab 下载 gitlab 的 RPM 包 https://packages.gitlab.com/gitlab/gitla ...
